
- •Table of Contents
- •List of Tables
- •List of Figures
- •List of Photos
- •Abbreviation
- •Chapter 1 Organizational Structure and Duties
- •Chapter 2 Acceptance of Equipment and Plants for putting in Operation
- •Chapter 3 Personnel Preparation
- •Chapter 4 Plan for Repair of Equipment, Plant and Construction
- •Chapter 5 Safety Technology
- •Chapter 6 Fire Prevention Equipment
- •Chapter 1 Plan
- •Chapter 1 General Provisions
- •Chapter 2 Civil Works and Mechanical Equipment for Civil Works
- •Section 1 Civil Works
- •Section 2 Check of Civil Works' Condition
- •Section 3 Mechanical Equipment for Civil Works
- •Chapter 3 Management of Water Sources in Powerhouses, Assurance of Meteorology and Hydrology
- •Section 1 Water Regulation
- •Section 2 Environment in Reservoir
- •Section 3 Hydro-Meteorological Activities
- •Chapter 4 Hydraulic Turbine / Generator
- •Chapter 1 General Provisions
- •Chapter 2 Fuel Transportation and Supply
- •Chapter 3 Pulverized Coal Processing
- •Chapter 4 Boiler and its Auxiliary
- •Chapter 5 Steam Turbine and its Auxiliary
- •Chapter 6 Unit-type of Thermal Power Plants
- •Chapter 7 Gas Turbine and its Auxiliary
- •Chapter 8 Diesel Generator
- •Chapter 9 Automation and Thermo-measuring Equipment
- •Chapter 10 Water Treatment and Hydration
- •Chapter 11 Pipelines and Valves
- •Chapter 12 Auxiliaries for Thermo-mechanical Section
- •Chapter 13 Environmental Protection Facilities
- •Chapter 1 General Provision
- •Chapter 2 Generator and Synchronous Compensator
- •Chapter 3 Electric Motor
- •Chapter 5 DISTRIBUTION NETWORK
- •Chapter 6 BATTERY SYSTEM
- •Chapter 7 OVERHEAD POWER LINES (OPL)
- •Chapter 8 Power Cable Lines
- •Chapter 9 PROTECTIVE RELAY AND AUTOMATION
- •Chapter 10 Grounding Equipment
- •Chapter 11 OVER-VOLTAGE PROTECTION
- •Chapter 13 Illumination
- •Chapter 14 Hydrogen Generation Station
- •Chapter 15 Energy Oil
- •Chapter 1 LOAD DISPATCH COMMAND
- •Chapter 3 OPERATOR
- •Chapter 4 DISPATCHING AND CONTROLLING DEVICES
Chapter 8 Power Cable Lines
Article 323. General provisions
Power cables are usually placed in the building, and underground cable works, and less of a problem, but maintenance and overhaul to them shall be done in order to prevent corrosion of metal parts around water or underground and control panels of the associated equipment (barrels of oil and warning systems, etc.)
Power cable lines shall be maintained and overhauled as the following table.
Table 323 Sample methods of maintenance and overhaul for each equipment
Equipment |
Conditions of equipment |
Methods of maintenance and overhaul |
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Crack and damage |
Concrete cover |
|
|
|
Directly buried cable |
Foreign substance inside |
Cleaning |
|
|
|
block |
block |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
Deformation of block hole |
Replacement |
|
|
|
|
Damage of lid and packing |
Replacement |
|
|
|
|
Corrosion and damage of |
Antirust painting, replacement |
|
||
Cable tunnel, |
ladder |
|
|
|
|
cable room, |
Crack and exfoliation of |
Repair by mortar |
|
|
|
cable cellar and |
inside wall |
|
|
|
|
cable canal |
Defect of waterproof lid at |
Fastening, replacement |
|
||
|
block edge |
|
|
|
|
|
Corrosion of metal parts |
Antirust painting, replacement |
|
||
Cable bridge and |
Corrosion, damage |
Antirust painting, replacement |
|
||
Loosening or falling off of |
|
|
|
|
|
cable trough |
Fastening, replacement |
|
|||
bolts |
|
||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Corrosion, damage or |
|
|
|
|
|
loosening of structure and |
Antirust painting, fastening, replacement |
|||
Cable rack |
bolts |
|
|
|
|
|
Defect of fixed foundation |
Repair |
by |
mortar, |
replacemen |
|
concrete |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Damage, discoloration |
Re-winding tape, replacement |
|
||
|
Oil leakage |
Stopping oil, replacement |
|
||
Cable, |
Degradation of anticorrosion |
Re-winding tape, replacement |
|
||
connection box and |
tape |
|
|||
|
|
|
|
||
terminal box |
Degradation of flame |
Replacement |
|
|
|
|
prevention |
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Defect of metal parts |
Antirust, painting, fastening, replacement |
|||
352
|
Equipment |
|
Conditions of equipment |
Methods of maintenance and overhaul |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Decrease or degradation of |
Replenishment, replacement |
|
|
|
|
insulation oil |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Oil supply tank, |
|
|
Corrosion or oil leakage of oil |
Antirust painting replacement |
|
oil fill tube and |
|
|
supply tank |
||
|
|
|
|||
valve |
|
|
|
Damage, or dirt discoloration |
|
|
|
|
|
