
- •Contents
- •Course Overview
- •Course Agenda
- •Document Conventions
- •Additional Information
- •Chapter 1: Course Introduction
- •Chapter 2: Junos Operating System Fundamentals
- •The Junos OS
- •Traffic Processing
- •Overview of Junos Devices
- •Chapter 3: User Interface Options
- •User Interface Options
- •The Junos CLI: CLI Basics
- •The Junos CLI: Operational Mode
- •The Junos CLI: Configuration Mode
- •Lab 1: The Junos CLI
- •Chapter 4: Initial Configuration
- •Factory-Default Configuration
- •Initial Configuration
- •Interface Configuration
- •Lab 2: Initial System Configuration
- •Chapter 5: Secondary System Configuration
- •User Configuration and Authentication
- •System Logging and Tracing
- •Network Time Protocol
- •Archiving Configurations
- •SNMP
- •Lab 3: Secondary System Configuration
- •Monitoring Platform and Interface Operation
- •Network Utilities
- •Maintaining the Junos OS
- •Password Recovery
- •Lab 4: Operational Monitoring and Maintenance
- •Appendix A: Interface Configuration Examples
- •Review of the Interface Configuration Hierarchy
- •Interface Configuration Examples
- •Using Configuration Groups
- •Appendix B: The J-Web Interface
- •Configuration
- •Lab 5 (Optional): The J-Web Interface
- •Appendix C: Acronym List
- •Appendix D: Answer Key
- •Chapter 1: Course Introduction
- •Chapter 2: Junos Operating System Fundamentals
- •Chapter 3: User Interface Options
- •Chapter 4: Initial Configuration
- •Chapter 5: Secondary System Configuration
- •Chapter 6: Operational Monitoring and Maintenance

Introduction to the Junos Operating System
Configuration
The slide highlights the topic we discuss next.
www.juniper.net |
The J-Web Interface • Appendix B–15 |
Introduction to the Junos Operating System
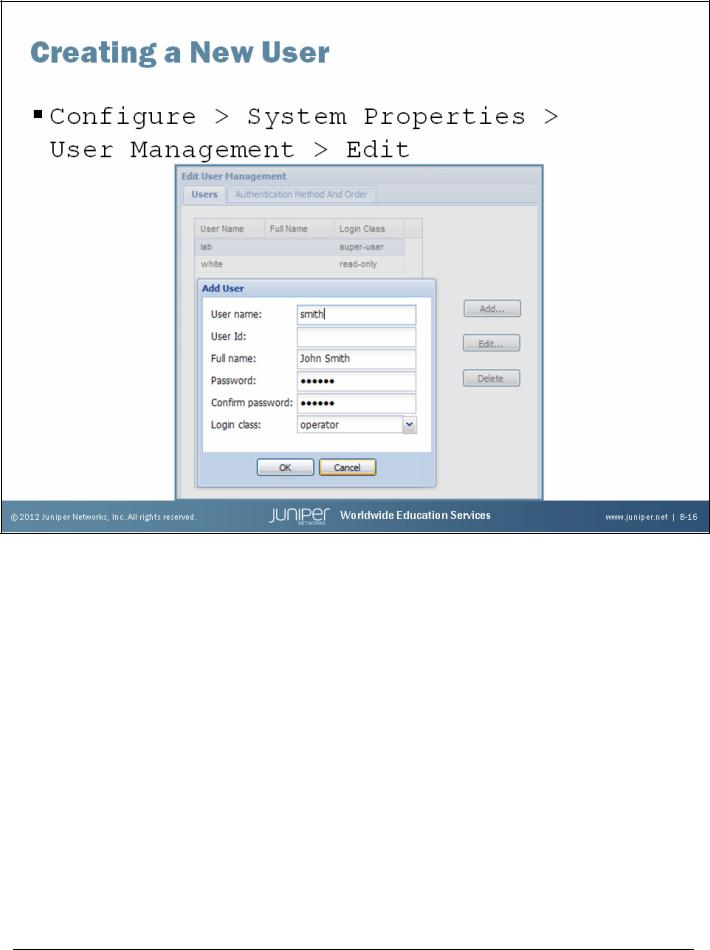
Creating a New User
You can use the Edit User Management page to add new users to the device’s local database. For each account, you define a login name and password for the user and specify a login class for access privileges.
