
- •Foreword
- •Table of contents
- •Figures
- •Tables
- •Boxes
- •1. Executive summary
- •Energy system transformation
- •Special focus 1: The cost-effectiveness of climate measures
- •Special focus 2: The Electricity Market Reform
- •Special focus 3: Maintaining energy security
- •Key recommendations
- •2. General energy policy
- •Country overview
- •Institutions
- •Supply and demand trends
- •Primary energy supply
- •Energy production
- •Energy consumption
- •Energy policy framework
- •Energy and climate taxes and levies
- •Assessment
- •Recommendations
- •3. Energy and climate change
- •Overview
- •Emissions
- •GHG emissions
- •Projections
- •Institutions
- •Climate change mitigation
- •Emissions targets
- •Clean Growth Strategy
- •The EU Emissions Trading System
- •Low-carbon electricity support schemes
- •Climate Change Levy
- •Coal phase-out
- •Energy efficiency
- •Low-carbon technologies
- •Adaptation to climate change
- •Legal and institutional framework
- •Evaluation of impacts and risks
- •Response measures
- •Assessment
- •Recommendations
- •4. Renewable energy
- •Overview
- •Supply and demand
- •Renewable energy in the TPES
- •Electricity from renewable energy
- •Heat from renewable energy
- •Institutions
- •Policies and measures
- •Targets and objectives
- •Electricity from renewable energy sources
- •Heat from renewable energy
- •Renewable Heat Incentive
- •Renewable energy in transport
- •Assessment
- •Electricity
- •Transport
- •Heat
- •Recommendations
- •5. Energy efficiency
- •Overview
- •Total final energy consumption
- •Energy intensity
- •Overall energy efficiency progress
- •Institutional framework
- •Energy efficiency data and monitoring
- •Regulatory framework
- •Energy Efficiency Directive
- •Other EU directives
- •Energy consumption trends, efficiency, and policies
- •Residential and commercial
- •Buildings
- •Heat
- •Transport
- •Industry
- •Assessment
- •Appliances
- •Buildings and heat
- •Transport
- •Industry and business
- •Public sector
- •Recommendations
- •6. Nuclear
- •Overview
- •New nuclear construction and power market reform
- •UK membership in Euratom and Brexit
- •Waste management and decommissioning
- •Research and development
- •Assessment
- •Recommendations
- •7. Energy technology research, development and demonstration
- •Overview
- •Energy research and development strategy and priorities
- •Institutions
- •Funding on energy
- •Public spending
- •Energy RD&D programmes
- •Private funding and green finance
- •Monitoring and evaluation
- •International collaboration
- •International energy innovation funding
- •Assessment
- •Recommendations
- •8. Electricity
- •Overview
- •Supply and demand
- •Electricity supply and generation
- •Electricity imports
- •Electricity consumption
- •Institutional and regulatory framework
- •Wholesale market design
- •Network regulation
- •Towards a low-carbon electricity sector
- •Carbon price floor
- •Contracts for difference
- •Emissions performance standards
- •A power market for business and consumers
- •Electricity retail market performance
- •Smart grids and meters
- •Supplier switching
- •Consumer engagement and vulnerable consumers
- •Demand response (wholesale and retail)
- •Security of electricity supply
- •Legal framework and institutions
- •Network adequacy
- •Generation adequacy
- •The GB capacity market
- •Short-term electricity security
- •Emergency response reserves
- •Flexibility of the power system
- •Assessment
- •Wholesale electricity markets and decarbonisation
- •Retail electricity markets for consumers and business