of oil level indicator and oil |
Cleaning, replacement |
|
|
|
|
pressure indicator |
|
Protective |
equipme |
Crack or damage of concrete |
Crack repair, replacement of concrete |
||
wall |
|||||
for oil leakage |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Defect of sensor |
Adjustment, replacement |
||
|
|
|
|
||
Oil |
pressure |
a |
Defect of device, sensor |
Adjustment, replacement |
|
system |
|
|
Defect of power source |
Connection of power source, replacement |
|
|
|
|
|
Snapping |
Re-connection, replacement |
|
|
|
|
Degradation or damage of |
Winding tape, replacement |
Grounding conductor |
|
insulation cover |
|||
|
|
||||
|
|
|
|
Degradation of anticorrosion |
Winding tape |
|
|
|
|
tape |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Draining facility, |
|
|
Defect of device |
Adjustment replacement |
|
lighting facility and |
|
Defect of power source |
Connection of power source, replacement |
||
ventilation facility |
|
Defect of metal parts |
Antirust painting replacement |
||
Article 324. Load cables
The maximum allowable load current of power cable lines shall be determined at the worst heat condition.
In case that additional cables are installed,the maximum allowable load current of other cables in the same section of additional cables shall be revised.
Therefore, the maximum allowable load current shall be understood in both power network management units and load dispatching units.
The maximum load current may be determined by testing results on sites which is carried out in the worst condition.
-Testing site shall be at the section of the highest cable temperature.
-Cable temperature shall be considered with the temperature of inner core based on the temperature outside cable sheath.
Article 325. Temperature in tunnels and cellars
The temperature in cable tunnel (cellar, etc.) where maintenance workers can access shall be 45deg C or below basically, as considering the following items.
- The physical condition of workers who carry out maintenance and repair.
353
-The overheat of cable (Calculation condition of the maximum allowable load current may be changed as the temperature in cable tunnel increases.).
In case that the temperature in cable tunnel exceeds 45 degrees Celsius, the following items shall be carried out.
-The temperature in cable tunnel is decreased by forcing and cooling ventilation systems
-The operating current is limited not to exceed the temperature of 45deg C in cable tunnel.
Article 326. Overload of cables
It shall be prohibited to use the cable which is over permissibletemperature because it is impossible for insulation materials (insulating paper and cross-linked polyethylene) to perform expected insulation strength. Specifications of insulating paperor cross-linked polyethylene of thecable shall be confirmed sufficiently before the operation because the permissible temperature is decided by them. As the point requiring attention in particul,ablecr permission temperature is notthe surface temperature that is lower than the core but the core temperature.
Article 327. Oil pressure
Oil pressure of oil-filled cables shall comply with the value prescribed by the manufacturer.
Article 328. File documents
Related technical materials shall be referred to Article 249 in Technical Regulation as well as Article 328.
Article 329. Supervision of implementation
On cable laying works and assembling works of cable connection boxes, management unit or power company shall check the works during the construction,and confirm that suitable construction is carried out by constructors since it is difficult to check in detail after the works are completed.
Article 330. Protection of metal structures
It is necessary to paintor galvanize the support rackto protect from rustbecause cable trays, cable racks easily corrode due to be installed in cable canals or cable tunnels with very high humidity environment.
In addition, it is necessary to carry out painting or other countermeasures for the support rack to protect it from the heat in case that the support rack is exposed to sunshine, and it is damaged from the
heat by direct sunshine.
Article 331. (moved to Article 276)
Article 332. Checking power cable
It shall be referred to Chapter 6 in Technical Regulation Vol.5 to check the electrical power cable.
When the failure occurs in the cable, the patrol shall be executedto detect the failure point, confirm the facilities damage, and necessary repair or restoration means shall be taken. The patrol shall be
354
executed promptly because the public may reach the danger such as electric shock and a fire, etc. by the failure cable, and the facilities damage may be expanded by unrepaired parts.
