
- •Features
- •Disclaimer
- •Overview
- •Block Diagram
- •Pin Descriptions
- •Port A (PA7..PA0)
- •Port B (PB7..PB0)
- •Port C (PC7..PC0)
- •Port D (PD7..PD0)
- •RESET
- •XTAL1
- •XTAL2
- •AVCC
- •AREF
- •Resources
- •Data Retention
- •AVR CPU Core
- •Introduction
- •Status Register
- •Stack Pointer
- •I/O Memory
- •Clock Systems and their Distribution
- •Clock Sources
- •Crystal Oscillator
- •External Clock
- •Idle Mode
- •Power-down Mode
- •Power-save Mode
- •Standby Mode
- •Analog Comparator
- •Brown-out Detector
- •Watchdog Timer
- •Port Pins
- •Resetting the AVR
- •Reset Sources
- •Power-on Reset
- •External Reset
- •Watchdog Reset
- •Watchdog Timer
- •Interrupts
- •I/O Ports
- •Introduction
- •Configuring the Pin
- •Reading the Pin Value
- •Unconnected pins
- •Alternate Port Functions
- •Register Description for I/O Ports
- •8-bit Timer/Counter0 with PWM
- •Overview
- •Registers
- •Definitions
- •Counter Unit
- •Normal Mode
- •Fast PWM Mode
- •8-bit Timer/Counter Register Description
- •Timer/Counter0 and Timer/Counter1 Prescalers
- •Internal Clock Source
- •Prescaler Reset
- •External Clock Source
- •16-bit Timer/Counter1
- •Overview
- •Registers
- •Definitions
- •Compatibility
- •Counter Unit
- •Input Capture Unit
- •Noise Canceler
- •Force Output Compare
- •Normal Mode
- •Fast PWM Mode
- •16-bit Timer/Counter Register Description
- •8-bit Timer/Counter2 with PWM and Asynchronous Operation
