
- •Table of Contents
- •List of Tables
- •List of Figures
- •PART 1 DEFINITIONS
- •Chapter 1-2 Definitions of Transmission and Distribution Lines
- •Chapter 1-5 Definitions of Metering
- •Chapter 1-6 Definitions of Earthing
- •PART 2 GENERAL REQUIREMENTS
- •Chapter 2-2 Electrical Equipment
- •Chapter 2-2-1 The Selection of the Conductor Cross-Section Area
- •Chapter 2-2-2 The Selection of Electrical Equipment by Short Circuit Conditions
- •Chapter 2-3 Transmission and Distribution Lines
- •Chapter 2-3-1 House and Outside Wiring Systems with Voltage up to 35kV
- •Chapter 2-3-2 Power Cable Line Systems with voltage up to 220kV
- •Chapter 2-3-3 Overhead Power Line Systems with voltage up to 500kV
- •Chapter 2-4 Distribution Equipment up to 1kV
- •Chapter 2-5 Substations above 1kV
- •Chapter 2-6 Measure the electrical energy (Metering)
- •Chapter 2-6-1 Metering System
- •Chapter 2-6-2 Electrical Measurements
- •PART 3 TRANSMISSION AND DISTRIBUTION LINES
- •Chapter 3-1 House and Outside Wiring Systems with Voltage up to 35kV
- •Chapter 3-1-1 The Selection of Types of House and Outside Wirings with voltage up to 1kV and Installation Methods
- •Chapter 3-1-2 House Wirings with Voltage up to 1kV
- •Chapter 3-1-3 Outside Wirings with Voltage up to 1kV
- •Chapter 3-1-4 House and Outside Wirings with Voltages above 1kV up to 35kV
- •Chapter 3-2 Power Cable Line Systems with Voltage up to 220kV
- •Chapter 3-2-1 The Selection of Cables
- •Chapter 3-2-3 Special Requirements for Power Cable Lines
- •Chapter 3-2-4 Cables Installed Underground
- •Chapter 3-2-6 Installation of Cable Lines in Production Halls, Water or Special Structures
- •Chapter 3-3 Overhead Power Line Systems with Voltage up to 500kV
- •Chapter 3-3-1 Power Conductors and Lightning Conductors
- •Chapter 3-3-3 Insulators
- •Chapter 3-3-4 Power Line Accessories
- •Chapter 3-3-5 Overvoltage Protection
- •Chapter 3-3-6 Poles
- •Chapter 3-3-7 Particular Requirement
- •Chapter 3-3-8 Traversing Non-Populated Areas
- •Chapter 3-3-9 Traversing Populated Areas
- •Chapter 3-3-10 Traversing Areas with Water
- •Chapter 3-3-11 Crossing or Going Nearby Overhead Power Lines
- •Chapter 3-3-13 Crossing or Going Nearby Special Structures and/or Places
- •Chapter 4-1 Distribution Equipment up to 1kV
- •Chapter 4-1-1 Electric Equipment Installation
- •Chapter 4-1-2 Distribution Panel Boards
- •Chapter 4-2 Distribution Equipment and Substations above 1kV
- •Chapter 4-2-2 Indoor Distribution Equipment and Substations
- •Chapter 4-2-3 Workshop Substation
- •Chapter 4-2-4 Distribution Equipment and On-Pole Substation
- •Chapter 4-2-5 Lighting Protection
- •Chapter 4-2-6 Lightning Protection for Rotation Machine
- •Chapter 4-2-7 Internal Overvoltage Protection
- •Chapter 4-2-8 Installation of Power Transformers
- •Chapter 4-2-9 Battery Systems
- •PART 5 PROTECTIVE RELAYS AND CONTROL SYSTEMS
- •Chapter 5-1 Protective Relays up to 1kV
- •Chapter 5-2 Protective Relays above 1kV
- •Chapter 5-2-1 Common Protection Methods
- •Chapter 5-2-2 Protection of Generators
- •Chapter 5-2-3 Protection of Transformers and Shunt Reactors
- •Chapter 5-2-4 Protection of Transformer and Generator Blocks
- •Chapter 5-2-5 Protection of Overhead Lines and Cables with Isolated Neutral
- •Chapter 5-2-6 Protection of Overhead Lines and Cables with Efficient Earthed Neutral
- •Chapter 5-2-7 Protection of Compensating Capacitors
- •Chapter 5-2-8 Protection of Busbars
- •Chapter 5-2-9 Protection of Synchronous Compensators
