

MOTOROLA
SEMICONDUCTOR TECHNICAL DATA
Order this document by MRF137/D
The RF MOSFET Line |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
RF Power Field-Effect Transistor |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||
N±Channel Enhancement±Mode |
|
|
|
|
|
|
MRF137 |
|
|||||||||||
. . . designed for wideband large±signal output and driver stages up to |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
400 MHz range. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
• Guaranteed 28 Volt, 150 MHz Performance |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
Output Power = 30 Watts |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
Minimum Gain = 13 dB |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
30 W, to 400 MHz |
|
|||||||||
Efficiency Ð 60% (Typical) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
N±CHANNEL MOS |
|
|||||||||
• Small±Signal and Large±Signal Characterization |
|
|
|
|
|
|
BROADBAND RF POWER |
||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
FET |
|
||||||||
• Typical Performance at 400 MHz, 28 Vdc, 30 W |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
Output = 7.7 dB Gain |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
• 100% Tested For Load Mismatch At All Phase Angles |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
With 30:1 VSWR |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
• Low Noise Figure Ð 1.5 dB (Typ) at 1.0 A, 150 MHz |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
• Excellent Thermal Stability, Ideally Suited For Class A |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
Operation |
|
D |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
• Facilitates Manual Gain Control, ALC and Modulation |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
Techniques |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
G |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
CASE 211±07, STYLE 2 |
|
||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||
MAXIMUM RATINGS |
|
|
|
S |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Rating |
|
|
|
Symbol |
|
|
|
Value |
|
Unit |
|||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Drain±Source Voltage |
|
|
|
VDSS |
|
65 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Vdc |
||||||
Drain±Gate Voltage |
|
|
|
VDGR |
|
65 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Vdc |
||||||
(RGS = 1.0 MΩ) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Gate±Source Voltage |
|
|
|
VGS |
|
± 40 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Vdc |
||||||
Drain Current Ð Continuous |
|
|
|
ID |
|
5.0 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Adc |
||||||
Total Device Dissipation @ TC = 25°C |
|
|
|
PD |
|
100 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Watts |
||||||
Derate above 25°C |
|
|
|
|
|
|
0.571 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
W/°C |
|||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Storage Temperature Range |
|
|
|
Tstg |
|
± 65 to +150 |
|
°C |
|||||||||||
Operating Junction Temperature |
|
|
|
TJ |
|
200 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
°C |
||||||
THERMAL CHARACTERISTICS |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
Characteristic |
|
|
|
Symbol |
|
|
|
Max |
|
Unit |
|||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Thermal Resistance, Junction to Case |
|
|
|
RθJC |
|
1.75 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
°C/W |
||||||
Handling and Packaging Ð MOS devices are susceptible to damage from electrostatic charge. Reasonable precautions in handling and packaging MOS devices should be observed.
REV 6
Motorola, Inc. 1994

ELECTRICAL CHARACTERISTICS (TC = 25°C unless otherwise noted.)
Characteristic |
Symbol |
Min |
Typ |
Max |
Unit |
|
|
|
|
|
|
OFF CHARACTERISTICS
Drain±Source Breakdown Voltage (VGS = 0, ID = 10 mA) |
