
- •The project has been funded by the European Commission. The Education, Audiovisual and
- •Registry Description
- ••what kind of information is actually stored there?
- •Registry Information
- •Registry’s Structure
- •Physically, Windows organizes the registry as hives stored in binary files. In addition,
- •Registry root keys:
- •HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE
- •HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE -HKML
- •HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE -HKML
- •And what about user data?
- •NTUSER.DAT location in Windows XP
- •NTUSER.DAT location in Windows 7
- •Registry Files Examination
- •Getting information about connected USB devices
- •When a removable USB device (for example, a flash drive) is connected to
- •Keys are created in this registry branch, each of which represents its own
- •To get the time of the last USB device connection, you should take
- •System Information
- •Getting information about connecting network cards
- •Network Neighborhood Information
- •Additional information may be found in the following key of the hive
- •Wireless network
- •Detailed information can be obtained by linking these identifiers with signatures from the
- •The summary data contains the following important information:
- •Use DCode-v4.02a-build-4.02.0.9306 to translate the date and time format
- •RESTORE POINTS vs. VOLUME SHADOW COPY
- •RESTORE POINTS vs. VOLUME SHADOW
- •RESTORE POINTS (Windows XP)
- •RESTORE POINTS (Windows 7)
- •RESTORE POINTS (Windows XP)
- •VOLUME SHADOW COPY
- •USER PROFILES
- •Which Version ?
- •Application Data
- •Application Data (subfolders)
- •SUMMARY

And what about user data?
•Each user of the system has their own user file
– NTUSER.DAT
•Different path for WINDOWS XP and 7 OS
•Hidden system files
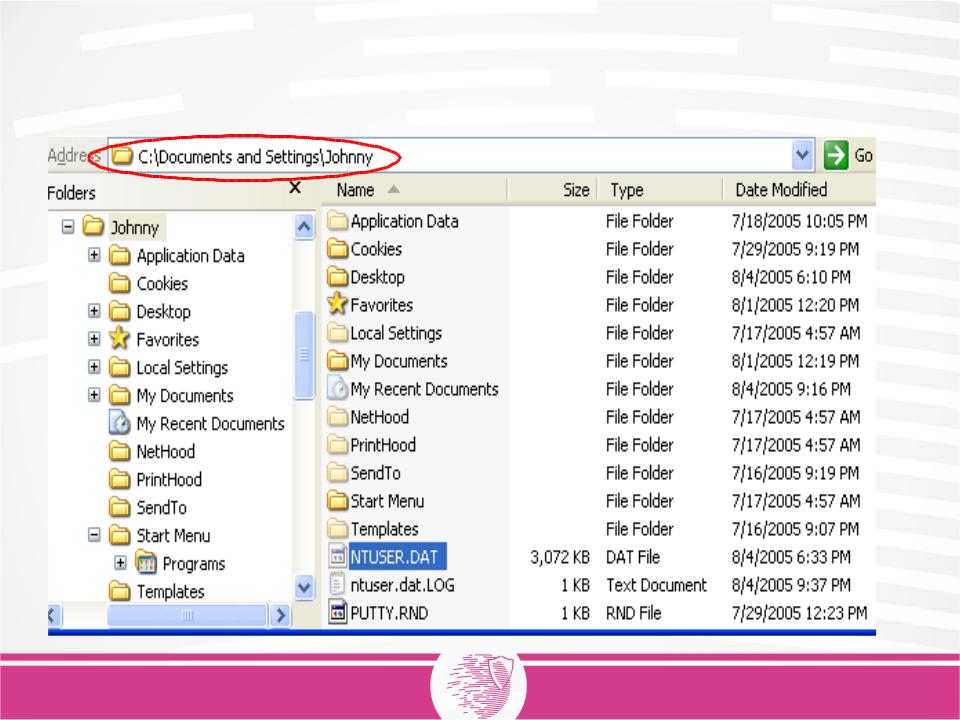
NTUSER.DAT location in Windows XP
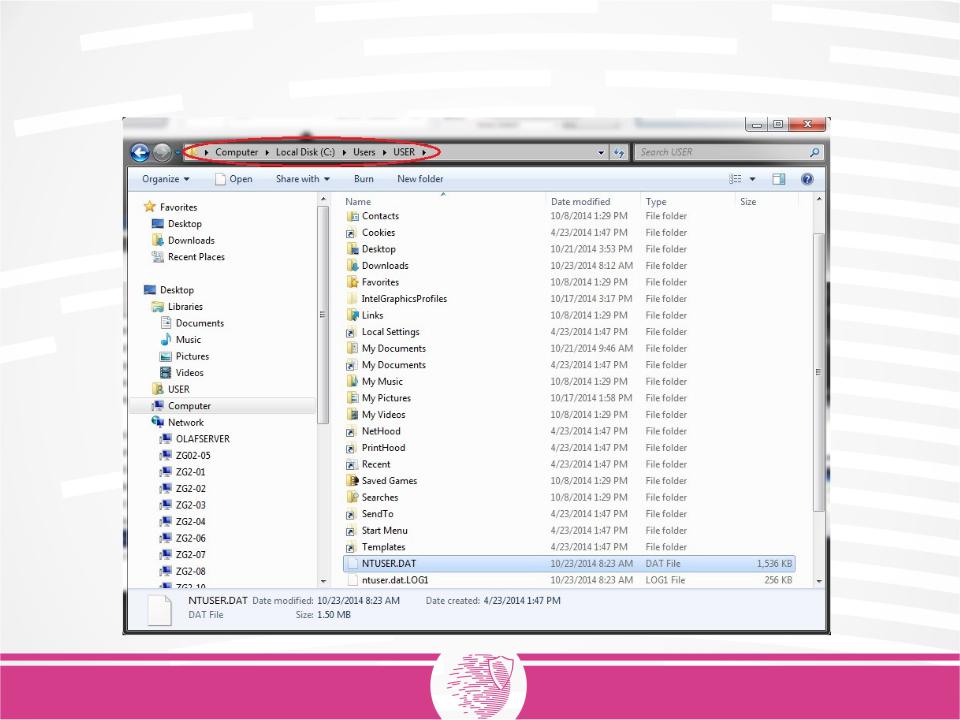
NTUSER.DAT location in Windows 7

Registry Files Examination
•Free Tools
–AccessData Registry Viewer
–MiTEC Windows Registry Recovery
–Registry Browser
–RegReport (automatically creates reports of information)
•https://ad-pdf.s3.amazonaws.com/Registry_Quick_Find_Chart_9- 27-10.pdf
•Find Registry Offsets (e.x. AccessData FTK Imager)
•https://ad-pdf.s3.amazonaws.com/Registry%20Offsets%209-8- 08.pdf

Getting information about connected USB devices
Analysis of the connected devices can give the researcher information about the media ever connected to the system. Such information may be useful, for example, in the case of investigating a data breach.
The expert needs to know which USB devices have been worked with, as well as the identifiers of these devices for matching with existing data.
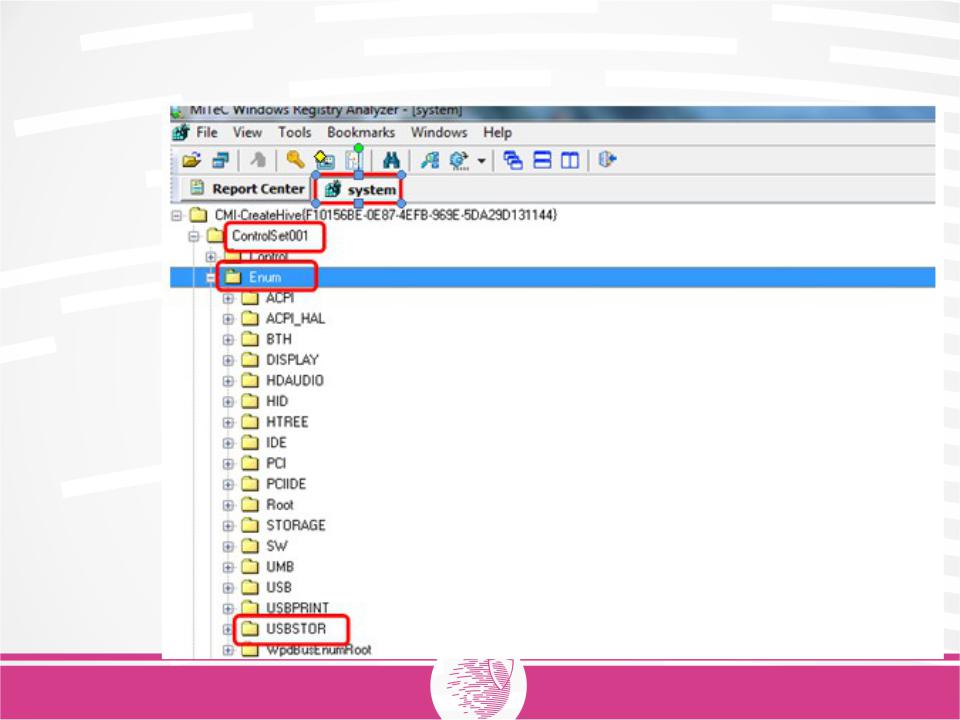
When a removable USB device (for example, a flash drive) is connected to a PC, information about it will be saved in HKLM> System> ControlSet00x> ENUM> USBSTOR.