- •Chapter 5-2-10 Protection of Underground Cable Lines
- •Chapter 5-3 Control Systems
- •Chapter 5-3-1 Control equipment and Auto-reclosers
- •Chapter 5-3-2 Auto Switching Power Supply Devices
- •Chapter 5-3-3 Auto-synchronization of Generators
- •Chapter 5-3-4 Auto-control Exciter Systems, Auto-control of Reactive Power, Auto-voltage Regulators
- •Chapter 5-3-5 Auto-control Frequency and Active Power
- •Chapter 5-3-6 Auto-prevention of Disturbances
- •Chapter 5-3-7 Auto-elimination of Asynchronous Mode
- •Chapter 5-3-8 Auto-prevention of Frequency Decrease
- •Chapter 5-3-9 Auto-prevention of Frequency Increase
- •Chapter 5-3-10 Auto-prevention of Voltage Decrease
- •Chapter 5-3-11 Auto-prevention of Voltage Increase
- •Chapter 5-3-13 Remote Telecontrol Systems
- •Chapter 5-4 Secondary Circuits
- •PART 6 EARTHING
- •Chapter 6-1 Purpose of earthing
- •Chapter 6-2 Components to be Earthed in Power Networks
- •Chapter 6-3 Components to be Earthed in Electrical Equipment
- •Chapter 6-4 Components Exempt from Earthing
- •Chapter 6-5 Protection against Earth Faults
- •Chapter 6-6 Earth Resistance Requirements of Earthing System
- •Chapter 6-7 Calculation of Earth Fault Current
- •Chapter 6-8 Earthing Conductors
- •Chapter 6-9 Installation Method of Earthing Systems
- •Chapter 6-10 Alternatives to Earthing Conductors
- •Chapter 6-11 Earthing of Mobile Electrical Equipment
- •Annex II.2.1 (I.3A)
- •Annex II.2.2 (I.3B)
- •Annex II.2.3 (I.3C)
- •Annex III.1 (II.1)
- •Annex III.3 (II.4)

switching overvoltage and etc.) based on the calculation of over-voltage levels. Acceptable limit of insulation level of 500kV equipment should be determined depend on the duration of its effect.
In 500kV power grid, operating over-voltage levels shall be limited to the values in the table332-2 of technical regulation.
In order to restrain dangerous over-voltage failures happened to the overhead line system, it shall be equipped with combination of varied lightning valves, electromagnetic potential transformer or other devices. Also, proper solutions to control substantial voltage increasing in a long time (such as the
installation of a currentlimiting- |
reactor, |
or |
methods related to |
the schematic diagram or system |
||||
automation) should be considered. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
The installation |
of protection |
devices |
for -voltageover |
control |
in500kV |
equipment shall |
be |
|
implemented based on the calculations of internal over-voltage in the power system. |
|
|||||||
For 220kV-500kV distribution equipments with air circuit breakers, the measures shall be applied for |
||||||||
elimination of |
over-voltage due to |
ferromagnetic |
resonance |
derived |
from switching |
voltage |
||
transformers and capacitor voltage divider of circuit breakers which are connected in series
Chapter 4-2-8 Installation of Power Transformers
Article 386. Oil-Filled equipment
In order to install and maintain the oil-filled equipment of the substation, mobile oil system shall be set up, including all equipments to transport oil filter or oil treatment
The site and scale of the oil mobile system shall be subject to the approved alternative.
Article 387. Power transformer requirements
As stipulated in Technical Regulation.
Article 388. Overload Operation of Power transformers
Regarding the overload operation of transformer, the current and temperature limitations are stated in the following table.
