
Глебовский Англ. яз. ч1 09
.pdf
Упражнение 4. Проанализируйте подчёркнутое в тексте предложение: выделитевнёмподлежащее, сказуемое и второстепенные члены и укажите часть речи, которой являются эти члены предложения.
Лексические упражнения
Упражнение 1. а) Переведите на русский язык
существительные:
cracking, load, member, reason, safety, working stress;
прилагательные и наречия:
allowable, efficient, here, near, several, twice, usual;
служебные слова: before, than;
глаголы:
determine, require, support.
б) Если Вы не знаете слово, найдите его в словаре. Выпишите из словаря то значение слова, в котором оно использовано в тексте.
Упражнение 2. Найдите перевод слов списка А в списке В.
A |
B |
A |
B |
обычный |
allowable |
близко |
here |
величина |
support |
предупреждение |
small |
несколько |
near |
нагрузка |
value |
маленький |
object |
деформация |
usual |
здесь |
outside |
допустимый |
warning |
элемент |
load |
наружный |
deformation |
поддерживать |
several |
предмет |
member |
Упражнение 3. Напишите предложения с каждым из перечисленных ниже слов:
fail – failure use – useful
ПрочитайтетранскрипциювспискеA, соотнеситееёссоответствующим словом из списка B и переведите слово на русский язык. Учтите, что не все слова списка В даны в списке А.
A
|
[ ]; [ |
[ ]; [ |
[ |
]; [ |
]; |
[ |
]; [ |
[ |
]; [ |
]; [ |
]; |
|
[ |
]; [ |
] |
|
|
|
|
B |
|
|
|
remain |
perpendicular |
various |
virus |
action |
|
hover |
perpetual |
therefore |
point |
allow |
|
axial |
engineer |
hay |
auction |
reman |
|
divide |
however |
high |
masonry |
fail |
|
ТекстA
STRENGTH AND STRESS
Part II
If a metal bar with a square cross section 2 in. by 2 in. breaks when we pull it with a force of 200,000 lb, its breaking strength is the same as the unit stress or:
Breaking strength = P/A
=200,000 lb / 2  2 sq in.
2 sq in.
=50,000 lb per sq in.
The deformation that we can allow in the bar depends on its use. Therefore, failure depends upon the purpose for which we use the material. Beams which support a roof can withstand any unit stress that does not break
20 |
21 |
them; but if the beams support a plaster ceiling, they fail at a unit stress that causes plaster cracking.
Designers determine the unit stress that can cause failure for various materials and their uses. However, they don’t design to stress a material to the point where it will fail. Instead, they select a lower unit stress (the allowable unit stress), and this is the maximum which they allow.
In order to determine unit stress engineers divide the force by the original area upon which it acts. Tensile and compressive unit stresses act on the crosssectional area perpendicular to the direction of the force. Shear unit stresses act on the cross-sectional area parallel to the direction of the force.
Shear unit stress does not act equally over an area, and the engineer must consider the unit stress at the location of the highest unit stress. The action of shear unit stresses is complex compared to that of the axial unit stresses, tension and compression.
Since forces change the cross sections in size, they influence the unit stresses. If a force remains constant, the actual unit stress changes when the cross section changes. Engineers determine unit stress on the basis of the area as it is before any force acts on it.
Notes:
breaking strength предел прочности
shear unit stress единичное напряжение сдвига (среза), единичное касательное напряжение
Ответьте на вопросы к тексту
1.What is the breaking strength of the metal bar?
2.How is it determined?
3.What does failure depend upon?
4.What unit stress can beams support?
5.What can happen in the case of a plaster ceiling?
6.Which unit stress do designers determine?
7.What do engineers do in order to determine unit stress?
8.How do tensile and compressive unit stresses act?
9.How do shear unit stresses act?
10.Why do forces influence the unit stresses?
11.What takes place if a force remains constant?
12.How do engineers determine unit stress?
Лексические упражнения
Упражнение 1. а) Переведите на русский язык
существительные:
reason, load, location, plaster, action, compression, point, metal, roof, ceiling, member, bar, tension, beam, cross section, direction, area, beam, purpose;
прилагательные и наречия:
axial, instead, actual, low, various, parallel, any, compared to, high, complex, therefore, perpendicular, square, the same, allowable, equally, constant;
служебные слова и обороты:
by, in order to, that, if, for, as, since, however;
глаголы:
stress, allow, change, remain, consider, influence, withstand.
