
- •Contents
- •Contributors
- •1 Introduction
- •2.1 Posterior Compartment
- •2.2 Anterior Compartment
- •2.3 Middle Compartment
- •2.4 Perineal Body
- •3 Compartments
- •3.1 Posterior Compartment
- •3.1.1 Connective Tissue Structures
- •3.1.2 Muscles
- •3.1.3 Reinterpreted Anatomy and Clinical Relevance
- •3.2 Anterior Compartment
- •3.2.1 Connective Tissue Structures
- •3.2.2 Muscles
- •3.2.3 Reinterpreted Anatomy and Clinical Relevance
- •3.2.4 Important Vessels, Nerves, and Lymphatics of the Anterior Compartment
- •3.3 Middle Compartment
- •3.3.1 Connective Tissue Structures
- •3.3.2 Muscles
- •3.3.3 Reinterpreted Anatomy and Clinical Relevance
- •3.3.4 Important Vessels, Nerves, and Lymphatics of the Middle Compartment
- •4 Perineal Body
- •References
- •MR and CT Techniques
- •1 Introduction
- •2.1 Introduction
- •2.2.1 Spasmolytic Medication
- •2.3.2 Diffusion-Weighted Imaging
- •2.3.3 Dynamic Contrast Enhancement
- •3 CT Technique
- •3.1 Introduction
- •3.2 Technical Disadvantages
- •3.4 Oral and Rectal Contrast
- •References
- •Uterus: Normal Findings
- •1 Introduction
- •References
- •1 Clinical Background
- •1.1 Epidemiology
- •1.2 Clinical Presentation
- •1.3 Embryology
- •1.4 Pathology
- •2 Imaging
- •2.1 Technique
- •2.2.1 Class I Anomalies: Dysgenesis
- •2.2.2 Class II Anomalies: Unicornuate Uterus
- •2.2.3 Class III Anomalies: Uterus Didelphys
- •2.2.4 Class IV Anomalies: Bicornuate Uterus
- •2.2.5 Class V Anomalies: Septate Uterus
- •2.2.6 Class VI Anomalies: Arcuate Uterus
- •2.2.7 Class VII Anomalies
- •References
- •Benign Uterine Lesions
- •1 Background
- •1.1 Uterine Leiomyomas
- •1.1.1 Epidemiology
- •1.1.2 Pathogenesis
- •1.1.3 Histopathology
- •1.1.4 Clinical Presentation
- •1.1.5 Therapy
- •1.1.5.1 Indications
- •1.1.5.2 Medical Therapy and Ablation
- •1.1.5.3 Surgical Therapy
- •1.1.5.4 Uterine Artery Embolization (UAE)
- •1.1.5.5 Magnetic Resonance-Guided Focused Ultrasound
- •2 Adenomyosis of the Uterus
- •2.1 Epidemiology
- •2.2 Pathogenesis
- •2.3 Histopathology
- •2.4 Clinical Presentation
- •2.5 Therapy
- •3 Imaging
- •3.2 Magnetic Resonance Imaging
- •3.2.1 Magnetic Resonance Imaging: Technique
- •3.2.2 MR Appearance of Uterine Leiomyomas
- •3.2.3 Locations, Growth Patterns, and Imaging Characteristics
- •3.2.4 Histologic Subtypes and Forms of Degeneration
- •3.2.5 Differential Diagnosis
- •3.2.6 MR Appearance of Uterine Adenomyosis
- •3.2.7 Locations, Growth Patterns, and Imaging Characteristics
- •3.2.8 Differential Diagnosis
- •3.3 Computed Tomography
- •3.3.1 CT Technique
- •3.3.2 CT Appearance of Uterine Leiomyoma and Adenomyosis
