
- •Update on Infective Endocarditis
- •Pathogenesis
- •Epidemiology
- •mitral valve prolapse
- •Mitral Valve Prolapse
- •Coagulase-negative Staphylococci
- •Prosthetic Heart Valve
- •IV Drug Use
- •Predisposing Factors
- •Polymicrobial Infective Endocarditis
- •Diagnostic (Duke) Criteria
- •Diagnostic (Duke) Criteria
- •Diagnostic (Duke) Criteria
- •Duke’s Major Criteria
- •Duke’s Major Criteria
- •Duke’s Minor Criteria
- •Duke’s Minor Criteria
- •Risk for Endocarditis
- •Risk for Endocarditis
- •Risk for Endocarditis
- •Treatment
- •New Treatments
- •New Treatments
- •New Treatments
- •SBE Prophylaxis
- •References

Update on Infective Endocarditis
Larry Baddour, MD
University of Tennessee
7/98 |
medslides.com 1 |

Pathogenesis
•Disruption of the endocardial layer as a complication of abnormal blood flow associated with underlying cardiac defect
•Bacterium-endothelium interaction with bacterial attachment and invasion of endothelial cells
7/98 |
medslides.com 2 |

Epidemiology
•Underlying valvular abnormality predisposing to infective endocarditis
–rheumatic fever
a common cause in the past
–mitral valve prolapse
currently represents the most common underlying cardiac abnormality
7/98 |
medslides.com 3 |

mitral valve prolapse
•risk for infective ednocarditis is 5x-8x
•mitral regurgitation increases the risk
•leaflet redundancy with myxomatous degeneration is a frequent finding
•age <20 , female predominate age >20 , male accounts for 60% age >50 , male accounts for 68%
7/98 |
medslides.com 4 |

Mitral Valve Prolapse
and Infective Endocarditis
N mu eb or cf sa se
20 |
Male |
|
|
|
|
18 |
|
|
|
|
|
Female |
|
|
|
|
|
16 |
|
|
|
|
|
14 |
|
|
|
|
|
12 |
|
|
|
|
|
10 |
|
|
|
|
|
8 |
|
|
|
|
|
6 |
|
|
|
|
|
4 |
|
|
|
|
|
2 |
|
|
|
|
|
0 |
20-29 |
30-39 |
40-49 |
50-59 |
>60 |
<19 |
7/98 |
Rev Infect Dis 1986;8:117-137 |
medslides.com 5

Coagulase-negative Staphylococci
•can produce native-valve endocarditis in mitral valve prolapse
•usually subacute, difficult to diagnose, and disregarded as a contaminant
•delay in diagnosis and treatment may account for the severe complications
–myocardial abscess formation
–valvular insufficiency requiring valve surgery
–death
7/98 |
medslides.com 6 |

Prosthetic Heart Valve
•positive blood culture in hospitalized patients with underlying prosthetic valves can be a harbinger of endocarditis
•43% patients with nosocomial bacteremia or fungemia had prosthetic valve infection
•a serious complication
7/98 |
medslides.com 7 |

IV Drug Use
•Recurrent
•Polymicrobial
•Staph aureus accounts for the majority of cases of endocarditis
•tricuspid valve, either alone or in combination, us most often infected
7/98 |
medslides.com 8 |
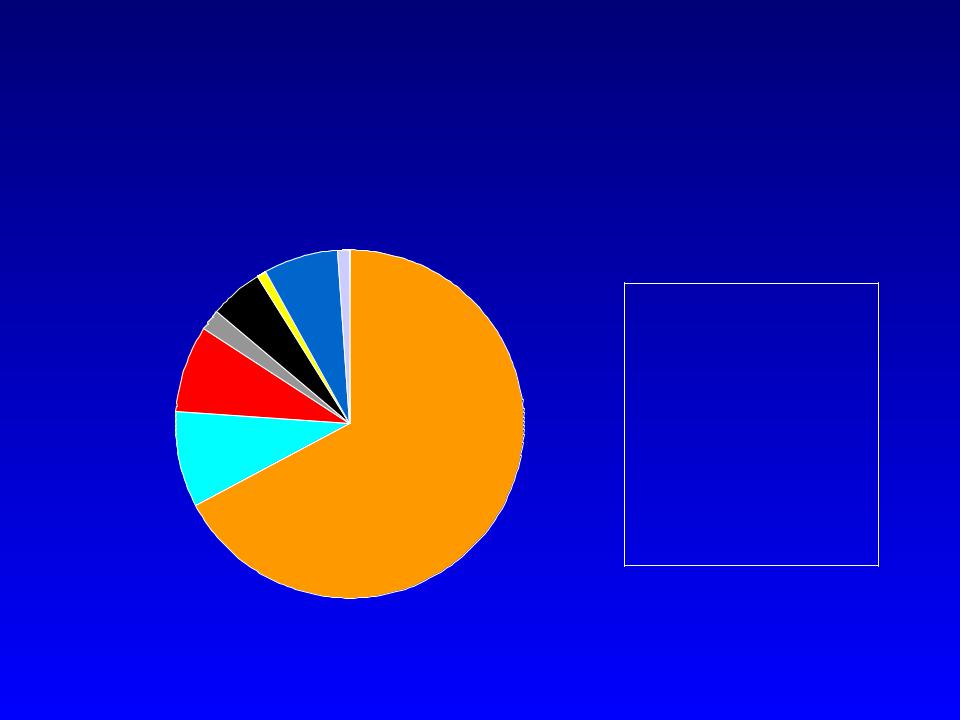
Predisposing Factors
Polymicrobial Infective Endocarditis

 Iv drug use
Iv drug use

 Central line
Central line

 Prosthetic valve
Prosthetic valve

 Previous IE
Previous IE

 Murmur
Murmur

 Dental procedure
Dental procedure

 Rheumatic disease
Rheumatic disease

 Miscellaneous
Miscellaneous
7/98 |
medslides.com 9 |

Polymicrobial Infective Endocarditis
clinical features
•IV drug use is the predominant risk factor
•younger age (mean 36.5 years)
•2/3 were male
•right-sided cardiac involvement in > 60%
•streptococci more frequent than S. aureus
•1/3 of patients died
•mortality rate is 4x higher for pure left- sides vs pure right-sided endocarditis
7/98 |
medslides.com 10 |
