
диссертации / 40
.pdf101
ПРАКТИЧЕСКИЕ РЕКОМЕНДАЦИИ
-При подозрении у новорожденного синдрома Дауна диагноз верифицируется путем исследования кариотипа с последующей консультацией медицинского генетика. Заподозрить синдром у глубоко недоношенного ребенка или у ребенка со «стертым» фенотипом может помочь анализ его дерматоглифики.
- Оценку антропометрических показателей целесообразно проводить ежемесячно в соответствии с предложенными нормограммами,
представленными в приложении. Адекватность питания необходимо регулярно определять по объему, основным нутриентам и калориям.
Предпочтительно грудное вскармливание детей до года.
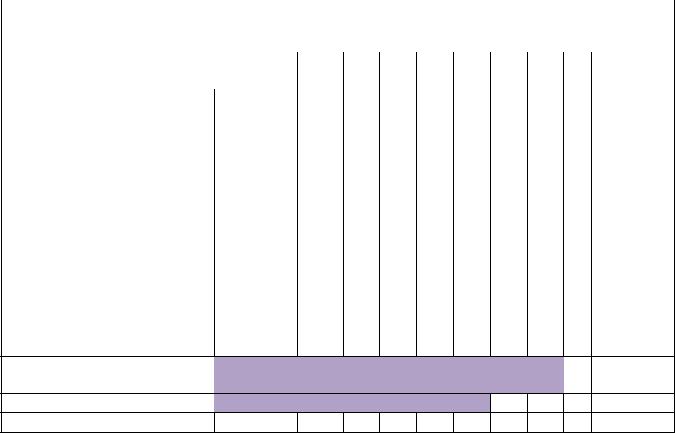
Предложен следующий график обследования детей (табл.12):
В возрасте до 1 месяца провести:
-Клинический анализ крови (для исключения полицитемии,
тромбоцитопении и миелопролиферативных изменений) и анализ мочи.
-ЭКГ, ЭХОКГ. При выявлении ВПС показана консультация кардиохирурга.
-Определить уровень тиреоидных гормонов в крови.
-Ультразвуковое исследования брюшной полости и почек для исключения врожденных аномалий внутренних органов.
-Ультразвуковое исследование тазобедренных суставов.
-Нейросонографичексое исследование.
-Консультация специалистов: офтальмолога, невролога, ортопеда, а
при необходимости и других специалистов.
Осуществлять регулярное (не реже 1 раза в год) наблюдение окулиста,
невролога, ортопеда, ЛОР, генетика и других специалистов по показаниям.
-Исследовать слух в возрасте 6-12 месяцев, в последующем – ежегодно,
при необходимости - чаще.
102
-Скрининг целиакии с определением в периферической крови уровня специфического Ig A к эндомизию, тканевой трансглютаминазе и общего уровня Ig A показан всем детям с СД в возрасте 2 лет*.
-Полисомнография проводится по показаниям с 3-4-х лет**.
-Всем детям с СД в возрасте 4-х лет показано рентгенологическое исследование шейного отдела позвоночника для исключения атлантоаксиальной нестабильности.
-Электроэнцефалография проводится по показаниям и/или перед проведением анестезиологического пособия.
Таблица 12.
График специализированного обследования детей с синдромом Дауна.
|
Возраст в |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Исследование |
годах |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
0 до 1 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
месяца |
6м |
1 1,5 |
2 2,5 |
3 3,5 4 от 5 до8 |
|||||||
кариотип/генетик |
кариотип |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Кардиология: ЭКГ, ЭхоКГ |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Аудиологическое |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
исследование |
скрининг |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Тиреоидные гормоны крови |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
НСГ |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Невролог |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Окулист |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Ортопед |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
ЛОР |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
УЗИ т/бедренных суставов |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Стоматолог |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Скрининг целиакии* |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Рентегограмма шеи (нестабильность)
Полисомнография**
Развитие, ранняя помощь
Инструкция: В пустые клетки вписывается дата исследования.
103
ЛИТЕРАТУРА
1.Гузеев Г. Г. Эффективность генетического консультирования.-
Москва. 2005.- С. 22–32.