V(BR)DSS |
65 |
|
Ð |
Ð |
|
Vdc |
|
Zero Gate Voltage Drain Current (VDS = 28 V, VGS = 0) |
IDSS |
Ð |
|
Ð |
4.0 |
|
mAdc |
|
Gate±Source Leakage Current (VGS = 20 V, VDS = 0) |
IGSS |
Ð |
|
Ð |
1.0 |
|
mAdc |
|
ON CHARACTERISTICS |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
Gate Threshold Voltage (VDS = 10 V, ID = 25 mA) |
VGS(th) |
1.0 |
|
3.0 |
6.0 |
|
Vdc |
|
Forward Transconductance (VDS = 10 V, ID = 500 mA) |
gfs |
500 |
|
750 |
Ð |
|
mmhos |
|
DYNAMIC CHARACTERISTICS |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
Input Capacitance (VDS = 28 V, VGS = 0, f = 1.0 MHz) |
Ciss |
Ð |
|
48 |
Ð |
|
pF |
|
Output Capacitance (VDS = 28 V, VGS = 0, f = 1.0 MHz) |
Coss |
Ð |
|
54 |
Ð |
|
pF |
|
Reverse Transfer Capacitance (VDS = 28 V, VGS = 0, f = 1.0 MHz) |
Crss |
Ð |
|
11 |
Ð |
|
pF |
|
FUNCTIONAL CHARACTERISTICS |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Noise Figure |
|
NF |
Ð |
|
1.5 |
Ð |
|
dB |
(VDS = 28 Vdc, ID = 1.0 A, f = 150 MHz) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Common Source Power Gain |
|
Gps |
|
|
|
|
|
dB |
(VDD = 28 Vdc, Pout = 30 W, |
f = 150 MHz (Figure 1) |
|
13 |
|
16 |
Ð |
|
|
IDQ = 25 mA) |
f = 400 MHz (Figure 14) |
|
Ð |
|
7.7 |
Ð |
|
|
Drain Efficiency (Figure 1) |
|
h |
50 |
|
60 |
Ð |
|
% |
(VDD = 28 Vdc, Pout = 30 W, f = 150 MHz, IDQ = 25 mA) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Electrical Ruggedness (Figure 1) |
|
y |
|
|
|
|
|
|
(VDD = 28 Vdc, Pout = 30 W, f = 150 MHz, IDQ = 25 mA, |
|
|
No Degradation in Output Power |
|
||||
VSWR 30:1 at All Phase Angles) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
R4 |
|
RFC2 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
C9 |
C10 |
+ VDD = 28 V |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
|
BIAS |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
ADJUST |
D1 |
|
+ |
|
|
|
|
R3 |
C7 |
C8 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
± |
|
|
|
|
R2 |
|
|
RFC1 |
|
|
|
|
|
C6 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
C5 |
|
C1 |
|
R1 |
|
|
|
RF |
RF |
L1 |
|
L2 |
L3 |
|
OUTPUT |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
INPUT |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
C2 |
DUT |
|
C3 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
C4 |
C1 |
Ð Arco 403, 3.0± 35 pF, or equivalent |
L1 |
Ð 2 Turns, 0.29 ″ ID, #18 AWG Enamel, Closewound |
|
C2 |
Ð Arco 406, 15± 115 pF, or equivalent |
L2 |
Ð 1±1/4 Turns, 0.2 ″ ID, #18 AWG Enamel, Closewound |
|
C3 Ð 56 pF Mini±Unelco, or equivalent |
L3 |
Ð 2 Turns, 0.2 ″ ID, #18 AWG Enamel, Closewound |
||
C4 |
Ð Arco 404, 8.0± 60 pF, or equivalent |
RFC1 Ð 20 Turns, 0.30 ″ ID, #20 AWG Enamel, Closewound |
||
C5 |
Ð 680 pF, 100 Mils Chip |
RFC2 Ð Ferroxcube VK±200 Ð 19/4B |
||
C6 |
Ð 0.01 mF, 100 V, Disc Ceramic |
R1 |
Ð 10 k W, 1/2 W Thin Film |
|
C7 |
Ð 100 mF, 40 V |
R2 |
Ð 10 k W, 1/4 W |
|
C8 |
Ð 0.1 mF, 50 V, Disc Ceramic |
R3 |
Ð 10 Turns, 10 k W |
|
C9, C10 Ð 680 pF Feedthru |
R4 |
Ð 1.8 k W, 1/2 W |
||
D1 Ð 1N5925A Motorola Zener |
Board Ð G10, 62 Mils |
|
Figure 1. 150 MHz Test Circuit |
|
|
MRF137 |
MOTOROLA RF DEVICE DATA |
2 |
|

|
50 |
|
f = 100 MHz |
|
|
|
20 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
(WATTS) |
40 |
|
|
|
150 MHz |
(WATTS) |
|
|
|
|
|
15 |
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|||
|
|
|
|
200 MHz |
|
||
POWER |
30 |
|
|
|
POWER |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
|
|
|
|
|
10 |
||
,OUTPUT |
20 |
|
|
|
|
,OUTPUT |
|
|
|
|
VDD = 28 V |
|
5 |
||
out |
|
|
|
|
out |
||
10 |
|
|
IDQ = 25 mA |
|
|
||
P |
|
|
|
P |
|
||
|
0 |
0.5 |
1 |
1.5 |
|
2 |
0 |
|
0 |
|
|
|
f = 100 MHz |
|
150 MHz |
|
|
|
|
200 MHz |
|
|
|
|
VDD = 13.5 V |
|
|
|
|
IDQ = 25 mA |
|
0 |
1 |
2 |
3 |
4 |
Pin, INPUT POWER (WATTS) |
Pin, INPUT POWER (WATTS) |
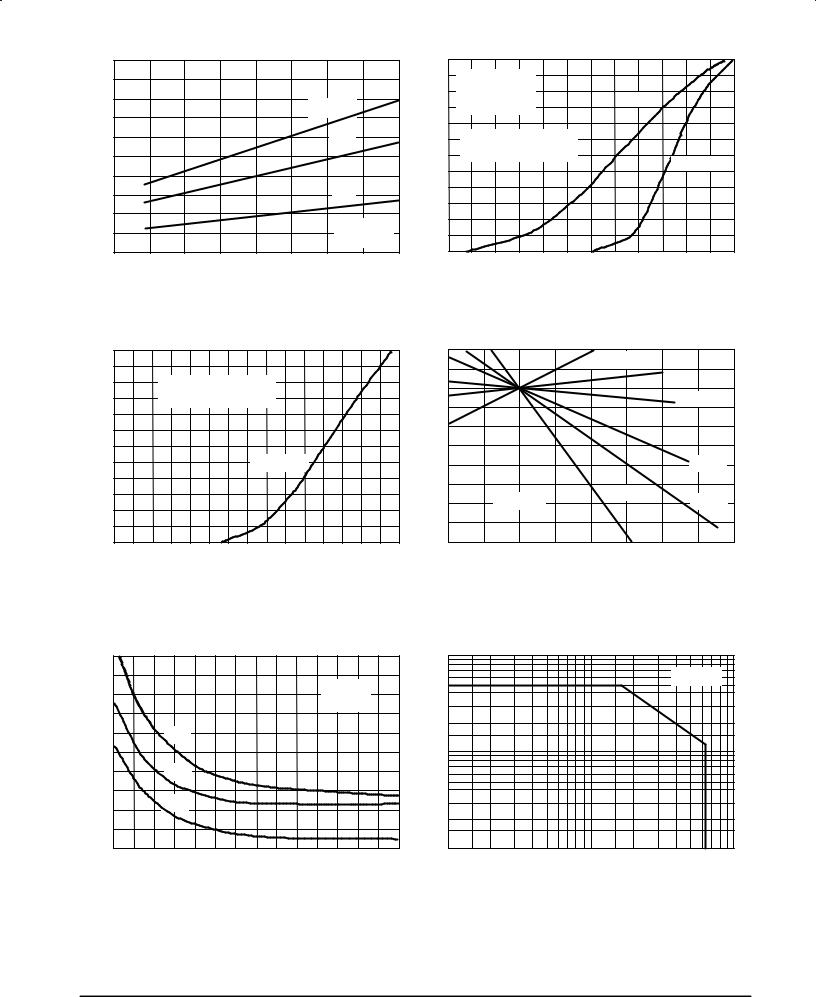