187
|
Table 388 |
Maximum Current and temperature limits applicable to loaded transformer |
|||||||
|
|
exceeding nameplate rating |
|
|
|
||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Distribution |
|
Medium power |
Large power |
||
|
|
Types of loading |
|
transformers |
|
transformers |
transformers |
|
|
|
|
|
(*1) |
|
(*1) |
(*1) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Normal life expectancy loading *2 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Current (p.u.) |
|
|
1.5 |
|
1.5 |
1.3 |
|
|
|
Winding hot-spot temperature and |
metall |
120 |
|
120 |
120 |
|
|
|
|
parts in contact with cellulosic |
insulation |
|
|
|
||||
|
material (°C) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Other metallic hot-spot temperature (in contact |
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
with oil, aramid paper, glass fibermaterials) |
140 |
|
140 |
140 |
|
|
||
|
(°C) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Top-oil temperature (°C) |
|
105 |
|
105 |
105 |
|
|
|
|
Long-time emergency loading *3 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Current (p.u.) |
|
|
1.8 |
|
1.5 |
1.3 |
|
|
|
Winding hot-spot temperature and |
metall |
140 |
|
140 |
140 |
|
|
|
|
parts in contact with cellulosic |
insul |
|
|
|
||||
|
material (°C) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Other metallic hot-spot temperature (in contact |
160 |
|
160 |
160 |
|
|
||
|
with oil, aramid paper, glass fibermaterials) |
|
|
|
|||||
|
(°C) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Top-oil temperature (°C) |
|
115 |
|
115 |
115 |
|
|
|
|
Short-time emergency loading *4 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Current (p.u.) |
|
|
2.0 |
|
1.8 |
1.5 |
|
|
|
Winding hot-spot temperature and |
metall |
*5 |
|
160 *5 |
160 *5 |
|
||
|
parts in contact with cellulosic |
insul |
|
|
|||||
|
material (°C) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Other metallic hot-spot temperature (in contact |
*5 |
|
180 *5 |
180 *5 |
|
|||
|
with oil, aramid paper, glass fiber materials) |
|
|
||||||
|
(°C) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Top-oil temperature (°C) |
|
*5 |
|
115 |
115 |
|
|
|
|
NOTE |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
*1 : The temperature and current limits are not intended to be valid simultaneously. The current may be |
|
|||||||
|
limited to a lower value than that shown in order to |
meet the raturetempe limitation requirement. |
|
||||||
|
Conversely, the temperature may be limited to a lower value than that shown in order to meet the current |
|
|||||||
|
limitation requirement. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
*2 : Normal life expectancy loading |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Higher ambient temperature or a higher-than-rated load current is applied during part of the cycle, but, |
|
|||||||
|
from the point of view of relative thermal ageing rate (according to the mathematical model) |
|
|||||||
|
loading is equivalent to the rated load at normal ambient temperature. This is achieved by |
|
|||||||
|
advantage of owl ambient temperatures or low load currents during the rest of the load cycle |
|
|||||||
|
planning purposes, this principle can be extended to provide for long periods of time whereby cy |
|
|||||||
|
with relative thermal ageing rates greater than unity are compensated orf by cycles with thermal ageing |
|
|||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
