
- •Table of Contents
- •List of Tables
- •List of Figures
- •PART 1 DEFINITIONS
- •Chapter 1-2 Definitions of Transmission and Distribution Lines
- •Chapter 1-5 Definitions of Metering
- •Chapter 1-6 Definitions of Earthing
- •PART 2 GENERAL REQUIREMENTS
- •Chapter 2-2 Electrical Equipment
- •Chapter 2-2-1 The Selection of the Conductor Cross-Section Area
- •Chapter 2-2-2 The Selection of Electrical Equipment by Short Circuit Conditions
- •Chapter 2-3 Transmission and Distribution Lines
- •Chapter 2-3-1 House and Outside Wiring Systems with Voltage up to 35kV
- •Chapter 2-3-2 Power Cable Line Systems with voltage up to 220kV
- •Chapter 2-3-3 Overhead Power Line Systems with voltage up to 500kV
- •Chapter 2-4 Distribution Equipment up to 1kV
- •Chapter 2-5 Substations above 1kV
- •Chapter 2-6 Measure the electrical energy (Metering)
- •Chapter 2-6-1 Metering System
- •Chapter 2-6-2 Electrical Measurements
- •PART 3 TRANSMISSION AND DISTRIBUTION LINES
- •Chapter 3-1 House and Outside Wiring Systems with Voltage up to 35kV
- •Chapter 3-1-1 The Selection of Types of House and Outside Wirings with voltage up to 1kV and Installation Methods
- •Chapter 3-1-2 House Wirings with Voltage up to 1kV
- •Chapter 3-1-3 Outside Wirings with Voltage up to 1kV
- •Chapter 3-1-4 House and Outside Wirings with Voltages above 1kV up to 35kV
- •Chapter 3-2 Power Cable Line Systems with Voltage up to 220kV
- •Chapter 3-2-1 The Selection of Cables
- •Chapter 3-2-3 Special Requirements for Power Cable Lines
- •Chapter 3-2-4 Cables Installed Underground
- •Chapter 3-2-6 Installation of Cable Lines in Production Halls, Water or Special Structures
- •Chapter 3-3 Overhead Power Line Systems with Voltage up to 500kV
- •Chapter 3-3-1 Power Conductors and Lightning Conductors
- •Chapter 3-3-3 Insulators
- •Chapter 3-3-4 Power Line Accessories
- •Chapter 3-3-5 Overvoltage Protection
- •Chapter 3-3-6 Poles
- •Chapter 3-3-7 Particular Requirement
- •Chapter 3-3-8 Traversing Non-Populated Areas
- •Chapter 3-3-9 Traversing Populated Areas
- •Chapter 3-3-10 Traversing Areas with Water
- •Chapter 3-3-11 Crossing or Going Nearby Overhead Power Lines
- •Chapter 3-3-13 Crossing or Going Nearby Special Structures and/or Places
- •Chapter 4-1 Distribution Equipment up to 1kV
- •Chapter 4-1-1 Electric Equipment Installation
- •Chapter 4-1-2 Distribution Panel Boards
- •Chapter 4-2 Distribution Equipment and Substations above 1kV
- •Chapter 4-2-2 Indoor Distribution Equipment and Substations
- •Chapter 4-2-3 Workshop Substation
- •Chapter 4-2-4 Distribution Equipment and On-Pole Substation
- •Chapter 4-2-5 Lighting Protection
- •Chapter 4-2-6 Lightning Protection for Rotation Machine
- •Chapter 4-2-7 Internal Overvoltage Protection
- •Chapter 4-2-8 Installation of Power Transformers
- •Chapter 4-2-9 Battery Systems
- •PART 5 PROTECTIVE RELAYS AND CONTROL SYSTEMS
- •Chapter 5-1 Protective Relays up to 1kV
- •Chapter 5-2 Protective Relays above 1kV
- •Chapter 5-2-1 Common Protection Methods
- •Chapter 5-2-2 Protection of Generators
- •Chapter 5-2-3 Protection of Transformers and Shunt Reactors
- •Chapter 5-2-4 Protection of Transformer and Generator Blocks
- •Chapter 5-2-5 Protection of Overhead Lines and Cables with Isolated Neutral
