
- •Final Report of the RK&M Initiative
- •Foreword
- •Acknowledgements
- •Table of contents
- •List of figures
- •List of tables
- •List of abbreviations and acronyms
- •The glossary of terms of records, knowledge and memory (RK&M) preservation
- •Executive summary
- •Key findings and recommendations
- •Chapter 1. Introduction
- •1.1. Background and scope of the RK&M initiative
- •The formulation of a dedicated initiative under the aegis of the RWMC
- •Modus operandi of the RK&M initiative
- •Key questions and objectives of the RK&M initiative
- •A product and process-oriented initiative
- •The fields of application and target audiences of the RK&M initiative
- •1.2. Evolutions in RK&M preservation thinking: A historical review
- •The RK&M reference bibliography
- •Popular themes in RK&M preservation literature
- •Landscape of Thorns
- •Atomic Priesthood
- •Summary of lessons learnt from the historical review
- •1.3. References
- •Chapter 2. RK&M preservation: Fundamentals
- •2.1. RK&M preservation and its connection to safety
- •The repository: From “seclusion and oblivion” to a societally embedded facility
- •Introducing the concept of oversight
- •2.2. Protecting humans and the environment
- •2.3. Supporting informed decision making
- •2.4. References
- •Chapter 3. RK&M preservation: Challenges and opportunities
- •3.1. Information life cycle management
- •3.2. Causes and consequences of RK&M loss
- •Lessons from RK&M loss in the nuclear field
- •Lessons from RK&M loss outside the nuclear field
- •3.3. RK&M preservation in a regulatory context
- •National RK&M preservation regulation
- •Planning responsibilities over time
- •International soft law
- •Regulation: a necessary condition for RK&M preservation
- •3.5. References
- •Chapter 4. Key characteristics of RK&M preservation approaches and mechanisms
- •4.1. Introducing the idea of a “systemic strategy” for RK&M preservation
- •4.2. Multiple time frames
- •The short term
- •The medium term
- •The long term
- •4.3. Multiple media
- •4.4. Multiple contents
- •4.5. Multiple transmission modes
- •4.6. Multiple actors
- •Multiple disciplines
- •Multiple interests, concerns and roles
- •4.7. Multiple locations
- •4.8. References
- •Chapter 5. RK&M preservation approaches and mechanisms
- •5.1. Introduction to the RK&M preservation “toolbox”
- •5.2. Dedicated record sets and summary files
- •5.3. Memory institutions
- •5.4. Markers
- •5.5. Time capsules
- •5.6. Culture, education and art
- •5.7. Knowledge management
- •5.8. Oversight provisions
- •5.9. International mechanisms
- •5.10. Regulatory framework
- •5.11. References
- •Chapter 6. Towards a systemic strategy for RK&M preservation
- •6.2. Meeting national needs
- •6.3. RK&M preservation starts today – life cycle thinking
- •6.4. RK&M preservation is an ongoing process
- •6.5. RK&M preservation is a participatory process
- •6.6. Illustration: Two fictional examples
- •Fictional example 1
- •Compliance activities
- •Best practice activities
- •Supporting activities
- •Fictional example 2
- •Compliance activities
- •Best practice activities
- •Supporting activities
- •6.7. References
- •Chapter 7. Conclusions and outlook
- •7.1. Conclusions
- •Embedding disposal facilities in society
- •Preventing inadvertent human intrusion and supporting informed decision making over time
- •Developing a systemic strategy for RK&M preservation
- •The importance of multi-disciplinarity and participation
- •7.2. Outlook
- •Upholding and elaborating an open and holistic attitude
- •Creating awareness, supporting engagement and starting RK&M preservation today
- •Developing international collaboration
- •7.3. Reference
- •Annex 1. RK&M glossary
- •Archive
- •Awareness
- •Control
- •Composite expressions
- •Cultural heritage
- •Data
- •Information
- •Knowledge
- •Composite expressions
- •Long term