Figure 2. Output Power versus Input Power |
Figure 3. Output Power versus Input Power |
|
40 |
|
|
|
|
|
50 |
(WATTS) |
|
f = 400 MHz |
|
|
VDD = 28 V |
(WATTS) |
|
|
IDQ = 25 mA |
|
|
40 |
|||
|
|
|
|
||||
30 |
|
|
|
|
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
POWER |
|
|
|
|
|
POWER |
30 |
20 |
|
|
|
|
|
||
,OUTPUT |
|
|
|
|
,OUTPUT |
|
|
|
|
|
|
VDD = 13.5 V |
20 |
||
10 |
|
|
|
|
|
||
out |
|
|
|
|
out |
10 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
P |
|
|
|
|
|
P |
|
|
0 |
2 |
4 |
6 |
8 |
10 |
0 |
|
0 |
|
|
|
|
Pin = 1 W |
|
|
|
|
0.5 W |
|
|
|
|
0.25 W |
|
|
|
|
IDQ = 25 mA |
|
|
|
|
f = 100 MHz |
|
12 |
16 |
20 |
24 |
28 |
Pin, INPUT POWER (WATTS) |
VDD, SUPPLY VOLTAGE (VOLTS) |
Figure 4. Output Power versus Input Power |
Figure 5. Output Power versus Supply Voltage |
|
50 |
|
|
|
|
50 |
|
|
|
|
(WATTS) |
40 |
|
|
Pin = 1.5 W |
(WATTS) |
40 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Pin = 2 W |
|
||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
POWER |
|
|
|
|
POWER |
|
|
|
|
|
30 |
|
|
0.75 W |
30 |
|
|
1.5 W |
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||
OUTPUT, |
|
|
|
|
OUTPUT, |
|
|
|
|
|
20 |
|
|
0.5 W |
20 |
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
0.75 W |
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
out |
10 |
|
|
|
out |
10 |
|
|
|
|
P |
|
|
IDQ = 25 mA |
P |
|
|
IDQ = 25 mA |
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
0 |
|
|
f = 150 MHz |
|
0 |
|
|
f = 200 MHz |
|
|
16 |
20 |
24 |
28 |
16 |
20 |
24 |
28 |
||
|
12 |
12 |
||||||||
|
|
VDD, SUPPLY VOLTAGE (VOLTS) |
|
|
|
VDD, SUPPLY VOLTAGE (VOLTS) |
|
|||
Figure 6. Output Power versus Supply Voltage |
Figure 7. Output Power versus Supply Voltage |
MOTOROLA RF DEVICE DATA |
MRF137 |
|
3 |
|
50 |
|
|
|
|
|
30 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
25 |
VDD = 28 V |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
(WATTS) |
40 |
|
|
|
|
(WATTS) |
IDQ |
= 25 mA |
|
|
400 MHz |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Pin = 8 W |
|
|
Pin = CONSTANT |
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
|
|
|
|
20 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
POWER |
|
|
|
|
|
POWER |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
30 |
|
|
5 W |
|
|
TYPICAL DEVICE SHOWN, |
|
|
|
|
|
||||
|
|
|
|
15 |
VGS(th) = 3 V |
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
150 MHz |
|
||||||
, OUTPUT |
20 |
|
|
|
|
, OUTPUT |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
|
|
|
2 W |
|
10 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
out |
10 |
|
|
|
|
out |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
P |
|
|
IDQ = 25 mA |
|
P |
5 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
0 |
|
|
f = 400 MHz |
|
|
0 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
16 |
20 |
24 |
28 |
|
|
± 6 |
± 4 |
± 2 |
0 |
1 |
2 |
3 |
||
|
12 |
|
± 9 ± 8 |
||||||||||||
|
|
VDD, SUPPLY VOLTAGE (VOLTS) |
|
|
|
|
VGS, GATE±SOURCE VOLTAGE (VOLTS) |
|
|
|
|||||
Figure 8. Output Power versus Supply Voltage |
Figure 9. Output Power versus Gate Voltage |
ID, DRAIN CURRENT (AMPS)
3 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
(NORMALIZED) |
1.02 |
|
|
|
ID = 1.25 A |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
1 A |
|
|
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
|
|
TYPICAL DEVICE SHOWN, |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
1 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
|
|
VGS(th) = 3 V |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
750 mA |
|
|
2 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
VOLTAGE |
0.98 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
SOURCE- |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
1 |
|
|
|
VDS = 10 V |
|
|
0.96 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
500 mA |