- •Chapter 5-2-6 Protection of Overhead Lines and Cables with Efficient Earthed Neutral
- •Chapter 5-2-7 Protection of Compensating Capacitors
- •Chapter 5-2-8 Protection of Busbars
- •Chapter 5-2-9 Protection of Synchronous Compensators
- •Chapter 5-2-10 Protection of Underground Cable Lines
- •Chapter 5-3 Control Systems
- •Chapter 5-3-1 Control equipment and Auto-reclosers
- •Chapter 5-3-2 Auto Switching Power Supply Devices
- •Chapter 5-3-3 Auto-synchronization of Generators
- •Chapter 5-3-4 Auto-control Exciter Systems, Auto-control of Reactive Power, Auto-voltage Regulators
- •Chapter 5-3-5 Auto-control Frequency and Active Power
- •Chapter 5-3-6 Auto-prevention of Disturbances
- •Chapter 5-3-7 Auto-elimination of Asynchronous Mode
- •Chapter 5-3-8 Auto-prevention of Frequency Decrease
- •Chapter 5-3-9 Auto-prevention of Frequency Increase
- •Chapter 5-3-10 Auto-prevention of Voltage Decrease
- •Chapter 5-3-11 Auto-prevention of Voltage Increase
- •Chapter 5-3-13 Remote Telecontrol Systems
- •Chapter 5-4 Secondary Circuits
- •PART 6 EARTHING
- •Chapter 6-1 Purpose of earthing
- •Chapter 6-2 Components to be Earthed in Power Networks
- •Chapter 6-3 Components to be Earthed in Electrical Equipment
- •Chapter 6-4 Components Exempt from Earthing
- •Chapter 6-5 Protection against Earth Faults
- •Chapter 6-6 Earth Resistance Requirements of Earthing System
- •Chapter 6-7 Calculation of Earth Fault Current
- •Chapter 6-8 Earthing Conductors
- •Chapter 6-9 Installation Method of Earthing Systems
- •Chapter 6-10 Alternatives to Earthing Conductors
- •Chapter 6-11 Earthing of Mobile Electrical Equipment
- •Annex II.2.1 (I.3A)
- •Annex II.2.2 (I.3B)
- •Annex II.2.3 (I.3C)
- •Annex III.1 (II.1)
- •Annex III.3 (II.4)

Table 315 Specification of the distribution board with heat-resistant (Japanese specification)
Class |
Specification of heat-resistant |
|
|
|
The distribution board shall be able to supply a power to the |
First-class |
equipment after overheating it at the maximum temperature |
heat-resistant |
840°C for 30 minutes. Internal devices shall withstand the heat |
|
at 280°C. |
|
The distribution board shall be able to supply a power to th |
Second-class |
equipment after overheating it at the maximum tempera |
heat-resistant |
280°C for 30 minutes. Internal devices shall withstand the heat |
|
at 120°C. |
Article 316. Prevention of Vibration for the Distribution Panel Boards
The provisions of this article shall refer to the Article 13 2 of section 4 in the volume 3.
Article 317. Safety Measures for Electrically Inexperienced Workers
In case of using distribution equipment with live non-insulated components, it shall be protected with protective barrier. Protective barrier shall be a wire mesh, solid wall or combined type with minimum height of 1.8m. Distance from wire mesh to live non-insulated parts shall be not less than 0.7m. As for the solid wall, it shall meet the guideline in the Article 311.
Article 318. Installation Outdoor
The outdoor installation of distribution equipment shall meet the following requirements.
-The equipment shall be placed on a flat plane at minimum elevation of 0.3m above ground surface. In case of cubicles, the elevation shall be at least 0.5m.