2.Задко Т. И. Синдром Дауна в сочетании с полной формой атриовентрикулярной коммуникации: актуальность, диагностика, сопутствующая патология, анатомия, особенности естественного течения, результаты хирургического лечения // Детские болезни сердца и сосудов. – 2005. – № 6. – С. 10–18.
3.Кеннет Л. Джонс. Наследственные синдромы по Дэвиду Смиту. Атлаc-справочник. Перевод с английского. - М., «Практика», 2011.-
С. 855-858.
4.Котлукова Н.П., О. И. Артеменко, М. П. Давыдова, О. Н. Ильина, Л. А. Курбатова Роль окислительного стресса и антиоксидантной системы в патогенезе врожденных пороков сердца / Н. П. // Педиатрия. – 2009. – Т. 87, № 1. – С. 24–28.
5.Лаутеслагер П. Двигательное развитие детей раннего возраста с синдромом Дауна. -М. :Монолит. 2003.- 356 с.
6.Современные подходы к болезни Дауна /Под ред. Д.Лейна, Б.Стрэтфорда: Перевод с англ. /Под редакцией М.Г.Блюминой.-
М.:Педагогика, 1991. – 336с.:ил.
7.Чубарова А. И. Лактулоза в диагностике и лечении функциональных запоров у детей раннего возраста // Вопросы современной педиатрии.
- 2004. - Т. 3, № 4.- С. 100–104.
8.Шабалов Н.П. Педиатрия.- Санкт-Петербург: СпецЛит, 2003.-С. 3757.
9.American Academy of Pediatrics. Committee on Sports Medicine and
Fitness . Atlantoaxial |
instability |
in |
Down |
syndrome: |
subject |
review. Pediatrics. - 1995.-р.151–153
10.Annerén G., Tuvemo T, Carlsson-Skwirut C. et al. Growth hormone
104
treatment in young children with Down’s syndrome: effects on growth and psychomotor development// Arch. Dis. Child.- 1999 -80.-р. 334-338.
11.Antonarakis S. E. Human chromosome 21: genome mapping and exploration circa 1993// Trends Genet. 1993.-( 9) - р.142-148,
12.Barnet A.B., Weiss I.P., Aysun S., Bernardo E.B., Saumweger R.W., Hines A . Hearing loss in infants with Down's syndrome. Paediatric Research.-1988.- р. 289.
13.Barreca A., Rasore-Quartino A., Acutis M.S.:Assessment of growth hormone insulin like growth factor-I axis in Downs syndrome// Journal of Endocrinological Investigation. -1994 -(17)- р. 431-436.
14.Bennet G.C., Rang M., Roye D.P., Aprin H. Dislocation of the hip in trisomy 21// J Bone Joint Surg Br. -1982-64(3) – р.289-294.
15.Bennett K.E., Haggard M.P. Behaviour and cognitive outcomes from middle ear disease // Arch.Dis.Child. -1999.- (80)- р.28-35.
16.Bloemers B.L.P., van Furth A.M., Weijerman M.E. et al Highincidence of recurrent wheeze in children with Down syndrome with and without previous respiratory syncytial virus lower respiratory tract infection// PediatrInfect Dis J.-2012.- (29)- р.39–42
17.Bower C.M., Richmond D. Tonsillectomy and adenoidectomy in patients with Down syndrome// International journal of pediatric otorhinolaryngology. – 1995 - 33(2) – р.141-148.
18.Caird M.S., Wills B.P., Dormans J.P. Down syndrome in children: the role of the orthopaedic surgeon// J Am Acad Orthop Surg -2006.–(14) - р.610– 619
19.Caputo A.R., Wagner R.S., Reynolds D.R., Guo S., Goel A.K.Down syndrome. Clinical reviewof ocular features // Clinical Paediatrics. -1989. -28- р.355-358.
20.Casey A.T., O’Brien M., Kumar V., Hayward R.D., Crockard H.A. Don't twist my child’s head off: iatrogenic cervical dislocation. //BMJ.- 1995- р.
105
1212-1213.
21.Catalano R.A. Down syndrome // Survey of Ophthalmology.- 1990.- (34) -
р.385-398
22.Cerqueira R.M., Rocha C.M., Fernandes C.D., Correia M.R. Celiac disease in Portuguese children and adults with Down syndrome// Eur J Gastroenterol Hepatol.- 2010 - 22(7) - р. 868-871.