The method of patrol
-In case of oil-filled power cable lines, patroller shall check oil supplier unitfor the oil level, oil pressure and oil amount, and confirm that there is no oil leakage.
-Patroller shall confirm that there is no civil work such as excavation or pile driving which damages
underground cable lines, and there is no shortcoming cableof sections gone outfrom the underground.
-Patroller shall confirm that there is no defect near cableroom, cable cellar andcable well and invisible points of power cable lines.
Article 333. Protection of electrochemical corrosion
Electrolytic corrosion shall be protected by protective covering outer sheath or electrolytic protection.
In case of a normal cable, protective covering outer sheath made of synthetic rubber protects electrolytic corrosion. In case that pipe type cable line are placed underground, the line shall be equipped with not only protective covering outer sheath but also an electrolytic protection shown in
the following table since a corrosion of steel pipe causes a serious failure.
|
Table 333 |
Electrolytic protection |
|
|
|
|
|
Electrolytic protection |
|
Applicable general cases |
|
|
|
||
|
Urban area (This system is adopted which causes little impact to other |
||
Anodic protection |
lines since urban area has low thermal resistance of soil, and there are |
||
|
many other lines adjacently) |
||
|
|
||
Impressed current protection |
Mountain area (This system is effective in casehighof thermal |
||
system |
resistance of soil, and there are a little other lines) |
||
Anodic protection and |
Long distance lines |
||
impressed current system |
|||
|
|
||
|
The place |
where cable lines can be easilyconnected to rails o |
|
Selective drainage corrosion |
electrical railway. (This system shall be considered the interference to |
||
|
other lines) |
|
|
Article 334. Protect of power cable line attach mechanical actions
When the excavation work is done on undergroundcable, the management unit of the cableshall investigate the construction contractor to the digging depth,heavy civil machines will be used and measures for protecting the cable before carrying the work out, and confirm that the site work can not damage the cable.
The management unit shall not permit the construction work, and the construction contractor shall not carry the work out in case that the work may damage the cable.
In addition, in the permitted constructionwork, the management unit shall check the safety of the cable, and confirm thatthe actual situation of the work does not differ from the situation ofprior investigation at the construction site.
355
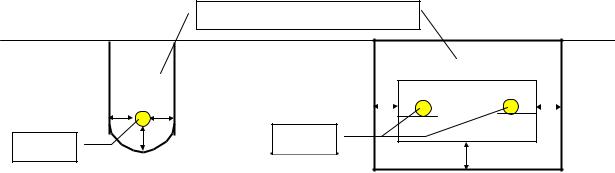
Article 335. Construction near power cable line
The construction area affecting underground power cable lines must be supervised by the cable management unit are shown in the image. Engineer’s supervision shall be requiredwhile performing the pavement rehabilitation and the macadam road paving, etc. .. above the underground cables and offset distance to underground cables shall not be more than 1 m.
In addition, when the distance from the underground cable to the ground surfaceis 0.7 m or less,the pavement work by heavy civil machine (Iyon, etc.) is prohibited. The use of the heavy civil machine which may damage the underground cable shall beconferred between the management unit and the construction contractor.
When boring or chemical grouting work carriedis out within 1m from the cable line, engineer's presence from the management unit shall be conducted in all cases. In case that the work is carried out at more than 1mfrom the cable ine,l engineer's presencefrom management unitmay be required depends on the situation.
|
|
Area needs engineer’s presence |
|
Ground level |
|
|
|
|
|
50cm |
50cm |
|
50cm |
|
|
Cable |
50cm |
Cable |
50cm |
|
|
||
|
|
|
Figure 335 Excavation Area needs Engineer's Presence from management unit
Article 336. Proclaim Information
The power network management unitshall inform the following contents for the people and the construction organization in the region where the cable is laid underground annual, and aim to receive cooperation from the people and the construction organization.
Information content
-The name and contact information of management unit
-The fact that permission of the management unit is necessary in implementation of construction.
- The area where contact to management unit is necessary prior to the construction(The area near the underground cable)
-The contents of the construction in cable corridor informed to the management unit (Construction time, construction place, constructor name, construction outline, heavy civil machine, etc.)
Article 337. Occupational safety
The maintenance work of the cable line shall be carried |
out after the worker confirm thatthe |
temperature, the oxygen concentrationand the illumination |
intensity of the workplace satisfy the |
following items on the labor safety. |
|
356 |
|
