
- •EMOTIONS
- •THE CONTENTS
- •Emotions are mental states brought on by neurophysiological changes, variously associated with thoughts,
- •Emotion is a response of a person to a situation in which he
- •EMOTIONS AND
- •CLASSIFICATION OF
- •POSITIVE AND NEGATIVE
- •Theory of emotional mixture
- •JAMES-LANGE THEORY
- •CANNON-BARD THEORY
- •THE PHYSIOLOGICAL
- •WHERE DO EMOTIONS HAPPEN?
- •EMOTIONAL DISORDERS
- •DEPRESSION SIGNALS
- •COPING WITH NEGATIVE
- •THANK YOU FOR YOUR
EMOTIONS
By Viktoria Voronaya

THE CONTENTS
1.The definition
2.Emotions and emotional reactions
3.Classification of emotions
4.James-Lange theory
5.Cannon-Bard theory
6.The physiological basis
7.Emotional disorders
8.Coping with negative emotions
Emotions are mental states brought on by neurophysiological changes, variously associated with thoughts, feelings, behavioral responses, and associated with feelings of pleasure or displeasure
Emotion is a response of a person to a situation in which he finds himself

EMOTIONS AND
EMOTIONAL REACTIONS
We are born with capacity of emotions
Emotion reactions are learned
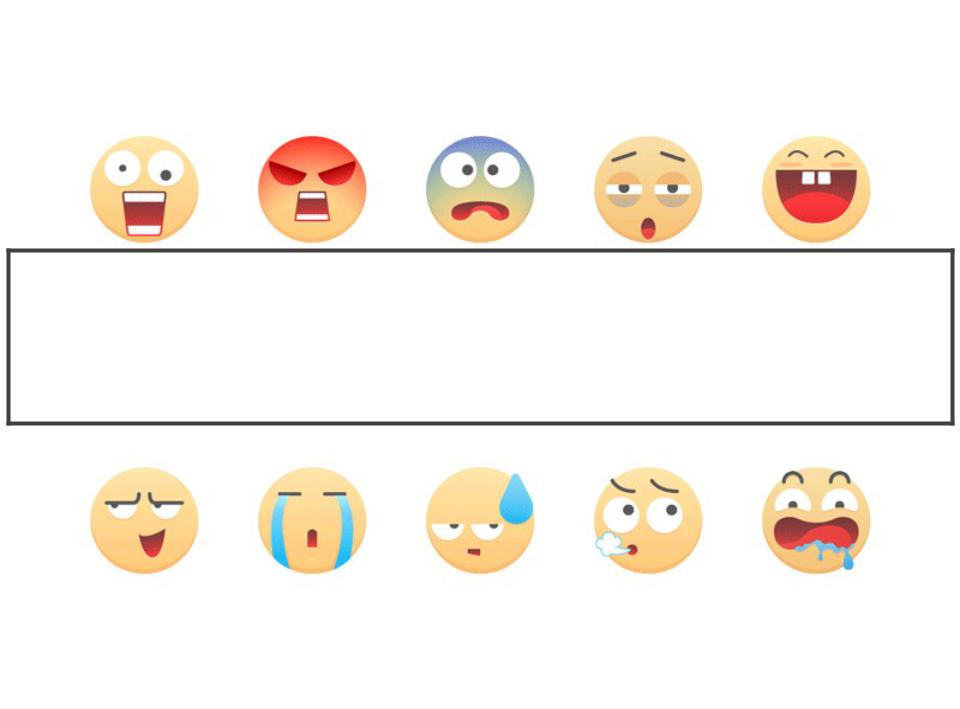
CLASSIFICATION OF
EMOTIONS
1.Intensity
2.Pleasantness-unpleasantness
3.Approach-avoidance

POSITIVE AND NEGATIVE
EMOTIONS
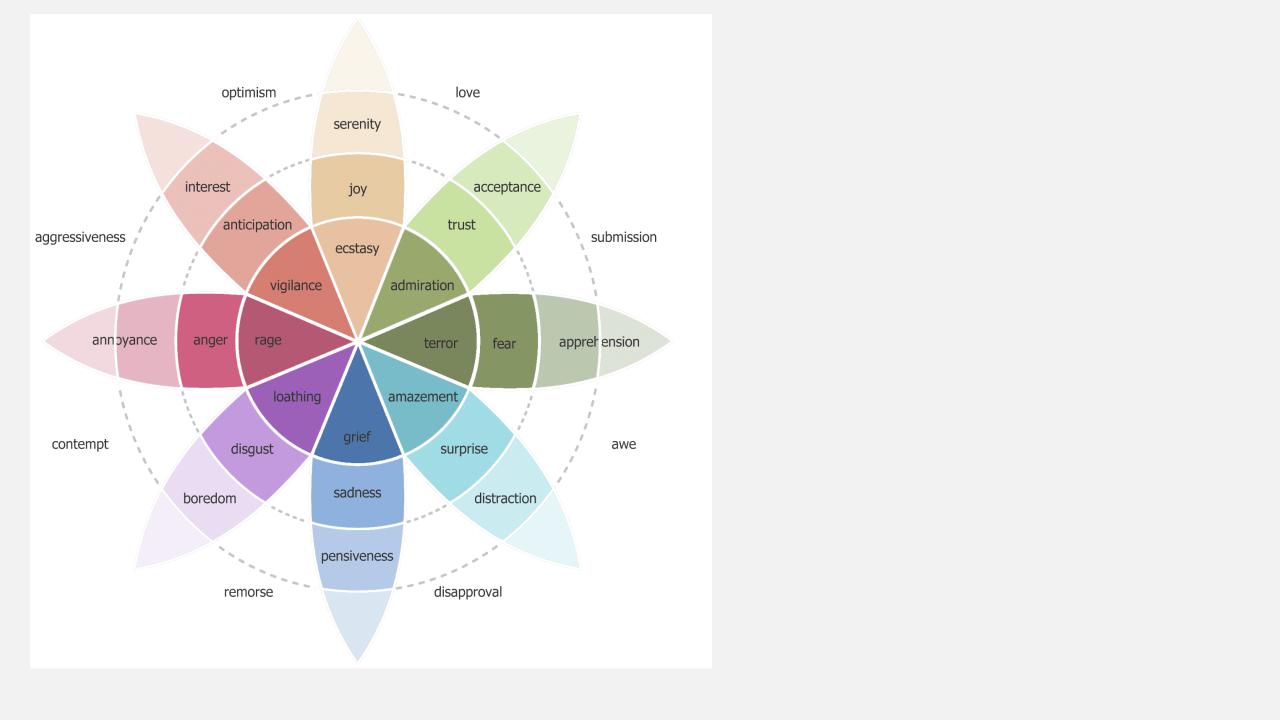
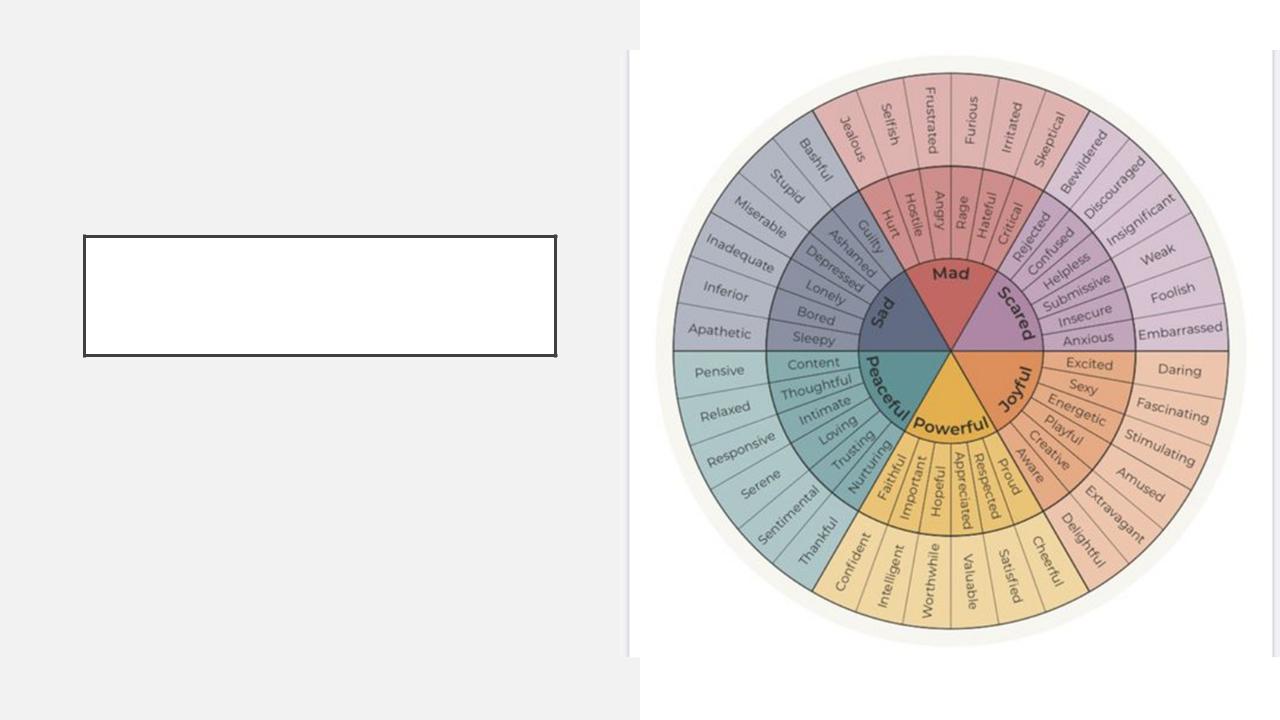
Theory of emotional mixture
There are 8 basic emotional reactions - anticipation, anger, joy, trust, surprise, fear, sadness, and disgust.
