
- •The project has been funded by the European Commission. The Education, Audiovisual and
- •Introduction to Ext file system
- •Filesystem structure
- •Filesystem structure
- •Filesystem structure
- •command mke2fs
- •Superblock
- •command dumpe2fs
- •command dumpe2fs
- •command dumpe2fs
- •Block Group Descriptor
- •Block Group Descriptor
- •Block Group Descriptor
- •Block Bitmap, Inode Bitmap
- •Inodes
- •Inode Table
- •Inodes
- •Inodes
- •Addressing
- •Addressing
- •Inodes
- •Inodes
- •Inode (example)
- •The contents of both of these blocks will be a list of 4-byte
- •Root Directory
- •Root Directory
- •Directory
- •The data structure of the second version of the directory entry
- •Directory
- •More on Ext file systems
- •More Linux file systems
- •The Sleuth kit (TSK)
- •Mounting file systems
- •Mounting file systems
- •Mounting file systems
- •Summary
- •References & Resources

The project has been funded by the European Commission. The Education, Audiovisual and Culture Executive program (EACEA), TEMPUS IV. The content of this presentation reflects the opinion of the author.
Module Digital Forensics
Ext file system

Introduction to Ext file system
•The Extended File System (ext)
•Standard file system for Linux since 1992
–also used on Android
•Four major versions
–ext (1992 – 1993): Original EXT file system
–ext2 (1993 – present): More advanced File System
–ext3 (2001 – present): Introduced Journaling
–ext4 (2008 – present): Refinements to ext3
2

Filesystem structure
Block (Ext) = cluster (FAT, NTFS)
The block size can be different (multiple of the sector size (512 bytes). It depends on the type of file system
Ext2 — 1Кb, 2Кb, 4Кb, 8Кb
Ext3 — 1Кb, 2Кb, 4Кb, 8Кb
Ext4 — from 1Кb to 64Кb

Filesystem structure
•Five structures:
–Blocks: basic storage unit in EXT
–Block Groups: Block organisational structure
–Inodes: contains file information
–Superblock: contains file system layout information
–Block Group Descriptor: pointer to structures in Block Groups
4