б) Какие из перечисленных глаголов являются неправильными? Укажите их формы. Укажите также правильные глаголы, имеющие особенности в написании при добавлении окончания -ed.
в) Какиеизперечисленныхсловмогутбытьдругимичастямиречи? Какими именно? Как они в этом случае переводятся на русский язык?
Упражнение 2. Переведите следующие слова на английский язык:
площадь; действие; точка, критическая точка; единичное напряжение; размер; направление; крыша; штукатурка; место; растрескивание; балка; поперечное сечение; металл; разрушение, потерянесущейспособности; инженер; потолок;
допускать; тянуть, натягивать; определять; позволять; изменять(ся); оставаться; выдерживать; зависеть (от); делить; влиять, воздействовать; учитывать, действовать; принимать во внимание; вызывать; ломать(ся); подвергать напряжению; поддерживать;
осевой; вместо; действительный, настоящий; сложный; по сравнению с; поэтому, следовательно; перпендикулярный; сильный, значительный; любой, всякий; низкий, слабый; различный; параллельный;
22 |
23 |
тем не менее; так как, поскольку; когда; до того как, прежде чем; который (2).
Упражнение 3. Какие термины, связанные с сопротивлением материалов, встречаютсявтексте? Перечислитеихидайтепереводнарусский язык.
Упражнение4. Какиеизуказанныхпереводовсловявляютсяошибочными? Укажите правильный перевод.
twice |
дважды |
therefore |
из-за |
actual |
активный |
plaster |
штукатурка |
high |
высокий |
several |
несколько |
ceiling |
потолок |
axial |
осевой |
reason |
вызывать |
due to |
для того чтобы |
near |
недалеко |
than |
затем |
various |
различный |
consider |
полагать |
step |
стадия |
also |
также |
need |
нуждаться в |
condition |
состояние |
low |
низкий |
basic |
основа |
instead |
внутри |
consist |
состоять (из) |
allow |
снижение |
roof |
крыша |
Упражнение 5. Вам даны три термина: |
|
||
|
building (здание) |
building material |
strength |
Выберите из приведённого ниже списка слов те, которые соотносятся с этими терминами:
project, calculate, aggregate, stress, layer, masonry, force, binder, block, crushed rock, stretch, unit stress, beam, limestone, wood, column, brick, architect, shear, strain, structure, ceiling, compression, cement, clay, fatigue, design, tension, gravel, hole, failure, drawing, sand, gravity, cracking, safety, withstand, rod, constant, concrete.
Учтите, что некоторые слова могут не относиться ни к одному из указанных терминов или относиться к нескольким из них.
Грамматические упражнения
Упражнение 1. Переведите предложения, обращая внимание на функции слова that.
1.The deformation that can be allowed in the bar depends on what it is used for.
2.Beams can withstand any unit stress that does not break them.
3.The action of shear unit stresses is complex compared to that of the axial unit stresses.
4.That was an allowable deformation.
5.They know that unit stress causes failure.
6.They used that metal bar with a square cross section.
7.That failure depends upon the material that is used is natural.
8.Beams fail at a unit stress that causes plaster cracking.
9.This material is better than that one.
10.The unit stress that causes failure can be determined for various materials.
Упражнение 2. Переведите следующие группы существительных:
metal bar, square cross section, failure strength, plaster cracking, shear unit stress, construction project, stress change, tension degree, steel invention, iron rod, plaster ceiling problem, brick layer, design procedure, building maintenance.
Упражнение 3. Прочтите следующие числительные:
862; 6076; 200,000; 373,200; 1,270,480; 12.05.2005; 597; 734; 10,754; 31.12.1998.
Упражнение 4. Прочтите количественные числительные и образуйте от них порядковые:
25; 87; 3; 32; 91; 14; 43; 75; 11; 68; 21; 15.
24 |
25 |

Упражнение5. Переведитепредложениясконструкциейthe… the….
1.The more we learn now the better engineers we will be.
2.The harder (hard – трудный) the problem the more interesting it is to solve (решать).
3.The sooner (soon – скоро) you come the better.
4.The more careful (тщательный) engineers are when they design a building the less problems the builders will have in its construction.
Упражнение 6. Переведите предложения с оборотом there + be.
1.Because there is so little deformation, there is no warning.
2.There will be hard problems which we must solve.
3.There was deformation in the bar.
4.There were beams which could withstand any unit stress.
5.There are beams which support a plaster ceiling.