- •The transition towards a smart and flexible power system
- •Recommendations
- •Overview
- •Supply and demand
- •Production, import, and export
- •Oil consumption
- •Retail market and prices
- •Infrastructure
- •Refining
- •Pipelines
- •Ports
- •Storage capacity
- •Oil security
- •Stockholding regime
- •Demand restraint
- •Assessment
- •Oil upstream
- •Oil downstream
- •Recommendations
- •10. Natural gas
- •Overview
- •Supply and demand
- •Domestic gas production
- •Natural gas imports and exports
- •Largest gas consumption in heat and power sector
- •Natural gas infrastructure
- •Cross-border connection and gas pipelines
- •Gas storage
- •Liquefied natural gas
- •Policy framework and markets
- •Gas regulation
- •Wholesale gas market
- •Retail gas market
- •Security of gas supply
- •Legal framework
- •Adequacy of gas supply and demand
- •Short-term security and emergency response
- •Supply-side measures
- •Demand-side measures
- •Gas quality
- •Recent supply disruptions
- •Interlinkages of the gas and electricity systems
- •Assessment
- •Recommendations
- •ANNEX A: Organisations visited
- •Review criteria
- •Review team and preparation of the report
- •Organisations visited
- •ANNEX B: Energy balances and key statistical data
- •Footnotes to energy balances and key statistical data
- •ANNEX C: International Energy Agency “Shared Goals”
- •ANNEX D: Glossary and list of abbreviations
- •Acronyms and abbreviations
- •Units of measure
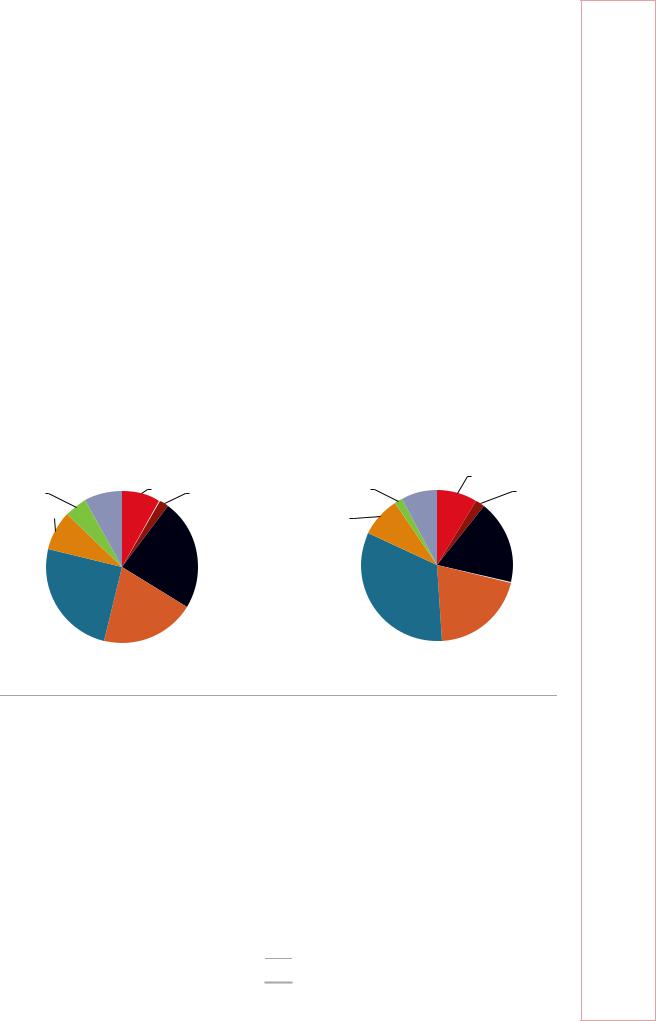
9. OIL
As for oil demand by fuel type, diesel is the most used oil product in the United Kingdom at 33% of the total oil demand in 2017 (up from 25% in 2007), followed by jet fuel and kerosene and motor gasoline (Figure 9.6). The share of motor gasoline has fallen from 23% in 2007 to 18% in 2017 as car owners switched to diesel vehicles and vehicle efficiency increased.
In July 2018, the government announced its intention to prohibit the sale of new petrol and diesel cars and vans by 2040 (and at least 50% of that target to be reached by 2030) as part of its air quality plan. It will have a large impact on the future trend of oil product consumption, which is currently dominated by transport-related fuels.
At the end of 2016, the International Maritime Organization (IMO) confirmed that, from January 2020, ships would have to use marine fuel with a sulphur content below 0.5% compared to the current 3.5% limit. The implementation of the IMO’s new marine fuel specifications will also affect the oil product mix of the country. As an island nation, shipping and the maritime sectors are among the most important industries to the UK economy. Oil used for international marine bunkers was 2.5 Mt (47 kb/d) in 2017 (which excludes 3.8 Mt or 71 kb/d in Gibraltar).
Figure 9.6 Oil demand by product, 2007 and 2017
|
2007 |
|
|
2017 |
|
|
|
Residual |
Other |
LPG* and |
|
Residual |
Other |
LPG* and |
|
fuels |
products** |
ethane |
|
fuels |
products** |
ethane |
|
5% |
8% |
8% |
Naphtha |
2% |
8% |
9% |
Naphtha |
Other gasoil |
|
|
2% |
Other gasoil |
|
|
2% |
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
9% |
|
|
|
8% |
|
Motor |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Motor |
|
|
|
gasoline |
|
|
|
gasoline |
|
|
18% |
|
|
|
|
23% |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Diesel |
|
|
Diesel |
Jet and |
|
|
|
Jet and |
|
kerosene |
|
|||
|
25% |
|
|
33% |
20% |
|
|
|
kerosene |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
20% |
|
|
|
|
|
Diesel alone accounts for 33% of the total oil demand, followed by jet fuel and motor gasoline.