23.Champion M.D., Hawley R.S. Playing for half the deck: the molecular biology of meiosis// Nat Cell Biol. -2002.- 4- р.50–56.
24.Chumlea W.C., Cronk C.E. Overweight among children with Trisomy 21//J. Ment Defic Res.- 1981 – 254-259.
25.Cremers M.J.G., Bol E., de Roos .F, van Gijn J. Risk of sports activities in children with Down's syndrome and atlantoaxial instability// Lancet. - 1993.-342-р.511-514.
26.Cremers M.J.G., Ramos L., Bol E., van. Gijn J. Radiological assessment of the atlantoaxial distance in Down's syndrome// Archives of Disease in Childhood.- 1993.- 69- р.347-350.
27.Cremers M.J.G., van der Tweel I., Boersma B., et al. Growth curves of Dutch children with Down’s syndrome// J Intellect Dis Res -1996.-40-
р.412–20.
28.Cronk C., Crocker A.C., Pueschel S.M. et al:Growth charts for children with Down syndrome: 1 month to 18 years of age// Paediatrics.- 1988 – 81- р.102-110.
29.Cullen S.,Ward O.C., Duff D., Denham B. Congenital heart disease in Down's syndrome:Is there a need for a formal screening programme? // Ir.J.Med.SC.- 1990.- р. 159-168.
30.Cunnif C., Frias J.L., Kaye C. et al. Health supervision for children with Down syndrome. American Academy of Pediatrics. Pediatrics.-2001. - 107:442–449.
31.Cunningham C., McArthur K. Hearing loss and treatment in young
106
Down’s syndrome children// Child: care health and development.- 1981- 7- р.357-374.
32.Dahle A.J., McCollister F.P. Hearing and otologic disorders in children with Down syndrome //American Journal of Mental Deficiency.-1986.- 90
(6)- р. 636-642.
33.Davidson R.G. Atlantoaxial Instability in Individuals With Down Syndrome: A Fresh Look at the Evidence // Pediatrics.- 1988.- 81- р. 857865.
34.Davies B. Auditory Disorders in Down’s Syndrome// Scan Audiol Suppl - 1988.-30- р.65-68.
35.de Miguel-Diez J., Villa-Asensi J.R., Alvarez-Sala J.L. Prevalence of sleep-disordered breathing in children with Down syndrome// Sleep. - 200326(8) – р.1006-1009.
36.Delabar, J. M., Theophile, D., Rahmani, Z., Chettouh, Z., Blouin, J. L., Prieur, M., Noel, B., Sinet, P. M. Molecular mapping of twenty-four features of Down syndrome on chromosome 21//Europ. J. Hum. Genet. – 1993-1- р.114-124,.
37.Delhanty J.D. Mechanisms of aneuploidy induction in human oogenesis and early embryogenesis// Cytogenet Genome Res.- 2005111- р.237– 244.
38.Dey A., Bhowmik K., Chatterjee A., Chakrabarty P.B., Sinha S., Mukhopadhyay K. Down Syndrome Related Muscle Hypotonia: Association with COL6A3 Functional SNP rs2270669// Frontiers in genetics. -2013 - р.4:57
39.Diamond L.S., Lynne D., Sigman B. Orthopedic disorders in patients with Down's syndrome. The orthopaedic clinics of North America.-1981- 12(1)
–р. 57-71.
40.Down J. L. H. Observations on an ethnic classification of idiots. London Hosp. Clin. Lect. Rep. 3.- 1866 – р.259–262.
107
41.Karlsson B J. Gustafsson, G. Hedov, S-A Ivarsson, G. Annerén.Thyroid dysfunction in Down’s syndrome: relation to age and thyroid autoimmunity//Arch Dis Child199879- р.242–245.
42.Fawzi Elhami Ali, Mahmoud A. Al-Bustan,Waleed A. Al-Busairi, Fatema A. Al-MullaEmad Y. Esbaita. Cervical spine abnormalities associated with Down syndrome. International Orthopaedics. -2006 - 30(4)- р. 284–289.