Упражнение 7. Переведите предложенияс модальнымиглаголами.
1.They could use a material with higher compressive strength
2.The builder must understand construction materials.
3.Each material can function well over a long time.
4.Builders may use different materials.
5.Basic materials must all be described.
Текст B
In the tests which engineers make in order to determine strength they subject a material to a force that increases until the material breaks. These tests take a few minutes. However, in a structure, forces may act for long periods of time, they may act, not act for some time, and act many times, and they may act suddenly with impact or shock.
A material changes slowly when a force acts on it for many years, even though the force is too small and can’t cause failure in a short time. This deformation is creep. The creep may result in failure.
Although a force of a certain amount cannot cause failure no matter how long it acts, it can cause failure if it acts and stops acting many times (hundreds
of thousands of times) even if it takes place over a shorter time. Application and removal of unit stress to the structural members of a bridge occurs each time a car goes along it. Failure from this cause is fatigue, and it occurs with very little deformation.
Because there is so little deformation, there is no warning and the break is sudden. However, it begins as a crack and becomes larger over many cycles until it fails. The smaller the unit stress, the more times it must occur to cause failure. There is a unit stress below which the material will not fail at any number of cycles. It is the endurance limit.
Notes:
cycle n. цикл, период
endurance limit предел выносливости, предел усталости no matter неважно, как бы ни
sudden неожиданный thousand n. тысяча
Ответьте на вопросы к тексту
1.What tests are made to determine strength?
2.What is “creep”?
3.What do we call “fatigue”?
4.What do we call “the endurance limit”?
Грамматические упражнения
Упражнение 1. Найдите в тексте предложение с конструкцией the … the … . Переведите её на русский язык.
Упражнение 2. Найдите в тексте группы существительных. Переведите их на русский язык.
Упражнение 3. Найдите в тексте модальные глаголы. Переведите их на русский язык.
Упражнение 4. Проанализируйте подчёркнутое в тексте предложение: выделитев нёмподлежащее, сказуемое и второстепенные члены и укажите часть речи, которой являются эти члены предложения.
26 |
27 |

Лексические упражнения
Упражнение 1. а) Переведите на русский язык
существительные:
application, crack, creep, impact, bridge, number, removal;
прилагательные и наречия:
structural, too, even, certain, little, few, long, slow;
служебные слова и обороты:
below, although, so, until, along, though, because;
глаголы:
result in, repeat, occur.
б) Если Вы не знаете слово, найдите его в словаре. Выпишите из словаря то значение слова, в котором оно использовано в тексте.
Упражнение 2. Найдите перевод слов списка А в списке В.
A |
B |
A |
B |
происходить |
creep |
тем не менее |
determine |
приложение |
however |
возрастать |
until |
определять |
take place |
ползучесть |
subject |
вызывать |
increase |
количество |
cause |
пока не |
time |
подвергать |
occur |
столь |
amount |
случаться |
break |
разрушение |
application |
раз |
so |
Упражнение 3. Напишите предложения с каждым из перечисленных ниже слов:
crack – cracking few – little
ПрочитайтетранскрипциювспискеA, соотнеситееёссоответствующим словом из списка B и переведите слово на русский язык. Учтите, что не все слова списка В даны в списке А.
A
|
|
[ |
]; [ |
[ |
|
]; [ |
|
|
[ |
]; [ |
]; [ |
]; [ |
|
[ |
]; [ |
]; [ |
]; |
|
|
[ |
]; [ |
|
] |
|
|
|
|
|
|
B |
|
|
|
|
|
through |
|
pertain |
throw |
|
percent |
very |
|
|
absorb |
|
insulation |
radius |
|
pattern |
contain |
|
|
measure |
|
temperature |
continue |
|
reduce |
|
mega |
|
vary |
|
thermal |
lightweight |
fabricate |
expensive |
|
||
ТекстA
THERMAL CONDUCTIVITYAND SOUND ABSORPTION
A building ought to be warmer than the outside air in cold climates and cooler than the outside air in hot climates. Heat flows to a cooler area like water flows to a lower level. The flow continues until outside and inside temperatures are equal. Heat movement takes place by conduction through any solid object that separates areas of different temperatures. The rate at which the movement of heat takes place varies with the material through which the heat passes. The rate is measured as thermal conductivity (U) of heat (in British thermal units (Btu)) that is transmitted per square foot of cross section per hour per °F difference in temperature between the two sides of the material. Insulation, which is material with a very low U, is used in order to make the
28 |
29 |
rate of heat flow as low as possible. The U of a material varies directly with its density. The best insulation, expanded plastic foam, consists of bubbles with the proportion of solid material less than 1 percent of the volume and the rest consists of air or gas. Insulation is also made of other porous materials.
