
- •Table of Contents
- •Copyright
- •Contributors
- •How to Use this Study Guide
- •Questions
- •Answers
- •Questions
- •Answers
- •Questions
- •Answers
- •4: Outcomes Research
- •Questions
- •Answers
- •5: Core Principles of Perioperative Care
- •Questions
- •Answers
- •Questions
- •Answers
- •7: Principles of Urologic Endoscopy
- •Questions
- •Answers
- •8: Percutaneous Approaches to the Upper Urinary Tract Collecting System
- •Questions
- •Answers
- •Questions
- •Answers
- •Questions
- •Answers
- •Questions
- •Answers
- •12: Infections of the Urinary Tract
- •Questions
- •Answers
- •Questions
- •Answers
- •Questions
- •Answers
- •15: Sexually Transmitted Diseases
- •Questions
- •Answers
- •Questions
- •Answers
- •Questions
- •Answers
- •Questions
- •Answers
- •Questions
- •Answers
- •20: Principles of Tissue Engineering
- •Questions
- •Answers
- •Questions
- •Answers
- •22: Male Reproductive Physiology
- •Questions
- •Answers
- •Questions
- •Answers
- •24: Male Infertility
- •Questions
- •Answers
- •Questions
- •Answers
- •Questions
- •Answers
- •Questions
- •Answers
- •28: Priapism
- •Questions
- •Answers
- •Questions
- •Answers
- •30: Surgery for Erectile Dysfunction
- •Questions
- •Answers
- •Questions
- •Answers
- •Questions
- •Answers
- •Questions
- •Answers
- •34: Neoplasms of the Testis
- •Questions
- •Answers
- •35: Surgery of Testicular Tumors
- •Questions
- •Answers
- •36: Laparoscopic and Robotic-Assisted Retroperitoneal Lymphadenectomy for Testicular Tumors
- •Questions
- •Answers
- •37: Tumors of the Penis
- •Questions
- •Answers
- •38: Tumors of the Urethra
- •Questions
- •Answers
- •39: Inguinal Node Dissection
- •Questions
- •Answers
- •40: Surgery of the Penis and Urethra
- •Questions
- •Answers
- •Questions
- •Answers
- •Questions
- •Answers
- •Questions
- •Answers
- •Questions
- •Answers
- •Questions
- •Answers
- •Questions
- •Answers
- •47: Renal Transplantation
- •Questions
- •Answers
- •Questions
- •Answers
- •Questions
- •Answers
- •50: Upper Urinary Tract Trauma
- •Questions
- •Answers
- •Questions
- •Answers
- •Questions
- •Answers
- •53: Strategies for Nonmedical Management of Upper Urinary Tract Calculi
- •Questions
- •Answers
- •54: Surgical Management for Upper Urinary Tract Calculi
- •Questions
- •Answers
- •55: Lower Urinary Tract Calculi
- •Questions
- •Answers
- •56: Benign Renal Tumors
- •Questions
- •Answers
- •57: Malignant Renal Tumors
- •Questions
- •Answers
- •Questions
- •Answers
- •59: Retroperitoneal Tumors
- •Questions
- •Answers
- •60: Open Surgery of the Kidney
- •Questions
- •Answers
- •Questions
- •Answers
- •62: Nonsurgical Focal Therapy for Renal Tumors
- •Questions
- •Answers
- •Questions
- •Answers
- •Questions
- •Answers
- •Questions
- •Answers
- •66: Surgery of the Adrenal Glands
- •Questions
- •Answers
- •Questions
- •Answers
- •Questions
- •Answers
- •Questions
- •Answers
- •Questions
- •Answers
- •71: Evaluation and Management of Women with Urinary Incontinence and Pelvic Prolapse
- •Questions
- •Answers
- •72: Evaluation and Management of Men with Urinary Incontinence
- •Questions
- •Answers
- •Questions
- •Answers
- •Questions
- •Answers
- •Questions
- •Answers
- •76: Overactive Bladder
- •Questions
- •Answers
- •77: Underactive Detrusor
- •Questions
- •Answers
- •78: Nocturia
- •Questions