-In electrical cubicles, if needed, drying devices such as a space heater and a dehumidifier device
shall be installed for ensuring normal operation of the components, relays, measuring instruments and electrical meters.
Chapter 4-2 Distribution Equipment and Substations above 1kV
Article 319. Scope of this Chapter
As stipulated in Technical Regulation..
Chapter 4-2-1 Outdoor Distribution Equipment and Outdoor
Substations
Article 320. Transport routes
As stipulated in Technical Regulation.
Article 321. Prohibition the cut conductor among the pole span when connection branch
When connecting branch with wires, wire must not be cut between pole span.
159
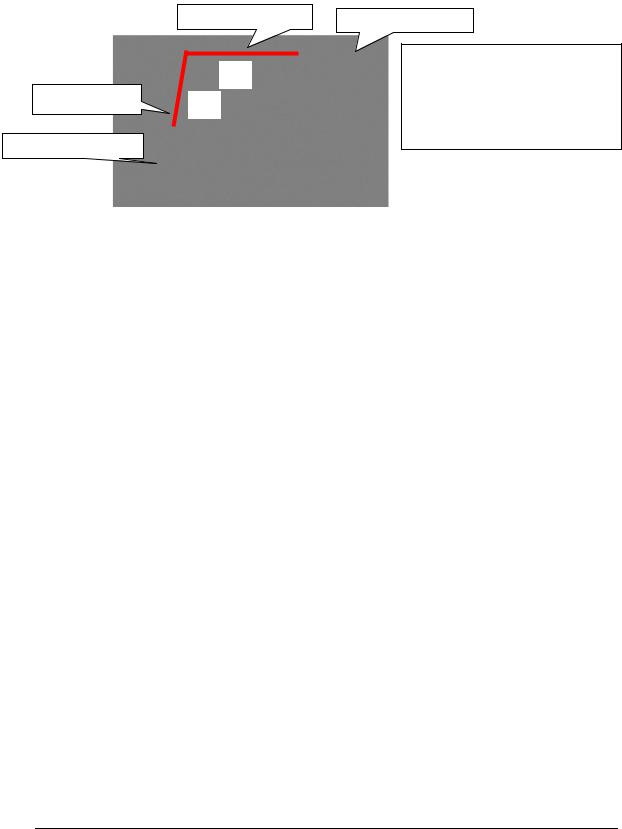
After compression work for a compression terminalor sleeve, or attachment of variousclamps on lead wires, in order to make sure that above installation works were carriedout tightly, it shall be checked that the electrical resistance of the compression portion or the clamp gripped portion is 100% or less of the electrical resistance of the gripped portion of the lead wire. This inspection is carried out by the voltage-drop method (see the following figure)
Compression portion
L1
Compression portion |
L2 |
|
Lead wire (ACSR 330mm2)
Lead wire (ACSR 330mm2)
It shall be checked that the resistance of compression portion length (L1+L2) is not greater than the resistance equivalent to ACSR 330mm2 (length=L1+L2).
Figure 321 Measurement of resistance of compression part using the voltage-drop method
Article 322. Arrangement of Branch Wire
The clearance between a branch wire and a live part that intersects with the wirel meetshal the minimum clearance provided in the article 331 in Technical Regulation.
Article 323. Calculation of Wind Load and Air Temperature
The wind load acting on conducting bars and structures shall be calculated based on the formula given in the Article 128.
In calculation of forces acting on flexible conducting bars and on ends of insulators of equipment or transformers, the weight of insulator strings and branching wires to equipments and transformers shall be calculated.
In calculation of forces acting on structures, the weight of workers with tools and means for installation shall be added as follows:
-250kg : for 500kV electric tower.
-200kg : in case of using suspension insulators for blocking anchor pole/tower with voltage up to 220kV.
-150kg : in case of using suspension insulators for support poles with voltage up to 220kV.
-100kg : in case of using post insulators.
Article 324. Mechanical Safety Factor Flexible Conductors
As stipulated in Technical Regulation.
