
- •Contents
- •Contributors
- •1 Introduction
- •2.1 Posterior Compartment
- •2.2 Anterior Compartment
- •2.3 Middle Compartment
- •2.4 Perineal Body
- •3 Compartments
- •3.1 Posterior Compartment
- •3.1.1 Connective Tissue Structures
- •3.1.2 Muscles
- •3.1.3 Reinterpreted Anatomy and Clinical Relevance
- •3.2 Anterior Compartment
- •3.2.1 Connective Tissue Structures
- •3.2.2 Muscles
- •3.2.3 Reinterpreted Anatomy and Clinical Relevance
- •3.2.4 Important Vessels, Nerves, and Lymphatics of the Anterior Compartment
- •3.3 Middle Compartment
- •3.3.1 Connective Tissue Structures
- •3.3.2 Muscles
- •3.3.3 Reinterpreted Anatomy and Clinical Relevance
- •3.3.4 Important Vessels, Nerves, and Lymphatics of the Middle Compartment
- •4 Perineal Body
- •References
- •MR and CT Techniques
- •1 Introduction
- •2.1 Introduction
- •2.2.1 Spasmolytic Medication
- •2.3.2 Diffusion-Weighted Imaging
- •2.3.3 Dynamic Contrast Enhancement
- •3 CT Technique
- •3.1 Introduction
- •3.2 Technical Disadvantages
- •3.4 Oral and Rectal Contrast
- •References
- •Uterus: Normal Findings
- •1 Introduction
- •References
- •1 Clinical Background
- •1.1 Epidemiology
- •1.2 Clinical Presentation
- •1.3 Embryology
- •1.4 Pathology
- •2 Imaging
- •2.1 Technique
- •2.2.1 Class I Anomalies: Dysgenesis
- •2.2.2 Class II Anomalies: Unicornuate Uterus
- •2.2.3 Class III Anomalies: Uterus Didelphys
- •2.2.4 Class IV Anomalies: Bicornuate Uterus
- •2.2.5 Class V Anomalies: Septate Uterus
- •2.2.6 Class VI Anomalies: Arcuate Uterus
- •2.2.7 Class VII Anomalies
- •References
- •Benign Uterine Lesions
- •1 Background
- •1.1 Uterine Leiomyomas
- •1.1.1 Epidemiology
- •1.1.2 Pathogenesis
- •1.1.3 Histopathology
- •1.1.4 Clinical Presentation
- •1.1.5 Therapy
- •1.1.5.1 Indications
- •1.1.5.2 Medical Therapy and Ablation
- •1.1.5.3 Surgical Therapy
- •1.1.5.4 Uterine Artery Embolization (UAE)
- •1.1.5.5 Magnetic Resonance-Guided Focused Ultrasound
- •2 Adenomyosis of the Uterus
- •2.1 Epidemiology
- •2.2 Pathogenesis
- •2.3 Histopathology
- •2.4 Clinical Presentation
- •2.5 Therapy
- •3 Imaging
- •3.2 Magnetic Resonance Imaging
- •3.2.1 Magnetic Resonance Imaging: Technique
- •3.2.2 MR Appearance of Uterine Leiomyomas
- •3.2.3 Locations, Growth Patterns, and Imaging Characteristics
- •3.2.4 Histologic Subtypes and Forms of Degeneration
- •3.2.5 Differential Diagnosis
- •3.2.6 MR Appearance of Uterine Adenomyosis
- •3.2.7 Locations, Growth Patterns, and Imaging Characteristics
- •3.2.8 Differential Diagnosis
- •3.3 Computed Tomography
- •3.3.1 CT Technique
- •3.3.2 CT Appearance of Uterine Leiomyoma and Adenomyosis
- •3.3.3 Atypical Appearances on CT and Differential Diagnosis
- •4.1 Indications
- •4.2 Technique
- •Bibliography