However, some structural materials also have a low U factor and therefore serve as insulation. Wood and certain types of lightweight concrete are two such materials.
Sound Absorption Loud sound should be avoided in most buildings and has to be reduced by the use of acoustic material which is to absorb it, whether it is produced in the building or outside. Sound is absorbed by air spaces in the material. Porous material is used, or material is fabricated with a pattern of openings so as to be able to absorb sound. Wood and porous concrete are the most effective in sound absorption.
Notes:
bubble n. пузырь, пузырёк cool adj. прохладный
expanded plastic foam пенопласт loud adj. громкий
porous adj. пористый
sound absorption звукопоглощение warm adj. теплый
Ответьте на вопросы к тексту
1.What ought a building to be in cold climates and in hot climates?
2.What is the reason for that?
3.What is the cause of heat movement?
4.What does the rate of heat movement depend on?
5.How is the rate of thermal conductivity measured?
6.What is insulation?
7.Why is expanded plastic foam the best insulation?
8.What other materials have good insulation?
9.How should loud sound be reduced?
10.What is sound absorbed by?
11.What materials are the most effective in sound absorption?
Лексические упражнения
Упражнение 1. а) Переведите на русский язык
существительные:
lightweight concrete, conduction, space, level, opening, density, movement, sound, percent, foot, heat, pattern, insulation, difference, thermal conductivity, flow, side, temperature;
прилагательные и наречия:
solid, outside, effective, acoustic, possible, like, direct, expensive, inside;
служебные слова и обороты: between, whether…or…, so as, through;
глаголы:
transmit, fabricate, continue, separate, absorb, avoid, reduce, measure, vary, pass.
б) Какие из перечисленных глаголов являются неправильными? Укажите их формы. Укажите также правильные глаголы, имеющие особенности в написании при добавлении окончания -ed.
в) Какиеизперечисленныхсловмогутбытьдругимичастямиречи? Какими именно? Как они в этом случае переводятся на русский язык?
Упражнение2. Переведитеследующие слова наанглийскийязык:
ползучесть; количество; разрушение, потеря несущей способности; прочность; площадь, пространство; тип; поперечное сечение; поток, течение; теплота; предмет, объект; изоляция; пространство, место; звук; плотность; скорость, степень; сторона; пропорция; состав;
производить, изготовлять; случаться; приводить к; производить, выпускать; поглощать; использовать; состоятьиз; проходить; повторять; позволять; служить; течь; полагать, считать; менять(ся); избегать; отличаться, разниться;
30 |
31 |
горячий; разный; действенный, эффективный (2); тепловой; близко, близкий; несколько; непосредственный, прямой; строительный; дорогой; внутренний; сплошной, целый;
как, подобно; слишком, также; для того, чтобы; через, сквозь; даже; между; хотя (2); снаружи; ниже, под; до, до тех пор пока; вдоль; потому что.
Упражнение3. Какиетермины, связанныесизоляционнымисвойствамиматериалов, встречаютсявтексте? Перечислите ихидайте перевод на русский язык.
Упражнение 4. Какие из указанных переводов слов являются ошибочными. Укажите правильный перевод.
degree |
степень |
compression |
сжатие |
serve |
служить |
the same |
несколько |
advantage |
преимущество |
hole |
весь |
aggregate |
механизм |
for |
так как |
layer |
укладка |
depend |
зависеть |
dimension |
размер |
number |
число |
case |
случай |
step |
этап |
each other |
друг друга |
together |
вместо |
weight |
весить |
impact |
ударная нагрузка |
sometimes |
что-то |
withstand |
стоять рядом |
mortar |
строительный раствор |
resist |
сопротивляться |
rod |
ржаветь |
excessive |
дорогой |
Упражнение 5. a) Дайте антонимы следующих слов: outside, cold, increase, give, short.
б) Дайте синонимы следующих слов:
because, change, divide, fabricate, under.
Грамматические упражнения
Упражнение 1. Переведите предложения, обращая внимание на глагол в страдательном залоге.
1.Loud sound is avoided in most buildings.
2.Unit strain was caused by unit stress.
3.The material will be stressed near to the failure stress.