Article 325. Mechanical Safety Factor Suspension Insulators
As stipulated in Technical Regulation.
160

Article 326. Mechanical Safety Factor Rigid Conductor
The short-circuit electromagnetic force which acts on busbar, post type insulator and rigid support structure shall be calculated based on the requirements regulated in article 81.
Article 327. Mechanical Safety Factor Bridging Flexible Conductors
As stipulated in Technical Regulation.
Article 328. Pole Material
The reinforced concrete pole and steel pole which are used as the supporting structure of distribution lines shall have the intensity which bears the load of the following table.
Table 328 |
The Load against supporting structure |
|
|
|
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
The type of supporting |
|
|
Application load |
|
|
|
|
structure |
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Reinforced concrete |
Wind load and the following vertical load |
|
|
|
|||
- Length ≤ 20m, |
- |
The weight |
load of strung |
wires, insulators |
and |
supporting |
|
|
structures, etc. |
|
|
|
|
||
- Design load ≤ 614.7kN |
|
|
|
|
|
||
- The vertical |
load caused by |
the tensile force of |
the |
guy wire |
|
||
|
|
||||||
|
|
case of using guy wires to support the supporting structure |
|
||||
Article 329. Designing for Intermediary or Dead-end Anchor Poles
The provisions of this article shall refer to the previous article.
Article 330. Creepage Distance for Insulator
For standardization purposes, Relation between surface pollution of insulators and creepage distance for insulators are specified in the following table.
Regarding the measurement of NSDD and ESDD, refer to the ANNEX C of IEC 60815-1.
|
|
|
Table 330 |
|
Basic USCD and SPS |
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
[IEC 60815-1] |
||
SPS *1 |
a (Very light) |
b (Light) |
c (Medium) |
d (Heavy) |
e (Very heavy) |
|
|||||
ESDD *2 |
Not |
great Not |
great Not |
great Not |
greate greater |
th |
|||||
[mg/cm2] |
than 0.004 |
|
than 0.02 |
|
than 0.1 |
|
than 0.5 |
|
0.5 |
|
|
NSDD *3 |
0.1 |
|
0.1 |
|
0.1 |
|
0.1 |
|
0.1 |
|
|
[mg/cm2] |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
USCD *4 |
22 |
|
28 |
|
35 |
|
44 |
|
55 |
|
|
[mm/kV] |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
*1 SPS (Site Pollution Severity): Definition of SPS is based on the IEC 60815-1. Concrete descriptions refer to the '22) Area classificationPolluted environment area' of the Article 1.
*2 ESDD (Equivalent Salt Deposit Density):The amount of sodium chloride that, when dissolved, gives the same conductance as that of the natural deposit removed from a given surface of the insulator divided by the area of this surface; generally expressed in mg/cm².
*3 NSDD (Non Soluble Deposit Density): The amount of the non-soluble residue removed from a given surface of the insulator divided by the area of this surface; generally expressed in mg/cm².
161

*4 USCD (Unified Specific Creepage Distance): The creepage distance of an insulator divided by the highest operating voltage across the insulator (forA.C. systems usually Um/√3 [phase to ground])
Quantity of suspension insulators is selected based on the formula given in the Article 248.
Article 331. Minimum Air Clearance of Outdoor Distribution and Substation Facilities
As stipulated in Technical Regulation.
Article 332. Withstand Voltage Test of Outdoor Distribution and Substation Equipment
As stipulated in Technical Regulation.
Article 333. Protective Barrier Clearances and Boundary Clearances
As stipulated in Technical Regulation.
Article 334. Minimum Height over Access Area
As stipulated in Technical Regulation.
Article 335. Minimum Working Clearance
As stipulated in Technical Regulation.
Article 336. Prohibited to Install Overhead Line above the outdoor distribution equipment
As stipulated in Technical Regulation.
Article 337. Fire Prevention Measures of Outdoor Substations
As stipulated in Technical Regulation.
Article 338. Railways in Substations
As stipulated in Technical Regulation.
162