- •Overview
- •Registers
- •Definitions
- •Counter Unit
- •Normal Mode
- •Fast PWM Mode
- •8-bit Timer/Counter Register Description
- •Slave Mode
- •Master Mode
- •Data Modes
- •USART
- •Overview
- •Clock Generation
- •External Clock
- •Frame Formats
- •Parity Bit Calculation
- •Parity Generator
- •Receiver Error Flags
- •Parity Checker
- •Disabling the Receiver
- •Using MPCM
- •Write Access
- •Read Access
- •Features
- •TWI Terminology
- •Transferring Bits
- •Address Packet Format
- •Data Packet Format
- •Overview of the TWI Module
- •SCL and SDA Pins
- •Bus Interface Unit
- •Address Match Unit
- •Control Unit
- •Using the TWI
- •Master Receiver Mode
- •Slave Receiver Mode
- •Miscellaneous States
- •Analog Comparator Multiplexed Input
- •Analog to Digital Converter
- •Features
- •Operation
- •Changing Channel or Reference Selection
- •ADC Input Channels
- •Analog Input Circuitry
- •Features
- •Overview
- •TAP Controller
- •PRIVATE0; $8
- •PRIVATE1; $9
- •PRIVATE2; $A
- •PRIVATE3; $B
- •Bibliography
- •IEEE 1149.1 (JTAG) Boundary-scan
- •Features
- •System Overview
- •Data Registers
- •Bypass Register
- •Reset Register
- •EXTEST; $0
- •IDCODE; $1
- •AVR_RESET; $C
- •BYPASS; $F
- •Scanning the ADC
- •ATmega16 Boundary-scan Order
- •Features
- •Application Section
- •Read-While-Write and no Read- While-Write Flash Sections
- •Prevent Reading the RWW Section during Self-Programming
