
6 курс / Неонатология / Научное_обоснование_механизмов_управления_младенческой
.pdf
231
Table 4.7. - Actual provision of the population with medical specialists, (per
10,000 population)
Years |
|
|
|
|
|
Provision |
2017 |
2018 |
2019 |
2020 |
2021 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Provision of the population with district |
|
|
|
|
|
therapists (per 10 thousand population) |
3,50 |
3,80 |
3,80 |
3,80 |
3,8 |
Provision of the population with district |
9,0 |
9,3 |
9,9 |
9,8 |
10,2 |
pediatricians (per 10 thousand child |
|
|
|
|
|
population) |
|
|
|
|
|
Provision of the population with general |
0,02 |
0,02 |
0,02 |
0,02 |
0,02 |
practitioners (per |
|
|
|
|
|
10 thousand population) |
|
|
|
|
|
However, there are positive trends in the increase in the number of outpatient visits from 3393,9 in 2017 to 4232,2 in 2021, visits per 1 inhabitant from 7,4 in 2017 to 8,5 in 2021, and the capacity of outpatient clinics has increased per 10 thousand population from 127,2 in 2017 to 135,7 in 2019 (Table 4.8).
Table 4.8 - Indicators of outpatient visits and planned capacity of outpatient clinics, per 10,000 population in the Republic
Years |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Indicator |
2017 |
2018 |
2019 |
2020 |
2021 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Total outpatient visits (thousand) |
3393,9 |
4045,5 |
4112,4 |
4146,6 |
4232,2 |
|
Visits on |
7,4 |
8,6 |
8,6 |
8,5 |
8,5 |
|
1 inhabitant |
||||||
|
|
|
|
|
||
The planned capacity of outpatient |
|
|
|
|
|
|
clinics for |
127,2 |
1375 |
138,4 |
138.3 |
135,7 |
|
10 thousand population |
|
|
|
|
|
4.2. Micro-level organizational and medical determinants
The perinatal center in the Republic of Ingushetia provided comfortable
conditions for the stay of the mother and the newborn, a combination of classical
232
obstetrics and the latest European technologies, the joint stay of the mother and child, modern methods of anesthesia, strict adherence to the principles of asepsis and antisepsis, round-the-clock provision of obstetric, gynecological, anesthetic, resuscitation highly qualified care for pregnant women , women in labor and childbirth, patients with gynecological pathology, round-the-clock medical care for newborns.
A round-the-clock hospital is organized for 205 beds, a maternity and postpartum department for 110 beds, a gynecology department for 45 beds, a pregnancy pathology department for 45 beds, a day hospital for 6 beds. The center had a physiotherapy room, a antenatal clinic, a cervical pathology room, and a prenatal diagnostics room. Schools are open: preconception training "Kid", breastfeeding school.
Main activities:
-outpatient care for the female population in a medical organization and at home;
-inpatient obstetric and gynecological care for women during pregnancy, childbirth, in the postpartum period, medical care for newborns, as well as women with diseases of the reproductive system;
-prevention, diagnosis and treatment of diseases of the reproductive system;
-provision of medical care in connection with artificial termination of pregnancy;
-Sanitary and hygienic education of women on breastfeeding, prevention of diseases of the reproductive system, abortion and sexually transmitted infections;
-establishment of medical indications and referral of women and newborns to healthcare institutions to provide them with specialized and high-tech medical care;
-examination of temporary incapacity for work, issuance of certificates of incapacity for work to women due to pregnancy and childbirth in the prescribed manner, referral of women with signs of permanent disability for medical and social examination in the prescribed manner;
-organization and provision of sanitary-hygienic and anti-epidemic regime in order to prevent and reduce the incidence of nosocomial infections in women, newborns and medical personnel;
Рекомендовано к изучению сайтом МедУнивер - https://meduniver.com/
233
-conducting a clinical and expert assessment of the quality of medical care for women and newborns;
-analysis of the causes of gynecological diseases, obstetric and extragenital complications in women, morbidity in newborns;
-implementation of statistical monitoring and analysis of the causes of maternal and perinatal mortality;
-ensuring vaccination of newborns and screening for hereditary diseases in the prescribed manner;
-catering for women and newborns during their stay in the maternity hospital;
-interaction with the ambulance station, polyclinics, children's polyclinics, as well as with other medical institutions (tuberculosis, skin and venereal, oncological dispensaries, centers for the prevention and control of AIDS and infectious diseases, etc.);
-maintenance of accounting and reporting medical documentation in the prescribed manner;
-organization of professional development of medical and paramedical personnel;
-compulsory medical activities (state measures for mobilization training, civil defense and emergency medical care in emergency situations, organization and conduct of mass immunization of the population, preventive work with the population, medical statistics, auxiliary medical activities - organizational methodological work).