188 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Distribution |
Medium power |
Large power |
|
Types of loading |
transformers |
transformers |
transformers |
|
(*1) |
(*1) |
(*1) |
||
|
||||
|
|
|
|
|
Normal life expectancy loading *2 |
|
|
|
|
rates less than unity |
|
|
|
*3 : Long-time emergency loading
Loading resulting from the prolonged outage of some system elements that will not be reconnected before the transformer reaches a new and higher steady-state temperature
*4 : Short-time emergency loading
Unusually heavy loading of a transient nature (less than 30 min) due to the occurrence of oneor more unlikely events which seriously disturb normal system loading
*5 : The limits on load current, hot-spot temperature, top-oil temperature and temperature of metallic parts other than windings and leads stated in the above table should not be exceeded. No limit is set for the top-oil and hotspot temperature under short-time emergency loading for distribution transformers because it is usually impracticable to control the duration of emergency loading in this case. It should be noted that when the hot- spot temperature exceeds 140°C, gas bubbles may develop which could jeopardize the dielectric strength of the transformer
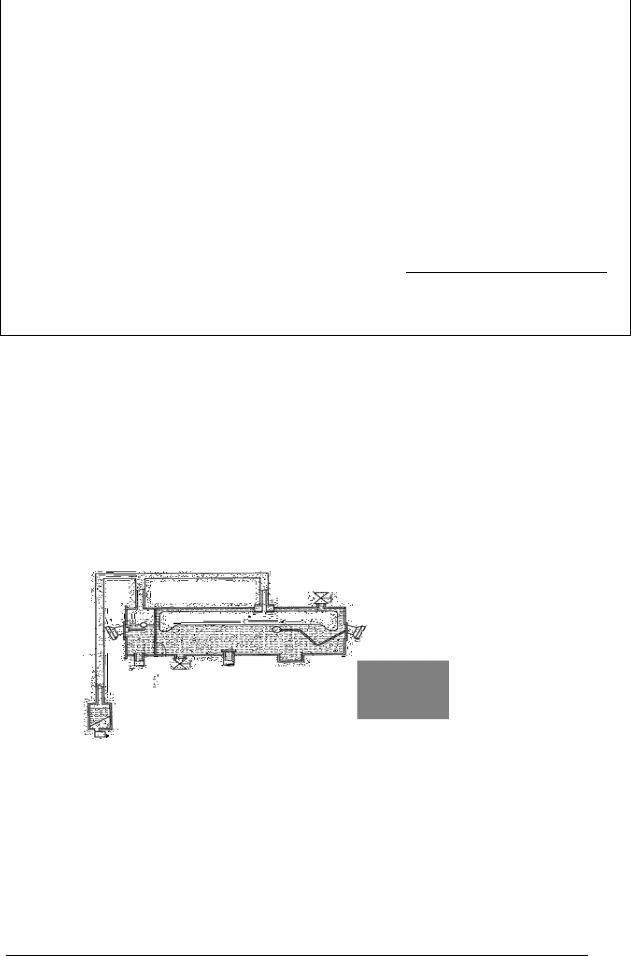
Article 389. Oil level monitoring
It is necessary to find an oil leakage of oil immersed equipment early in terms of prevention of insulation performance degradation and environmental pollution. Because of this, oil level gauges should have a upper limit and lower limit level, and in case of the large transformer, because the oil
level widely changes according to the oil temperature, |
the characteristic curve which shows the |
|
relation between oil temperature and oil level should be provided on site in order to easily confirm the |
||
adequate oil level according to the oil temperature under operation. |
||
Rubber bag type conservator |
|
|
Rubber bag |
Dial oil level |
|
Insulation oil |
||
gauge |
||
Breather
Figure 389 Installation example of oil level gauge
Article 390. Buchholz relays
Buchholz relay is used for the following detection.
189
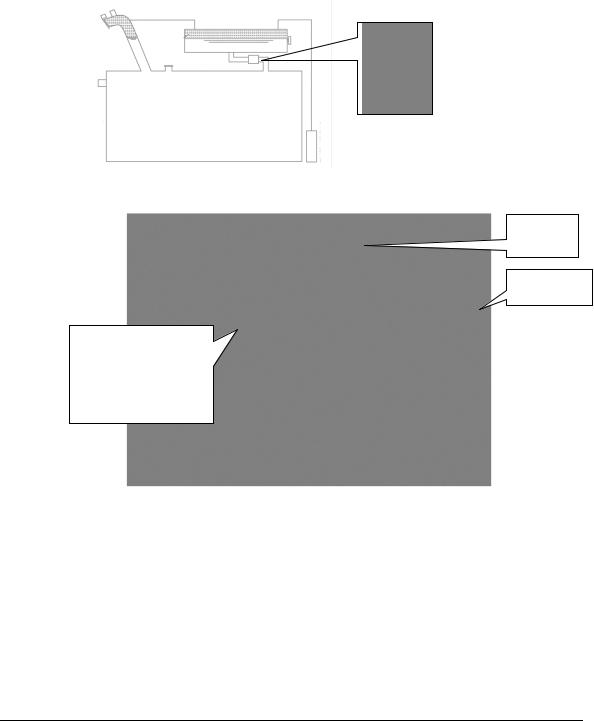
- Decomposed gas caused byminor accidents, such as partial discharge and overheating of abnormalities in internal transformer.
- Rapid oil flow due to a major accident, such as transformer internal short-circuit detection. |
|
|
For this reason, the relay is mounted in the middle of the connecting pipe between the conservator and |
|
|
main tank of the transformer. (see the figure 390-1) |
|
|
Therefore, the adderl for approach to the upper part of transformer shall |
be installed |
so that |
maintenance personnel can safely check the relay operation state and |
amount of |
generated |
decomposed gas and collect the gas at the time of the relay operation. |
|
|
However, the mounting position of the ladder shall be determined in consideration of the working clearance between workers and the live parts, such as bushings which are installed in the upper part.
Conservator
Main tank
Buchholz Relay
Figure 390-1 Installation example of Buchholz Relay (Japanese case)
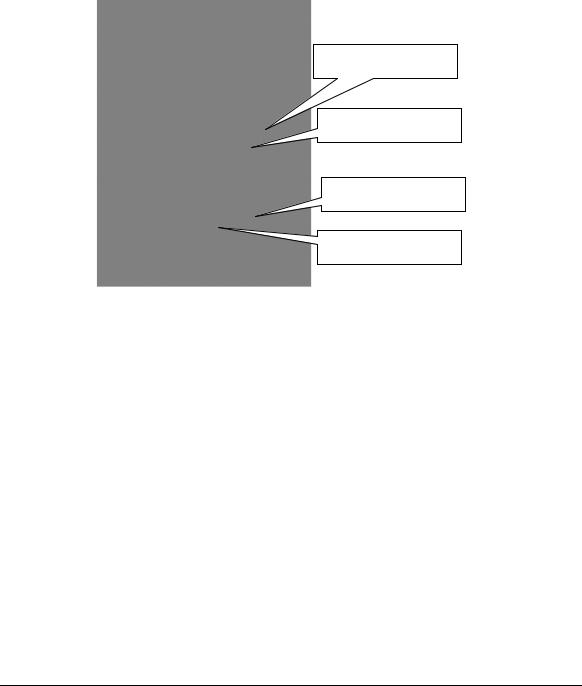
Buchholz
Relay
Maintenance
Ladder
Upper live parts are protected by the enclosure for safety (substitute of keeping working clearance)
Figure 390-2 Installation example of maintenance ladder (Japanese case)
Article 391. Lightning arrester for transformers
As stipulated in Technical Regulation.