Filesystem structure
Reserved part (1024 B)
…
Group 0 |
Group 1 |
Group 2 |
Group 3 |
Group 4 |
Group 5 |
Group n-2 Group n-1 Group n |
All blocks of the Ext partition are combined into Block Groups .
This has a positive effect on read / write operations as it reduces read / write time for large amounts of data.
All Block Groups are of equal size. An exception may be the last Block Group .
These groups are arranged in series, one after the other.
Blocks inside the group are numbered sequentially, starting with 0. Numbering of blocks in the file system through from beginning to end
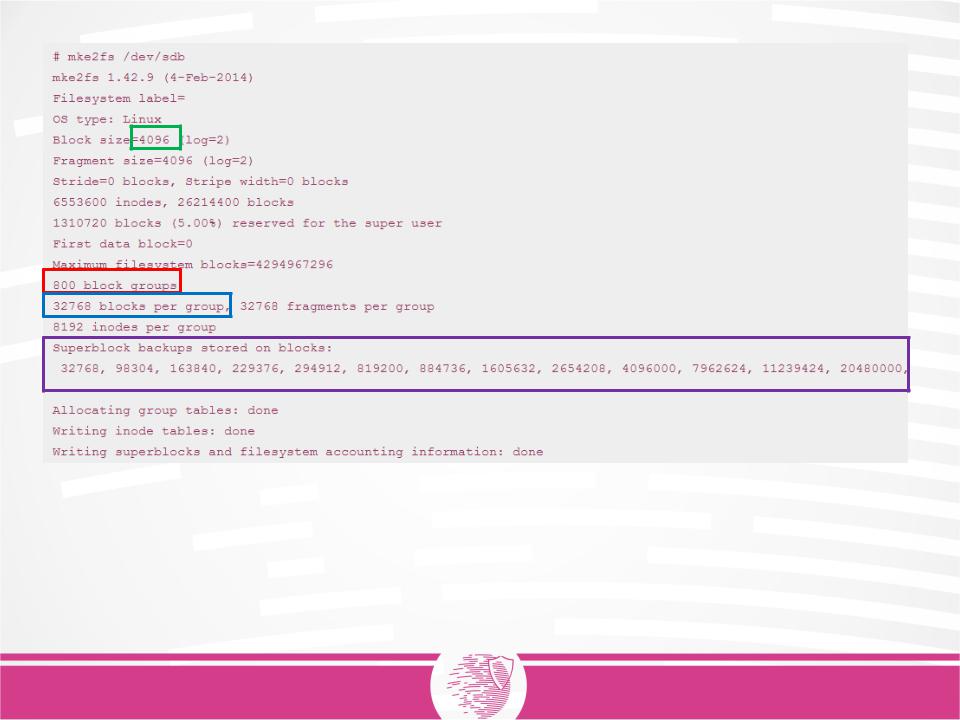
command mke2fs
The block size is 4096 bytes. 800 block groups
32768 blocks in a group (8 * 4096)
Also visible are the blocks in which backup copies of the superblock are stored.
In the UFS system, on the basis of which ExtX was developed, the blocks are divided into fragments. ExtX code for Linux does not support this division, although there is a field in the superblock in which the fragment size can be stored.
|
Filesystem structure |
|
|
Group |
Inode |
Data Blocks |
|
Descriptors |
Bitmap |
||
|
. . . . . .
Super Block |
Block |
Inode Table |
(Superblock |
Bitmap |
|
backup) |
|
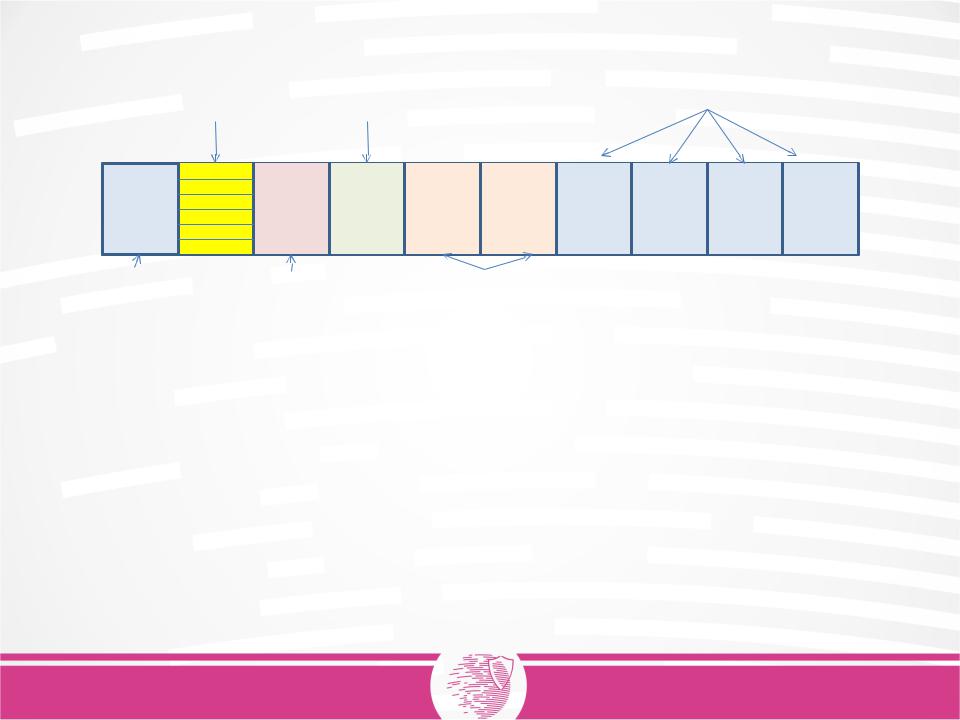
The structure of Block Group |
|
|
Each Block Group contains blocks with the following structures: Superblock (optional): copy of superblock
Block Group Descriptor: location of block group structures Block Usage Bitmap: Block allocation status
Inode Usage Bitmap: Inode allocation status Inode Table: Inode information – file metadata Data Blocks: File data.

Superblock
•Describes the structure of the file system
•The superblock is the main element of the ext file system. It contains general information about the file system:
•the total number of blocks and inodes in the file system,
•the number of free blocks and inodes in the file system,
•file system block size,
•the number of blocks and inodes in a group of blocks,
•inode size,
•file system identifier (magic number 0xEF53 for the ext file system family),
•date of the last file system check,
•the number of mounts made,
•file system status flag Located at offset 1024 bytes
•Copies in other places of the file system
8

command dumpe2fs |
Superblock |
|
9

command dumpe2fs |
Superblock |
|
10