- •3.3.3 Atypical Appearances on CT and Differential Diagnosis
- •4.1 Indications
- •4.2 Technique
- •Bibliography
- •Cervical Cancer
- •1 Background
- •1.1 Epidemiology
- •1.2 Pathogenesis
- •1.3 Screening
- •1.4 HPV Vaccination
- •1.5 Clinical Presentation
- •1.6 Histopathology
- •1.7 Staging
- •1.8 Growth Patterns
- •1.9 Treatment
- •1.9.1 Treatment of Microinvasive Cervical Cancer
- •1.9.2 Treatment of Grossly Invasive Cervical Carcinoma (FIGO IB-IVA)
- •1.9.3 Treatment of Recurrent Disease
- •1.9.4 Treatment of Cervical Cancer During Pregnancy
- •1.10 Prognosis
- •2 Imaging
- •2.1 Indications
- •2.1.1 Role of CT and MRI
- •2.2 Imaging Technique
- •2.2.2 Dynamic MRI
- •2.2.3 Coil Technique
- •2.2.4 Vaginal Opacification
- •2.3 Staging
- •2.3.1 General MR Appearance
- •2.3.2 Rare Histologic Types
- •2.3.3 Tumor Size
- •2.3.4 Local Staging
- •2.3.4.1 Stage IA
- •2.3.4.2 Stage IB
- •2.3.4.3 Stage IIA
- •2.3.4.4 Stage IIB
- •2.3.4.5 Stage IIIA
- •2.3.4.6 Stage IIIB
- •2.3.4.7 Stage IVA
- •2.3.4.8 Stage IVB
- •2.3.5 Lymph Node Staging
- •2.3.6 Distant Metastases
- •2.4 Specific Diagnostic Queries
- •2.4.1 Preoperative Imaging
- •2.4.2 Imaging Before Radiotherapy
- •2.5 Follow-Up
- •2.5.1 Findings After Surgery
- •2.5.2 Findings After Chemotherapy
- •2.5.3 Findings After Radiotherapy
- •2.5.4 Recurrent Cervical Cancer
- •2.6.1 Ultrasound
- •2.7.1 Metastasis
- •2.7.2 Malignant Melanoma
- •2.7.3 Lymphoma
- •2.8 Benign Lesions of the Cervix
- •2.8.1 Nabothian Cyst
- •2.8.2 Leiomyoma
- •2.8.3 Polyps
- •2.8.4 Rare Benign Tumors
- •2.8.5 Cervicitis
- •2.8.6 Endometriosis
- •2.8.7 Ectopic Cervical Pregnancy
- •References
- •Endometrial Cancer
- •1.1 Epidemiology
- •1.2 Pathology and Risk Factors
- •1.3 Symptoms and Diagnosis
- •2 Endometrial Cancer Staging
- •2.1 MR Protocol for Staging Endometrial Carcinoma
- •2.2.1 Stage I Disease
- •2.2.2 Stage II Disease
- •2.2.3 Stage III Disease
- •2.2.4 Stage IV Disease
- •4 Therapeutic Approaches
- •4.1 Surgery
- •4.2 Adjuvant Treatment
- •4.3 Fertility-Sparing Treatment
- •5.1 Treatment of Recurrence
- •6 Prognosis
- •References
- •Uterine Sarcomas
- •1 Epidemiology
- •2 Pathology
- •2.1 Smooth Muscle Tumours
- •2.2 Endometrial Stromal Tumours
- •3 Clinical Background
- •4 Staging
- •5 Imaging
- •5.1 Leiomyosarcoma
- •5.2.3 Undifferentiated Uterine Sarcoma
- •5.3 Adenosarcoma
- •6 Prognosis and Treatment
- •References
- •1.1 Anatomical Relationships
- •1.4 Pelvic Fluid
- •2 Developmental Anomalies
- •2.1 Congenital Abnormalities
- •2.2 Ovarian Maldescent
- •3 Ovarian Transposition
- •References
- •1 Introduction
- •4 Benign Adnexal Lesions