Each primary emotional reaction can vary in intensity
Plutchik's Wheel of Emotions
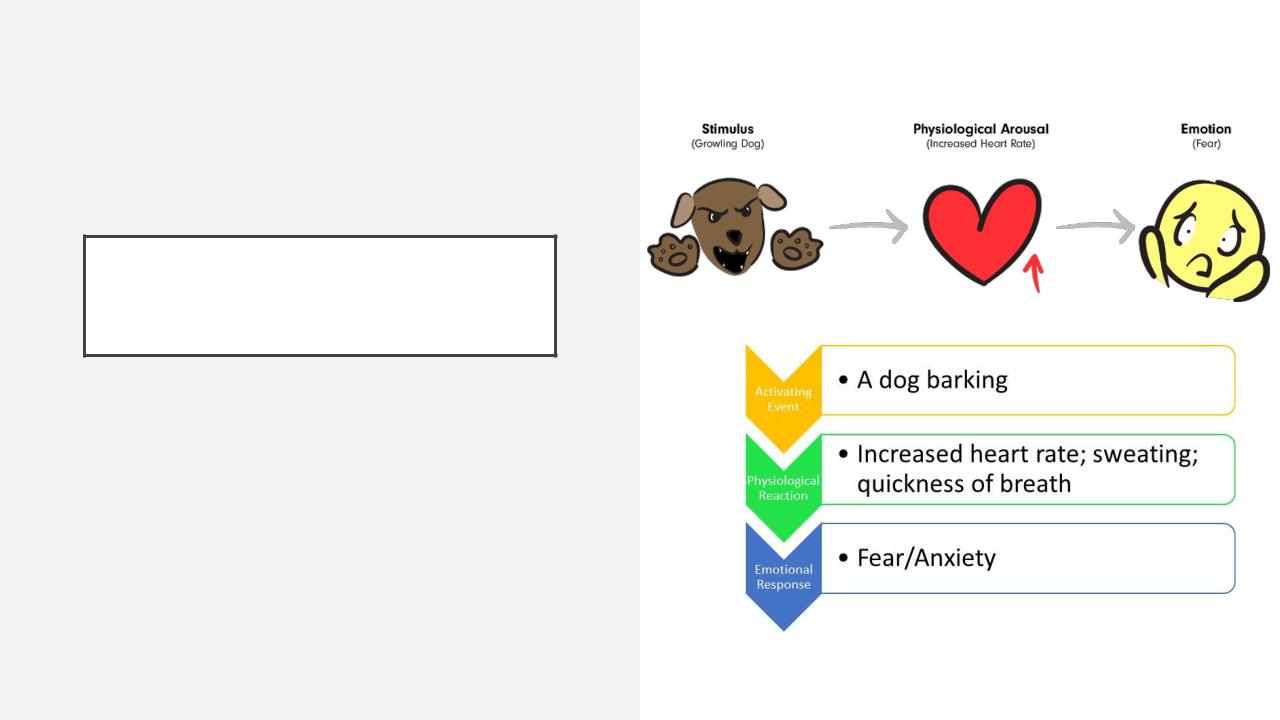
JAMES-LANGE THEORY
Was developed independently by william James and Carl Lange
Physiological reactions creates the experience of emotions
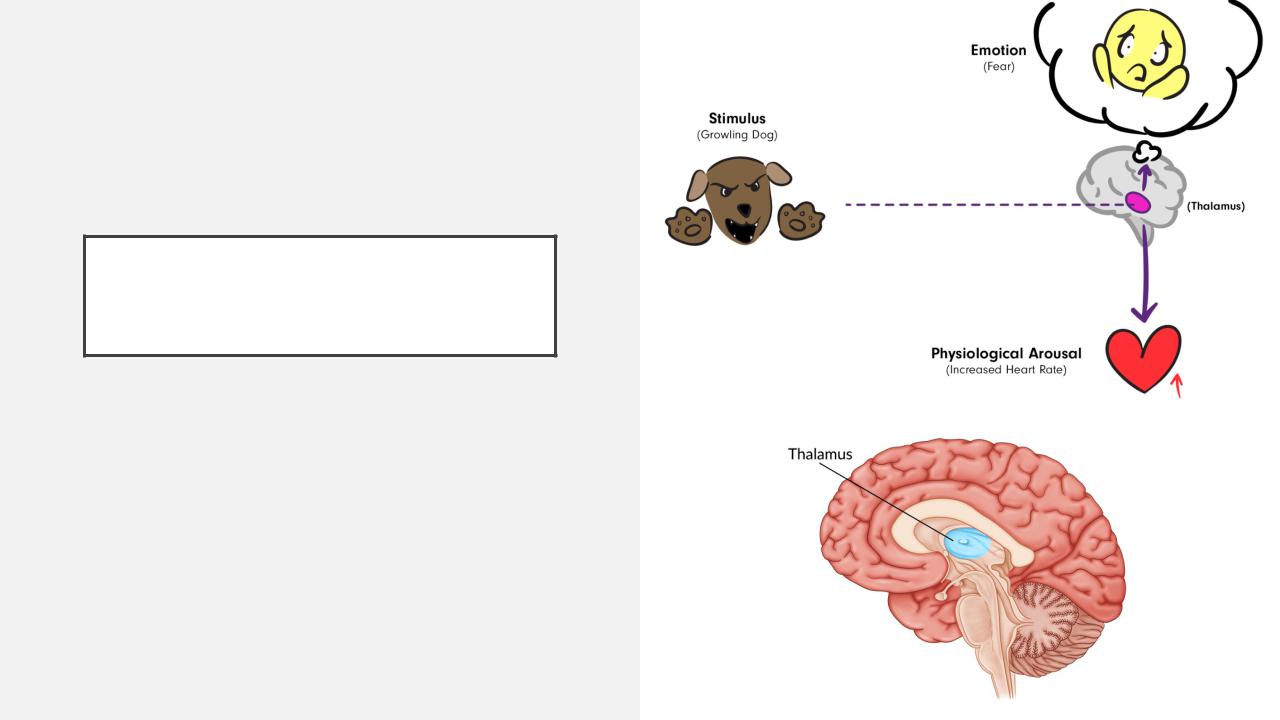
CANNON-BARD THEORY
The thalamus is the coordinating center of reactions
From thalamus reaction goes
•to other parts of the brain (produce emotions)
•to the rest of the body (produce physiological response)