43.Fenton T. A. New growth chart for preterm babies: Babson and Benda's chart updated with recent data and a new format //BMC Pediatrics.- 2003.- р. 3-13.
44.Fernandes A. et al. Characterization of the somatic evolution of Portuguese children with Trisomy 21Preliminary results// Down syndrome Reseach and Practice.- 2001.- 6(3)-р. 134-138.
45.Ferreira C.T., Leite J.C., Taniguchi A., Vieira S.M., Pereira-Lima J., da Silveira T.R. Immunogenicity and safety of an inactivated hepatitis A vaccine in children with Down syndrome// J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr. - 2004 .- 39(4).-р. 337-40.
46.Fogl T. Using dermstoglyphics from Doun syndrome and class populations to study the genetics of complex trait. -2004-р. 129-150.
47.Fong C. T., Brodeur G. M. Down's syndrome and leukemia: epidemiology, genetics, cytogenetics and mechanisms of leukemogenesis// Cancer Genet. Cytogenet. -1987.-28- р.55-76.
48.Fort P., Lifshitz F., Bellisario R., et al . Abnormalities of thyroid function in infants with Down syndrome// J Pediatr.-1984.- 104- р. 545-549.
49.Freeman S.B., Torfs C.A., Romitti M.H. et al. Congenital gastrointestinal defects in Down syndrome: a report from the Atlanta and National Down Syndrome Projects// Clin Genet.-2009.- 75- р.180–184.
50.Frid C., Drott P., Lundell B., Rasmussen F., Anneren G . Mortality in
Down’s syndrome in relation to congenital malformations.// J.Int.Disab.Res.- 199943(3)- р.234-241.
108
51.Fudge J.C. Jr, Li S., Jaggers J., O'Brien S.M., Peterson E.D., Jacobs J.P., Welke K.F., Jacobs M.L., Li J.S., Pasquali S.K. Congenital heart surgery outcomes in Down syndrome: analysis of a national clinical database// Pediatrics. 2010.-126(2)р.315-322.
52.Fuentes, J. J., Pritchard M. A., Planas, A. M., Bosch A., Ferrer I., Estivill X. A new human gene from the Down syndrome critical region encodes a proline-rich protein highly expressed in fetal brain and heart// Hum. Molec. Genet.-1995.- 4 –р. 1935-1944.
53.George E.K., Mearin M.L., Bouquet J., von Blomberg B.M.E. et al . High frequency of coeliac// Arch Dis Child.-1996-р.135-142.
54.Gibson P.A., Newton R.W., Selby K. et al. Longitudinal study of thyroid function in Down’s syndrome in the first two decades// Arch Dis Child.- 2005.- 9- р.575–578.
55.Hankinson T.C., Anderson R.C. Craniovertebral junctionabnormalities in Down syndrome// Neurosurgery.-2010.- 66-р.32–38.
56.Hassold T, Hunt P. To err (meiotically) is human: the genesis of human aneuploidy //Nat Rev Genet – 2001.-2-р.280–291.
57.Henry E., Walker D., Wiedmeier S.E., Christensen R.D. Hematological abnormalities during the first week of life among neonates with Down syndrome: data from a multihospital healthcare system// Am J Med Genet
.- 2007.- 143(1)- р.42-50.
58.Hestnes A., Sands T., Fostad K. Ocular findings in Down syndrome// Journal of Mental Deficiency.-1991.- 35- р.194-203.
59.Hiles D.A., Hoyme S.H., McFarlane F. Down’s syndrome and strabismus//
American Orthoptic Journal. – 1974-24-р.63-68.
60.Hook E. G. Epidemiology of Down syndrome.In: Pueschel, S. M.; Rynders, J. E. : Down Syndrome. Advances in Biomedicine and the Behavioral Sciences. Cambridge: Ware Press (pub.)- 1982.- P. 11.
61.Irving C., Basu A., Richmond S. et al. Twenty-year trends in prevalence
109
and survival of Down syndrome// Eur J Hum Genet.- 2008.-16- р.1336–
1340.
62.Jacobs I.N., Gray R.F., Todd N.W. Upper airway obstruction in children with Down syndrome// Archives of otolaryngologyhead and neck surgery. – 1996.- 122(9) – р.45-50.