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
GATE, |
0.94 |
|
VDS = 28 V |
|
25 mA |
|
200 mA |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
GS |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
V |
0.92 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
0 |
1 |
2 |
3 |
4 |
5 |
6 |
7 |
|
0 |
25 |
50 |
75 |
100 |
125 |
150 |
175 |
|
|
± 25 |
||||||||||||||||
|
|
VGS, GATE±SOURCE VOLTAGE (VOLTS) |
|
|
|
|
|
TC, CASE TEMPERATURE (°C) |
|
|
|
||||||
Figure 10. Drain Current versus Gate Voltage |
Figure 11. Gate Source Voltage versus |
(Transfer Characteristics) |
Case Temperature |
|
200 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
10 |
|
180 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
5 |
|
160 |
|
|
|
|
|
VGS = 0 V |
DRAIN CURRENT (AMPS) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
CAPACITANCE (pF) |
140 |
|
|
|
|
|
f = 1 MHz |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
2 |
|||
120 |
|
Coss |
|
|
|
|
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
100 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
1 |
||
80 |
|
Ciss |
|
|
|
|
0.5 |
||
60 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
C, |
|
|
C |
|
|
|
|
, |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
D |
|
||
|
40 |
|
rss |
|
|
|
|
I |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
20 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
0 |
4 |
8 |
12 |
16 |
20 |
24 |
28 |
0.1 |
|
0 |
|
|||||||
|
|
|
VDS, DRAIN±SOURCE VOLTAGE (VOLTS) |
|
|
||||
|
|
|
|
|
TC = 25°C |
|
1 |
2 |
5 |
10 |
20 |
60 |
100 |
VDS, DRAIN±SOURCE VOLTAGE (VOLTS)
Figure 12. Capacitance versus |
Figure 13. DC Safe Operating Area |
Drain±Source Voltage |
|
MRF137 |
MOTOROLA RF DEVICE DATA |
4 |
|

|
|
|
R4 |
|
C10 |
C11 |
RFC2 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
VDD = 28 V |
||||
|
BIAS |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
C12 |
C13 |
|
|
|
|
ADJUST |
R3 |
D1 |
|
|
+ |
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
± |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
C9 |
RFC1 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
R2 |
|
|
|
|
|
C8 |
|
|
|
|
R1 |
|
|
|
|
|
RF |
|
|
|
|
|
Z4 |
Z5 |
Z6 |
|
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
OUTPUT |
||||
RF |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Z1 |
Z2 |
Z3 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
INPUT |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
C5 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
DUT |
|
C7 |
C3 |
C4 |
|
|
|
|
C1 |
C6 |
C2 |
|
|
|
||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
C1, C2, C3, C4 Ð 0± 20 pF Johanson, or equivalent |
R4 Ð 1.8 k W, 1/2 W |
|
C5, C8 Ð 270 pF, 100 Mil Chip |
Z1 |
Ð 2.9 ″ x 0.166″ Microstrip |
C6, C7 Ð 24 pF Mini±Unelco, or equivalent |
Z2, Z4 Ð 0.35 ″ x 0.166″ Microstrip |
|
C9 Ð 0.01 mF, 100 V, Disc Ceramic |
Z3 |
Ð 0.40 ″ x 0.166″ Microstrip |
C10 Ð 100 mF, 40 V |
Z5 |
Ð 1.05 ″ x 0.166″ Microstrip |
C11 Ð 0.1 mF, 50 V, Disc Ceramic |
Z6 |
Ð 1.9 ″ x 0.166″ Microstrip |
C12, C13 Ð 680 pF Feedthru |
RFC1 Ð 6 Turns, 0.300 ″ ID, #20 AWG Enamel, Closewound |
|
D1 Ð 1N5925A Motorola Zener |
RFC2 Ð Ferroxcube VK±200 Ð 19/4B |
|
R1, R2 Ð 10 k W, 1/4 W |
Board Ð Glass Teflon, 62 Mils |
|
R3 Ð 10 Turns, 10 k W |
|
|
Figure 14. 400 MHz Test Circuit
Zin 150 |
200 |
|
400 |
|
400 |
|
|
|
200 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
f = 100 MHz |
|
ZOL* |
|
150 |
|
||
|
f = 100 MHz |
|
|
|
VDD = 28 V, IDQ = 25 mA, |
||
|
Pout = 30 W |
|
|
f |
Zin{ |
ZOL* |
|
MHz |
Ohms |
Ohms |
|
100 |
2.11 |
± j11.07 |
8.02 ± j2.89 |
150 |
1.77 |
± j7.64 |
5.75 ± j3.02 |
200 |
1.85 |
± j3.75 |
3.52 ± j2.67 |
400 |
1.74 |
+ j3.62 |
2.88 ± j1.52 |
ZOL* = Conjugate of the optimum load impedance into which the device output operates ata given output power, voltage and frequency.