- •Simple Assembly Code Example for a Boot Loader
- •Fuse Bits
- •Latching of Fuses
- •Signature Bytes
- •Calibration Byte
- •Page Size
- •Signal Names
- •Chip Erase
- •Reading the Flash
- •Reading the EEPROM
- •Data Polling Flash
- •Data Polling EEPROM
- •AVR_RESET ($C)
- •PROG_ENABLE ($4)
- •Data Registers
- •Reset Register
- •Programming Enable Register
- •Programming Command Register
- •Virtual Flash Page Read Register
- •Performing Chip Erase
- •Reading the Flash
- •Reading the EEPROM
- •Electrical Characteristics
- •Absolute Maximum Ratings*
- •DC Characteristics
- •External Clock Drive Waveforms
- •External Clock Drive
- •Two-wire Serial Interface Characteristics
- •ADC Characteristics
- •Idle Supply Current
- •Pin Pullup
- •Pin Driver Strength
- •Register Summary
- •Instruction Set Summary
- •Ordering Information
- •Packaging Information
- •Errata
 ATmega16(L)
ATmega16(L)
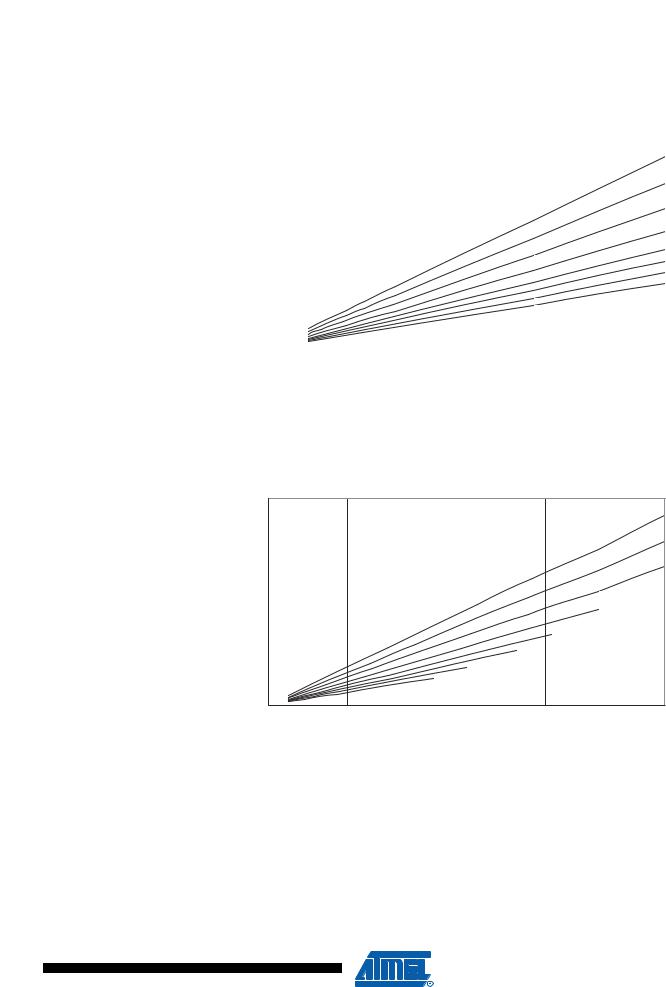
Idle Supply Current |
Figure 156. Idle Supply Current vs. Frequency (0.1 - 1.0 MHz) |
ICC (mA)
IDLE SUPPLY CURRENT vs. FREQUENCY
0.1 - 1.0 MHz
0.8 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
5.5V |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
0.7 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
5.0V |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
0.6 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