Appendix B–16 • The J-Web Interface |
www.juniper.net |
Introduction to the Junos Operating System
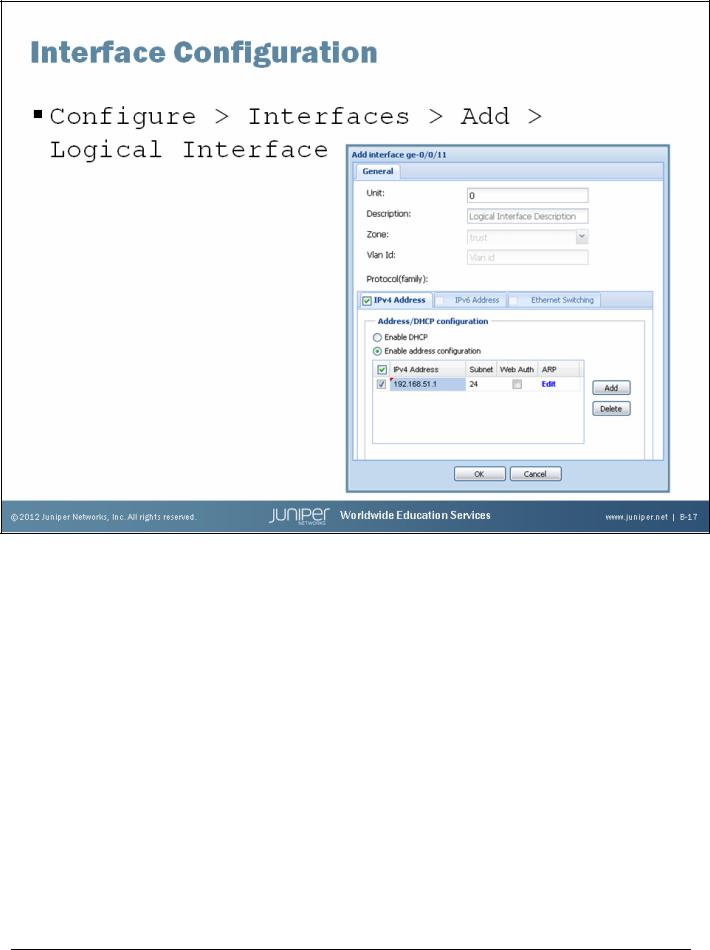
Interface Configuration
You can use J-Web to configure logical interfaces on your Fast Ethernet or Gigabit Ethernet interfaces. You must have at least one logical interface configured on your physical Ethernet interface.
www.juniper.net |
The J-Web Interface • Appendix B–17 |
Introduction to the Junos Operating System
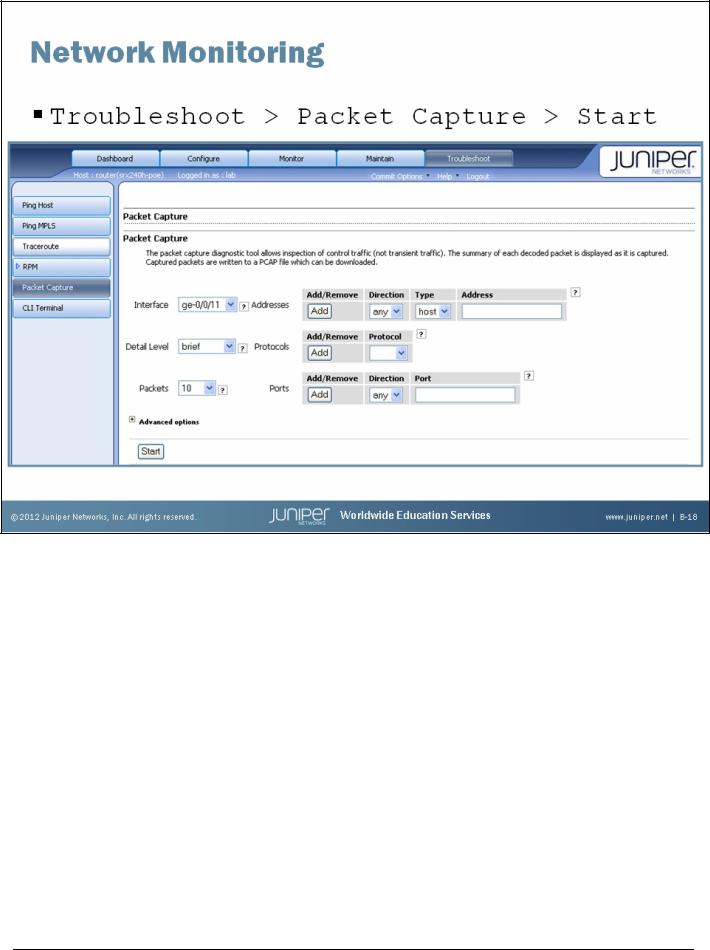
Network Monitoring
You can use the J-Web packet capture diagnostic tool when you need to quickly capture and analyze router control traffic on a device. Packet capture on the J-Web interface allows you to capture traffic destined for or originating from the Routing Engine. You can use the J-Web packet capture tool to compose expressions with various matching criteria to specify the packets that you want to capture. You can either choose to decode and view