Figure 15. Large±Signal Series Equivalent Input and Output Impedance, Zin, ZOL*
MOTOROLA RF DEVICE DATA |
MRF137 |
|
5 |

f |
|
S11 |
|
S21 |
|
S12 |
|
S22 |
||||
(MHz) |
|S11| |
|
± φ |
|S21| |
|
± φ |
|S12| |
|
± φ |
|S22| |
|
± φ |
2.0 |
0.977 |
|
± 32 |
59.48 |
|
163 |
0.011 |
|
67 |
0.661 |
|
± 36 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
5.0 |
0.919 |
|
± 70 |
48.67 |
|
142 |
0.024 |
|
44 |
0.692 |
|
± 78 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
10 |
0.852 |
|
± 109 |
33.50 |
|
122 |
0.032 |
|
29 |
0.747 |
|
± 117 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
20 |
0.817 |
|
± 140 |
19.05 |
|
106 |
0.037 |
|
16 |
0.768 |
|
± 146 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
30 |
0.814 |
|
± 153 |
13.11 |
|
99 |
0.038 |
|
14 |
0.774 |
|
± 157 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
40 |
0.811 |
|
± 159 |
9.88 |
|
95 |
0.038 |
|
13 |
0.782 |
|
± 162 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
50 |
0.812 |
|
± 164 |
7.98 |
|
92 |
0.038 |
|
12 |
0.787 |
|
± 165 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
60 |
0.813 |
|
± 166 |
6.66 |
|
89 |
0.038 |
|
12 |
0.787 |
|
± 168 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
70 |
0.815 |
|
± 168 |
5.708 |
|
86 |
0.038 |
|
11 |
0.787 |
|
± 169 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
80 |
0.816 |
|
± 170 |
5.003 |
|
84 |
0.038 |
|
11 |
0.787 |
|
± 170 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
90 |
0.817 |
|
± 171 |
4.560 |
|
83 |
0.038 |
|
12 |
0.787 |
|
± 171 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
100 |
0.817 |
|
± 172 |
4.170 |
|
81 |
0.039 |
|
13 |
0.787 |
|
± 172 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
110 |
0.818 |
|
± 173 |
3.670 |
|
80 |
0.039 |
|
13 |
0.788 |
|
± 172 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
120 |
0.820 |
|
± 173 |
3.420 |
|
79 |
0.039 |
|
13 |
0.788 |
|
± 173 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
130 |
0.821 |
|
± 173 |
3.170 |
|
79 |
0.039 |
|
13 |
0.788 |
|
± 173 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
140 |
0.822 |
|
± 174 |
2.980 |
|
78 |
0.039 |
|
13 |
0.788 |
|
± 173 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
150 |
0.823 |
|
± 175 |
2.826 |
|
77 |
0.039 |
|
14 |
0.788 |
|
± 173 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
160 |
0.824 |
|
± 175 |
2.650 |
|
76 |
0.039 |
|
14 |
0.790 |
|
± 174 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
170 |
0.825 |
|
± 176 |
2.438 |
|
75 |
0.039 |
|
14 |
0.792 |
|
± 174 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
180 |
0.827 |
|
± 176 |
2.325 |
|
73 |
0.039 |
|
15 |
0.793 |
|
± 174 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
190 |
0.829 |
|
± 177 |
2.175 |
|
72 |
0.039 |
|
16 |
0.796 |
|
± 174 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
200 |
0.831 |
|
± 177 |
2.084 |
|
71 |
0.039 |
|
16 |
0.799 |
|
± 174 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
225 |
0.836 |
|
± 178 |
1.824 |
|
69 |
0.039 |
|
18 |
0.805 |
|
± 174 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
250 |
0.846 |
|
± 178 |
1.621 |
|
66 |
0.039 |
|
21 |
0.816 |
|
± 174 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
275 |
0.853 |
|
± 179 |
1.462 |
|
64 |
0.039 |
|
23 |
0.822 |
|
± 174 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
300 |
0.853 |
|
± 179 |
1.319 |
|
61 |
0.040 |
|
25 |
0.833 |
|