Article 392. Wheels platform
As stipulated in Technical Regulation.
190
Article 393. Gradient for the site
As stipulated in Technical Regulation.
Article 394. Supplementary oil drums
As stipulated in Technical Regulation.
Article 395. Explosion-prevention tube
In case of installing a bursting tube in a transformer, that outlet shall curve downward and keep some distance from the control device so that the operator can safely operate the device.
When pressure relief devices operate at the time of internalfaults of a transformer, the insulation oil
will discharge from the outlet of the bursting tube. Therefore the outlet should connect the oil catchment tank in terms of the oil outflow prevention.(see the following figure)
Bursting Tube or (
Transformer)
Bursting Tube (for Tap changer)
Catchment tank (for
Transformer)
Catchment tank (for
Tap changer)
Figure 395 Installation example of bursting tube and catchment tank
Article 396. Series regulating transformer
As stipulated in Technical Regulation.
Article 397. Automatic fire extinguishers
For fire extinguishing equipment of outdoor equipment,using faucets or the fire extinguishing equipment of sprinkler type are adopted.For indoor equipment, the fire fighting is more difficult than outdoor one. Therefore, it is desirable to install thefollowing automatic fire extinguishing equipment which has high performance in the transformer compartment
In addition, the specification of distribution boards and control boards for the fire extinguishing equipment shall have been manufactured according to requirement stipulated in the article 315.
191

Table 397 |
Automatic fire extinguishing equipment for indoor equipment |
|||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
||||||
|
(Inactive gas fire extinguishing |
|
|
(Haloid fire extinguishing systems) |
||||||
|
|
systems) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Kind of |
Carbon |
Nitrogen |
|
Halon 1301 |
Trifluorometh |
|
HFC-227ea |
|||
extinguishan |
|
ane |
|
Heptafluoroprop |
||||||
dioxide |
|
|
||||||||
t |
(N2) |
|
(CF3BR) |
HFC-23 |
|
ane |
||||
|
(CO2) |
|
|
|||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
(CHF3) |
|
(CF3CHFCF3) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
Q≥tV+5K |
0.740≥Q≥0.51 |
|
Q≥0.32V+2. |
0.80V≥Q≥0.52 |
|
0.72V≥Q≥0.55V |
|||
|
|
|
6V |
|
|
4K |
|
V |
|
|
|
where |
where |
|
|
where |
where |
|
where |
||
|
-Q: |
Require |
-Q: |
Require |
-Q,V,K:refer |
-Q,V:refer |
|
-Q,V:refer to the |
||
|
quantity |
quantity |
|
|
to |
the items |
the items |
o |
items of Carbon |
|
|
extinguishant |
extinguishant |
|
of |
Carbon |
Carbon dioxide |
dioxide type |
|||
|
-t: |
Requir |
-V:Volume |
o dioxide type |
type |
|
|
|||
|
quantities |
protective |
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
extinguishant |
compartment |
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
per |
1m3 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
protective |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
compartment |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
-V:Volume o |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
protective |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Required |
compartment |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
quantities of |
-K: |
Aperture |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
extinguishan |
area |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
tprotective compartment
Minimum |
limit |
of |
parameter |
|
Q |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Minimum |
|
|
|
|
required |
|
V[m3] |
t[kg] |
quantity of |
||
|
|
|
extinguish |
|
|
|
|
ant |
|
V<50 |
1.00 |
- |
||
|
|
|
||
50≤V<15 |
0.90 |
50 |
||
0 |
|
|
|
|
150≤V<1 |
0.80 |
135 |
||
500 |
||||
|
|
|
||
1550≤V |
0.75 |
1,200 |
||
The ventilation system for transformer compartment shall be stopped automatically in
Remarks case of fire. In order to cut off the air supply in case of fire, fire dampers which close themselves by the gas pressure of fire extinguishing shall be installed
192
