
книги / Journal Selection Process [╨┤╨╗╤П ╨╕╨╖╨┤╨░╤В╨╡╨╗╨╡╨╣ ╨╜╨░╤Г╤З╨╜╤Л╤Е ╨╢╤Г╤А╨╜╨░╨╗╨╛╨▓]
..pdf
-Web of Science Core Collection Journal Selection Process:
SCIE – SSCI – AHCI
Introducing Emerging Sources Citation Index
-The Role of Citations and Journal Impact Factor in the
Journal Selection Process
James Testa
VP Emeritus Editorial Development & Publisher Relations
4th International Conference on Scientific Communication in the Digital Age, Ukraine
1

THE JOURNAL SELECTION PROCESS:
MAIN OBJECTIVES
1.To evaluate and select the best scholarly journal content available today for coverage in Web of Science Core Collection.
As a result, the Web of Science Core Collection is known as the worldwide source for top tier scholarly research published in the best international and regional journals.
2. Provide the worldwide publishing community with objective standards useful in building worldclass publications.
Thomson Reuters, through Web of Science, has built lasting partnerships with the global scholarly publishing community. We work together to improve the quality of scholarly communication everywhere in the world.
2

Web of Science Core Collection (Journals)
Flagship Citation Indexes:
Science Citation Index Expanded
Social Science Citation Index
Arts & Humanities Citation Index
New Edition in
Web of Science Core Collection:
Emerging Sources Citation Index
…a broader view of the scholarly literature.
…considering Impact and output |
3 |
|

From ESCI to SCIE, SSCI or AHCI?
What is possible?
Journals submitted for evaluation:
•May be evaluated and accepted for SCIE, SSCI,AHCI
•May be evaluated and accepted for ESCI (and not SCIE,SSCI, AHCI)
•ESCI journals may be re-evaluated later for coverage in SCIE, SSCI, AHCI)
NOTE:
•Journals deselected from SCIE,SSCI, AHCI may migrate to coverage in ESCI.
4

ESCI is a True Citation Index
•Every cited reference from every issue is indexed.
•Track citation activity at the Journal Level.
•Track citation activity at the article level.
•ESCI citation activity used when evaluating journal for SCIE,SSCI,AHCI adding more transparency.
•No Journal Impact Factor published for ESCI journals.
5

Bradford’s Law of Scattering
Garfield’s Law of Concentration
6
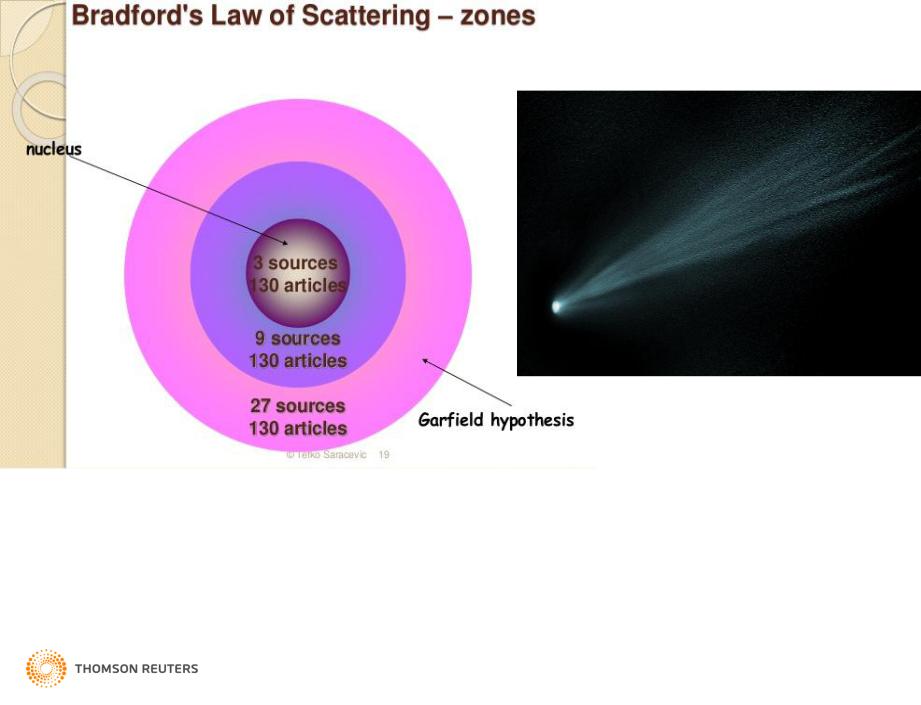
“Articles of interest to a specialist must occur not only in the periodicals specializing in his subject, but also from time to time, in other periodicals, which grow in number as the relation of their fields to that of the subject lessens, and the number of articles on his subject in each periodical diminishes”.
-S. C. Bradford
7

Garfield’s Law of Concentration
Analysis of the Scholarly Literature –
2014 Journal Citation Reports
11,813 Journals: all categories of Science & Social Science
•525 journals
•50% of all citations received by the 11,813 journals
•25 % of all papers published in the11,813 journals
•4,470 journals
•80% of all papers published in the 11,813 journals
•85% of all citations received by the 11,813 journals
8

Garfield’s Law of Concentration
“The tail of the literature of one discipline consists, in large part, of the cores of the literature of other disciplines.”
- E. Garfield
•As a result, the core literature of all scientific disciplines at the time (1972) involved a group of not more than 1,000 journals and may even possibly be reduced to as few as 500 journals.
•A relatively small number of journals account for the bulk of what is published and what is cited.
9

Journal |
Editorial |
International |
Citation |
|
Publishing |
||||
Focus: |
||||
Content |
Analysis |
|||
|
||||
Standards |
Authors, EAB |
|||
|
|
|||
•Peer review |
•How does this |
•Does this journal |
|
|
|
Total Citations: |
|||
|
journal compare |
|||
•Ethical publishing |
target an |
|||
|
||||
with covered |
•Integration of the |
|||
practices |
International or |
|||
journals of similar |
journal into the |
|||
|
Regional |
|||
•Meets technical |
literature over time |
|||
scope? |
||||
audience? |
||||
requirements |
|
|||
|
Impact Factor: |
|||
•Is this subject |
|
|||
|
|
|||
(XML / PDF) |
•Is international |
|
||
already well |
•Recent citation |
|||
|
representation |
|||
•Timeliness of |
activity |
|||
covered? |
||||
among Authors |
||||
publication |
|
|||
|
Author, EAB |
|||
•Will this journal |
and EAB |
|||
|
||||
|
citations in the |
|||
•International editorial |
members at an |
|||
enrich WoS with |
||||
literature. |
||||
conventions |
appropriate level |
|||
novel content? |
|
|||
|
for this journal? |
•Citation metrics |
||
•English-language |
|
|||
|
have meaning only |
|||
|
|
|||
bibliographic |
|
|
in the editorial |
|
information |
|
|
context appropriate |
|
Thomson Reuters Journal Selection Process |
||||
for Web of Science: SCIE, SSCI, AHCI |
||||
Arts & Humanities journals are exceptional |
for the journal |
. |
|
•English full text may not be required |
|
||
|
|
|
|
•Novel, well focused content (often regional) is essential |
|
|
|
•Citation analysis plays a much smaller role. |
|
|
10 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