the captured packets in the J-Web interface as they are captured, or save the captured packets to a file and analyze them offline using packet analyzers such as Ethereal. The J-Web packet capture tool does not capture transient traffic.
Alternatively you can use the CLI monitor traffic command to capture and display packets matching a specific criteria.
Appendix B–18 • The J-Web Interface |
www.juniper.net |
Introduction to the Junos Operating System
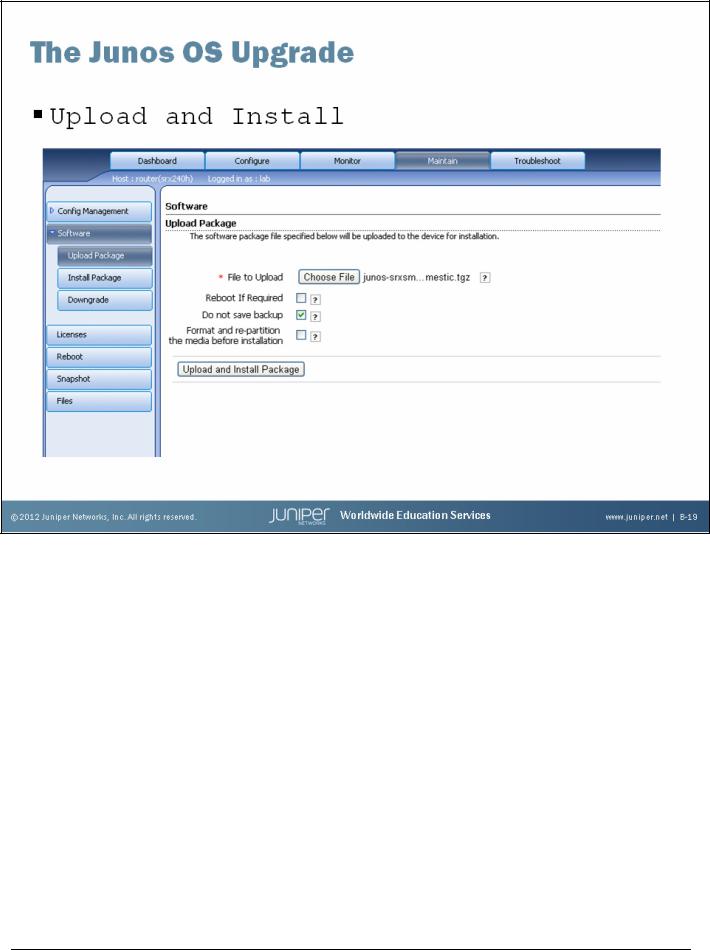
The Junos OS Upgrade
You can use the J-Web interface to install software packages uploaded from your computer.
www.juniper.net |
The J-Web Interface • Appendix B–19 |

Introduction to the Junos Operating System
This Appendix Discussed:
•The J-Web GUI and its tabs, key screens, and functions;
•How to add a new user;
•Basic interface configuration;
•Basic network monitoring; and
•Upgrading the Junos OS.
Appendix B–20 • The J-Web Interface |
www.juniper.net |