4.The rate is measured as thermal conductivity of heat.
5.Usually failure unit stress is determined experimentally.
6.This unit stress is called the working unit stress.
7.Sound will be absorbed by air spaces in the material.
8.Unit strain can be shown by stretching a rubber band.
9.Sound must reduced by the used of acoustic material.
10.Important factors are listed here.
11.The loads can be calculated.
12.Insulation was also made of other porous material.
13.That ability depends on the size and shape of the object and the material of which it is made.
14.Unit stress is expressed as pounds per square inch.
Упражнение 2. Определите функцию глагола to be в следующих предложениях.
1.The engineers are designing a new building now.
2.The building insulation was to be examined (обследовать).
3.Steel and cement were introduced in the nineteenth century.
4.Modern cement which was called Portland cement was invented in 1824.
5.Portland cement is a mixture of limestone and clay.
6.Construction materials are to perform under specific conditions of usage.
7.In the basis of all these qualifications is the knowledge of materials.
8.The plans explain briefly what materials are to be used.
9.They were discussing (обсуждать) sound insulation of a house when we came.
10.All basic materials are to be described.
32 |
33 |

Упражнение 3. Переведите предложения, обращая внимание на заменители модальных глаголов.
1.The designer has to make plans which consist of drawings.
2.This design should be discussed.
3.The designer also explains the characteristics which the materials are to have.
4.Failure takes place when an object is not able to serve its purpose.
5.New insulation materials had to be developed (разрабатывать).
6.In cold climate buildings ought to have thermal insulation.
7.Sound should be avoided in most buildings and has to be reduced by the use of acoustic material.
8.Material is fabricated with a pattern of openings so as to be able to absorb sound.
Упражнение 4. Переведите предложения, обращая внимание на степени сравнения прилагательных.
1.He had much more serious problems than we thought (полагать).
2.The thermal insulation of this building is the worst.
3.The unit stress at the location of the highest stress must be considered.
4.It will be easier to calculate the load if we use this method.
5.The material which was selected is the best.
6.The smaller the unit stress, the more times it must be repeated to cause failure.
Упражнение 5. Переведите предложения, обращая внимание на функции слова that.
1.Heat flows to an area that is cooler.
2.That the sound insulation of the house was bad was to be considered.
3.That is the design that we are to discuss.
4.Those tests were made by the engineers.
5.We know that concrete is a mixture of cement, sand, aggregate and water.
6.Beams that support a roof can be made of steel, concrete or wood.
Упражнение 6. Переведите следующие группы существительных:
heat movement, movement rate, material density, sound absorption, air spaces, creep deformation, stress location, failure cause, sound insulation, construction material.
Текст B
The most important properties of building materials are their cost, their mechanical properties, which include their weight, their thermal and acoustic properties, their durability and their resistance to fire. Other important properties which are connected with the basic properties of the material are the ease of manufacture of the material, the corrosion and chemical resistance and the texture and appearance of the material.
Building materials may be divided into natural and artificial. The examples of natural building materials are wood, sand, clay. The examples of artificial building materials are cement, concrete, brick. The most important mechanical properties of building materials are their weight, tensile strength, shear strength, compressive strength, fatigue resistance, elasticity and creep under load. Other important mechanical properties are their strain capacity and their resistance to rain and moisture. All these properties of materials are based on those values which are given by standard tests and, in many cases the full details of the test ought to be known in order to assess the material. Some properties, for example the compressive strength of concrete, depend on the way the test is done and are based on other general properties.
Notes:
assess v. определять, оценивать manufacture n. производство, изготовление
strain capacity деформационная способность, податливость texture n. структура; текстура
Ответьте на вопросы к тексту
1.What are the most important properties of building materials?
2.Are there any other important properties of building materials? What are they?
3.What are the two types of building materials?
34 |
35 |
4.What are the examples of each type?
5.What are the important mechanical properties of building materials?
6.What values are they based on?
7.Does the way the test is done influence any properties?
Грамматические упражнения
Упражнение 1. Найдите в тексте глаголы в страдательном залоге. Переведите их на русский язык.
Упражнение 2. Проанализируйте подчёркнутое в тексте предложение: выделитевнёмподлежащее, сказуемое и второстепенные члены и укажите часть речи, которой являются эти члены предложения.
Лексические упражнения
Упражнение 1. а) Переведите на русский язык
существительные:
resistance, cost, capacity, example, durability, way, moisture, appearance;
прилагательные и наречия: chemical, mechanical, general, full;
служебные слова и обороты: which, the most, under, in order to;
глаголы:
base, connect, include, divide.