- •Answers
- •Questions
- •Answers
- •Questions
- •Answers
- •Questions
- •Answers
- •82: Retropubic Suspension Surgery for Incontinence in Women
- •Questions
- •Answers
- •83: Vaginal and Abdominal Reconstructive Surgery for Pelvic Organ Prolapse
- •Questions
- •Answers
- •Questions
- •Answers
- •85: Complications Related to the Use of Mesh and Their Repair
- •Questions
- •Answers
- •86: Injection Therapy for Urinary Incontinence
- •Questions
- •Answers
- •87: Additional Therapies for Storage and Emptying Failure
- •Questions
- •Answers
- •88: Aging and Geriatric Urology
- •Questions
- •Answers
- •89: Urinary Tract Fistulae
- •Questions
- •Answers
- •Questions
- •Answers
- •Questions
- •Answers
- •92: Tumors of the Bladder
- •Questions
- •Answers
- •Questions
- •Answers
- •Questions
- •Answers
- •95: Transurethral and Open Surgery for Bladder Cancer
- •Questions
- •Answers
- •Questions
- •Answers
- •Questions
- •Answers
- •Questions
- •Answers
- •99: Orthotopic Urinary Diversion
- •Questions
- •Answers
- •Questions
- •Answers
- •Questions
- •Answers
- •Questions
- •Answers
- •Questions
- •Answers
- •Questions
- •Answers
- •Questions
- •Answers
- •Answers
- •Questions
- •Answers
- •108: Prostate Cancer Tumor Markers
- •Questions
- •Answers
- •Questions
- •110: Pathology of Prostatic Neoplasia
- •Questions
- •Answers
- •Questions
- •Answers
- •Questions
- •Answers
- •Questions
- •Answers
- •114: Open Radical Prostatectomy
- •Questions
- •Answers
- •Questions
- •Answers
- •116: Radiation Therapy for Prostate Cancer
- •Questions
- •Answers
- •117: Focal Therapy for Prostate Cancer
- •Questions
- •Answers
- •Questions
- •Answers
- •119: Management of Biomedical Recurrence Following Definitive Therapy for Prostate Cancer
- •Questions
- •Answers
- •120: Hormone Therapy for Prostate Cancer
- •Questions
- •Answers
- •Questions
- •Answers
- •Questions
- •Answers
- •Questions
- •Answers
- •124: Perinatal Urology
- •Questions
- •Answers
- •Questions
- •Answers
- •126: Pediatric Urogenital Imaging
- •Questions
- •Answers
- •Questions
- •Answers
- •Questions
- •Answers
- •Questions
- •Answers
- •Questions
- •Answers
- •Questions
- •Answers
- •Questions
- •Answers
- •133: Surgery of the Ureter in Children
- •Questions
- •Answers
- •Questions
- •Answers
- •Questions
- •Answers
- •Questions
- •Answers
- •137: Vesicoureteral Reflux
- •Questions
- •Answers
- •138: Bladder Anomalies in Children
- •Questions
- •Answers
- •139: Exstrophy-Epispadias Complex
- •Questions
- •Answers
- •140: Prune-Belly Syndrome
- •Questions
- •Answers
- •Questions
- •Answers
- •Questions
- •Answers
- •Questions
- •Answers
- •144: Management of Defecation Disorders
- •Questions
- •Answers
- •Questions
- •Answers
- •Questions
- •Answers
- •147: Hypospadias
- •Questions
- •Answers
- •Questions
- •Answers
- •Questions
- •Answers
- •Questions
- •Answers
- •Questions
- •Answers
- •152: Adolescent and Transitional Urology
- •Questions
- •Answers
- •Questions
- •Answers
- •154: Pediatric Genitourinary Trauma
- •Answers
- •Questions
- •Answers
- •Questions
- •Answers

48
Pathophysiology of Urinary Tract
Obstruction
Kirstan K. Meldrum
Questions
1.Which of the following histopathologic findings has been shown to have a negative impact on recovery of renal function at the time of pyeloplasty?