- •Cervical Cancer
- •1 Background
- •1.1 Epidemiology
- •1.2 Pathogenesis
- •1.3 Screening
- •1.4 HPV Vaccination
- •1.5 Clinical Presentation
- •1.6 Histopathology
- •1.7 Staging
- •1.8 Growth Patterns
- •1.9 Treatment
- •1.9.1 Treatment of Microinvasive Cervical Cancer
- •1.9.2 Treatment of Grossly Invasive Cervical Carcinoma (FIGO IB-IVA)
- •1.9.3 Treatment of Recurrent Disease
- •1.9.4 Treatment of Cervical Cancer During Pregnancy
- •1.10 Prognosis
- •2 Imaging
- •2.1 Indications
- •2.1.1 Role of CT and MRI
- •2.2 Imaging Technique
- •2.2.2 Dynamic MRI
- •2.2.3 Coil Technique
- •2.2.4 Vaginal Opacification
- •2.3 Staging
- •2.3.1 General MR Appearance
- •2.3.2 Rare Histologic Types
- •2.3.3 Tumor Size
- •2.3.4 Local Staging
- •2.3.4.1 Stage IA
- •2.3.4.2 Stage IB
- •2.3.4.3 Stage IIA
- •2.3.4.4 Stage IIB
- •2.3.4.5 Stage IIIA
- •2.3.4.6 Stage IIIB
- •2.3.4.7 Stage IVA
- •2.3.4.8 Stage IVB
- •2.3.5 Lymph Node Staging
- •2.3.6 Distant Metastases
- •2.4 Specific Diagnostic Queries
- •2.4.1 Preoperative Imaging
- •2.4.2 Imaging Before Radiotherapy
- •2.5 Follow-Up
- •2.5.1 Findings After Surgery
- •2.5.2 Findings After Chemotherapy
- •2.5.3 Findings After Radiotherapy
- •2.5.4 Recurrent Cervical Cancer
- •2.6.1 Ultrasound
- •2.7.1 Metastasis
- •2.7.2 Malignant Melanoma
- •2.7.3 Lymphoma
- •2.8 Benign Lesions of the Cervix
- •2.8.1 Nabothian Cyst
- •2.8.2 Leiomyoma
- •2.8.3 Polyps
- •2.8.4 Rare Benign Tumors
- •2.8.5 Cervicitis
- •2.8.6 Endometriosis
- •2.8.7 Ectopic Cervical Pregnancy
- •References
- •Endometrial Cancer
- •1.1 Epidemiology
- •1.2 Pathology and Risk Factors
- •1.3 Symptoms and Diagnosis
- •2 Endometrial Cancer Staging
- •2.1 MR Protocol for Staging Endometrial Carcinoma
- •2.2.1 Stage I Disease
- •2.2.2 Stage II Disease
- •2.2.3 Stage III Disease
- •2.2.4 Stage IV Disease
- •4 Therapeutic Approaches
- •4.1 Surgery
- •4.2 Adjuvant Treatment
- •4.3 Fertility-Sparing Treatment
- •5.1 Treatment of Recurrence
- •6 Prognosis
- •References
- •Uterine Sarcomas
- •1 Epidemiology
- •2 Pathology
- •2.1 Smooth Muscle Tumours
- •2.2 Endometrial Stromal Tumours
- •3 Clinical Background
- •4 Staging
- •5 Imaging
- •5.1 Leiomyosarcoma
- •5.2.3 Undifferentiated Uterine Sarcoma
- •5.3 Adenosarcoma
- •6 Prognosis and Treatment
- •References
- •1.1 Anatomical Relationships
- •1.4 Pelvic Fluid
- •2 Developmental Anomalies
- •2.1 Congenital Abnormalities
- •2.2 Ovarian Maldescent
- •3 Ovarian Transposition
- •References
- •1 Introduction
- •4 Benign Adnexal Lesions
- •4.1.1 Physiological Ovarian Cysts: Follicular and Corpus Luteum Cysts
- •4.1.1.1 Imaging Findings in Physiological Ovarian Cysts
- •4.1.1.2 Differential Diagnosis
- •4.1.2 Paraovarian Cysts
- •4.1.2.1 Imaging Findings