4.5V |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
0.5 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
4.0V |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
0.4 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
3.6V |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
3.3V |
0.3 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
3.0V |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
2.7V |
0.2 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
0.1 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
0 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
0 |
0.1 |
0.2 |
0.3 |
0.4 |
0.5 |
0.6 |
0.7 |
0.8 |
0.9 |
1 |
|||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Frequency (MHz) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Figure 157. Idle Supply Current vs. Frequency (1 - 20 MHz)
ICC (mA)
IDLE SUPPLY CURRENT vs. FREQUENCY
1 - 20 MHz
16
5.5V
14
5.0V
12
4.5V
10
8
4.0V
6
3.6V
4
3.3V
3.0V
2
2.7V
0
0 |
2 |
4 |
6 |
8 |
10 |
12 |
14 |
16 |
18 |
20 |
Frequency (MHz)
303
2466P–AVR–08/07
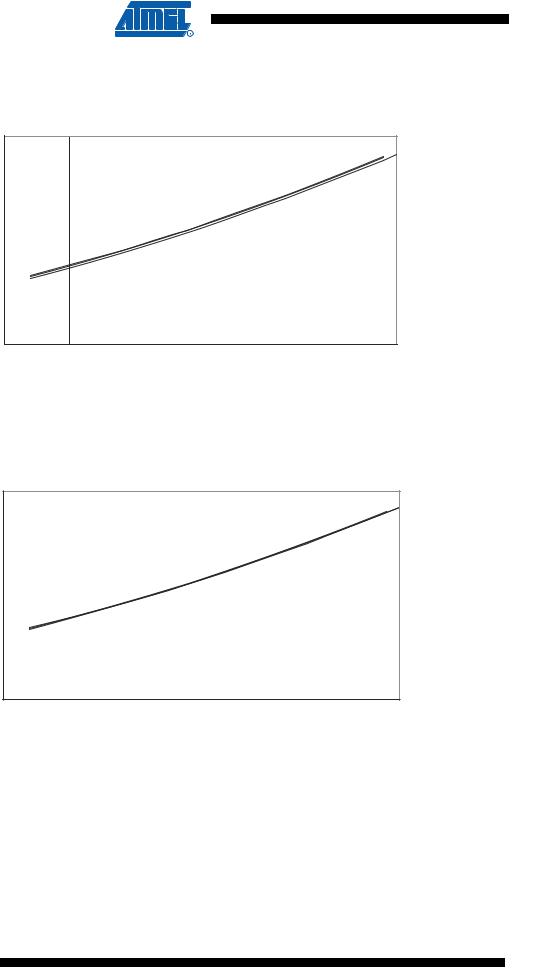
Figure 158. Idle Supply Current vs. VCC (Internal RC Oscillator, 8 MHz)
ICC (mA)
IDLE SUPPLY CURRENT vs. VCC
INTERNAL RC OSCILLATOR, 8 MHz
8
-40°C  25°C
25°C
7
85°C
6
5
4
3
2
1
0
2.5 |
3 |
3.5 |
4 |
4.5 |
5 |
5.5 |
VCC (V)
Figure 159. Idle Supply Current vs. VCC (Internal RC Oscillator, 4 MHz)
ICC (mA)
IDLE SUPPLY CURRENT vs. VCC