- •4.1.1 Physiological Ovarian Cysts: Follicular and Corpus Luteum Cysts
- •4.1.1.1 Imaging Findings in Physiological Ovarian Cysts
- •4.1.1.2 Differential Diagnosis
- •4.1.2 Paraovarian Cysts
- •4.1.2.1 Imaging Findings
- •4.1.2.2 Differential Diagnosis
- •4.1.3 Peritoneal Inclusion Cysts
- •4.1.3.1 Imaging Findings
- •4.1.3.2 Differential Diagnosis
- •4.1.4 Theca Lutein Cysts
- •4.1.4.1 Imaging Findings
- •4.1.4.2 Differential Diagnosis
- •4.1.5 Polycystic Ovary Syndrome
- •4.1.5.1 Imaging Findings
- •4.1.5.2 Differential Diagnosis
- •4.2.1 Cystadenoma
- •4.2.1.1 Imaging Findings
- •4.2.1.2 Differential Diagnosis
- •4.2.2 Cystadenofibroma
- •4.2.2.1 Imaging Features
- •4.2.3 Mature Teratoma
- •4.2.3.1 Mature Cystic Teratoma
- •Imaging Findings
- •Differential Diagnosis
- •4.2.3.2 Monodermal Teratoma
- •Imaging Findings
- •4.2.4 Benign Sex Cord-Stromal Tumors
- •4.2.4.1 Fibroma and Thecoma
- •Imaging Findings
- •4.2.4.2 Sclerosing Stromal Tumor
- •Imaging Findings
- •4.2.5 Brenner Tumors
- •4.2.5.1 Imaging Findings
- •4.2.5.2 Differential Diagnosis
- •5 Functioning Ovarian Tumors
- •References
- •1 Introduction
- •2.1 Context
- •2.2.2 Indications According to Simple Rules
- •References
- •CT and MRI in Ovarian Carcinoma
- •1 Introduction
- •2.1 Familial or Hereditary Ovarian Cancers
- •3 Screening for Ovarian Cancer
- •5 Tumor Markers
- •6 Clinical Presentation
- •7 Imaging of Ovarian Cancer
- •7.1.2 Peritoneal Carcinomatosis
- •7.1.3 Ascites
- •7.3 Staging of Ovarian Cancer
- •7.3.1 Staging by CT and MRI
- •Imaging Findings According to Tumor Stages
- •Value of Imaging
- •7.3.2 Prediction of Resectability
- •7.4 Tumor Types
- •7.4.1 Epithelial Ovarian Cancer
- •High-Grade Serous Ovarian Cancer
- •Low-Grade Serous Ovarian Cancer
- •Mucinous Epithelial Ovarian Cancer
- •Endometrioid Ovarian Carcinomas
- •Clear Cell Carcinomas
- •Imaging Findings of Epithelial Ovarian Cancers
- •Differential Diagnosis
- •Borderline Tumors
- •Imaging Findings
- •Differential Diagnosis
- •Recurrent Ovarian Cancer
- •Imaging Findings
- •Differential Diagnosis
- •Value of Imaging
- •Malignant Germ Cell Tumors
- •Dysgerminomas
- •Imaging Findings
- •Differential Diagnosis
- •Immature Teratomas
- •Imaging Findings
- •Malignant Transformation in Benign Teratoma
- •Imaging Findings
- •Differential Diagnosis
- •Sex-Cord Stromal Tumors
- •Granulosa Cell Tumors
- •Imaging Findings
- •Sertoli-Leydig Cell Tumor
- •Imaging Findings
- •Ovarian Lymphoma
- •Imaging Findings
- •Differential Diagnosis
- •7.4.3 Ovarian Metastases
- •Imaging Findings
- •Differential Diagnosis
- •7.5 Fallopian Tube Cancer
- •7.5.1 Imaging Findings