In 2017, the number of medical workers reached 500 people, including 130 doctors and pharmacists, and 370 nurses. The highest category had 49 doctors and pharmacists and 78 nurses, the first - 57 doctors and pharmacists and 48 nurses, the second - 24 doctors and pharmacists and 48 nurses. 27 doctors and pharmacists and 196 paramedical workers did not have a category. They had the title of "Honored Doctor of the Russian Federation" - 3 doctors, "Honored Health Worker of the Russian Federation" - 5 paramedical workers.
An analysis of applications to the GBUZ Perinatal Center indicated a twofold increase in the number of applicants in the interval 2017 - 2021. The absolute increase
234
was 170 in 2018, 820 in 2019, 1847 in 2020, 1960 in 2021, characterizing the general demographic trends in the Russian Federation. There was a steady upward trend in the number of applications (the slope was 610,56).
The total number of bed days in 2017 was 62,197, rising unevenly to 77,752 in 2021. In general, in the studied interval, a steady upward trend in the number of beddays spent was formed, which characterized the growing need for obstetric services in the perinatal center.
The average number of days a bed was occupied per year was 239 in 2017 and rose steadily to 307 in 2021. The base growth rate increased from 117,15% to 128,45%. The average level of the series was 294,73 days, the average absolute increase was 6,8. The regression equation characterized the growth trend: y = 66,4 + 2.0 t.
The bed turnover in the perinatal center increased from 29,3 in 2017 to 45 in 2021. The base growth rate increased from 129% to 153,6%. The average level of the series was 40,48, the average absolute increase was 1,57. A stable growth trend has formed: y = 19 + 0,65 t.
The average bed downtime in the study period decreased from 4,3 to 1,25 days. The base growth rates decreased from 51,16 to 29,09, the average absolute increase was -0,31. The dynamics equation characterized the emerging downward trend: y = - 2,9 - 0.1 t.
The share of rural residents in the structure of all applications in the studied interval was 9,43% - 15,74%, increasing by 6,31%. The total number of visits increased from 582 to 1835. The base growth rate varied from 122% to 315,3%, highlighting the threefold increase in the number of visits to the perinatal center of the rural population. The average level of the series was 1052,5, the average absolute increase was 139,22. The regression equation testified to a steady growth trend in such calls: y = 2716.8 +
109.2t.
At the same time, they spent bed-days from 6596 in 2017 to 11040 in 2021. The
chain growth rate was 94,67% in 2018 and increased to 123,5% in 2021. The underlying growth rate was 94,67% in 2017, rising to 167,4% in 2021. The average level of the series was 7411 days, the average absolute increase was 493,77. The
Рекомендовано к изучению сайтом МедУнивер - https://meduniver.com/
235
regression equation y = 12759 + 512,41t characterized a steady growth trend for this indicator.
There were 1,493 admissions to the gynecological department in 2017, and by 2021 their number has increased by 1,5 times, reaching 2,194.
However, the proportion of those admitted to the gynecological department decreased from 26,6% to 18,8%, giving way to women in labor. They spent 13789 - 15599 bed-days. The growth trend was formed and stable: y = 9408 + 377,8 t.The number of rural residents admitted in the studied interval was 158 - 408, which was 10,5% - 18,5% of all those admitted to the gynecological department. At the same time, a steady growth trend was noted: y = 300,7 + 12,1 t. They spent 1730 - 2357 bed-days, which accounted for 12,5% - 15,1% of the total number of all bed-days in the gynecological department. At the same time, a steady growth trend was formed for incoming rural residents: y = 939,4 + 37.7 t.
The Department of Pathology of Pregnancy received 1773 - 3397 in the interval from 2017 to 2021.
The absolute increase was uneven, the chain growth rates varied from 120,8% to 105%, the basic ones - from 120,8% to 191,6%, the average level of the series was 2529,5, the average absolute increase was 180,4, the growth trend of the indicator was stable, as evidenced by a slope equal to 187,6.