INTERNAL RC OSCILLATOR, 4 MHz
4
25°C  -40°C
-40°C
3.5
85°C
3
2.5
2
1.5
1
0.5
0
2.5 |
3 |
3.5 |
4 |
4.5 |
5 |
5.5 |
VCC (V)
304 ATmega16(L)
2466P–AVR–08/07
 ATmega16(L)
ATmega16(L)
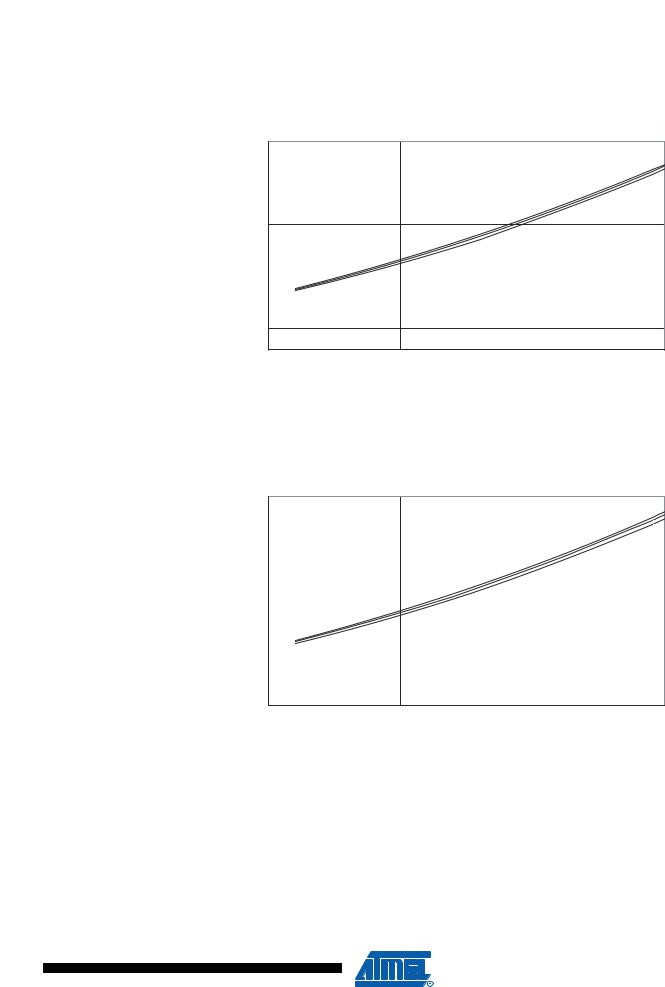
Figure 160. Idle Supply Current vs. VCC (Internal RC Oscillator, 2 MHz)
ICC (mA)
IDLE SUPPLY CURRENT vs. VCC
INTERNAL RC OSCILLATOR, 2 MHz
2
1.8 |
|
25°C |
|
85°C
1.6
-40°C
1.4
1.2
1
0.8
0.6
0.4
0.2
0
2.5 |
3 |
3.5 |
4 |
4.5 |
5 |
5.5 |
VCC (V)
Figure 161. Idle Supply Current vs. VCC (Internal RC Oscillator, 1 MHz)
ICC (mA)
IDLE SUPPLY CURRENT vs. VCC
INTERNAL RC OSCILLATOR, 1 MHz
1
25°C
0.9
85°C
0.8
0.7
0.6
0.5
0.4
0.3
0.2
0.1
0
2.5 |
3 |
3.5 |
4 |
4.5 |
5 |
5.5 |
VCC (V)
305
2466P–AVR–08/07
Power-Down Supply
Current
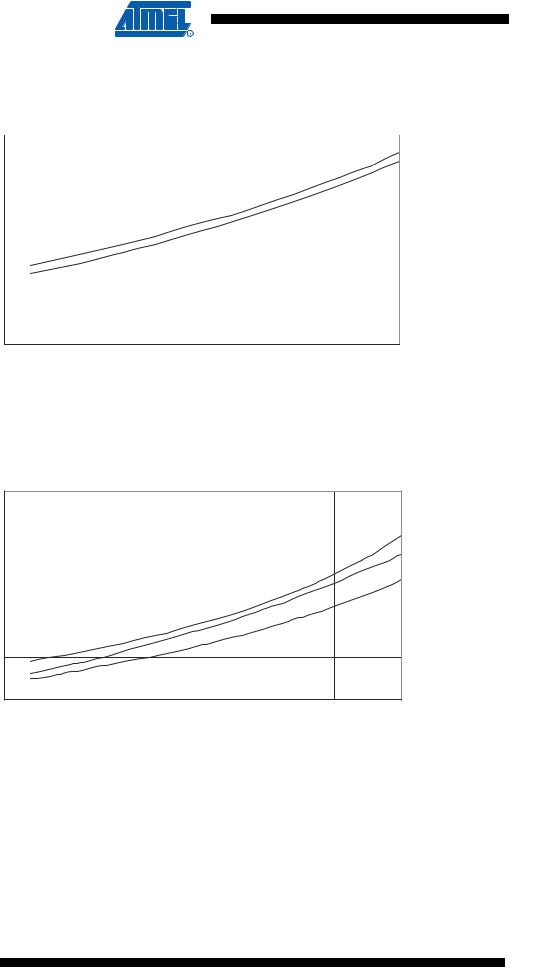
Figure 162. Idle Supply Current vs. VCC (32 kHz External Oscillator)
|
|
|
IDLE SUPPLY CURRENT vs. VCC |
||
|
40 |
|
32kHz EXTERNAL OSCILLATOR |
||
|
|
|
|
85°C |
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
35 |
|
|
|
25°C |
|
|
||||
|
30 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
(uA) |
25 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
20 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
CC |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
I |
|
|
|
|
|
|
15 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
10
5
0
2.5 |
3 |
3.5 |
4 |
4.5 |
5 |
5.5 |
VCC (V)