б) Если Вы не знаете слово, найдите его в словаре. Выпишите из словаря то значение слова, в котором оно использовано в тексте.
Упражнение 2. Найдите перевод слов списка А в списке В.
A |
B |
A |
B |
зависеть от |
property |
огонь |
artificial |
их |
these |
легкий |
shear strength |
коррозия |
fatigue |
кирпич |
clay |
сопротивление сдвигу |
fire |
усталость |
corrosion |
стандартный |
standard |
свойство |
easy |
глина |
brick |
эти |
their |
искусственный |
same |
тот же |
depend on |
Упражнение 3. Напишите предложения с каждым из перечисленных ниже слов:
appear – appearance resist – resistance
Текст C
MODERN BUILDINGS AND STRUCTURAL MATERIALS
Many great buildings which were built centuries ago can still be seen in Greece and Italy, France and England. All of these buildings were construction solutions to difficult construction problems. These great buildings were not the result of scientific knowledge. They were constructed on the basis of experience, often as the result of trial and error. They have survived because of the great strength that was built into them – strength greater than necessary in most cases.
Today, however, the engineer has the advantage not only of empirical information, but also of scientific information that allows him to make careful design. When a modern engineer plans a structure, he considers the total weight of all its component materials. This is known as the dead load, which is the weight of the structure itself. He has also to consider the live load, the weight of all the people, cars, furniture, machines, etc. that the structure is to support when it is in use. In structures such as bridges that are to support fast traffic, he has to consider the impact, the force at which the live load will be exerted on the structure. He must also determine the safety factor, that is, an additional capacity to make the structure stronger than the combination of the three other factors.
36 |
37 |
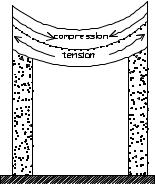
The modern engineer should also understand the different stresses to which the materials in a structure are subject. They include the opposite forces of compression and tension. In compression the material is pushed together; in tension the material is pulled apart or stretched, like a rubber band. In the figure below, the top surface is bent inwards, and the material in it is in compression. The bottom surface is bent outward, and the material in it is in tension.
In addition to tension and compression, another force which is called shear should be considered. Shear is the tendency of a material to crack and break along the lines of stress. The shear may occur in a vertical plane, but it may also run along the horizontal axis of the beam, the neutral plane, where there is neither tension nor compression.
Altogether, three forces can act on a structure: vertical – those that act up or down; horizontal – those that act in horizontal plane; and those that act upon it with a turning motion. Forces that act at an angle are a combination of horizontal and vertical forces. Since the buildings that are designed by engineers are to be stationary or stable, these forces must be balanced. The vertical forces, for example, ought to be equal to each other. If a beam supports a load above, the beam itself has to have sufficient strength to counterbalance that weight. The horizontal forces must also equal each other so that there is not too much thrust either to the right or to the left. And forces that may pull the structure around must be equal to the forces that pull in the opposite direction.
Notes:
altogether adv. в целом, всего
empirical information n. эмпирическая информация furniture n. мебель
machine n. оборудование, станок, устройство push (~ together) v. зд. сжимается
scientific adj. научный
stationary adj. устойчивый, неподвижный survive v. уцелеть
today adv. в наше время, теперь trial and error (метод) проб и ошибок
turning motion вращательное движение
Ответьте на вопросы к тексту
1.Where can great buildings, which were built centuries ago, be seen?
2.How were these buildings constructed?
3.Why did they survive?
4.What are the advantages a modern engineer has?
5.What does a modern engineer take into account to plan a structure?
6.What stresses must a modern engineer understand?
7.What are the forces that can act on a structure?
8.How must the forces be balanced?
Лексическое упражнение
В списке А даны некоторые слова и выражения, которыеиспользованы в тексте для домашнего чтения. Найдите их правильный перевод в списке В.
А |
B |
А |
B |
additional |
вертикальный |
above |
уравновешивать |
angle |
внутрь |
axis |
временная нагрузка |
because of |
дополнительный |
bottom |
вправо |
component |
и так далее |
combination |
всё ещё |
construct |
с тем чтобы |
crack |
достаточный |
dead load |
линия |
etc. |
над |
exert |
нажим, усилие |
inwards |
оказывать (действие) |
necessary |
необходимый |
line |
ось |
38 |
39 |