Among those admitted to the Department of Pregnancy Pathology, the proportion of villagers in the studied interval increased from 10,1% to 14,2%. The core growth rate dynamically increased from 109,8% to 136,8%, the average level of the series was 208,3, the average absolute increase was 33,44, the average growth rate increased from 1,87% to 2,17%, the slope regression equation, equal to 22,2 testified to a steady growth trend in the proportion of village residents.
The share of home births was 0,7% in 2017 and decreased to 0,4% by 2021, the base growth rate decreased from 183,3% to 116,7%.
The number of full-term babies increased by 1.8 times: from 3070 in 2017 to 5620 in 2021.
236
Their share by 2021 was 90%, which, against the background of an increase in the number of births, testified to an improvement in the quality of work of a clinical maternity hospital against the backdrop of complex medical, social and economic transformations in the healthcare system. The chain growth rates, varying from 121% to 101,5%, indicated an annual decrease in the growth of the indicator, and the base ones, amounting to 121% - 183,1%, reflected the accumulated potential of the number of children born full-term. The average level of the series was 4609,7 full-term births, the average absolute increase was 283,3, the average growth rates varied from 1,99 to 2,07, and the equation of dynamics, which had the form y = 7541,2 + 302,86 t, testified to formed trend of growth in the number of full-term children.
Against the background of an increase in the number of births, there was an increase by 1.58 times in the number of premature babies from 309 in 2017 to 487 in 2021.At the same time, the proportions of premature babies were 7,5%, 7,7%, 6,7%, 6,6%, 8,3% in 2017-2021, respectively. Chain growth rates of 97,1% - 103,8% and basic growth rates of 97,1% - 157,6%, respectively, confirmed the growth of the indicator. The average level of the series was 383,6, the average absolute increase was 19,8, the average growth rates ranged from 1,99 to 2,04, the regression equation y \u003d 630,6 + 25,3 t indicated a steady upward trend in the number of premature babies among all births.
Preterm births in the studied interval occupied 6,8% - 7,6%, chain growth rates were 93,7% - 102,9%, basic – 93,7% - 159,9%, the average level of the series was 262,3, the average absolute increase was 19,1, the regression equation y = 735,3 + 29,53 t testified to the formed trend of increasing preterm birth, which was determined by the increase in the number of births, the age of mothers and the burden of pathology of puerperas. Multiple births in 2017 were 1,2%, in 2018 0,8%, in 2019 1%, in 2020 0,98%, in 2021 1,1. Chain 75,6% - 110% and basic 75.6% - 134,1% growth rates indicated an increase in the proportion of multiple births, and the slope in the regression equation y = 62,6 + 2.5 t confirmed a steady growth trend.
Thus, the assessment of the provision of medical personnel in the health care of the Republic showed a significant lag in the actual number of medical personnel from
Рекомендовано к изучению сайтом МедУнивер - https://meduniver.com/
237
the normative one, established by the targets of the Federal project. The actual values of the provision of medical personnel during the project activities increased, but did not always reach the required values. The exception was the indicator of provision with paramedical personnel, which reached the required level by 2021.
Analysis of the activities of the hospital for 2017 - 2021 reflected the increased workload of medical personnel, an increase in the intensity of work due to steady growth:
-appeals to the perinatal center;
-number of bed-days spent;
-number of days the bed is occupied;
-bed turnover;
-appeals of rural residents;
-number of bed-days spent by rural residents;
-the number of patients admitted to the gynecological department and the reduction in the proportion of gynecological patients;
-rural residents among those admitted to the gynecological department;
-bed-days spent by rural residents in the gynecological department;
-the number of women admitted to the department of pathology of pregnancy and the number of bed-days they spent.
There has been an emerging trend towards a decrease in the average bed downtime from 4,3 to 1,25 days.
The intensity of the work of the perinatal center increased due to the increase in the number of births. At the same time, the growth trend was stable and formed.
The proportion of home births in the total population was minimal and decreased from 0,7% to 0,4%.
The number of children born in the study period increased, and the growth trend was stable.
The number of full-term children increased by 1,8 times, their share was 90% - 93%, which indicated an improvement in the quality of the work of the Perinatal Center against the backdrop of increasing state support for motherhood and childhood.
238
Due to the increase in the number of births, there was a numerical increase in premature babies, although the proportion of premature babies in the entire population of those born remained practically unchanged, ranging from 7.5% to 8%.
The proportion of live births was stable, amounting to 99,2% - 99,4% in 2017-
2021.
The proportions of live full-term children were 91,5% - 92,2%, and the total number of live full-term children was steadily increasing.