Figure 163. Power-Down Supply Current vs. VCC (Watchdog Timer Disabled)
|
|
POWER-DOWN SUPPLY CURRENT vs. VCC |
|
|
||
2.5 |
|
|
WATCHDOG TIMER DISABLED |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
2 |
|
|
|
|
|
85°C |
|
|
|
|
|
|
-40°C |
1.5 |
|
|
|
|
|
25°C |
(uA) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
CC |
|
|
|
|
|
|
I |
|
|
|
|
|
|
1 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
0.5 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
0 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
2.5 |
3 |
3.5 |
4 |
4.5 |
5 |
5.5 |
|
|
|
VCC (V) |
|
|
|
306 ATmega16(L)
2466P–AVR–08/07
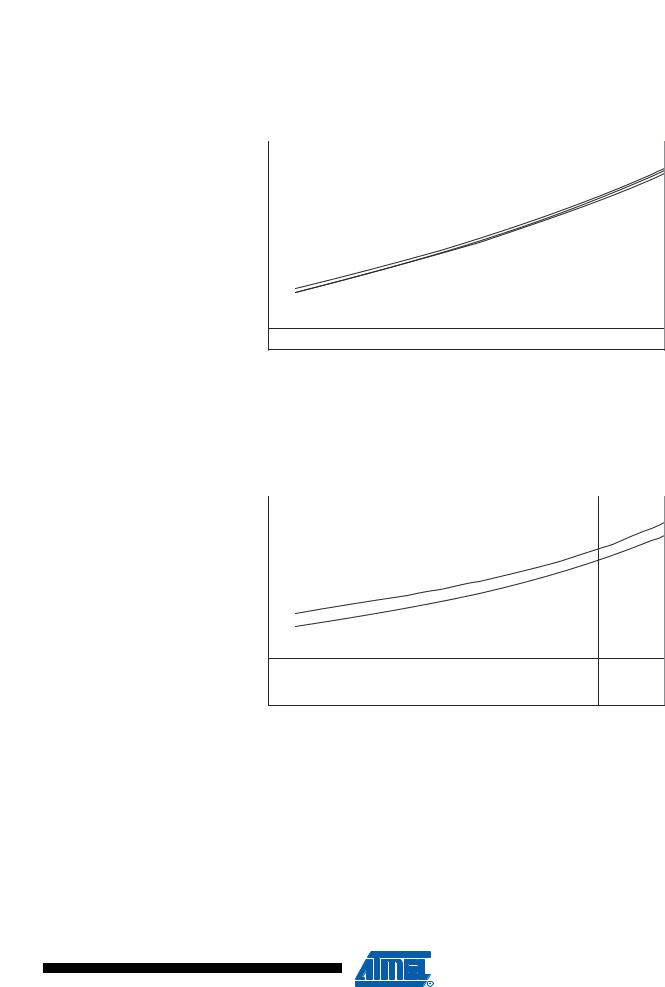
 ATmega16(L)
ATmega16(L)
Power-Save Supply
Current
Figure 164. Power-Down Supply Current vs. VCC (Watchdog Timer Enabled)
POWER-DOWN SUPPLY CURRENT vs. VCC
WATCHDOG TIMER ENABLED
|
20 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
18 |
|
|
-40°C |
|
|
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
16 |
|
85°C |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
25°C |
|||
|
|
|
||
|
14 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
(uA) |
12 |
|
|
|
|
|
|||
10 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
CC |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
I |
8 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
6
4
2
0
2.5 |
3 |
3.5 |
4 |
4.5 |
5 |
5.5 |
VCC (V)
Figure 165. Power-Save Supply Current vs. VCC (Watchdog Timer Disabled)