- •Marker
- •Mediated/non-mediated transmission
- •Medium term
- •Memory
- •Message
- •Monument
- •Oversight
- •Record
- •Redundancy
- •Short term
- •Stakeholder
- •Systemic strategy
- •Very short term
- •References
- •Annex 2. Descriptions of RK&M preservation mechanisms
- •2.1. Mechanism description sheet: template
- •2.2. Mechanism description sheets
- •Dedicated record sets and summary files
- •Key information file (KIF)
- •Set of essential records (SER)
- •Memory institutions
- •Archives
- •Libraries
- •Museums
- •Markers
- •Surface markers
- •Monuments
- •Sub-surface markers
- •Deep geological markers
- •Surface traces
- •Time capsules
- •Large visible time capsules
- •Large invisible time capsules
- •Small time capsules
- •Culture, education and art
- •Industrial heritage
- •Alternative reuse of the disposal site/infrastructure
- •Heritage inventories and catalogues
- •Local history societies
- •Intangible cultural heritage
- •Education, research and training
- •Public information dissemination activities
- •Knowledge management
- •Knowledge retention tools
- •Knowledge risk analysis
- •Knowledge sharing philosophy
- •Oversight provisions
- •Monitoring
- •Land use control
- •Clear and planned responsibilities
- •International mechanisms
- •International regulations and agreements
- •International standards and guidelines
- •International inventories and catalogues
- •International co-operation
- •International education and training programmes
- •International archiving initiatives
- •Regulatory framework
- •National regulatory framework
- •Safeguards
- •2.3. Mechanisms overview table
- •Annex 3. Deliverables of the RK&M initiative
- •Workshop and conference proceedings
- •Studies
- •Reports
- •Website
- •Annex 4. Members and participating organisations of the RK&M initiative
- •NEA PUBLICATIONS AND INFORMATION
DESCRIPTIONS OF RK&M PRESERVATION MECHANISMS
Mechanism |
|
Safeguards |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Whereas the general aim of RK&M preservation is to keep awareness of disposal sites and to enable future generations |
||
|
to make informed decisions, the general aim of safeguards, from a security and malevolent use of nuclear material |
||
|
point of view, can be said to be the opposite. Tensions may thus arise between the classified and expertocratic nature |
||
|
of safeguards on the one hand, and the open, participatory nature of RK&M preservation on the other. |
||
Specific issues/ |
The current regulation on safeguards includes all kinds of facilities that handle nuclear material, but for geological |
||
repositories considerations are still at a conceptual level. Discussions are ongoing within the IAEA and the European |
|||
challenges |
|||
Commission on how international safeguards should be implemented in such facilities, considering both the |
|||
|
|||
|
operational and the post-closure phase and the desired continuity between those phases (including issues such as |
||
|
institutional continuity, handling of classified documents, economic provisions, etc.). |
||
|
Safeguards only apply to disposal facilities containing fissile material, and will thus not support to RK&M |
||
|
preservation for other repositories. |
||
International |
International organisations (Euratom and IAEA) are central to the development and conduct of safeguards provisions. |
||
dimension |
|||
|
|
||
|
International mechanisms: international regulations and agreements; international inventories and catalogues; |
||
Connection to |
international co-operation; international education and training programmes; international archives |
||
Regulatory framework: national regulatory framework |
|||
other |
|||
Oversight provisions: monitoring; clear and planned responsibilities; land use control |
|||
approaches/ |
|||
Knowledge management: knowledge risk analysis |
|||
