
- •Lecture topic:
- •INFILTRATIVE PULMONARY
- •Infiltrative pulmonary tuberculosis is characterized by the presence of inflammatory changes in the
- •TUBERCULOSIS INFILTRATE:
- •INFILTRATES CLASSIFICATION ACCORDING TO LOCALIZATION AND VOLUME OF LUNG TISSUE LESION
- •Infiltrative TB
- •Pericissuritis
- •Rounded infiltrate
- •Lobar infiltrate
- •Bronchiolobular version
- •Infiltrative TB
- •CLINIC:
- •RADIOLOGICAL CHARACTERISTICS
- •RADIOLOGICAL CHARACTERISTICS
- •THREE MAIN VARIANTS PATHOLOGICAL
- •X-RAY DIAGNOSIS
- •FLOW OPTIONS:
- •Differential diagnosis Infiltrative tuberculosis:
- •CASEOSIS PNEVMONIA is one of the the most severe form of tuberculosis, is
- •CLINICAL FORMS:
- •STAGES OF CASEOUS
- •OUTCOMES OF CASEOUS PNEUMONIA:
- •THE CLINIC OF CASEOUS PNEUMONIA:
- •RADIOLOGICAL CHARACTERISTICS:
- •CASEOUS PNEUMONIA:
- •CASEOUS PNEUMONIA:
- •CASEOUS PNEUMONIA:
- •CASEOUS PNEUMONIA:
- •CASEOUS PNEUMONIA:
- •X-RAY DIAGNOSIS:
- •TUBEKULEMA OF THE Lungs is a clinical form of tuberculosis in which a