The number of live preterm infants steadily increased in parallel with the growth in the number of births, however, the proportion of live preterm infants in the structure of all live births decreased from 8,5% to 7,7%. About 7% of preterm births were accepted. The proportion of multiple births fluctuated around 1%.
Рекомендовано к изучению сайтом МедУнивер - https://meduniver.com/
239
CHAPTER 5. HEALTH-DEMOGRAPHIC AND HEALTH-SOCIAL
DETERMINANTS OF INFANT MORTALITY
5.1. Medical-demographic determinants
As numerous causes and factors that determine the change in the magnitude of infant mortality are medical and demographic (birth rate, fertility, morbidity of pregnant women, women in labor and childbirth, newborns), medical and social, characterizing the mother's lifestyle during pregnancy, living conditions, attitudes towards one's health , genetic characteristics, the serial number of pregnancy and childbirth, age and others that form the health of the mother and child and indicators of its assessment.
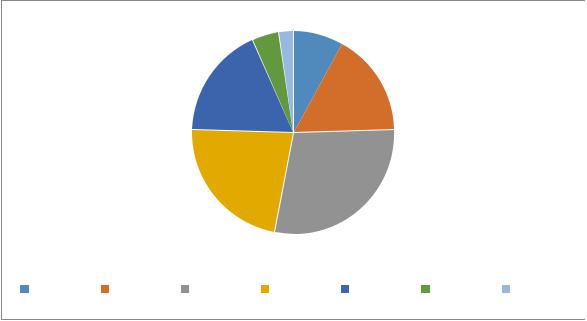
In the age structure of puerperas, the first place was occupied by women aged 25-29 years, accounting for 28,64%, the second - 30-34 years old with a share of 22,54%, the third - 35-39 years old with a share of 17,84%, the fourth - 20-24 years old – 16,43%, fifth - 15-19 years old – 7,98%, sixth - 40-44 years old – 4,23%, seventh - 45-49 years old – 2,35% (figure 5.1) .
Figure 5.1. Age structure of puerperas, (%).

240
The calculation of the birth rate and its dynamics indicated a trend of decreasing the indicator from 21,5‰ to 16,3‰ (the regression coefficient was 0,6) (Table 5.1).
Table 5.1 - Dynamics of the birth rate, ‰
Indicator |
2017 |
2018 |
2019 |
2020 |
2021 |
Total fertility rate |
21,5 |
18,5 |
16,3 |
16,6 |
16,3 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Age-specific fertility rates at the age of 20-24 had a steady downward trend from 103.9‰ in 2017 to 96,1‰ in 2021 (the regression coefficient was 0,61). In other age intervals, they increased from 2017 to 2021, respectively: up to 20 years old - from 16,5 to 26,2‰; at 25-29 years old - from 102.1‰ to 121,7‰; 76,7‰ to 84,0‰, at 3539 years old - from 49,6‰ to 52,1‰, at 40-44 years old - from 17,2‰ to 17,4‰, at 45-49 - 1,3‰ to 1,6‰, respectively (Table 26). The total fertility rate increased insignificantly from 1,8 to 1,9, and testified to the narrowed mode of reproduction of the population of the Republic (Table 26).
Table 26 - Age-specific and total fertility rates in the Republic of Ingushetia, ‰
Age
Years
2017
2018
2019
2020
2021
Younger than |
20 |
20-24 |
25-29 |
30-34 |
35-39 |
40-44 |
45-49 |
15-49 |
Total fertility rate |
16,5 |
103,9 |
102,1 |
76,7 |
49,6 |
17,2 |
1,3 |
55,8 |
1,8 |
|
12,5 |
99,5 |
107,9 |
79,2 |
51,3 |
17,2 |
0,8 |
56,1 |
1,8 |
|
15,3 |
100,2 |
112,4 |
78,3 |
48,8 |
19,6 |
0,9 |
56,7 |
1,8 |
|
26,1 |
91,3 |
116,8 |
75,9 |
52,5 |
19,6 |
1,7 |
56,9 |
1,8 |
|
26,2 |
96,1 |
121,7 |
84,0 |
52,1 |
17,4 |
1,6 |
57,4 |
1,9 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
94,8% of the interviewed puerperas were married, and only 5,2% were divorced (figure 5.2).
As a rule (in 70,9% of cases), women lived as a family, apart from their parents, and only 29,1% lived with their parents and other relatives (figure 5.3).
Рекомендовано к изучению сайтом МедУнивер - https://meduniver.com/