- •Differential Diagnosis
- •References
- •Endometriosis
- •1 Introduction
- •2.1 Sonography
- •3 MR Imaging Findings
- •References
- •Vagina and Vulva
- •1 Introduction
- •3.1 CT Appearance
- •3.2 MRI Protocol
- •3.3 MRI Appearance
- •4.1 Imperforate Hymen
- •4.2 Congenital Vaginal Septa
- •4.3 Vaginal Agenesis
- •5.1 Vaginal Cysts
- •5.1.1 Gardner Duct Cyst (Mesonephric Cyst)
- •5.1.2 Bartholin Gland Cyst
- •5.2.1 Vaginal Infections
- •5.2.1.1 Vulvar Infections
- •5.2.1.2 Vulvar Thrombophlebitis
- •5.3 Vulvar Trauma
- •5.4 Vaginal Fistula
- •5.5 Post-Radiation Changes
- •5.6 Benign Tumors
- •6.1 Vaginal Malignancies
- •6.1.1 Primary Vaginal Carcinoma
- •6.1.1.1 MRI Findings
- •6.1.1.2 Lymph Node Drainage
- •6.1.1.3 Recurrence and Complications
- •6.1.2 Non-squamous Cell Carcinomas of the Vagina
- •6.1.2.1 Adenocarcinoma
- •6.1.2.2 Melanoma
- •6.1.2.3 Sarcomas
- •6.1.2.4 Lymphoma
- •6.2 Vulvar Malignancies
- •6.2.1 Vulvar Carcinoma
- •6.2.2 Melanoma
- •6.2.3 Lymphoma
- •6.2.4 Aggressive Angiomyxoma of the Vulva
- •7 Vaginal Cuff Disease
- •7.1 MRI Findings
- •8 Foreign Bodies
- •References
- •Imaging of Lymph Nodes
- •1 Background
- •3 Technique
- •3.1.1 Intravenous Unspecific Contrast Agents
- •3.1.2 Intravenous Tissue-Specific Contrast Agents
- •References
- •1 Introduction
- •2.1.1 Imaging Findings
- •2.1.2 Differential Diagnosis
- •2.1.3 Value of Imaging
- •2.2 Pelvic Inflammatory
- •2.2.1 Imaging Findings
- •2.3 Hydropyosalpinx
- •2.3.1 Imaging Findings
- •2.3.2 Differential Diagnosis
- •2.4 Tubo-ovarian Abscess
- •2.4.1 Imaging Findings
- •2.4.2 Differential Diagnosis
- •2.4.3 Value of Imaging
- •2.5 Ovarian Torsion
- •2.5.1 Imaging Findings
- •2.5.2 Differential Diagnosis
- •2.5.3 Diagnostic Value
- •2.6 Ectopic Pregnancy
- •2.6.1 Imaging Findings
- •2.6.2 Differential Diagnosis
- •2.6.3 Value of Imaging
- •3.1 Pelvic Congestion Syndrome
- •3.1.1 Imaging Findings
- •3.1.2 Differential Diagnosis
- •3.1.3 Value of Imaging
- •3.2 Ovarian Vein Thrombosis
- •3.2.1 Imaging Findings
- •3.2.2 Differential Diagnosis
- •3.2.3 Value of Imaging
- •3.3 Appendicitis
- •3.3.1 Imaging Findings
- •3.3.2 Value of Imaging
- •3.4 Diverticulitis
- •3.4.1 Imaging Findings
- •3.4.2 Differential Diagnosis
- •3.4.3 Value of Imaging
- •3.5 Epiploic Appendagitis
- •3.5.1 Imaging Findings
- •3.5.2 Differential Diagnosis
- •3.5.3 Value of Imaging
- •3.6 Crohn’s Disease
- •3.6.1 Imaging Findings
- •3.6.2 Differential Diagnosis
- •3.6.3 Value of Imaging
- •3.7 Rectus Sheath Hematoma
- •3.7.1 Imaging Findings
- •3.7.2 Differential Diagnosis
- •3.7.3 Value of Imaging
- •References
- •MRI of the Pelvic Floor