|
|
|
POWER-SAVE SUPPLY CURRENT vs. VCC |
||
|
18 |
|
WATCHDOG TIMER DISABLED |
||
|
|
|
|
85°C |
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
16 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||
|
|
|
|
|
25°C |
|
14 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
12 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
(uA) |
10 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
CC |
8 |
|
|
|
|
I |
|
|
|
|
|
6
4
2
0
2.5 |
3 |
3.5 |
4 |
4.5 |
5 |
5.5 |
VCC (V)
307
2466P–AVR–08/07
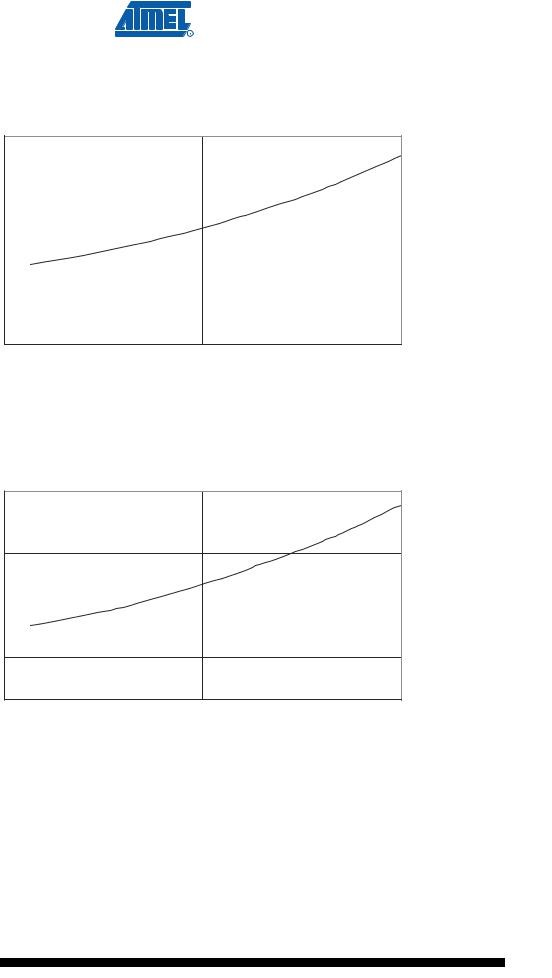
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Standby Supply |
Figure 166. Standby Supply Current vs. VCC (455 kHz Resonator, Watchdog Timer Disabled) |
||||
Current |
|
|
|
|
|
ICC (uA)
STANDBY SUPPLY CURRENT vs. VCC
455 kHz RESONATOR, WATCHDOG TIMER DISABLED
60
50
40
30
20
10
0
2.5 |
3 |
3.5 |
4 |
4.5 |
5 |
5.5 |
VCC (V)
Figure 167. Standby Supply Current vs. VCC (1 MHz Resonator, Watchdog Timer Disabled)
STANDBY SUPPLY CURRENT vs. VCC
1 MHz RESONATOR, WATCHDOG TIMER DISABLED
50
ICC (uA)
45
40
35
30
25
20
15
10
5
0
2.5 |
3 |
3.5 |
4 |
4.5 |
5 |
5.5 |
VCC (V)
308 ATmega16(L)
2466P–AVR–08/07
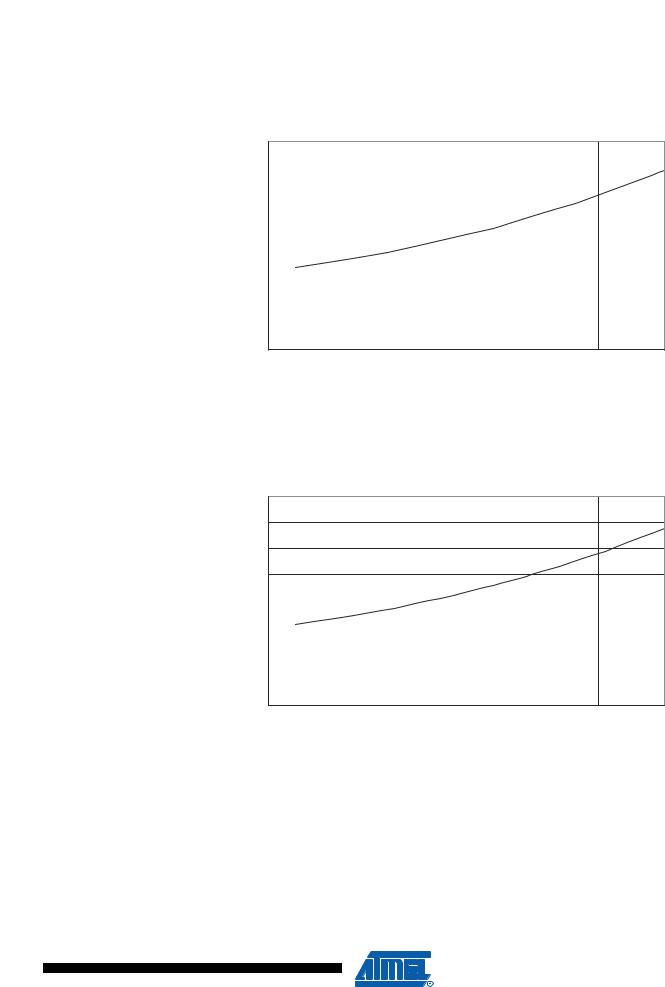
 ATmega16(L)
ATmega16(L)
Figure 168. Standby Supply Current vs. VCC (2 MHz Resonator, Watchdog Timer Disabled)
ICC (uA)
STANDBY SUPPLY CURRENT vs. VCC
2 MHz RESONATOR, WATCHDOG TIMER DISABLED