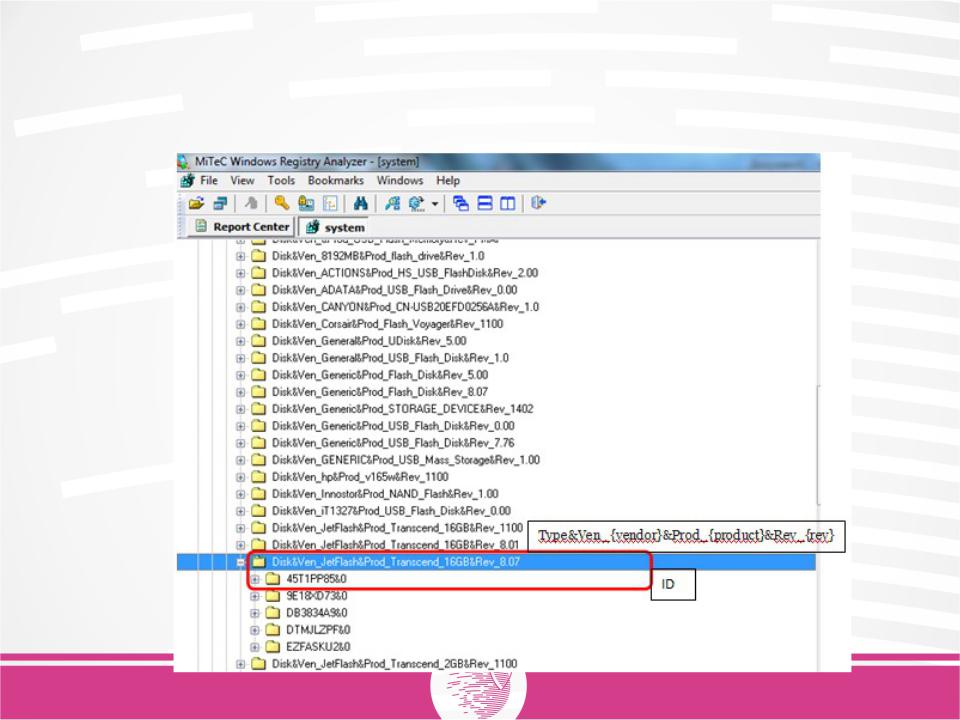
Keys are created in this registry branch, each of which represents its own class of devices. The key name is in the following format:
Type & Ven_ {vendor} & Prod_ {product} & Rev_ {rev}.
These keys create subkeys that represent the device instance. The subkey number is the serial number of the device.