- •1 Introduction
- •2 Imaging Techniques
- •3.1 Indications
- •3.2 Patient Preparation
- •3.3 Patient Instruction
- •3.4 Patient Positioning
- •3.5 Organ Opacification
- •3.6 Sequence Protocols
- •4 MR Image Analysis
- •4.1 Bony Pelvis
- •5 Typical Findings
- •5.1 Anterior Compartment
- •5.2 Middle Compartment
- •5.3 Posterior Compartment
- •5.4 Levator Ani Muscle
- •References
- •Evaluation of Infertility
- •1 Introduction
- •2 Imaging Techniques
- •2.1 Hysterosalpingography
- •2.1.1 Cycle Considerations
- •2.1.2 Technical Considerations
- •2.1.3 Side Effects and Complications
- •2.1.5 Pathological Findings
- •2.1.6 Limitations of HSG
- •2.2.1 Cycle Considerations
- •2.2.2 Technical Considerations
- •2.2.2.1 Normal and Abnormal Anatomy
- •2.2.3 Accuracy
- •2.2.4 Side Effects and Complications
- •2.2.5 Limitations of Sono-HSG
- •2.3 Magnetic Resonance Imaging
- •2.3.1 Indications
- •2.3.2 Technical Considerations
- •2.3.3 Limitations
- •3 Ovulatory Dysfunction
- •4 Pituitary Adenoma
- •5 Polycystic Ovarian Syndrome
- •7 Uterine Disorders
- •7.1 Müllerian Duct Anomalies
- •7.1.1 Class I: Hypoplasia or Agenesis
- •7.1.2 Class II: Unicornuate
- •7.1.3 Class III: Didelphys
- •7.1.4 Class IV: Bicornuate
- •7.1.5 Class V: Septate
- •7.1.6 Class VI: Arcuate
- •7.1.7 Class VII: Diethylstilbestrol Related
- •7.2 Adenomyosis
- •7.3 Leiomyoma
- •7.4 Endometriosis
- •References
- •MR Pelvimetry
- •1 Clinical Background
- •1.3.1 Diagnosis
- •1.3.2.1 Cephalopelvic Disproportion
- •1.3.4 Inadequate Progression of Labor due to Inefficient Contraction (“the Powers”)
- •2.2 Palpation of the Pelvis
- •3 MR Pelvimetry
- •3.2 MR Imaging Protocol
- •3.3 Image Analysis
- •3.4 Reference Values for MR Pelvimetry
- •5 Indications for Pelvimetry
- •References
- •MR Imaging of the Placenta
- •2 Imaging of the Placenta
- •3 MRI Protocol
- •4 Normal Appearance
- •4.1 Placenta Variants
- •5 Placenta Adhesive Disorders
- •6 Placenta Abruption
- •7 Solid Placental Masses
- •9 Future Directions
- •References
- •Erratum to: Endometrial Cancer
236 |
R. Forstner |
|
|
a |
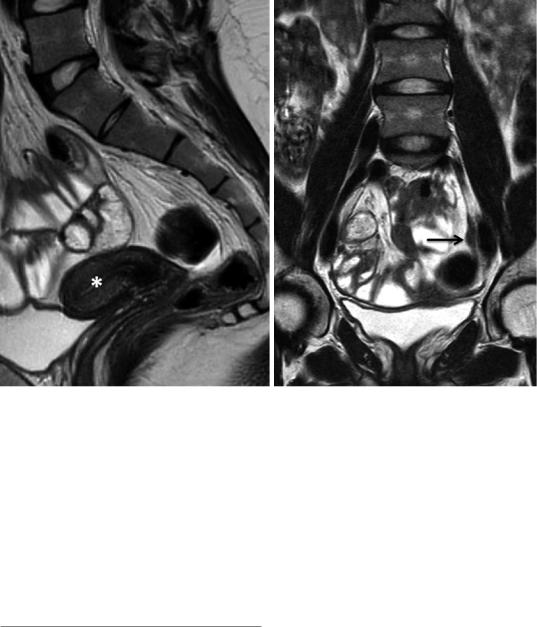
b |
Fig. 12 Streak gonads. In a 23-year-old female, uterine hypoplasia (*) is demonstrated on the sagittal T2WI (a). Normal ovaries are not identified. A bandlike soft tissue
structure (arrow) adjacent to the external iliac vessel presents a left streak gonad (b)
Differential diagnosis Differential diagnosis of a unilateral missing ovary includes ectopic ovary and atrophy resulting from adnexal torsion. Mullerian duct anomalies support congenital etiology and warrant search along the psoas muscle outside the pelvis.
