- •In the discipline "Numerical methods"
- •Performed the root separation procedure. Found the segments containing one root of the equation.
- •Implemented the procedure for specifying the roots of the equation using the given method.
- •Programs listing and the number of iterations to find each root.
- •A table (graph) of the dependence of the number of approximations on the solution method. Analyze the results.
MINISTRY OF EDUCATION AND SCIENCE OF UKRAINE
KHARKIV NATIONAL UNIVERSITY OF RADIO ELECTRONICS
Department of ST
Report
on the implementation of laboratory work No. 3
"Solution of Algebraic & Transcendental Equations "
In the discipline "Numerical methods"
Complied by student KNT-23-1: Roman, Kravchenko
Kharkiv 2024 |
Accepted: P.E. Sytnikova,
|
Purpose of the work: study of approximate methods of solving algebraic and
transcendental equations.
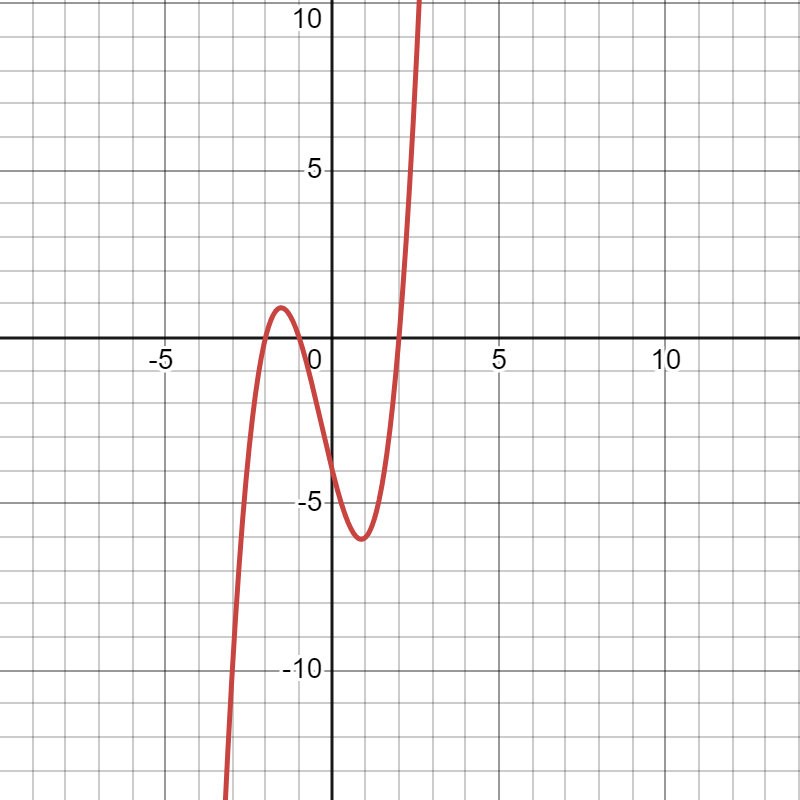
Variant 11:
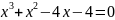 and ε = 0,001
and ε = 0,001
Methods: Bisection, Newton’s, Combined
Performed the root separation procedure. Found the segments containing one root of the equation.
Manual solving:

Programming solving:
#include <vector> #include <iostream>
//Parameters of cubic parabola constexpr double a = 1.; constexpr double b = 1; constexpr double c = -4; constexpr double d = -4;
//Returns value of function with the specified input static double value_of_function(const double x) { return a * pow(x, 3) + b * pow(x, 2) + c * x + d; }
//Find the value of first derivative of a function static double value_of_first_derivative(const double x) { return 3 * a * pow(x, 2) + 2 * b * x + c; }
//Find the critical point of cubic parabola static std::vector<double> find_the_critical_points() { std::vector<double> crit_points;
double temp_a = a * 3.; double temp_b = b * 2.;
//discriminant double D = temp_b * temp_b - 4. * temp_a * c;
if (D > 0) { //find the roots double x1 = (-temp_b + sqrt(D)) / (2. * temp_a); double x2 = (-temp_b - sqrt(D)) / (2. * temp_a);
//return roots in ascending order if (x1 > x2) std::swap(x1, x2);
crit_points.insert(crit_points.end(), { x1,x2 }); } else if (D == 0) crit_points.emplace_back(-temp_b / (2. * temp_a));
else { std::cout << "\nThe given function has no critical points.\n" << "The separation of the roots CAN NOT be performed.\n";
exit(EXIT_FAILURE); }
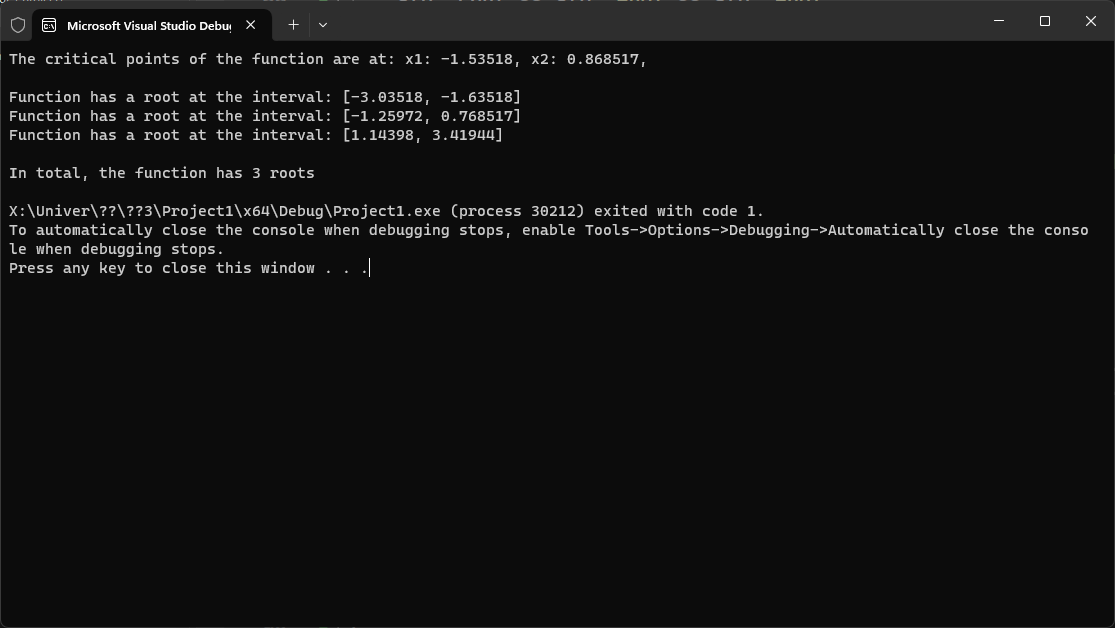