*LPG = liquefied petroleum gases.
**Other products include bitumen, lubricants, petroleum coke, refinery gas, white spirit, paraffin waxes, aviation gasoline, and other undefined oil products.
Note: Includes international aviation, which is not included in Figure 9.5.
Source: IEA (2018b) Oil Market Report 2018, www.iea.org/statistics/.
Retail market and prices
The United Kingdom operates an open market in which the wholesale price of petroleum products is set by market dynamics. The government influences retail prices for consumers solely through taxation.
171
ENERGY SECURITY
IEA. All rights reserved.
9. OIL
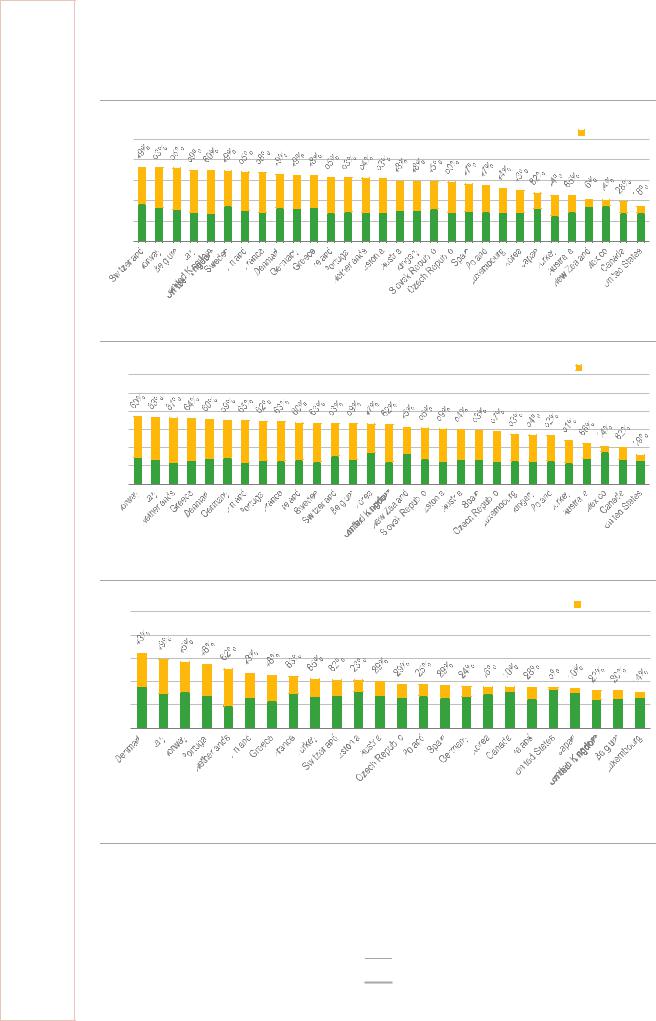
Figure 9.7 Oil fuel prices in IEA member countries, Q4 2018
Automotive diesel fuel
2.5 |
USD/L |
Tax component |
|
|
|
2.0 |
|
|
1.5 |
|
|
1.0 |
|
|
0.5 |
|
|
0 |
|
|
Premium unleaded gasoline (95 RON)
3.0 |
USD/L |
Tax component |
|
|
|
2.5 |
|
|
2.0 |
|
|
1.5 |
|
|
1.0 |
|
|
0.5 |
|
|
0 |
|
|
Light fuel oil
2.5 |
USD/L |
Tax component |
|
|
|
2.0 |
|
|
1.5 |
|
|
1.0 |
|
|
0.5 |
|
|
0.0 |
|
|
The United Kingdom has one of the highest retail prices for diesel oil with high taxes among the IEA member countries, while it has the third lowest price for light fuel oil.
Notes: Data are not available for gasoline in Japan and for light fuel oil in Australia, Hungary, Mexico, New Zealand, Slovak Republic, and Sweden. RON = research octane number.
Source: IEA (2019b), Energy Prices and Taxes 2019, www.iea.org/statistics/.
172
IEA. All rights reserved.