63.Jannot A.S., Pelet A., Henrion-Caude A., Chaoui A., Masse-Morel M., Arnold S., Sanlaville D., Ceccherini I., Borrego S., Hofstra R.M., Munnich A., Bondurand N., Chakravarti A., Clerget-Darpoux F., Amiel J., Lyonnet S. Chromosome 21 Scan in Down Syndrome Reveals DSCAM as a Predisposing Locus in Hirschsprung Disease// PLoS One. [электронный ресурс PubMed] -2013.- 6;8(5):e62519 doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0062519.
64.Jansson J., Johansson C. Down syndrome and celiac disease// J.Ped. Gastroenterology-1995.- р.556-559.
65.John J.E., Cook A.R. Hyperthyroidism in patients with Mongolism// J Clin Endocrinol. -1962.-22- р.665-668.
66.Kaplan D. J., Fleshman J.K., Bender T.R., Baum C., Clark P.S. Long term effects of otitismedia. A ten year cohort of Alaskan Eskimo Children// Pediatrics.- 1973.-52-р.577-585.
67.Karlsson B., Gustafsson J., Hedov G., Ivarsson S.A, Anneren G .Thyroid dysfunction in Down’s syndrome: relation to age and thyroid autoimmunity.// Arch. Dis Childhood.-1998.-79-р. 242-245.
68.Keiser H., Montague J., Wold D., Maune S., Pattison D. Hearing loss of Down's syndrome adults.// Amer.J.Ment. Deficiency. -1981-85-р.467-472.
69.Korenberg J. R., Chen X.-N., Schipper R., Sun Z., Gonsky R., Gerwehr S., Carpenter N., Daumer C., Dignan P., Disteche C., Graham J. M., Jr. Hugdins, L. McGillivray, B.Miyazaki, K. Ogasawara, N. Park J. P., Pagon R., Pueschel S., Sack G., Say B., Schuffenhauer S., Soukup S., Yamanaka T. Down syndrome phenotypes: the consequences of chromosomal
110
imbalance// Proc. Nat. Acad. Sci. – 1994-91 – р. 4997-5001. 70.Korenberg J., Kawashima H., Pulst S., Ikeuchi T., Ogasawara N.,
Yamamoto K., Schonberg S., Kojis T., Allen L., Magenis E., Ikawa H., Taniguchi N., Epstein C. Molecular definition of the region of chromosome 21 that causes features of the Down syndrome phenotype// Am. J. Hum. Genet. – 1990.-47- р.236-246.
71.Kowalczyk K., Pukajło K., Malczewska A., Król-Chwastek A., Barg E.L.
Тhyroxine therapy and growth processes in children with Down syndrome// Advances in clinical and experimental medicin: official organ Wroclaw Medical University. -2013. - 22(1) –р. 85-92.
72.Kucik J.E., Shin M., Siffel C., Marengo L., Correa A. Congenital Anomaly Multistate Prevalence and Survival Collaborative.Trends in survival among children with Down syndrome in 10 regions of the United States// Pediatrics. – 2013.- 131(1)- р27-36.
73.Kupferman J.C., Druschel C.M., Kupchik G.S. Increased prevalence of renal urinary tract anomalies in children with Down syndrome// Pediatrics. -2009.- 124-р.615–621.
74.Laughlin G.M.,Wynne J., Victoria B.E . Sleep apnea as a possible cause of pulmonary hypertension in Down syndrome.// Journal of Pediatrics.-1981- 98-р.435-437
75.Lemperle G &Radu D. Facial plastic surgery in children with Down's syndrome// Plastic and ReconstrSurg. – 1980.-66- р.337-342.
76.Libb JW, et al . Hearing disorder and cognitive function of individuals with Down syndrome.// Am. J of Mental Deficiency.-1985.-90-р. 353-356.
77.Licastro F., Chiricolo M., Mocchegiani E., Fabris N., Zannoti M., Beltrandi E., Mancini R., Parente R., Arena G., Masi M. Oral zinc supplementation in Down's syndrome subjects decreased infections and normalized some humoral and cellular immune parameters// J Intellect Disabil Res. - 1994 -38 ( Pt 2)-р.149-162.