± 174 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
325 |
0.856 |
|
± 179 |
1.194 |
|
59 |
0.040 |
|
27 |
0.828 |
|
± 174 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
350 |
0.857 |
|
+ 179 |
1.089 |
|
56 |
0.040 |
|
30 |
0.842 |
|
± 174 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
375 |
0.861 |
|
+ 179 |
1.014 |
|
54 |
0.042 |
|
32 |
0.849 |
|
± 174 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
400 |
0.865 |
|
+ 178 |
0.927 |
|
51 |
0.043 |
|
35 |
0.856 |
|
± 174 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
425 |
0.875 |
|
+ 178 |
0.876 |
|
49 |
0.045 |
|
37 |
0.866 |
|
± 174 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
450 |
0.881 |
|
+ 178 |
0.810 |
|
46 |
0.046 |
|
40 |
0.870 |
|
± 174 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
475 |
0.886 |
|
+ 177 |
0.755 |
|
44 |
0.046 |
|
43 |
0.875 |
|
± 174 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
500 |
0.887 |
|
+ 177 |
0.694 |
|
41 |
0.051 |
|
43 |
0.888 |
|
± 174 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
525 |
0.888 |
|
+ 176 |
0.677 |
|
39 |
0.052 |
|
43 |
0.890 |
|
± 174 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
550 |
0.896 |
|
+ 176 |
0.625 |
|
36 |
0.055 |
|
45 |
0.898 |
|
± 174 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
575 |
0.907 |
|
+ 175 |
0.603 |
|
34 |
0.058 |
|
45 |
0.913 |
|
± 174 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
600 |
0.910 |
|
+ 175 |
0.585 |
|
32 |
0.061 |
|
45 |
0.918 |
|
± 174 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
625 |
0.910 |
|
+ 174 |
0.563 |
|
30 |
0.065 |
|
45 |
0.945 |
|
± 174 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
650 |
0.920 |
|
+ 174 |
0.543 |
|
28 |
0.069 |
|
46 |
0.952 |
|
± 174 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
675 |
0.938 |
|
+ 173 |
0.533 |
|
26 |
0.074 |
|
47 |
0.974 |
|
± 174 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
700 |
0.943 |
|
+ 171 |
0.515 |
|
24 |
0.078 |
|
47 |
0.958 |
|
± 176 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
725 |
0.934 |
|
+ 170 |
0.491 |
|
22 |
0.079 |
|
46 |
0.953 |
|
± 177 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
750 |
0.940 |
|
+ 170 |
0.475 |
|
22 |
0.084 |
|
48 |
0.943 |
|
± 177 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
775 |
0.953 |
|
+ 169 |
0.477 |
|
21 |
0.090 |
|
48 |
0.957 |
|
± 177 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
800 |
0.959 |
|
+ 168 |
0.467 |
|
17 |
0.093 |
|
48 |
0.957 |
|
± 179 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
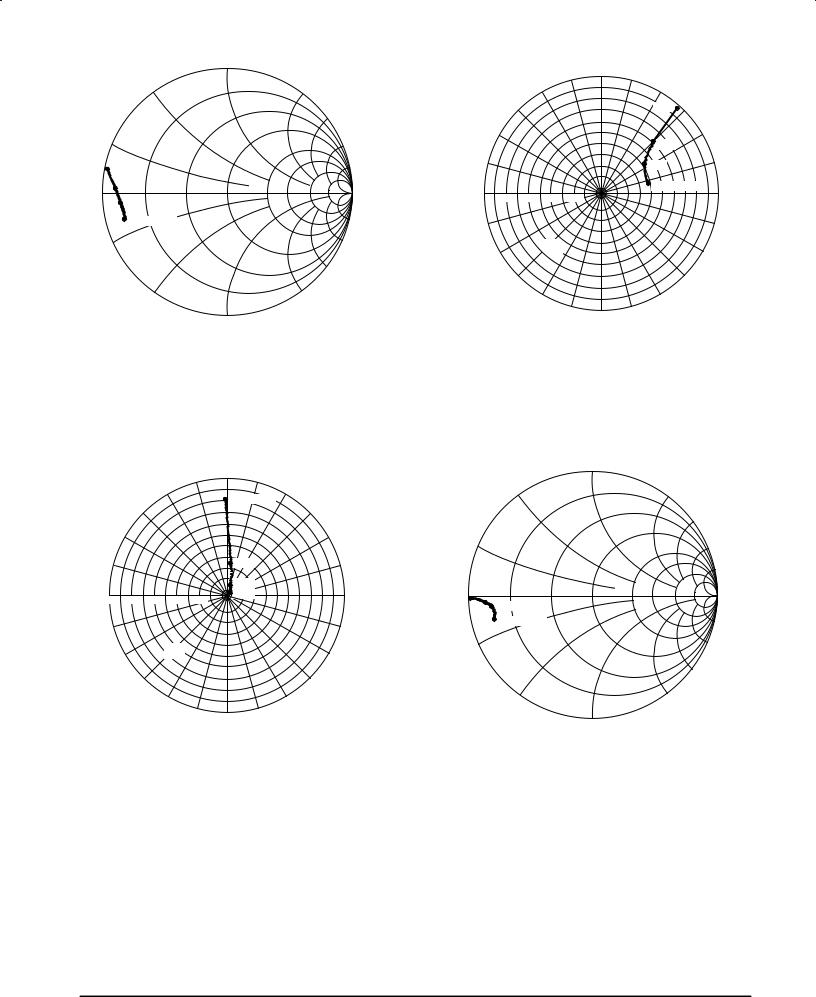
Table 1. Common Source Scattering Parameters
50 Ω System
VDS = 28 V, ID = 0.75 A
MRF137 |
MOTOROLA RF DEVICE DATA |
6 |
|
|
|
|
+ j50 |
|
|
|
|
|
+ j25 |
|
|
|
|
+ j100 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
+ j150 |
+ j10 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
+ j250 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
800 |
|
|
|
|
|
+ j500 |
|
400 |
25 |
50 |
100 |
150 |
250 |
500 |
0 |
10 |
||||||
150 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
f = 50 MHz |
|
|
|
|
|
± j500 |
± j10 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
± j250 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
S11 |
|
|
|
± j150 |
|
± j25 |
|
|
|
|
± j100 |
|
± j50
Figure 16. S11, Input Reflection Coefficient
versus Frequency
|
|
|
VDS = 28 V |
ID = 0.75 A |
|
|
|
|
|
|
+ 90° |
|
|
|
|
+120° |
|