- •4.1.2.2 Differential Diagnosis
- •4.1.3 Peritoneal Inclusion Cysts
- •4.1.3.1 Imaging Findings
- •4.1.3.2 Differential Diagnosis
- •4.1.4 Theca Lutein Cysts
- •4.1.4.1 Imaging Findings
- •4.1.4.2 Differential Diagnosis
- •4.1.5 Polycystic Ovary Syndrome
- •4.1.5.1 Imaging Findings
- •4.1.5.2 Differential Diagnosis
- •4.2.1 Cystadenoma
- •4.2.1.1 Imaging Findings
- •4.2.1.2 Differential Diagnosis
- •4.2.2 Cystadenofibroma
- •4.2.2.1 Imaging Features
- •4.2.3 Mature Teratoma
- •4.2.3.1 Mature Cystic Teratoma
- •Imaging Findings
- •Differential Diagnosis
- •4.2.3.2 Monodermal Teratoma
- •Imaging Findings
- •4.2.4 Benign Sex Cord-Stromal Tumors
- •4.2.4.1 Fibroma and Thecoma
- •Imaging Findings
- •4.2.4.2 Sclerosing Stromal Tumor
- •Imaging Findings
- •4.2.5 Brenner Tumors
- •4.2.5.1 Imaging Findings
- •4.2.5.2 Differential Diagnosis
- •5 Functioning Ovarian Tumors
- •References
- •1 Introduction
- •2.1 Context
- •2.2.2 Indications According to Simple Rules
- •References
- •CT and MRI in Ovarian Carcinoma
- •1 Introduction
- •2.1 Familial or Hereditary Ovarian Cancers
- •3 Screening for Ovarian Cancer
- •5 Tumor Markers
- •6 Clinical Presentation
- •7 Imaging of Ovarian Cancer
- •7.1.2 Peritoneal Carcinomatosis
- •7.1.3 Ascites
- •7.3 Staging of Ovarian Cancer
- •7.3.1 Staging by CT and MRI
- •Imaging Findings According to Tumor Stages
- •Value of Imaging
- •7.3.2 Prediction of Resectability
- •7.4 Tumor Types
- •7.4.1 Epithelial Ovarian Cancer
- •High-Grade Serous Ovarian Cancer
- •Low-Grade Serous Ovarian Cancer
- •Mucinous Epithelial Ovarian Cancer
- •Endometrioid Ovarian Carcinomas
- •Clear Cell Carcinomas
- •Imaging Findings of Epithelial Ovarian Cancers
- •Differential Diagnosis
- •Borderline Tumors
- •Imaging Findings
- •Differential Diagnosis
- •Recurrent Ovarian Cancer
- •Imaging Findings
- •Differential Diagnosis
- •Value of Imaging
- •Malignant Germ Cell Tumors
- •Dysgerminomas
- •Imaging Findings
- •Differential Diagnosis
- •Immature Teratomas
- •Imaging Findings
- •Malignant Transformation in Benign Teratoma
- •Imaging Findings
- •Differential Diagnosis
- •Sex-Cord Stromal Tumors
- •Granulosa Cell Tumors
- •Imaging Findings
- •Sertoli-Leydig Cell Tumor
- •Imaging Findings
- •Ovarian Lymphoma
- •Imaging Findings
- •Differential Diagnosis
- •7.4.3 Ovarian Metastases
- •Imaging Findings
- •Differential Diagnosis
- •7.5 Fallopian Tube Cancer
- •7.5.1 Imaging Findings
- •Differential Diagnosis
- •References
- •Endometriosis
- •1 Introduction
- •2.1 Sonography
- •3 MR Imaging Findings
- •References
- •Vagina and Vulva
- •1 Introduction
- •3.1 CT Appearance
- •3.2 MRI Protocol
- •3.3 MRI Appearance
- •4.1 Imperforate Hymen
- •4.2 Congenital Vaginal Septa
- •4.3 Vaginal Agenesis