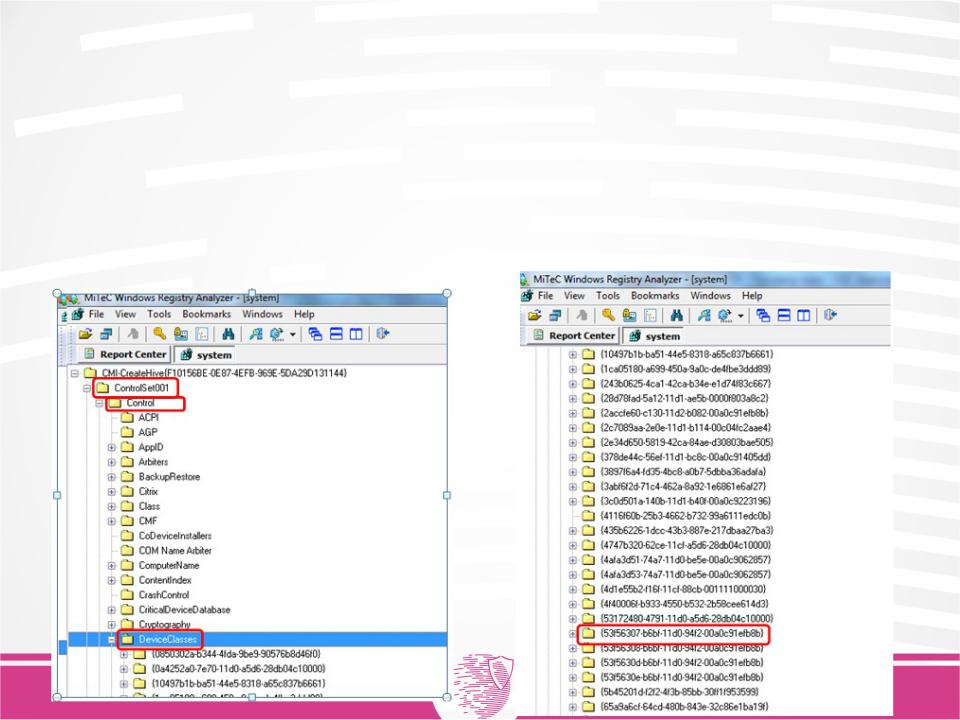
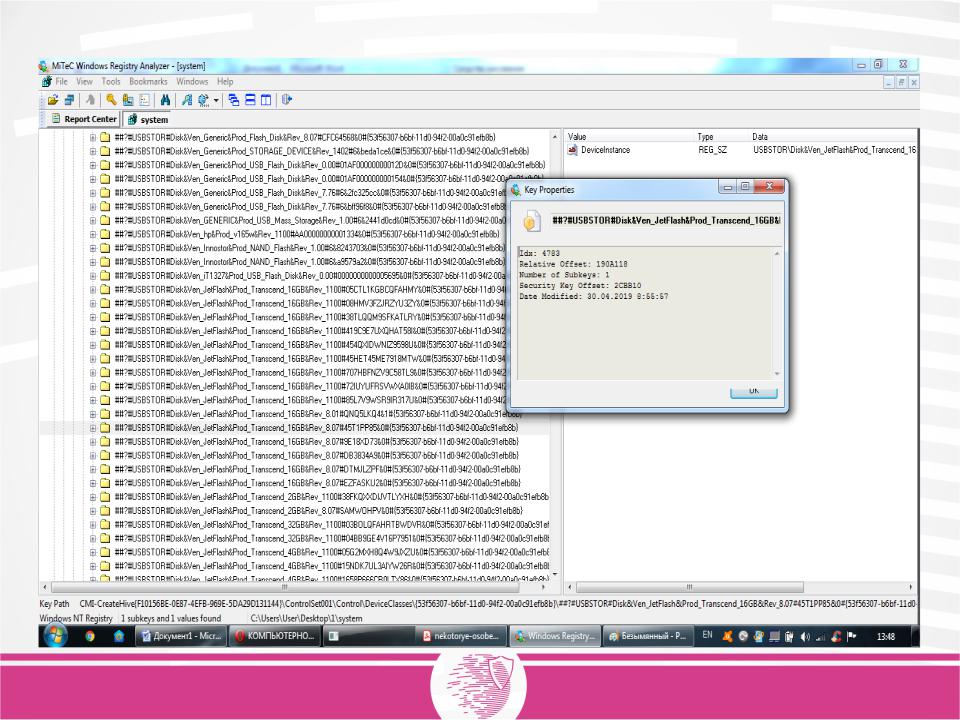
To get the time of the last USB device connection, you should take the timestamp of one of the dongle keys SYSTEM \ ControlSet00x \ Control \ DeviceClasses \ {53f56307-b6bf-11d0-94f2-00a0c91efb8b} \.
The subkey is searched for by the name, which should contain the serial number of the USB device for which you need to determine the date of the last connection.
It is established that the system stores a complete list of USB devices that have ever connected to the system.
System Information
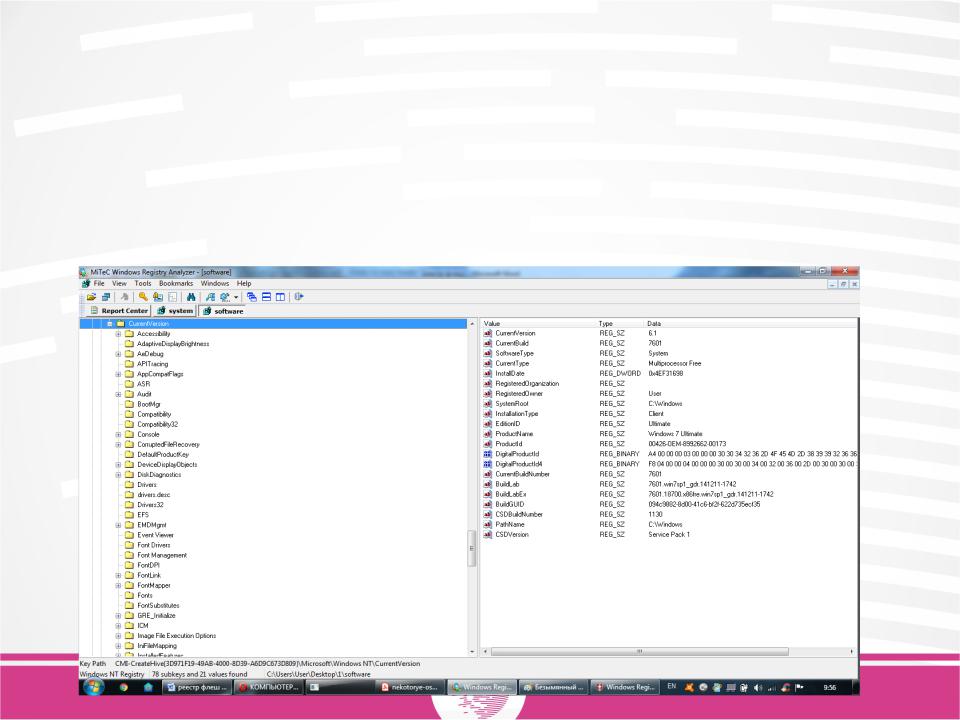
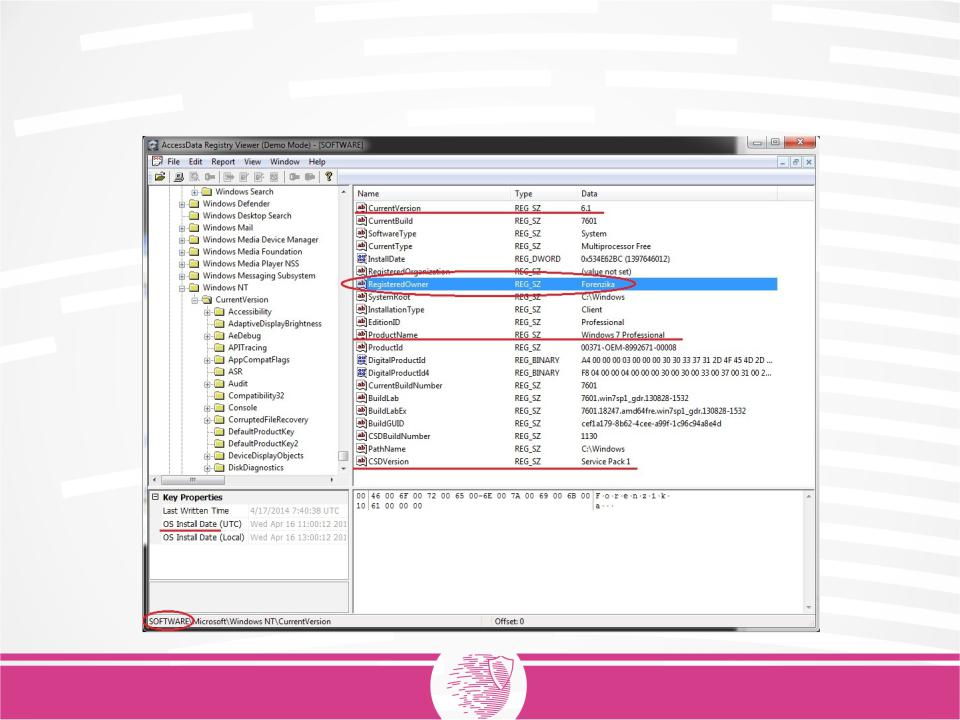
The values of the key "SOFTWARE \ Microsoft \ Windows NT \ CurrentVersion" store various parameters of the operating system:
version, edition, build number, information about the service pack and so on.
In addition, registration information is stored in this section, which can be useful when analyzing cases of unlicensed software use.
•HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SOFTWARE\ Microsoft\Windows NT\CurrentVersion

•HKEY_CURRENT_USER\Software\Microsoft\Windows\ CurrentVersion\Explorer\UserAssist
Free tool: http://www.nirsoft.net/utils/userassist_view.html