3\ Ovarian Transposition
Surgical transposition of the ovaries is accomplished before therapeutic irradiation of the pelvis in women to preserve ovarian function. Ovaries, supportive ligaments, and their vascular supply are surgically mobilized outside the pelvis, most commonly laterally to the paracolic gutters anterior of the psoas muscles (Wo and Viswanathan 2009).
Other sites of transposition are the lower paracolic gutters close to the iliac fossa. Lateral transposition is performed in patients with cervical cancer, vaginal cancer, pelvic sarcoma, and Hodgkin disease. Medial transposition refers to attachment of the ovaries to the surface of the uterus (Kier and Chambers 1989; Bashist and Freidman 1989). Surgical clips are typically affixed to each ovary to mark its location.
Imaging findings
Transposed ovaries can be identified by their characteristic morphologic feature of follicles that undergo follicular maturation. Metallic clips help to identify the ovaries on CT (Fig. 14) (Bashist and Freidman 1989). Furthermore, following the ovarian vessels downwards from the mid-lumbar region aids in identifying the ovaries (Lee et al. 2003).
Ovaries and Fallopian Tubes: Normal Findings and Anomalies |
237 |
|
|
|
|
a |
b |
|
c |
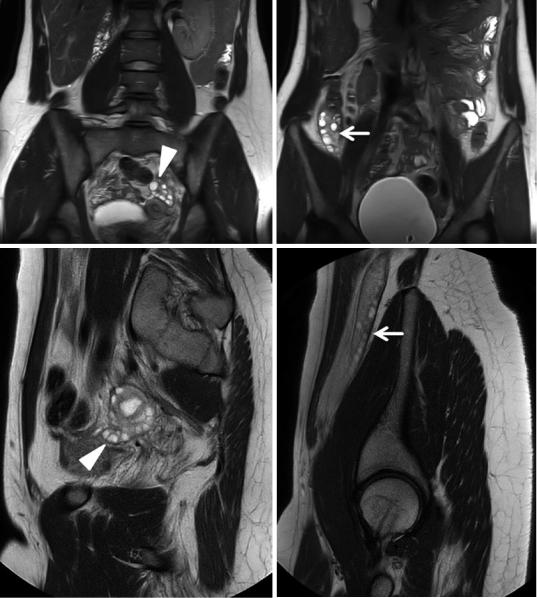
d |
Fig. 13 Ovarian maldescent associated with uterine malformation. Coronal (a, b) and sagittal (c, d) T2WI. The left ovary is in normal position adjacent to the unicornuate uterus (arrowhead) (a, c). The left ovary is in atypical
high position anterior to the psoas muscle (d). It contains multiple peripheral follicles (b) and displays an atypical elongated shape (arrow) (d)
Ovarian vessels in lateral transposition deviate laterally near the iliac fossa instead of coursing inferiorly (Saksouk and Johnson 2004). Transposed ovaries should not be misdiagnosed as peritoneal implants. Medical history and metallic surgical clip markings in CT will facilitate dif-
ferentiation, as well as meticulous analysis of ovarian morphology including ovarian follicles on T2WI (Sella et al. 2005). Identification of featureless and small atrophic ovaries is feasible due to the surgical clips in CT, but it may be difficult in MRI.