a.Increased collagen deposition in the renal parenchyma
b.Extensive glomerulosclerosis
c.Mesangial cell proliferation
d.Increased collagen deposition and extensive glomerulosclerosis
e.Increased matrix metalloproteinase-9 (MMP-9), interleukin-18 (IL-18), and transforming growth factor-β (TGF-β)
2.Which of the following statements correctly defines the ability of magnetic resonance urography (MRU) to assess renal function?
a.MRU with gadopentetate dimeglumine contrast accurately estimates global renal function.
b.MRU with gadopentetate dimeglumine contrast accurately estimates differential renal function.
c.MRU with contrast is not indicated to assess renal function in patients with renal insufficiency.
d.MRU correlates well with renal scintigraphy.
e.All of the above.
3.There is a low risk for development of nephrogenic systemic fibrosis after contrast MRI in patients with:
a.obstructive uropathy.
b.normal renal function.
c.diabetic nephropathy.
d.ischemic nephropathy.
e.none of the above.
4.Internalized ureteral stent failure is more common in patients with:
a.advanced cancer.
b.normal renal function.
c.solitary kidneys.
d.horseshoe kidneys.
e.duplicated collecting systems.
5.The fibroblasts that accumulate in the renal interstitium in response to obstruction are derived from which sources?
a.Resident fibroblasts within the interstitium
b.Bone marrow
c.Transformed renal tubular epithelial cells
d.None of the above
e.All of the above
6.Which of these predict poor functional recovery after relief of ureteral obstruction?
a.Absence of pyelolymphatic backflow
b.Good compliance of the collecting system
c.Presence of minimal obstruction
d.Normal renal cortical thickness
e.Absence of infection
7.Ureteral stenting is preferred versus percutaneous nephrostomy in patients with:
a.advanced cervical cancer.
b.uncorrected coagulopathy.
c.ureteral stone with suspected sepsis.
d.hydronephrosis of pregnancy.
e.all of the above.
8.Postobstructive diuresis is:
a.generally prolonged.
b.usually self-limited.
c.not associated with hypernatremia.
d.common with unilateral obstruction in a patient with two kidneys.
e.associated with concentrated urine initially.
9.The release of tumor necrosis factor-α (TNF-α) in obstructive uropathy is stimulated by:
a.angiotensin II.
b.cysteinyl aspartate-specific proteinases.
c.cytochrome c.
d.tissue inhibitors of metalloproteinases (TIMPs).
e.all of the above.
.Which of the following characterizes obstructive nephropathy when compared with hydronephrosis?
a.Bilateral ureteral dilation
b.Unilateral ureteral dilation
c.Renal function impairment
d.Calyceal blunting
e.None of the above
.Which of these urinary changes occur after relief of bilateral ureteral obstruction?
a.Increased sodium excretion
b.Water retention
c.Decreased potassium excretion
d.Decreased magnesium excretion
e.None of the above
.Which of the following is thought to play a role in postobstructive diuresis after release of bilateral ureteral obstruction?
a.Increased renal aquaporin-2 water channels
b.Increased renal aquaporin-3 water channels
c.Increased antidiuretic hormone (ADH)
d.Increased atrial natriuretic peptide (ANP)
e.Increased aldosterone
.After 8 hours of unilateral ureteral obstruction, which of the following occurs in the obstructed kidney?
a.Increased renal blood flow
b.Increased glomerular filtration
c.Shift of blood flow from the inner to the outer cortex
d.Decreased ureteral pressure
e.None of the above
.Atrial natriuretic peptide induces which of the following?
a.Decrease in urinary sodium excretion
b.Increase in afferent arteriolar dilation
c.Increase in efferent arteriolar dilation
d.Decrease in glomerular filtration rate (GFR)
e. Increase in renin production
.Which of the following occurs after bilateral ureteral obstruction?