+ 60° |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
f = 50 MHz |
|
+150° |
|
|
|
|
|
+ 30° |
|
|
|
|
|
150 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
400 |
|
180°10 |
8 |
6 |
4 |
2 |
800 |
0° |
±150° |
|
|
S21 |
|
|
± 30° |
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
±120° |
|
± 60° |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
± 90° |
|
|
Figure 18. S21, Forward Transmission Coefficient versus Frequency
VDS = 28 V ID = 0.75 A
|
|
|
|
|
+ 90° |
|
|
+120° |
|
|
+ 60° |
|
|
|
|
|
800 |
+150° |
|
|
|
|
+ 30° |
|
|
|
|
|
600 |
|
|
|
|
|
400 |
180°0.1 |
|
|
|
|
f = 50 MHz |
.08 |
.06 |
.04 |
.02 |
0° |
|
±150° |
|
|
S12 |
|
± 30° |
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
±120° |
|
± 60° |
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
± 90° |
Figure 17. S12, Reverse Transmission Coefficient versus Frequency
VDS = 28 V ID = 0.75 A
|
|
|
+ j50 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
+ j25 |
|
|
|
+ j100 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
+ j150 |
+ j10 |
|
|
|
|
|
+ j250 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
+ j500 |
0 |
800 |
25 |
50 |
100 |
150 |
250 |
500 |
|
400 |
150 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
f = 50 MHz |
|
|
|
|
± j500 |
± j10 |
|
|
|
|
|
± j250 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
S22 |
|
|
|
± j150 |
|
|
± j25 |
|
|
|
± j100 |
|
± j50
Figure 19. S22, Output Reflection Coefficient versus Frequency
VDS = 28 V ID = 0.75 A
MOTOROLA RF DEVICE DATA |
MRF137 |
|
7 |

DESIGN CONSIDERATIONS
The MRF137 is a RF power N±Channel enhancement mode field±effect transistor (FET) designed especially for VHF power amplifier applications. Motorola RF MOS FETs feature a vertical structure with a planar design, thus avoiding the processing difficulties associated with V±groove vertical power FETs.
Motorola Application Note AN211A, FETs in Theory and Practice, is suggested reading for those not familiar with the construction and characteristics of FETs.
The major advantages of RF power FETs include high gain, low noise, simple bias systems, relative immunity from thermal runaway, and the ability to withstand severely mismatched loads without suffering damage. Power output can be varied over a wide range with a low power dc control signal, thus facilitating manual gain control, ALC and modulation.
DC BIAS
The MRF137 is an enhancement mode FET and, therefore, does not conduct when drain voltage is applied. Drain current flows when a positive voltage is applied to the gate. See Figure 10 for a typical plot of drain current versus gate voltage. RF power FETs require forward bias for optimum performance. The value of quiescent drain current (IDQ) is not critical for many applications. The MRF137 was characterized at IDQ = 25 mA, which is the suggested minimum value of IDQ. For special applications such as linear amplification, IDQ may have to be selected to optimize the critical parameters.
The gate is a dc open circuit and draws no current. Therefore, the gate bias circuit may generally be just a simple
resistive divider network. Some special applications may require a more elaborate bias system.
GAIN CONTROL
Power output of the MRF137 may be controlled from its rated value down to zero (negative gain) by varying the dc gate voltage. This feature facilitates the design of manual gain control, AGC/ALC and modulation systems. (See Figure 9.)