238 |
R. Forstner |
|
|
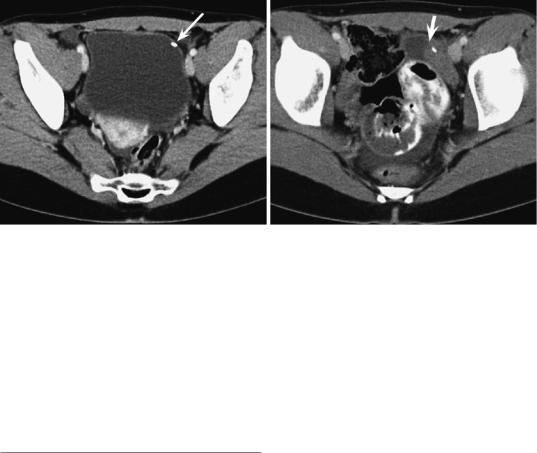
a |
b |
Fig. 14 Surgical transposition. Transaxial CT after transposition of the ovary (a) and after radiation therapy (b). During endoscopical transposition, the left ovary was marked by a clip (arrow). In the follow-up, the cystic and
Differential diagnosis Familiarity with history of ovarian transposition is crucial to establish the correct diagnosis. The differential diagnosis includes mucocele of appendix, peritoneal implants, colonic masses, lymphoceles, and lymph node metastases.
References
Addley HC, Vargas HA, Moyle PL, Crawford R, Sala E (2010) Pelvic imaging following chemotherapy and radiation therapy for gynecologic malignancies. Radiographics 3:1843–1856
Allen JW, Cardall S, Kittijarukhajorn M, Siege CL (2012) Incidence of ovarian maldescent in women with müllerian duct anomalies: evaluation by MRI. AJR Am J Roentgenol 198:W381–W385
Bashist B, Freidman WN, Killackey MA (1989) Surgical transposition of the ovary: radiological appearance. Radiology 173:857–860
Clement PB (2002) Anatomy and histology of the ovary. In: Kurman RJ (ed) Blaustein’s pathology of the female genital tract. Springer, New York, pp 649–674 Cohen HL, Tice HM, Mandel FS (1990) Ovarian volumes measured by US: bigger than we think. Radiology
177:189–192
Dabirash H, Mohammad K, Moghadami-Tabrizi N (1994) Ovarian malposition in women with uterine anomalies. Obstet Gynecol 83:293–294
Davis JA, Gosink BB (1986) Fluid in the female pelvis: cyclic patterns. J Ultrasound Med 5:75
solid lesion presents the normal transposed ovary which undergoes cyclic changes. Without the clip (arrow), it may easily be misdiagnosed as a tumor. Ascites is a sequelae of radiation
Diop AD, Fontarensky M, Montoriol PF, Da Ines D (2014) CT imaging of peritoneal carcinomatosis and its mimics. Diagn Interv Imaging 95:861–872
Dueck A, Poenaru D, Jamieson MA (2001) Unilateral ovarian agenesis and fallopian tube maldescent. Pediatr Surg Int 17:228–229
Foshager MC, Walsh JW (1994) CT anatomy of the female pelvis: a second look. Radiographics 14:51–66
Ghattamaneni S, Bhuskute NM, Weston MJ, Spencer JA (2009) Discriminitive MRI features of fallopian tube masses. Clin Radiol 64:815–831
Hahn-Pedersen J, Larsen PM (1984) Supernumary ovaries. Acta Obstet Gynecol Scand 63:365–366
Karaosmanoglu D, Karcaaltincaba M, Karcaaltincaba D, Akata D, Ozmen M (2009) MDCT of the ovarian vein. Normal anatomy and pathology. AJR Am J Roentgenol 192:295–299
Kier R, Chambers SK (1989) Surgical transposition of the ovaries: imaging findings in14 patients. AJR 153:1003–1006 Kim DC, Bennett GL, Somberg M, Campbell N et al (2016) A multidisciplinary approach to improving appropriate follow-up imaging of ovarian cysts. A quality improvement initiative. J Am Coll Radiol
13:535–541
Langer JE, Oliver ER, Lev-Toaff AS, Coleman BG (2012) Imaging of the female pelvis through the life cycle. Radiographics 32:1575–1597
