
Eng / Emergency situation
.pdf
PATHOGENESIS OF INFECTIOUS-TOXIC SHOCK AT
THE LEVEL OF ORGAN SYSTEMS
relative and absolute hypovolemia
development of acute renal failure
"shock lung"

EARLY PHASE OF INFECTIOUS-TOXIC SHOCK ( 1st DEGREE)
arterial hypotension may be absent
tachycardia, decreased pulse pressure
shock index up to 0.7-1.0 (ratio of heart rate to maximum blood pressure, normally it is 0.6, with shock 1.2-1.5 or more)
signs of intoxication: muscle pain, abdominal pain of uncertain localization, severe headache
CNS disorders: depression, anxiety, agitation, hyperreflexia
from the urinary system: a decrease in the rate of urination less than 25 ml / h

Second degree (phase of severe shock, subcompensated ITSH)
BP drops to 90 mm Hg. and below
Tachycardia over 100 beats per minute
Muffled heart sounds, ECG - signs of diffuse myocardial hypoxia
Shock index up to 1.0-1.4
Decreased T to subnormal numbers
Lethargy and apathy
Anuria (urine output less than 1.0 ml/hour)
Increasing shortness of breath, moist rales in the lungs
The skin is cold, moist, acrocyanosis.
The gradient of skin and rectal T -8-15° is growing - an indicator of the centralization of blood circulation
Development of DIC

Third degree (decompensated TSS)
Critical drop in blood pressure below 50 mm Hg. Art.
Tachycardia, thready pulse
Shock index 1.5 or more
Increasing acrocyanosis
cold skin, cyanotic spots on the trunk and extremities
MON: shortness of breath, oliguria, anuria, sometimes jaundice
Impairment of consciousness up to coma
body temperature below 36˚С
Involuntary defecation

Laboratory diagnostics of TSS
Definition of KOS
Blood gas status
electrolyte balance
Hematocrit
Hemoglobin
Leukogram
Blood glucose, urea, creatinine, ALT, AST
Hemostasis status (platelets, clotting and bleeding time, coagulogram)

In the early phase of TSS develop:
Respiratory alkalosis
metabolic acidosis
Accumulation of lactic acid and increased lactate/pyruvate ratio
Reduced clotting time

In the phase of severe shock:
Consumption coagulopathy is on the rise
Thrombocytopenia
The level of fibrinogen decreases to 1g/l and the activity of 2,5,8 and 12 factors
Fibrin monomers and fibrinogen breakdown products appear
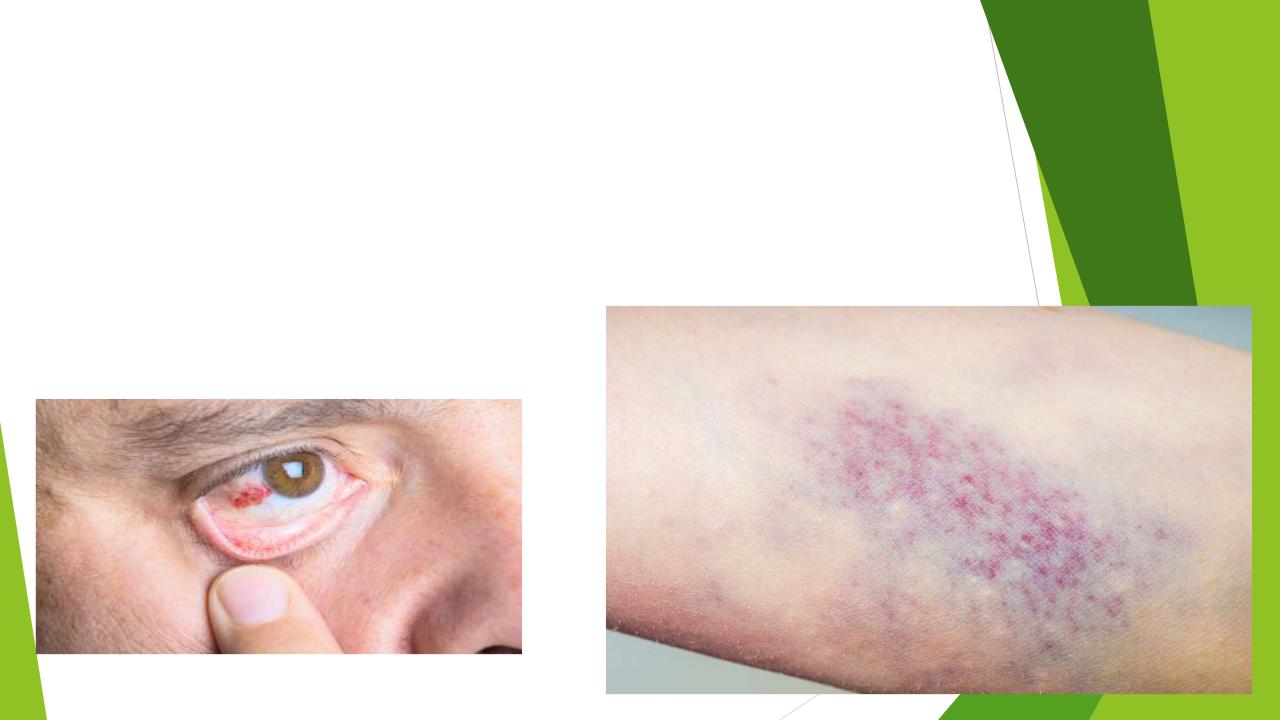
Thrombohemorrhagic syndrome
disseminated intravascular coagulation (DIC)
consumption coagulopathy

Violation of the hemostasis system
at first, the process of hypercoagulability predominates (an increase in the content of fibrinogen and other coagulation factors),
then there is a loss of fibrin in small vessels with the formation of blood clots.
As a result of thrombosis of large vessels, gangrene of the fingers of the extremities may develop.
The subsequent decrease in the content of fibrinogen in the blood (consumption coagulopathy) often causes massive bleeding and hemorrhages in various tissues and organs.

Classification DIC syndrome
There are 3 main types: Acute DIC syndrome. Subacute DIC syndrome. Chronic DIC syndrome.