AMPLIFIER DESIGN
Impedance matching networks similar to those used with bipolar VHF transistors are suitable for MRF137. See Motorola Application Note AN721, Impedance Matching Networks Applied to RF Power Transistors. The higher input impedance of RF MOS FETs helps ease the task of broadband network design. Both small signal scattering parameters and large signal impedances are provided. While the s±parameters will not produce an exact design solution for high power operation, they do yield a good first approximation. This is an additional advantage of RF MOS power FETs.
RF power FETs are triode devices and, therefore, not unilateral. This, coupled with the very high gain of the MRF137, yields a device capable of self oscillation. Stability may be achieved by techniques such as drain loading, input shunt resistive loading, or output to input feedback. Two port parameter stability analysis with the MRF137 s±parameters provides a useful tool for selection of loading or feedback circuitry to assure stable operation. See Motorola Application Note AN215A for a discussion of two port network theory and stability.
MRF137 |
MOTOROLA RF DEVICE DATA |
8 |
|

PACKAGE DIMENSIONS
Q |
1 |
2
S K
A |
|
|
|
|
|
|
U |
|
NOTES: |
|
|
|
|
M |
|
1. DIMENSIONING AND TOLERANCING PER ANSI |
||||
|
Y14.5M, 1982. |
|
|
|
||
M |
|
2. CONTROLLING DIMENSION: INCH. |
|
|||
|
|
INCHES |
MILLIMETERS |
|||
|
|
|
||||
4 |
|
DIM |
MIN |
MAX |
MIN |
MAX |
|
A |
0.960 |
0.990 |
24.39 |
25.14 |
|
|
B |
|||||
R |
B |
0.370 |
0.390 |
9.40 |
9.90 |
|
|
|
C |
0.229 |
0.281 |
5.82 |
7.13 |
|
|
D |
0.215 |
0.235 |
5.47 |
5.96 |
3 |
|
E |
0.085 |
0.105 |
2.16 |
2.66 |
|
H |
0.150 |
0.108 |
3.81 |
4.57 |
|
|
|
|||||
D |
|
J |
0.004 |
0.006 |
0.11 |
0.15 |
|
K |
0.395 |
0.405 |
10.04 |
10.28 |
|
|
|
M |
40 |
50 |
40 |
50 |
|
|
Q |
0.113 |
0.130 |
2.88 |
3.30 |
|
|
R |
0.245 |
0.255 |
6.23 |
6.47 |
|
|
S |
0.790 |
0.810 |
20.07 |
20.57 |
|
|
U |
0.720 |
0.730 |
18.29 |
18.54 |
|
|
STYLE 2: |
|
|
J |
PIN 1. |
SOURCE |
|
|
2. |
GATE |
|
C |
3. |
SOURCE |
H |
4. |
DRAIN |
|
E |
SEATING |
|
|
|
|
PLANE |
|
CASE 211±07
ISSUE N
MOTOROLA RF DEVICE DATA |
MRF137 |
|
9 |

Motorola reserves the right to make changes without further notice to any products herein. Motorola makes no warranty, representation or guarantee regarding the suitability of its products for any particular purpose, nor does Motorola assume any liability arising out of the application or use of any product or circuit, and specifically disclaims any and all liability, including without limitation consequential or incidental damages. ªTypicalº parameters can and do vary in different applications. All operating parameters, including ªTypicalsº must be validated for each customer application by customer's technical experts. Motorola does not convey any license under its patent rights nor the rights of others. Motorola products are not designed, intended, or authorized for use as components in systems intended for surgical implant into the body, or other applications intended to support or sustain life, or for any other application in which the failure of the Motorola product could create a situation where personal injury or death may occur. Should Buyer purchase or use Motorola products for any such unintended or unauthorized application, Buyer shall indemnify and hold Motorola and its officers, employees, subsidiaries, affiliates, and distributors harmless against all claims, costs, damages, and expenses, and reasonable attorney fees arising out of, directly or indirectly, any claim of personal injury or death associated with such unintended or unauthorized use, even if such claim alleges that Motorola was negligent regarding the design or manufacture of the part. Motorola and  are registered trademarks of Motorola, Inc. Motorola, Inc. is an Equal Opportunity/Affirmative Action Employer.
are registered trademarks of Motorola, Inc. Motorola, Inc. is an Equal Opportunity/Affirmative Action Employer.
Literature Distribution Centers:
USA: Motorola Literature Distribution; P.O. Box 20912; Phoenix, Arizona 85036.
EUROPE: Motorola Ltd.; European Literature Centre; 88 Tanners Drive, Blakelands, Milton Keynes, MK14 5BP, England. JAPAN: Nippon Motorola Ltd.; 4-32-1, Nishi-Gotanda, Shinagawa-ku, Tokyo 141, Japan.
ASIA PACIFIC: Motorola Semiconductors H.K. Ltd.; Silicon Harbour Center, No. 2 Dai King Street, Tai Po Industrial Estate, Tai Po, N.T., Hong Kong.
◊ |
MRF137/D |
|
*MRF137/D* |