Lee JH, Jeong YK, Park JK et al (2003) Ovarian vascular pedicle sign revealing organ origin of mass lesion on helical CT. AJR 181:131–137
Lerman H, Metser U, Grisaru D et al (2004) Normal and abnormal 18F-DG endometrial and ovarian uptake in pre-and postmenopausal patients: assessment by PET/ CT. J Nucl Med 45:266–271
Ovaries and Fallopian Tubes: Normal Findings and Anomalies |
239 |
|
|
Levine D, Brown DL, Andreotti RF et al (2010) Management of asymptomatic ovarian and other adnexal cysts imaged at US: Society of Radiologists in Ultrasound consensus conference statement. Radiology 256:943–954
Morisawa N, Kido A, Koyama T, Okada T, Kataoka M et al (2012) Changes in the normal ovary during menstrual cycle in reproductive age on the diffusionweighted image. J Comput Assist Tomogr 36:319–322 Nunley WC, Pope TL, Bateman BG (1984) Upper reproductive tract radiographic findings in DES-exposed
female offspring. AJR 142:337–339
Outwater EK, Mitchell DG (1996) Normal ovaries and functional cysts: MR appearance. Radiology 198:397–402 Outwater EK, Talerman A, Dunton C (1996) Normal
adnexa uteri specimens: anatomic basis of MR imaging features. Radiology 201:751–755
Pavlik EJ, DePriest PD, Gallion HH, Ueland FR, Reedy MB, Kryscio RJ, van Nagell JR Jr (2000) Ovarian volume related to age. Gynecol Oncol 77:410–412
Rezvani M, Shaabab AM (2011) Fallopian tube disease in the nonpregnant patient. Radiographics 31: 527–548
Saksouk FA, Johnson SC (2004) Recognition of the ovaries and ovarian origin of pelvic masses with CT. Radiographics 24:133–146
Seidman JD, Russell P, Kurman RJ (2002) Surface epithelial tumors of the ovary. In: Kurman RJ (ed) Blaustein’s
pathology of the female genital tract. Springer, New York, pp 791–904
Sella T, Mironov S, Hricak H (2005) Imaging of transposed ovaries in patients with cervical carcinoma. AJR Am J Roentgenol 184:1602–1610
Spencer JA, Gore RM (2011) The adnexal incidentaloma: a practical approach to management. Cancer Imaging 11:48–51
Spencer JA, Forstner R, Cunha TM, Kinkel K, on behalf of the ESUR Female Imaging Sub-Committee (2010) ESUR guidelines for MR imaging of the sonographically indeterminate adnexal mass: an algorithmic approach. Eur Radiol 20:25–35
Stevens SK (1992) The adnexa. In: Higgins CB, Hricak H, Helms CA (eds) MRI of the body. Raven Press, New York, pp 865–889
Trinidad C, Tardaguila F, Fernandez GC (2004) Ovarian maldescent. Eur Radiol 14:805–808
Well D, Yang H, Houseni M, Iruvuri S, Alzeair S et al (2007) Age-related changes in the pelvic reproductive end organs. Semin Nucl Med 37:137–184
Welt CK (2016) Ovarian development and failure (menopause) in normal women. Barbeiri RL, Crowley WF (Section eds), Martin KA (Dep ed). www.uptodate. com
Wo JY, Viswanathan AN (2009) Impact of radiotherapy on fertility, pregnancy, and neonatal outcomes in female cancer patients. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 73:1304–1312