80
70
60
50
40
30
20
10
0
2.5 |
3 |
3.5 |
4 |
4.5 |
5 |
5.5 |
VCC (V)
Figure 169. Standby Supply Current vs. VCC (2 MHz Xtal, Watchdog Timer Disabled)
ICC (uA)
STANDBY SUPPLY CURRENT vs. VCC
2 MHz XTAL, WATCHDOG TIMER DISABLED
80
70
60
50
40
30
20
10
0
2.5 |
3 |
3.5 |
4 |
4.5 |
5 |
5.5 |
VCC (V)
309
2466P–AVR–08/07
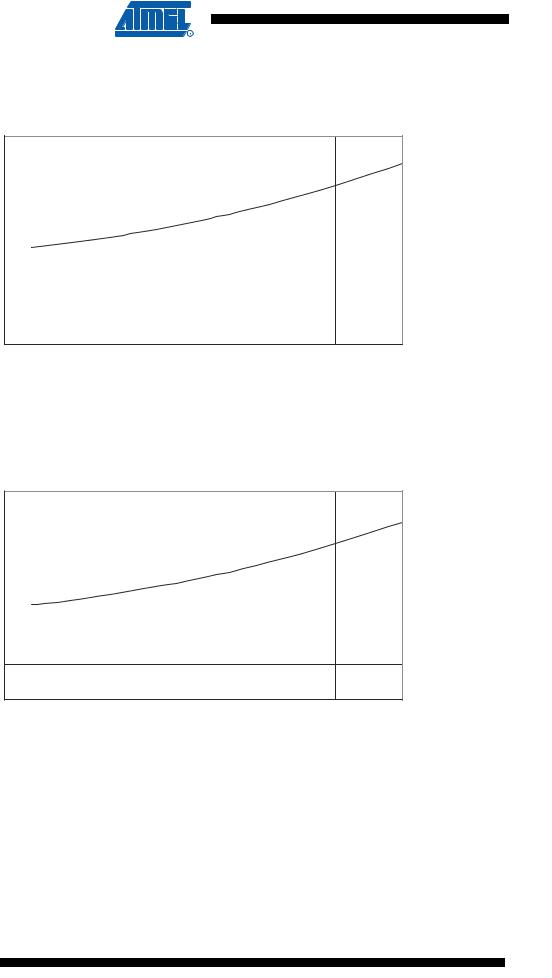
Figure 170. Standby Supply Current vs. VCC (4 MHz Resonator, Watchdog Timer Disabled)
ICC (uA)
STANDBY SUPPLY CURRENT vs. VCC
4 MHz RESONATOR, WATCHDOG TIMER DISABLED
120
100
80
60
40
20
0
2.5 |
3 |
3.5 |
4 |
4.5 |
5 |
5.5 |
VCC (V)
Figure 171. Standby Supply Current vs. VCC (4 MHz Xtal, Watchdog Timer Disabled)
ICC (uA)
STANDBY SUPPLY CURRENT vs. VCC
4 MHz XTAL, WATCHDOG TIMER DISABLED
120
100
80
60
40
20
0
2.5 |
3 |
3.5 |
4 |
4.5 |
5 |
5.5 |
VCC (V)
310 ATmega16(L)
2466P–AVR–08/07
 ATmega16(L)
ATmega16(L)
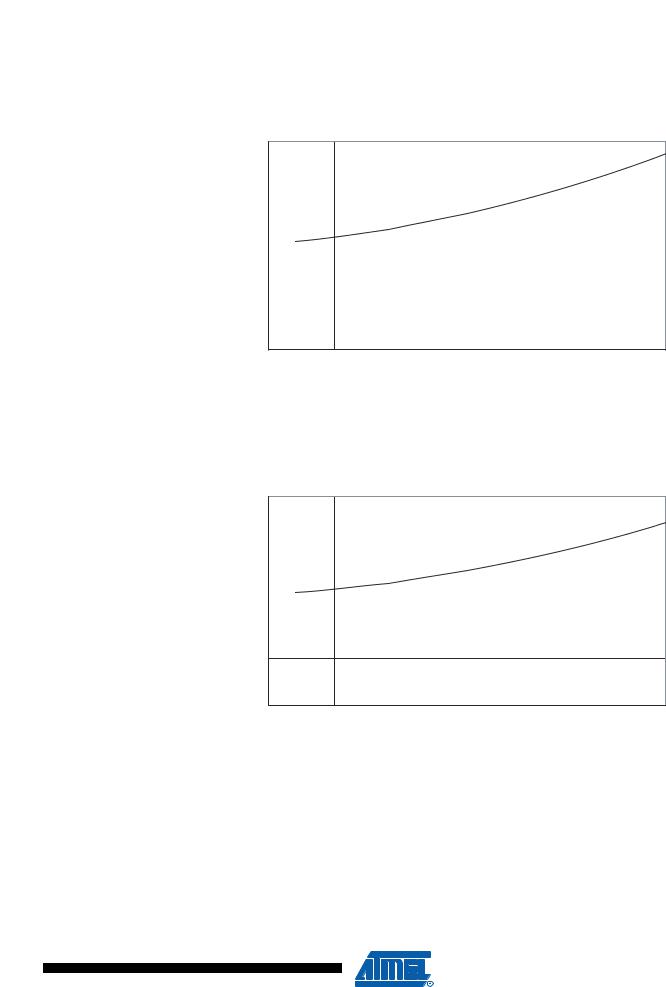
Figure 172. Standby Supply Current vs. VCC (6 MHz Resonator, Watchdog Timer Disabled)
ICC (uA)
STANDBY SUPPLY CURRENT vs. VCC
6 MHz RESONATOR, WATCHDOG TIMER DISABLED
140
120
100
80
60
40
20
0
2.5 |
3 |
3.5 |
4 |
4.5 |
5 |
5.5 |
VCC (V)
Figure 173. Standby Supply Current vs. VCC (6 MHz Xtal, Watchdog Timer Disabled)
ICC (uA)
STANDBY SUPPLY CURRENT vs. VCC
6 MHz XTAL, WATCHDOG TIMER DISABLED
180
160
140
120
100
80
60
40
20
0
2.5 |
3 |
3.5 |
4 |
4.5 |
5 |
5.5 |
VCC (V)
311
2466P–AVR–08/07