a.Shift of blood flow to the outer renal cortex
b.Decrease in atrial natriuretic peptide
c.Decrease in collecting system pressure during the first day
d.Increase in renal plasma flow at 8 hours
e.None of the above
.Which of the following may promote tubular interstitial fibrosis in the obstructed kidney?
a.Increase in renal metalloproteinase levels
b.Increase in expression of transforming growth factor-β
c.Administration of enalapril
d.Administration of losartan
e.Decrease in inflammatory cell infiltration
.A difference between unilateral ureteral obstruction (UUO) and bilateral ureteral obstruction (BUO) is that:
a.fractional excretion of sodium after relief of obstruction is greater in BUO.
b.atrial natriuretic peptide levels are higher in UUO.
c.risk of postobstructive diuresis is less with BUO.
d.urinary pH is higher in UUO.
e.new-onset hypertension is more common with UUO.
.What is one of the earliest pathologic findings associated with urinary tract obstruction?
a.Glomerulosclerosis
b.Tubulointerstitial fibrosis
c.Inflammatory cell infiltration
d.Apoptosis
e.Parenchymal thinning
.Which of the following statements is TRUE of compensatory renal growth?
a.Glomerular number increases.
b.Insulin-like growth factor-1 is inhibitory.
c.It increases with age.
d.It is primarily related to cellular hypertrophy rather than hyperplasia.
e.It is more common with partial obstruction.
.The chance for renal recovery after ureteral obstruction is most influenced by: a. early relief of obstruction.
b.presence of extrarenal pelvis.
c.presence of a solitary kidney.
d.uninfected urine.
e.normal blood pressure.
.Which of the following is expected in a kidney that has been obstructed for 1 month?
a.Increased renal pelvic pressure
b.Downregulation in sodium transporters
c.Reduced urinary pH
d.Reduced tubulointerstitial fibrosis
e.Increased aquaporin-2 water channels
.Hydronephrosis is most suggestive of significant obstruction in the presence of:
a.an elevated resistive index.
b.an increase in ureteral jet frequency.
c.a T1/2 of 15 minutes after Lasix administration on a MAG3 renogram.
d.a pelvic calcification on noncontrast computed tomography (CT).
e.a dramatic delay in radiotracer uptake on a MAG3 Lasix renogram
.A reduction in concentrating ability of the obstructed kidney is due to:
a.decreased ADH expression.
b.maintenance of a medullary hypertonicity and reduced GFR.
c.increased renal aquaproin-1 water channels.
d.decreased renal aquaporin-2 water channels.
e.urea backflux from the inner medullary collecting duct.
.A persistent concentrating defect after relief of BUO is primarily due to:
a.continued excessive secretion of atrial natriuretic peptide.
b.decreased synthesis of aquaporins.
c.decreased synthesis of cyclic adenosine monophosphate (AMP).
d.persistent hypokalemia.
e.decreased release of ADH from the posterior pituitary.
.In studies of complete UUO for 24 hours, renal blood flow has been shown to:
a.briefly cease with ureteral clamping and then gradually return toward control.
b.gradually decline over the course of the constriction.
c.increase by 25% and remain elevated during the obstruction.
d.increase over an hour and then steadily decrease.
e.remain unchanged during clamping and undergo reactive hyperemia on
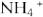
release.
.Ureteral and tubular pressure changes in experimental unilateral ureteral occlusion over 24 hours are characterized by:
a.a continued increase due to urine secretion.
b.an immediate decrease as flow ceases.
c.an increase followed by a decrease.
d.no change due to extravasation of tubule fluid.
e.no change due to contralateral renal compensation.