std::cout << "The critical points of the function are at: "; for (size_t i = 0; i < crit_points.size(); ++i) std::cout << "x" << i+1 << ": " << crit_points[i] << ", "; std::cout << std::endl << std::endl;
return crit_points; }
//Specifies whether function has a root at the interval static bool has_root_at_the_interval(const double left, const double right) { double left_value = value_of_function(left); double right_value = value_of_function(right);
return left_value * right_value < 0; }
//Finds the correct intervals where function has different signs static std::vector<double> find_intervals() { //vector of function critical points const std::vector<double> crit_points = find_the_critical_points();
//points of intervals std::vector<double> points;
//value to increase/decrease points' value double dx = 0.1;
double right_limit; double left_limit;
const int MAX_ITERATIONS = 3000; for (size_t i = 0; i < crit_points.size(); i++) { //set the right limit as a difference between current critical point and dx right_limit = crit_points[i] - dx;
//set the left limit with smaller value than right limit left_limit = right_limit - dx;
//iterate while the function values in current points don't have different signs int j = 0; while (j <= MAX_ITERATIONS) { if (i > 0) dx = std::abs(left_limit - crit_points[i - 1]) / 2; left_limit -= dx;
//found two points with different function signs if (has_root_at_the_interval(left_limit, right_limit)) { points.insert(points.end(), { left_limit, right_limit }); break; }
++j; //the left limit value exceeded the left critical point so no root in here. if (i > 0 && left_limit < crit_points[i - 1]) break; } } //set the rightmost interval(the left limit is greater than the last critical point) left_limit = crit_points.back() + dx; right_limit = left_limit + dx;
int j = 0; while (j <= MAX_ITERATIONS) { right_limit += dx; if (has_root_at_the_interval(left_limit, right_limit)) { points.insert(points.end(), { left_limit, right_limit }); break; }
++j; }
points[0] -= 1; points[points.size() - 1] += 1; return points; }
static void root_separation() { std::vector<double> intervals = find_intervals();
for (size_t i = 0 ; i < intervals.size()-1; i += 2) { std::cout << "Function has a root at the interval: [" << intervals[i] << ", " << intervals[i + 1] << "]\n"; } std::cout << std::endl << "In total, the function has " << intervals.size() / 2 << " roots\n"; } |
Program’s output:
The function graph: