
- •The project has been funded by the European Commission. The Education, Audiovisual and
- •hexadecimal system
- •ADDRESSING
- •Boot
- •FAT Filesystem (File Allocation Table)
- •FAT12 is used only on floppy disks and FAT volumes smaller than 16
- •Sector
- •Cluster
- •Cluster
- •The default number of sectors per cluster (with FAT12) is
- •Layout
- •Layout
- •Logical Organisation FAT 12/16
- •Logical Organisation FAT 32
- •Layout
- •Calculation of the start address of the data area FAT12/16
- •Calculation of the start address of the data area FAT32
- •The Boot Sector
- •The Boot Sector
- •The Boot Sector
- •BIOS-Parameter-Block (BPB)
- •The Boot Sector
- •The Boot Sector
- •The Boot Sector
- •The Boot Sector
- •The Boot Sector
- •The Boot Sector
- •The Boot Sector
- •The Boot Sector
- •Logical organisation FAT 32
- •FSINFO Sector
- •FSINFO Sector
- •Meta data of the file system
- •Metadata of the file system
- •Root Directory
- •Subdirectories
- •start cluster
- •File Allocation Table (FAT)
- •File Allocation Table (FAT)
- •FAT-Chaining
- •FAT-Chaining
- •File Allocation Table
- •File
- •File
- •File
- •File
- •File
- •File
- •File
- •File
- •the FAT will find the rest
- •Creation of a file
- •Deleting files in the FAT
- •The algorithm of file recovery

The project has been funded by the European Commission. The Education, Audiovisual and Culture Executive program (EACEA), TEMPUS IV. The content of this presentation reflects the opinion of the author.
File System Analysis (Win) FAT
Digital Forensic
Developers:
J. Rolnik
T. Willkomm
A. Kühn

hexadecimal system |
decimal system |
|
binary system |
|
||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
0hex |
|
0dec |
0 |
0 |
|
0 |
0 |
|
1hex |
|
1dec |
0 |
0 |
|
0 |
1 |
|
2hex |
|
2dec |
0 |
0 |
|
1 |
0 |
|
3hex |
|
3dec |
0 |
0 |
|
1 |
1 |
|
4hex |
|
4dec |
0 |
1 |
|
0 |
0 |
|
5hex |
|
5dec |
0 |
1 |
|
0 |
1 |
|
6hex |
|
6dec |
0 |
1 |
|
1 |
0 |
|
7hex |
|
7dec |
0 |
1 |
|
1 |
1 |
|
8hex |
|
8dec |
1 |
0 |
|
0 |
0 |
|
9hex |
|
9dec |
1 |
0 |
|
0 |
1 |
|
Ahex |
|
10dec |
1 |
0 |
|
1 |
0 |
|
Bhex |
|
11dec |
1 |
0 |
|
1 |
1 |
|
Chex |
|
12dec |
1 |
1 |
|
0 |
0 |
|
Dhex |
|
13dec |
1 |
1 |
|
0 |
1 |
|
Ehex |
|
14dec |
1 |
1 |
|
1 |
0 |
|
Fhex |
|
15dec |
1 |
1 |
|
1 |
1 |
0000 0010 1110 1111 = 02EFhex |
|
1110 1111 = 0EFhex |
|
|
||||
|
|
|
|
if it does not begin with a decimal digit |
|
|||

ADDRESSING
0000 |
0001 |
0002 |
0003 |
0004 |
0005 |
0006 |
0007 |
0008 |
0009 |
000A |
000B |
000C |
000D |
000E |
000F |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
0000 0000 |
0000 0000 |
0000 0000 |
0000 0000 |
0000 0000 |
0000 0000 |
0000 0000 |
0000 0000 |
0000 0000 |
0000 0000 |
0000 0000 |
0000 0000 |
0000 0000 |
0000 0000 |
0000 0000 |
0000 0000 |
0000 0000 |
0000 0001 |
0000 0010 |
0000 0011 |
0000 0100 |
0000 0101 |
0000 0110 |
0000 0111 |
0000 1000 |
0000 1001 |
0000 1010 |
0000 1011 |
0000 1100 |
0000 1101 |
0000 1110 |
0000 1111 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
0010 |
0011 |
0012 |
0013 |
0014 |
0015 |
0016 |
0017 |
0018 |
0019 |
001A |
001B |
001C |
001D |
001E |
001F |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
0000 0000 |
0000 0000 |
0000 0000 |
0000 0000 |
0000 0000 |
0000 0000 |
0000 0000 |
0000 0000 |
0000 0000 |
0000 0000 |
0000 0000 |
0000 0000 |
0000 0000 |
0000 0000 |
0000 0000 |
0000 0000 |
0001 0000 |
0001 0001 |
0001 0010 |
0001 0011 |
0001 0100 |
0001 0101 |
0001 0110 |
0001 0111 |
0001 1000 |
0001 1001 |
0001 1010 |
0001 1011 |
0001 1100 |
0001 1101 |
0001 1110 |
0001 1111 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
0020 |
0021 |
0022 |
0023 |
0024 |
0025 |
0026 |
0027 |
0028 |
0029 |
002A |
002B |
002C |
002D |
002E |
002F |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
0000 0000 |
0000 0000 |
0000 0000 |
0000 0000 |
0000 0000 |
0000 0000 |
0000 0000 |
0000 0000 |
0000 0000 |
0000 0000 |
0000 0000 |
0000 0000 |
0000 0000 |
0000 0000 |
0000 0000 |
0000 0000 |
0010 0000 |
0010 0001 |
0010 0010 |
0010 0011 |
0010 0100 |
0010 0101 |
0010 0110 |
0010 0111 |
0010 1000 |
0010 1001 |
0010 1010 |
0010 1011 |
0010 1100 |
0010 1101 |
0010 1110 |
0010 1111 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
0030 |
0031 |
0032 |
0033 |
0034 |
0035 |
0036 |
0037 |
0038 |
0039 |
003A |
003B |
003C |
003D |
003E |
003F |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
0000 0000 |
0000 0000 |
0000 0000 |
0000 0000 |
0000 0000 |
0000 0000 |
0000 0000 |
0000 0000 |
0000 0000 |
0000 0000 |
0000 0000 |
0000 0000 |
0000 0000 |
0000 0000 |
0000 0000 |
0000 0000 |
0011 0000 |
0011 0001 |
0011 0010 |
0011 0011 |
0011 0100 |
0011 0101 |
0011 0110 |
0011 0111 |
0011 1000 |
0011 1001 |
0011 1010 |
0011 1011 |
0011 1100 |
0011 1101 |
0011 1110 |
0011 1111 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
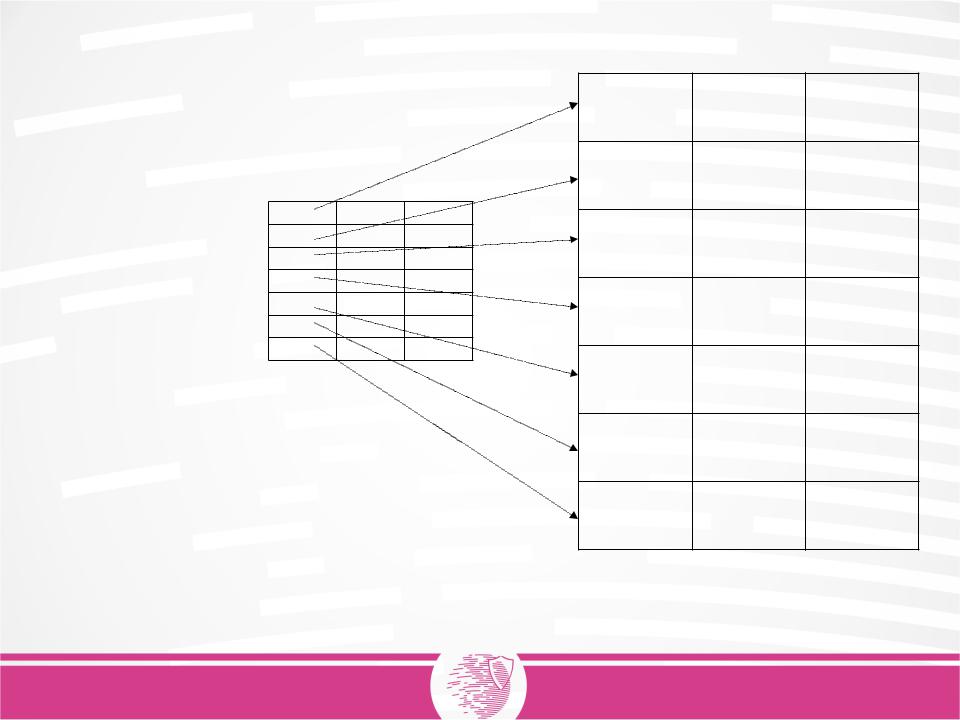
Boot |
Root |
FAT area |
area |
Directory |
|
|
|
32 bytes |
32 |
|
|
sect |
|
– 1 entry |
|
|
|
Number of the first cluster of the file is stored in the directory element containing the record of the file
Each cluster corresponds to a FAT element
Clusters
Cluster Cluster Cluster
Cluster Cluster Cluster
Cluster Cluster Cluster
Cluster Cluster Cluster
Cluster Cluster Cluster
Cluster Cluster Cluster
Cluster Cluster Cluster

FAT Filesystem (File Allocation Table)
•The FAT file system was developed in the late 1970s as a simple file system for the MS-DOS operating system
•Currently there are three FAT file system types:
•FAT12
•FAT16
•FAT32
•The difference in these FAT types, and the reason for the names, is the size, in bits, of the entries in the actual FAT structure on the disk.
•They work the same way, but differ in the number of addressable allocation units (clusters)
5

FAT12 is used only on floppy disks and FAT volumes smaller than 16 MB. FAT12 uses a 12-bit file allocation table entry to address an entry in the filesystem.
FAT16. MS-DOS, Windows 95/98/NT/2000/XP, Windows Server 2003, and some UNIX OSs support FAT16 natively. FAT16 is also commonly used for multimedia devices such as digital cameras and audio players. FAT16 uses a 16-bit file allocation table entry to address an entry in the filesystem. FAT16 volumes are limited to a maximum size of 2 GB in MS-DOS and Windows 95/98. Windows NT and newer OSs increase the maximum volume size for FAT16 to 4 GB.
FAT32. Windows 95 Original Equipment Manufacturer (OEM) Service Release 2 (OSR2), Windows 98/2000/XP, and Windows Server 2003 support FAT32 natively, as do some multimedia devices. FAT32 uses a 32-bit file allocation table entry to address an entry in the filesystem. The maximum FAT32 volume size is 2 terabytes (TB).
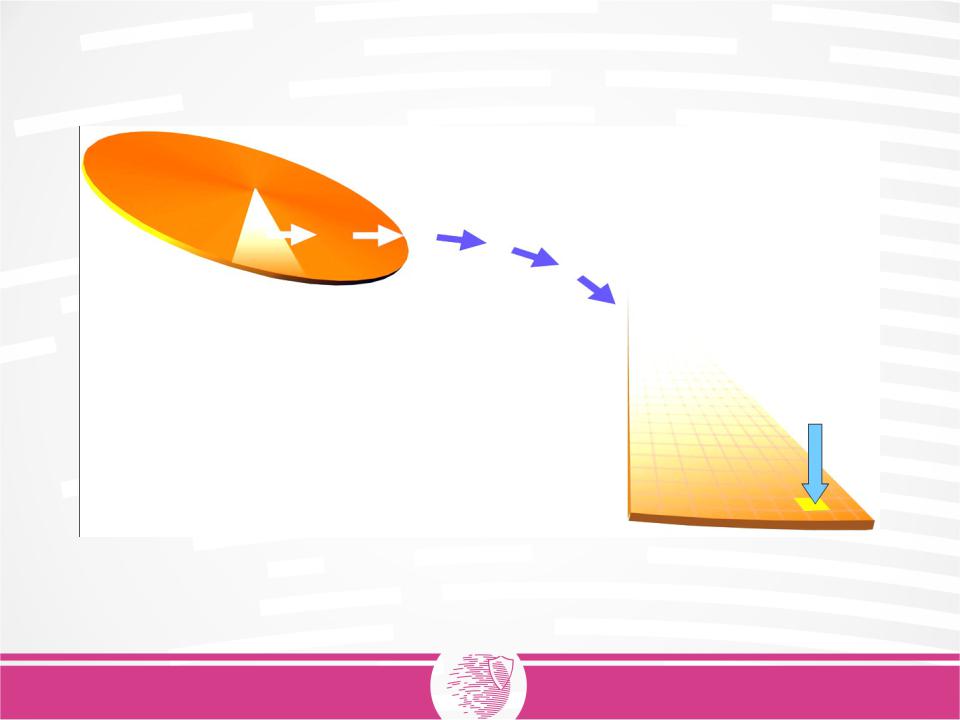
Sector
One sector = 512 bytes
2048 bytes (optical disks)
4096 байт (Advanced Format)
A sector is the smallest writable unit on a hard disc drive.
7
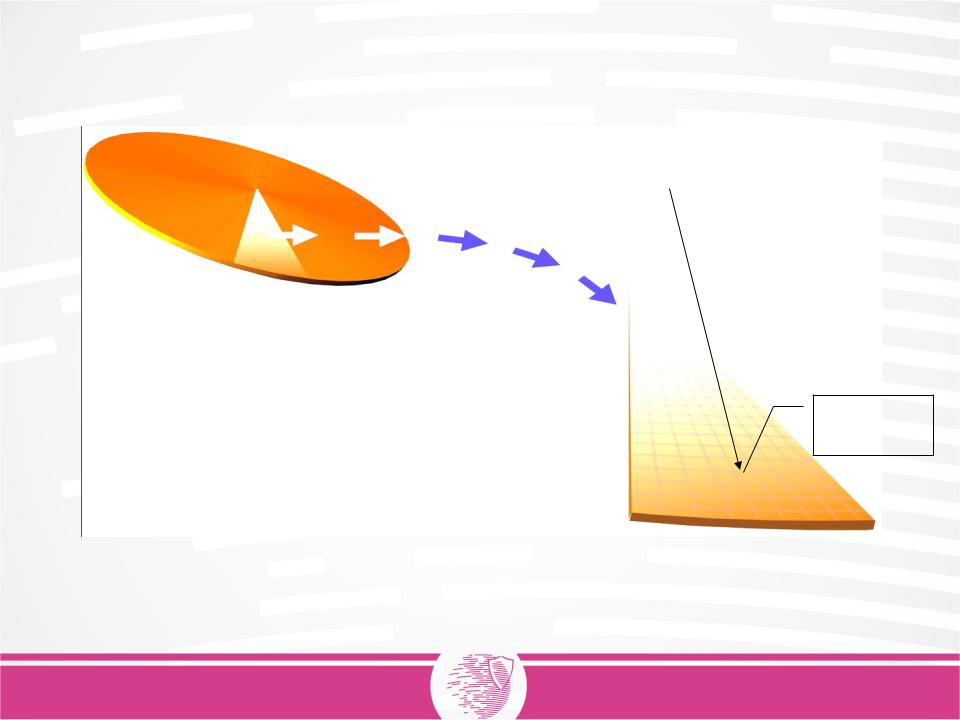
Cluster
One sector = 512 bytes
A Cluster is the smallest addressable unit in a volume.
It can have the size of a sector
=> 1 sector per cluster
It can also contain 2 or more sectors
=> 2 to max. 64 sectors per cluster
The number of sectors per cluster is stored in the bootblock (VBR)
512
Number sectors in cluster = 2N
8
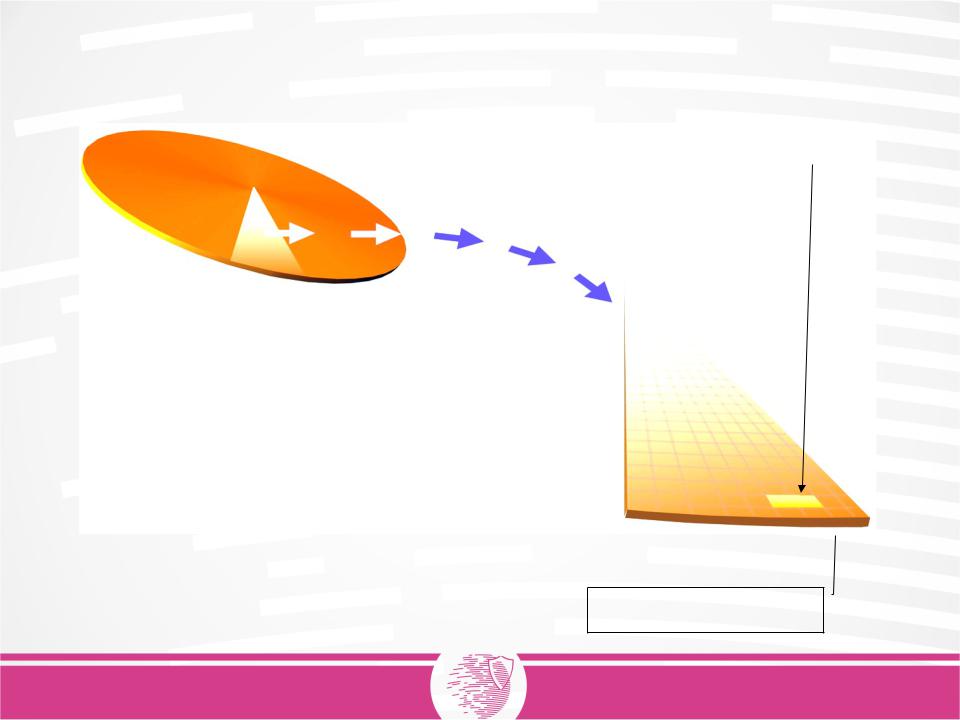
Cluster
2 sectors per cluster = 1024 Bytes
A Cluster is the smallest addressable unit in a volume.
It can have the size of a sector
=> 1 sector per cluster
It can also contain 2 or more sectors
=> 2 to max. 64 sectors per cluster
The number of sectors per cluster is stored in 1024 byte cluster the bootblock (VBR)
9

FAT 12
•12 bit FAT means, that the FAT entry is a 12 Bit- value!
•With 12 bits the max. value will be 2^12
2 12 = 4096
•The total number of addressable allocation units is 4096
•allocation unit = cluster
3

FAT 16
•16 bit FAT means, that the FAT entry is a 16 Bit- value!
•With 16 bits the max. value will be 2^16
2 16 = 65536
•The total number of addressable allocation units is 65536
•allocation unit = cluster
4

FAT 32
•32 bit FAT means, that the FAT entry is a 32 Bit-value!
•The FAT 32 file system reserves 4 bits for itself, so that only 28 bits are left for cluster addresses
•With 28 bits the max. value will be 2^28
2 28 = 268435456
•The total number of addressable allocation units is 268435456
•allocation unit = cluster
5