- •5.1 Vaginal Cysts
- •5.1.1 Gardner Duct Cyst (Mesonephric Cyst)
- •5.1.2 Bartholin Gland Cyst
- •5.2.1 Vaginal Infections
- •5.2.1.1 Vulvar Infections
- •5.2.1.2 Vulvar Thrombophlebitis
- •5.3 Vulvar Trauma
- •5.4 Vaginal Fistula
- •5.5 Post-Radiation Changes
- •5.6 Benign Tumors
- •6.1 Vaginal Malignancies
- •6.1.1 Primary Vaginal Carcinoma
- •6.1.1.1 MRI Findings
- •6.1.1.2 Lymph Node Drainage
- •6.1.1.3 Recurrence and Complications
- •6.1.2 Non-squamous Cell Carcinomas of the Vagina
- •6.1.2.1 Adenocarcinoma
- •6.1.2.2 Melanoma
- •6.1.2.3 Sarcomas
- •6.1.2.4 Lymphoma
- •6.2 Vulvar Malignancies
- •6.2.1 Vulvar Carcinoma
- •6.2.2 Melanoma
- •6.2.3 Lymphoma
- •6.2.4 Aggressive Angiomyxoma of the Vulva
- •7 Vaginal Cuff Disease
- •7.1 MRI Findings
- •8 Foreign Bodies
- •References
- •Imaging of Lymph Nodes
- •1 Background
- •3 Technique
- •3.1.1 Intravenous Unspecific Contrast Agents
- •3.1.2 Intravenous Tissue-Specific Contrast Agents
- •References
- •1 Introduction
- •2.1.1 Imaging Findings
- •2.1.2 Differential Diagnosis
- •2.1.3 Value of Imaging
- •2.2 Pelvic Inflammatory
- •2.2.1 Imaging Findings
- •2.3 Hydropyosalpinx
- •2.3.1 Imaging Findings
- •2.3.2 Differential Diagnosis
- •2.4 Tubo-ovarian Abscess
- •2.4.1 Imaging Findings
- •2.4.2 Differential Diagnosis
- •2.4.3 Value of Imaging
- •2.5 Ovarian Torsion
- •2.5.1 Imaging Findings
- •2.5.2 Differential Diagnosis
- •2.5.3 Diagnostic Value
- •2.6 Ectopic Pregnancy
- •2.6.1 Imaging Findings
- •2.6.2 Differential Diagnosis
- •2.6.3 Value of Imaging
- •3.1 Pelvic Congestion Syndrome
- •3.1.1 Imaging Findings
- •3.1.2 Differential Diagnosis
- •3.1.3 Value of Imaging
- •3.2 Ovarian Vein Thrombosis
- •3.2.1 Imaging Findings
- •3.2.2 Differential Diagnosis
- •3.2.3 Value of Imaging
- •3.3 Appendicitis
- •3.3.1 Imaging Findings
- •3.3.2 Value of Imaging
- •3.4 Diverticulitis
- •3.4.1 Imaging Findings
- •3.4.2 Differential Diagnosis
- •3.4.3 Value of Imaging
- •3.5 Epiploic Appendagitis
- •3.5.1 Imaging Findings
- •3.5.2 Differential Diagnosis
- •3.5.3 Value of Imaging
- •3.6 Crohn’s Disease
- •3.6.1 Imaging Findings
- •3.6.2 Differential Diagnosis
- •3.6.3 Value of Imaging
- •3.7 Rectus Sheath Hematoma
- •3.7.1 Imaging Findings
- •3.7.2 Differential Diagnosis
- •3.7.3 Value of Imaging
- •References
- •MRI of the Pelvic Floor
- •1 Introduction
- •2 Imaging Techniques
- •3.1 Indications
- •3.2 Patient Preparation
- •3.3 Patient Instruction
- •3.4 Patient Positioning
- •3.5 Organ Opacification
- •3.6 Sequence Protocols
- •4 MR Image Analysis
- •4.1 Bony Pelvis
- •5 Typical Findings
- •5.1 Anterior Compartment
- •5.2 Middle Compartment
- •5.3 Posterior Compartment
- •5.4 Levator Ani Muscle
- •References
- •Evaluation of Infertility