- •LAYERS OF THE
- •TYPES OF TUBERCULOMAS:
- •CLINICAL COURSE
- •CLINIC OF TUBERCULOMA:
- •RADIOLOGICAL
- •X-RAY DIAGNOSIS:
- •PULMONARY TUBERCULOMA:
- •PULMONARY TUBERCULOMA:
- •Differential diagnosis:
- •Thank you for attention!

THE CLINIC OF CASEOUS PNEUMONIA:
1.Develops acutely.
2.In the initial stage the intoxication syndrome (fever, chills, weakness, marked sweating, sharp deterioration of appetite), shortness of breath, dry cough, sometimes with a small amount of difficultly separated sputum.
3.At the second stage, bronchopulmonary and pleural syndrome is sharply intensified: wet cough with large amounts of sputum, chest pain, hemoptysis, increasing dyspnea, acrocyanosis, hectic fever of irregular type, cachexia.
4.Shorter percussion sound over the area Shortened percussion sound over the affected area, weakened bronchial breathing, Moist fine-bellied rales → then sonorous, numerous, medium- and large-bellied rales, tachycardia, accent of tone II over pulmonary artery, enlargement of the liver..

RADIOLOGICAL CHARACTERISTICS:
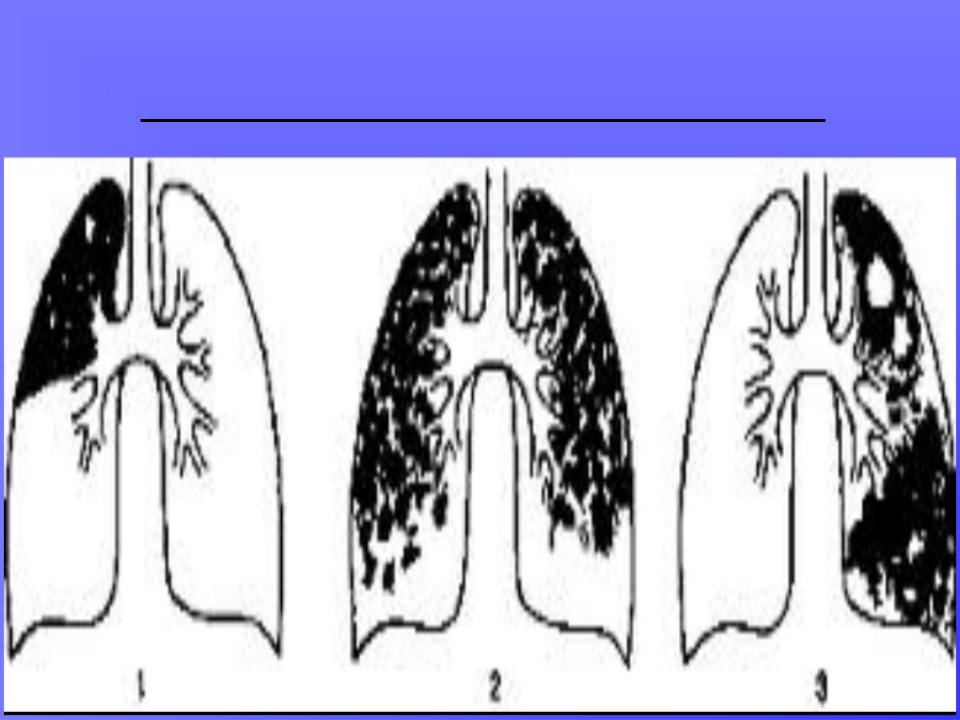
1.With lobar caseous pneumonia - darkening all or most of the lobe of the lung, first homogeneous, then areas appear enlightenment of irregular bay- like shapes with fuzzy contours. In adjacent segments and foci are visible in the other lung bronchogenic dropout. Affected lobe of lung reduced in volume.
2.With lobular caseous pneumonia - visible large focal shadows and small tricks with a diameter of about 1.5 cm. Shadows have irregular shape, medium or high intensity, fuzzy contours. At CT multiple decay cavities are found in the lungs.
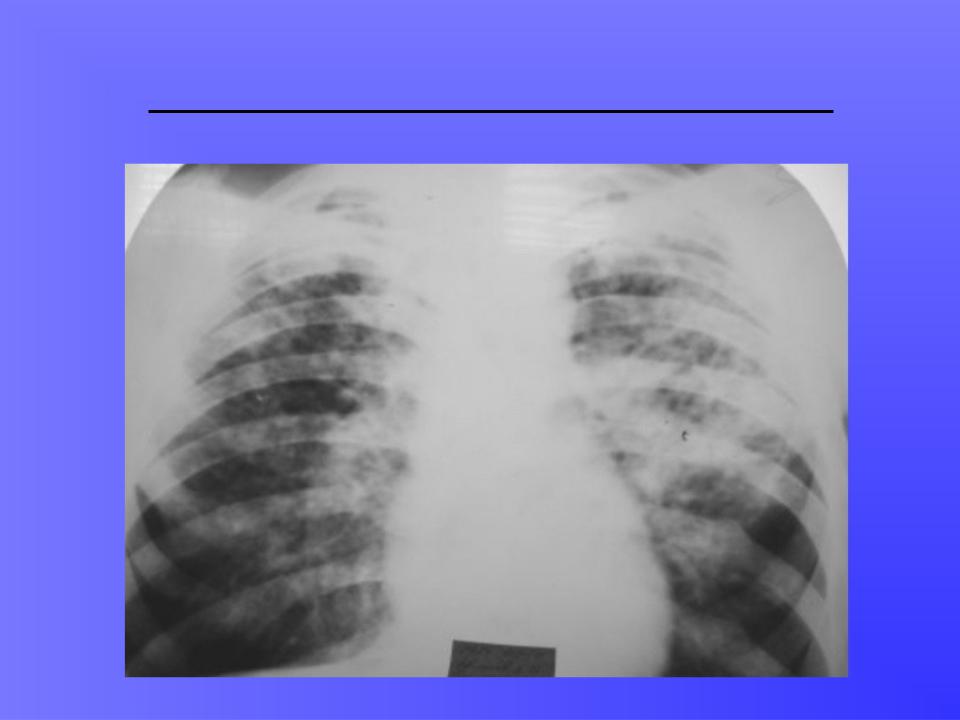
CASEOUS PNEUMONIA:
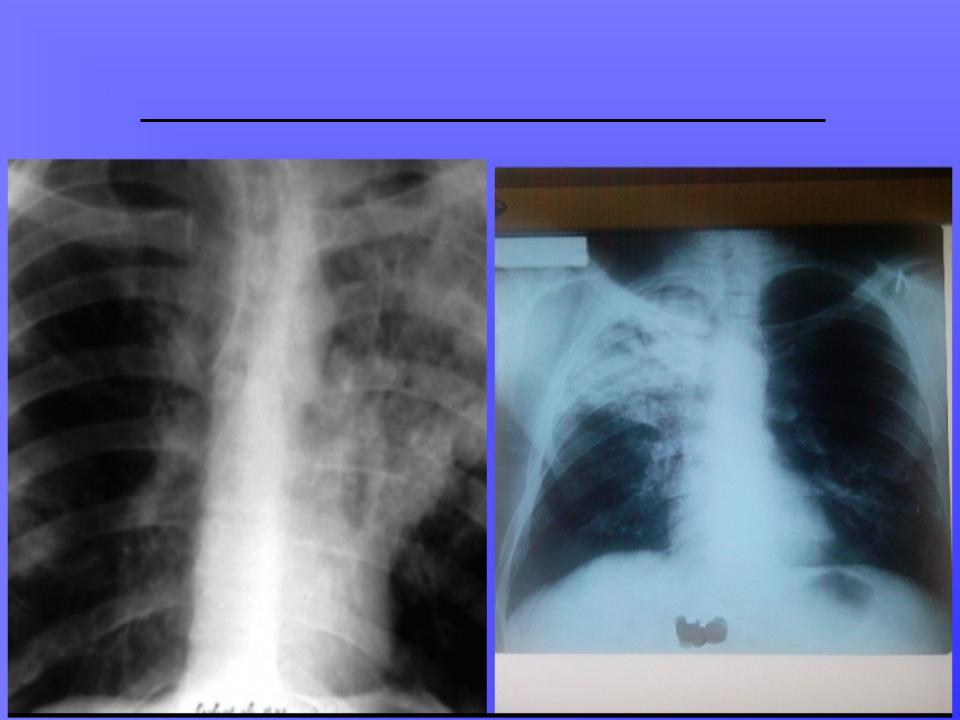
CASEOUS PNEUMONIA:
CASEOUS PNEUMONIA:
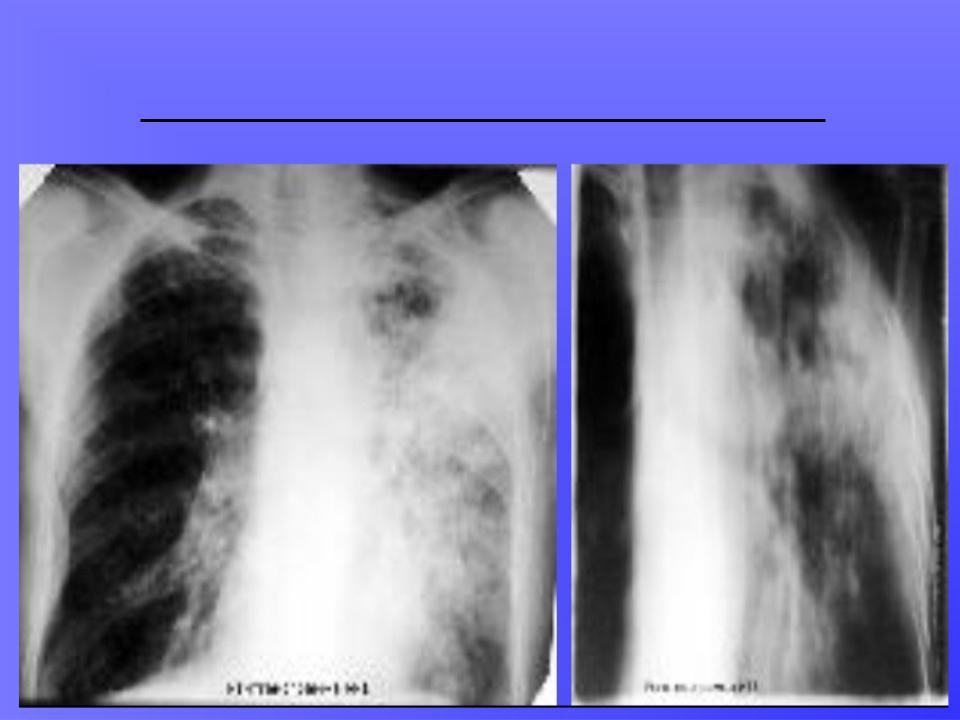
CASEOUS PNEUMONIA:
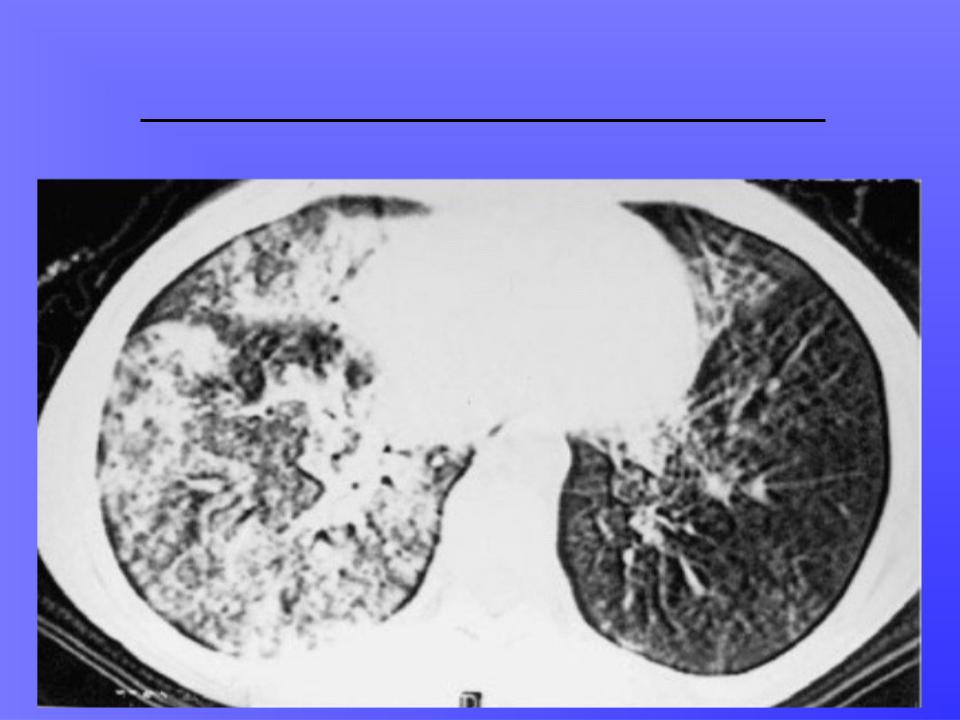
CASEOUS PNEUMONIA:

X-RAY DIAGNOSIS:
1.Extent is from a lobe to affecting the entire lung.
2.The intensity of the shadow is high.
3.The structure of the shadow is heterogeneous with multiple brightenings due to due to destructive changes.
4.Shape of the mediastinum - significant displacement to the side of the lesion (due to Due to loss of elasticity of pulmonary tissue and development of atelectasis individual lobules).

TUBEKULEMA OF THE Lungs is a clinical form of tuberculosis in which a lung tissue forms a caseous-necrotic mass with a diameter of more than 12 mm in diameter, bounded from adjoining lung tissue by a two-layer capsule.
Tuberculoma is found in 2 to 6% of newly diagnosed patients tuberculosis, mostly in adults aged 20 - 35 years.

LAYERS OF THE
TUBERCULOMA CAPSULE:
1.The inner layer formed by Tuberculous granulations, surrounds the caseous nucleus tuberculoma.
2.The outer layer, represented by concentrically arranged fibrous fibers, surrounds tuberculoma from the adjacent sparsely altered lung tissue.