.Which of the following have been implicated in the initial rise in renal blood flow in UUO?
a.Adenosine and bradykinin
b.Atrial natriuretic peptide and platelet-activating factor
c.Dopamine and acetylcholine
d.Prostaglandin and nitric oxide
e.Endothelin and angiotensin II
.Which of the following best explains the greater fractional excretion of sodium that follows the release of BUO compared with UUO?
a.Better-preserved glomerular filtration rate with UUO than with BUO
b.Greater expansion of extracellular volume with BUO than with UUO
c.More contralateral compensation with BUO than with UUO
d.Less atrial natriuretic protein production with BUO than with UUO
e.More secretion of aldosterone with BUO than with UUO
.Obstruction causes which of the following disturbances in the renal regulation of acid-base balance?
a.Decreased bicarbonate reclamation in the proximal tubule
b.Decreased H+-adenosine triphosphate (ATP)ase expression in the collecting duct
c.Greater buffering of acid loads by glutamine breakdown to NH3
d.Decreased proportion of H+ buffered as titratable acid rather than as
e.Urine pH above 7.4
.A 5-year-old child presents to the emergency room with symptoms of acute renal colic. Which is the most appropriate initial imaging study to obtain for his evaluation?
a.Excretory urogram
b.Magnetic resonance urography
c.Low-dose noncontrast CT
d.Ultrasound
e.Whitaker test
.Which of the following contribute(s) to obstruction-induced tubulointerstitial fibrosis?
a.Angiotensin II
b.IL-18
c.Transforming growth factor-β
d.TNF-α
e.All of the above
.Obstruction induces apoptosis, or programmed cell death, of nephrons. Which key family of enzymes is involved in apoptosis?
a.Aminopeptidases
b.Caspases
c.Metalloproteinases
d.Phosphatases
e.Reverse transcriptases
.Which of the following studies best predicts whether renal functional recovery will occur after reconstruction of an obstructed kidney?
a.Diuretic-mercaptoacetyltriglycine (MAG)-3 scan
b.Diuretic-diethyltriaminepentaacetic acid (DTPA) scan
c.Duplex ultrasonography of the kidneys
d.Dimercaptosuccinic acid (DMSA) renogram
e.Unenhanced magnetic resonance urogram
.Which of the following mediators has been implicated in obstruction-induced apoptosis?
a.TNF-α
b.TGF-β
c.Angiotensin II
d.IL-18
e.a, b, and d
.Why are nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) beneficial in managing the pain associated with renal colic?
a.They reduce collecting system pressure.
b.They increase renal blood flow.
c.They can be associated with gastrointestinal bleeding.
d.They are safe to use in patients with renal insufficiency.
e.They provide good pain control but are inferior to opioids in managing
renal colic.
.A 10-year-old patient presents to the emergency room with abdominal pain and is found to have significant right hydronephrosis and no ureteral dilation on ultrasound. The next step in management is:
a.Cystoscopy with a retrograde pyelogram
b.Robotic pyeloplasty
c.MAG3 Lasix renogram
d.Magnetic resonance urogram
e.Observation
.A 55-year-old, otherwise healthy woman has a chronically obstructed left kidney and normal right kidney. Which differential renal function for the left kidney would best serve as a cutoff point below which nephrectomy should be performed and above which salvage should be considered?
a.5%
b.10%
c.25%
d.35%
e.45%
.Angiotensin-converting enzyme (ACE) inhibitors or angiotensin receptor blockers attenuate the decrease in GFR caused by ureteral obstruction by reducing constriction at which level?
a.Afferent arteriole
b.Efferent arteriole
c.Glomerular capillary
d.Juxtaglomerular mesangial cell
e.Renal artery
.Epithelial-mesenchymal transition is a process that:
a.involves conversion of renal tubular epithelial cells into mesangial cells.
b.is simulated by bone morphogenetic protein-7 (BMP-7).
c.involves conversion of renal tubular epithelial cells into matrixproducing fibroblasts.
d.is inhibited by TGF-β1.
e.is of little significance in obstruction-induced renal fibrosis.
.Postobstructive diuresis and natriuresis are seen more often following relief of BUO rather than UUO because:
a. renal sodium transporters are decreased only during BUO.