- •1 Introduction
- •2 Imaging Techniques
- •2.1 Hysterosalpingography
- •2.1.1 Cycle Considerations
- •2.1.2 Technical Considerations
- •2.1.3 Side Effects and Complications
- •2.1.5 Pathological Findings
- •2.1.6 Limitations of HSG
- •2.2.1 Cycle Considerations
- •2.2.2 Technical Considerations
- •2.2.2.1 Normal and Abnormal Anatomy
- •2.2.3 Accuracy
- •2.2.4 Side Effects and Complications
- •2.2.5 Limitations of Sono-HSG
- •2.3 Magnetic Resonance Imaging
- •2.3.1 Indications
- •2.3.2 Technical Considerations
- •2.3.3 Limitations
- •3 Ovulatory Dysfunction
- •4 Pituitary Adenoma
- •5 Polycystic Ovarian Syndrome
- •7 Uterine Disorders
- •7.1 Müllerian Duct Anomalies
- •7.1.1 Class I: Hypoplasia or Agenesis
- •7.1.2 Class II: Unicornuate
- •7.1.3 Class III: Didelphys
- •7.1.4 Class IV: Bicornuate
- •7.1.5 Class V: Septate
- •7.1.6 Class VI: Arcuate
- •7.1.7 Class VII: Diethylstilbestrol Related
- •7.2 Adenomyosis
- •7.3 Leiomyoma
- •7.4 Endometriosis
- •References
- •MR Pelvimetry
- •1 Clinical Background
- •1.3.1 Diagnosis
- •1.3.2.1 Cephalopelvic Disproportion
- •1.3.4 Inadequate Progression of Labor due to Inefficient Contraction (“the Powers”)
- •2.2 Palpation of the Pelvis
- •3 MR Pelvimetry
- •3.2 MR Imaging Protocol
- •3.3 Image Analysis
- •3.4 Reference Values for MR Pelvimetry
- •5 Indications for Pelvimetry
- •References
- •MR Imaging of the Placenta
- •2 Imaging of the Placenta
- •3 MRI Protocol
- •4 Normal Appearance
- •4.1 Placenta Variants
- •5 Placenta Adhesive Disorders
- •6 Placenta Abruption
- •7 Solid Placental Masses
- •9 Future Directions
- •References
- •Erratum to: Endometrial Cancer
312 |
R. Forstner |
|
|
a |
b |
c
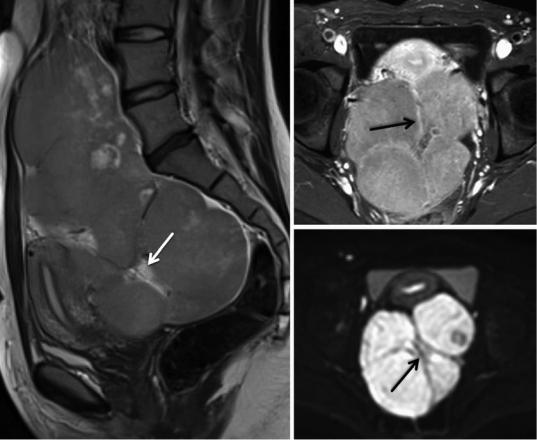
Fig. 23 Dysgerminoma of the right ovary in a 32-year-old female. A large, well-delineated multinodular solid lesion is located cranially and anterior of the uterus (a). It displays predominantly intermediate SI on the T2-weighted
image (a) and moderate contrast enhancement (b), but clearly restricted diffusion (b = 1,000 mm2) on DWI (c). Multiple septa (arrows) can be identified
1998; Bazot et al. 1999; Yamaoka et al. 2003). In CT, punctate foci of fat and calcifications are diagnostic clues for the presence of an immature teratoma (Bazot et al. 1999). In case of cystic lesions, they are typically filled with serous fluid and may rarely contain fatty sebaceous material (Diop et al. 2014). In MRI, small foci of fat with high SI on T1 (Fig. 24) and signal loss on the fat saturation sequence are typically found (Yamaoka et al. 2003). Malignant type of enhancement of the solid aspects may be seen. Capsular penetration is found in almost 50% of cases and is a pathognomonical feature of malignancy (Comerci et al. 1994).
