
Maths / Trig volume and area
.docxTrigonometry, Volume and Area
Trigonometry
Right-angled triangles can be studied in maths to help us solve real-life problems.
E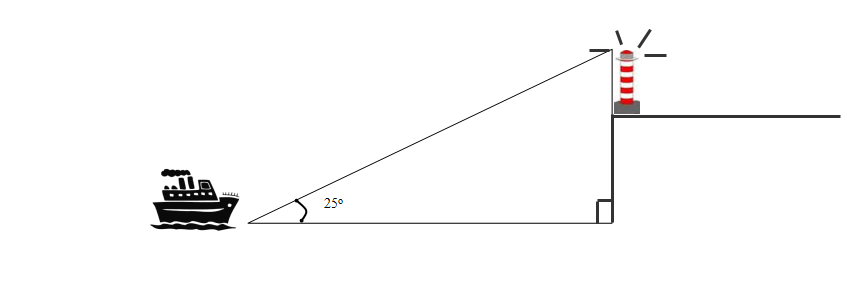 xample:
xample:
How far is the ship from crashing on the rocks?

Hypotenuse = Longest side
Opposite
= Side you hit when you fire a gun from the

Adjacent = Remaining side (next to )
 =
=

 =
=
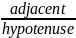
 =
=

SOH – CAH – TOA (Sock - A - Toa)
Examples: find the unknown sides
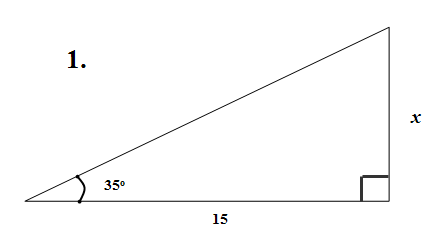
1. = 35o
opposite – x
adjacent = 15
As we have 0 and A: it must be TOA ie. Tangent
tan
=

tan35o
=

15 tan35o = x
10.5 = x
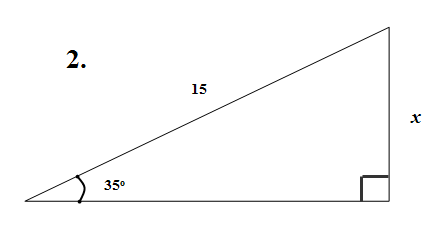
2. = 35o
opposite = x
hypotenuse = 15
We have O and H ; therefore we use sine
Sin35o =
= sin35o
x = 15 sin35o
x = 8.6
Find the unknown angle:
Example 1.
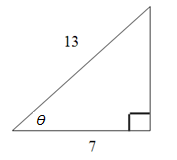
Adjacent = 7
Hypotenuse = 13
We have A and H : therefore we use cosine
Cos
= 
=
cos-1
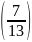
= 57.4o
Example 2.
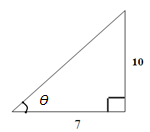
Adjacent = 7
Opposite = 10
We have A and O; therefore we use tangent
tan
= 
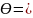 tan-1
tan-1

= 55o
Practice Questions
Calculate the unknown
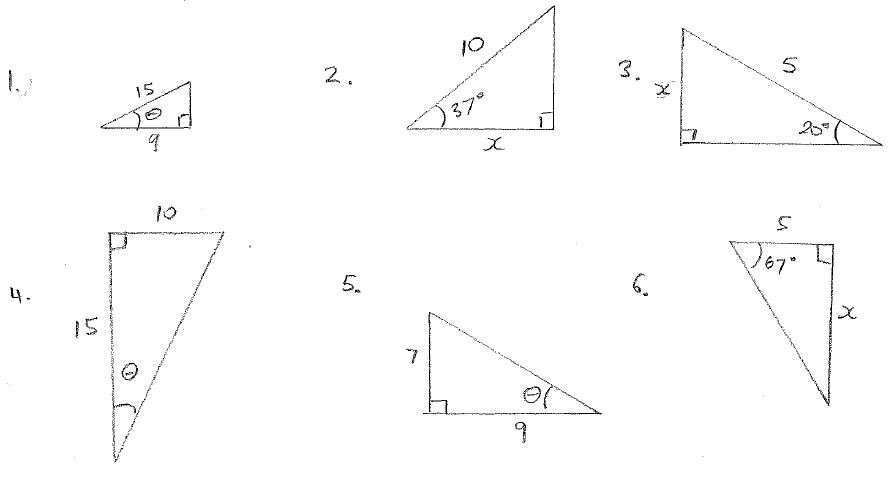
Answers
1. Cos
= 
=
cos1