mechanisms |
|||
Memory institutions: archives |
|||
|
|||
|
Dedicated record sets and summary files: SER |
||
|
• Ormai, P. (2011). The Connection between the Areas of Safeguards and Physical Protection and Record and Memory |
||
Information |
|
Keeping. In: NEA (2012). The Preservation of Records, Knowledge and Memory (RK&M) Across Generations: Scoping |
|
resources |
|
the Issue. Workshop proceedings. 11-13 October 2011, Issy-les-Moulineaux, France. Item 26. |
|
issued by the |
• NEA (2013). The Preservation of Records, Knowledge and Memory (RK&M) Across Generations: Improving Our |
||
RK&M initiative |
|
Understanding. Proceedings of the second RK&M Workshop. 12-13 September 2012, Issy-les-Moulineaux, |
|
|
|
France. Items 9 & 10, OECD, Paris. |
|
|
• European Commission (2005). Commission Regulation (Euratom) No 302/2005 of 8 February 2005 on the |
||
|
|
application of Euratom safeguards - Council/Commission statement. |
|
|
• IAEA (1972). The structure and content of agreements between the Agency and States required in connection |
||
|
|
with the treaty on the non-proliferation of nuclear weapons. INFCIRC/153. IAEA, Vienna. |
|
|
• IAEA (1996). Issues in Radioactive Waste Disposal. IAEA-Tecdoc-909. IAEA, Vienna. |
||
Other |
• IAEA (2010). Technological Implications of International Safeguards for Geological Disposal of Spent Fuel and |
||
information |
|
Radioactive Waste. NW-T-1.21. IAEA, Vienna. |
|
resources |
• IAEA (2011). Model Integrated Safeguards Approach for a Geological Repository. IAEA Department of |
||
|
|
Safeguards (SGCP-CCA) SG-PR-1306. IAEA, Vienna. |
|
|
• IAEA (2017). Technologies Potentially Useful for Safeguarding Geological Repositories. ASTOR Group Report |
||
|
|
2011-2016. STR-384. IAEA, Vienna. |
|
|
• NEA (1995). Future human actions at disposal sites: a report from the NEA Working Group on Assessment of |
||
|
|
Future Human Actions at Radioactive Waste Disposal Sites. OECD, Paris. |
|
|
• Safeguards and verification | IAEA, see www.iaea.org/topics/safeguards-and-verification |
||
Examples |
• Safeguards to avoid misuse - European Commission, see https://ec.europa.eu/energy/en/topics/nuclear- |
||
|
energy/safeguards-avoid-misuse |
||
|
|
||
•For a national example, see www.onr.org.uk/safeguards/index.htm
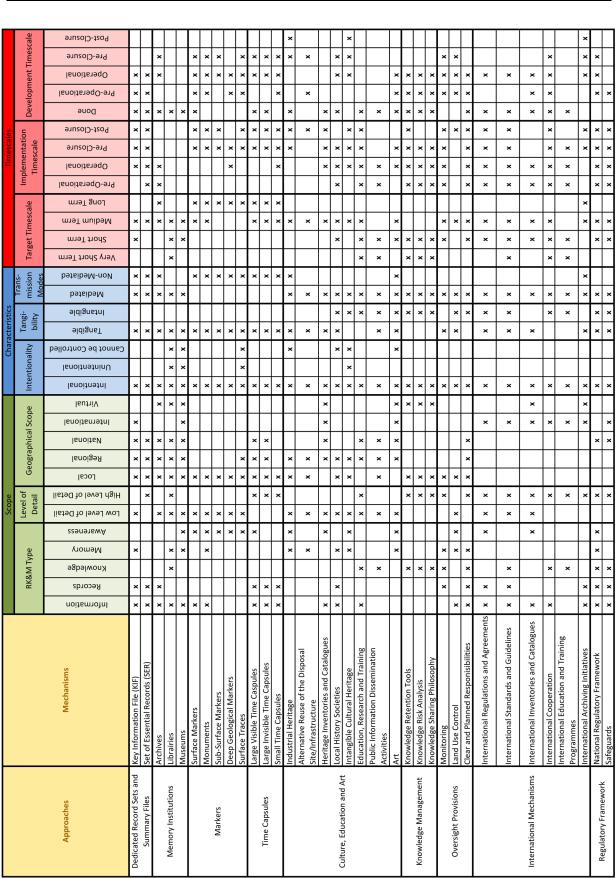
2.3.Mechanisms overview table
This annex provides an overview table of the way the different RK&M preservation mechanisms vary with regard to their key characteristics, based on the filled out tick boxes of the mechanism description sheets (Annex 2.2). It aids to visualise diversity among the key characteristics, which is fundamental to the idea of a systemic strategy.
This table can also be used as a practical tool to compare and combine approaches and mechanisms in such a way that, in order to achieve robustness, different mechanisms of a variety of approaches are selected (rows) that cover a variety of key characteristics (columns). The table can be downloaded in Excel format from the RK&M initiative website at www.oecdnea.org/rwm/rkm.
The limitations of the overview table are the following. The table only includes mechanism description components that were elaborated by using tick boxes in the mechanism description sheets (Annex 2.2). Establishing diversity with regard to involved actors and comparing main strengths/benefits and issues/challenges is thus a task for which the table does not offer visual assistance. The table also does not display the inter-connectedness among the mechanisms, which is the second fundamental of a systemic strategy.
PRESERVATION OF RK&M ACROSS GENERATIONS: FINAL REPORT OF THE RK&M INITIATIVE, NEA No. 7421, © OECD 2019 |
175 |
DESCRIPTIONS OF RK&M PRESERVATION MECHANISMS
176 |
PRESERVATION OF RK&M ACROSS GENERATIONS: FINAL REPORT OF THE RK&M INITIATIVE, NEA No. 7421, © OECD 2019 |