Malignant Transformation in Benign Teratoma
Malignant transformation of benign teratomas is rare and reported in 0.17% of dermoid cysts (Comerci et al. 1994). It is associated with advanced age (mean 59 years) and a large (>6 cm) unilateral benign teratoma. In the vast majority, squamous cell cancer (up to 85%), or rarely carcinoid tumors, and adenoor chorionic cancer arise from the cyst wall or from ectodermal elements of benign teratomas (Choudhary et al. 2009).
Imaging Findings
Fat within an ovarian mass is diagnostic of a teratoma. Signs indicative of malignancy include a
CT and MRI in Ovarian Carcinoma |
313 |
|
|
a
b
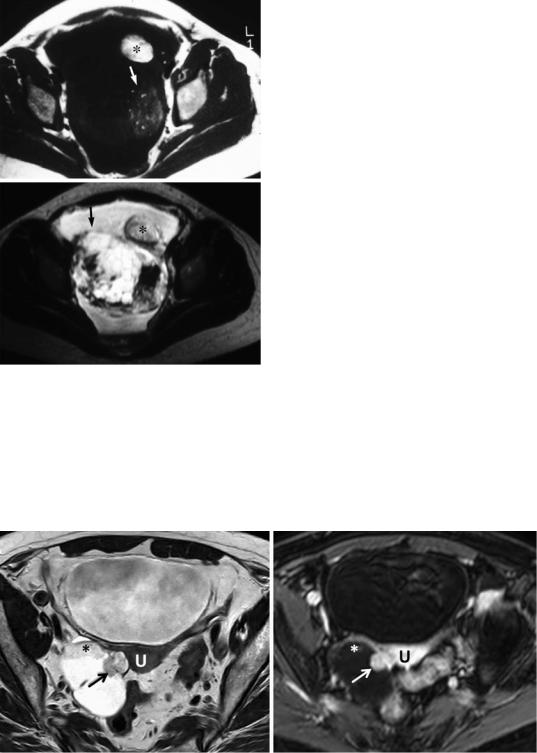
Fig. 24 Mature and immature teratoma in a 20-year-old female. T1weighted image (a) and T2-weighted image with FS (b) at the acetabular level. Ascites surrounds bilateral ovarian lesions. The left tumor (*) represents a benign dermoid with predominantly fatty tissue. Posteriorly an inhomogeneous mixed solid and cystic lesion (arrow) with small hemorrhagic loculi is seen, which is better identified on the T2-weighted image (b). The tiny spots of high SI on T1-weighted image represent areas of fat (arrow) in (a). Courtesy of TM Cunha, Lisbon
a
solid well-vascularized large mural nodule, often arising from the Rokitansky protuberance, breach of the capsule, or extracapsular growth and metastases (Fig. 25) (Choudhary et al. 2009; Kido et al. 1999). Elevation of tumor markers CEA and CA-125 in an older female with a large fat-/sebaceum-containing mass is diagnostic of malignant degeneration of a dermoid cyst (Dos Santos et al. 2007).
Differential Diagnosis
Immature teratomas are usually large at presentation and occur in young females. In contrast to the majority of benign cystic teratomas, malignant teratomas tend to be predominantly solid with small foci of fat and scattered calcifications. Elevation of alpha-1-fetoprotein assists in establishing the diagnosis and is found in 33–65% of immature teratomas (Yamaoka et al. 2003). Mature and immature teratomas coexist in approximately 20% of cases. If no fat is identified, an immature teratoma cannot be differentiated from a monodermal benign teratoma, e.g., of struma ovarii, from malignant germ cell tumors, or from ovarian cancer (Dujardin et al. 2014). Pitfalls include struma ovarii, where nodules may show avid contrast enhancement similar to malignant degeneration (Forstner et al. 2016a). However, only capsular breach proves the malignant transformation (Choudhary et al. 2009).
b
Fig. 25 Malignant transformation. In a 64-year-old female, a mural nodule breaching the capsule of a benign teratoma is seen on the T2WI (arrow) (a). FS GdT1 WI
(b) shows the intensely enhancing nodule (arrow) with extracapsular growth. Fat (*) within the teratoma. U uterus