= 53.1o
2.  =
Cos 37o
=
Cos 37o
X = 10 cos 37o
= 7.99
3. Sin
20o
=

= sin20o
X = 5 sin20o
= 1.71
4. Opposite = 10
Adjacent = 15
We have O and A ; therefore we use tangent
tan
= 
tan-1

= 33.7o
5. Opposite = 7
Adjacent = 9
We have O and A ; therefore we use tangent
tan
= 
tan-1

= 37.97o
6. = 67o
Opposite = x
Adjacent = 5
We have O and A ; therefore we use tangent
= tan 67o
x
 5
tan 67o
5
tan 67o
= 11.8
Area
Let’s review the rules for some basic shapes
1
s
 .
Square
.
Square
Area = s x s (side x side)
2 . Rectangle L
. Rectangle L
Area = L x W w
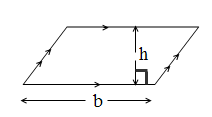
3. Parallelogram
Area = b x h (perpendicular height)

4. Trapezium
Area
=

 h
h

5. Triangle
Area = bh

6. Circle
Area
=

Practice Questions
Calculate the area of the following shapes:

1. Square 5cm

2. Rectangle 15mm
3cm
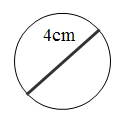
3. Circle
4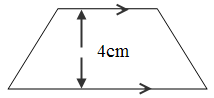 . Trapezium 50mm
. Trapezium 50mm
 10cm
10cm
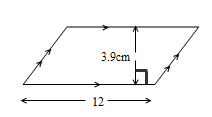
5. Parallelogram
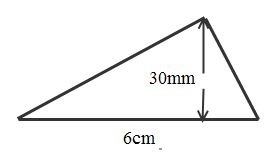
6. Triangle
Answers
1. Area of square = S x S
= 5 x 5
= 25 cm2
2. Area of rectangle = L x W
= 3 x 1.5 (make sure you use W= 1.5cm not 15mm)
= 4.5 cm2
3. Area
of circle = 
=  (radius =
diameter) (
(radius =
diameter) ( = 3.14159)
= 3.14159)
= 12.57 cm2
4. Area of Trapezium = x h
=
 x 4
x 4
= 30 cm2
5. Area of Parallelogram = b x h
= 12 x 3.9
= 46.8 cm2
6. Area of Triangle = bh
= x 6 x 3
= 9cm2
Volume
The volume of an 3D object represents how much space it occupies. The capacity refers to how much solid, liquid or gas it could hold.
1 .
Cylinder
.
Cylinder
Volume
=

= area of circle
x height
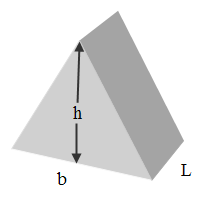
2. Triangular Prism
Volume = bh x L
= area of triangle
x length
3
H
. Rectangular PrismV
W
olume = L x W x H= area of rectangle L
x height
4 . Cube
. Cube
Volume = S2 x H
= area of square x Height H
S
Practice Questions
Find the volume
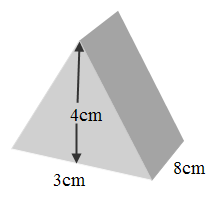
1.

2.
3.
4.2cm
4.2cm
4.2 cm
4 .
.
2cm
3 cm
10.2cm
Answers
1. Volume of triangular prism = bh x L
= x 3 x 4 x 8
= 48cm3
2. Volume of cylinder =
=  x
20
x
20
= 6283.10 cm3
3. Volume of cube = S x S x S
= 4.2 x 4.2 x 4.2
= 74.1 cm3
4. Volume of rectangular prism = L x W x H
= 10.2 x 3 x 2
= 61.2 cm3
