
- •In accordance with the modern rule of transfusiology, it is necessary to transfuse only one-group (according to the ab0 system) and single-rhesus blood.
- •Determination of blood group and Rh factor Determination of blood groups by standard isohemagglutinating sera
- •Intravenous blood transfusion
- •Infiltration anesthesia according to a.V. Vishnevsky combines the positive qualities of infiltration and conduction anesthesia.
- •Intravenous anesthesia
- •Intraosseous anesthesia
- •Intravenous anesthesia
- •Inhalation anesthesia
- •Vomiting, regurgitation
Inhalation anesthesia
Inhalation anesthesia is achieved with the help of easily evaporating (volatile) liquids (halothane, isoflurane, etc.) or gaseous narcotic substances (dinitrogen oxide).
Halothane - colorless liquid with a sweetish odor. The boiling point is 50.2 ° C. The preparation is highly soluble in fats. Stored in dark vials, non-explosive. It has a powerful narcotic effect: the introduction of anesthesia is very quick (3-4 minutes), the stage of arousal is absent or weak, awakening occurs quickly. The transition from one stage of anesthesia to another is quick, and therefore an overdose of the drug is possible. Acting on the body, halothane inhibits cardiovascular activity, leads to a slowdown in the heart rate and a decrease in blood pressure. The drug is toxic to the liver, but does not irritate the respiratory tract, dilates the bronchi, and therefore can be used in patients with respiratory diseases. It increases the sensitivity of the heart muscle to epinephrine and norepinephrine, therefore, these drugs should not be used against the background of halothane anesthesia.
Diethyl ether, chloroform, cyclopropane are not used in modern anesthesiology.
Isoflurane is a colorless liquid that does not decompose under light. Also applies to fluoride anesthetics. The surgical level of anesthesia can be maintained with 1–2.5% of the drug in an oxygen-dinitrogen oxide mixture. It potentiates the action of all muscle relaxants. With spontaneous ventilation, it causes dose-dependent respiratory depression. The use of the drug in anesthetic concentration leads to a slight decrease in cardiac output, while there is a slight increase in heart rate. Isoflurane less than other fluorine-containing anesthetics sensitizes the myocardium to catecholamines. In small concentrations, it does not affect blood loss during cesarean section, and therefore it is widely used in obstetrics. When using the drug, even with prolonged anesthesia, no cases of toxic effects on the liver and kidneys have been recorded.
Sevoflurane was recently registered in Russia, but it has been used in the USA, Japan and the EU countries for about 10 years. Anesthesia is more manageable, introductory mask anesthesia is possible, which is convenient in pediatrics and outpatient practice. No toxic reactions have been described when using the drug.
Dinitrogen oxide is a “laughing gas”, colorless, odorless, non-explosive, but in combination with diethyl ether and oxygen it supports combustion. The gas is stored in gray metal cylinders, where it is in a liquid state under a pressure of 50 atm. Dinitrogen oxide is an inert gas, it does not interact with any organs and systems in the body, it is released by the lungs unchanged. For anesthesia
80
dinitrogen oxide is used only in combination with oxygen, in its pure form it is toxic. The following ratios of dinitrogen oxide and oxygen are used: 1: 1; 2: 1; 3: 1; 4: 1. The latter ratio is 80% dinitrogen oxide and 20% oxygen. A decrease in the oxygen concentration in the inhaled mixture below 20% is unacceptable, as this leads to severe hypoxia. Under the influence of dinitrogen oxide, the patient quickly and calmly falls asleep, bypassing the stage of excitement. Awakening occurs immediately as soon as the supply of dinitrogen oxide stops. The lack of dinitrogen oxide is its weak narcotic effect, even in the highest concentration (80%) it gives superficial anesthesia. There is no muscle relaxation. Against the background of anesthesia with dinitrogen oxide, small, low-traumatic surgical interventions can be performed.
Muscle relaxants Muscle relaxants: short-acting (suxamethonium chloride, mivacuria chloride), relaxation time 5-20 minutes, medium-acting (20-35 minutes) - atracuria benzylate, rocuronium bromide; long-acting (40-60 min) - pipcuronium bromide.
Anesthesia machines
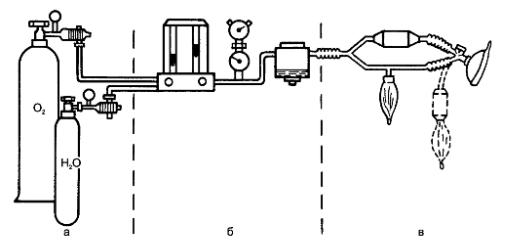
To carry out inhalation anesthesia with volatile and gaseous narcotic substances, special devices are used - anesthesia machines. The main units of the anesthesia apparatus: 1) cylinders for gaseous substances (oxygen, dinitrogen oxide); 2) dosimeters and vaporizers for liquid narcotic substances (for example, halothane); 3) breathing circuit (Fig. 21). Oxygen is stored in blue cylinders under a pressure of 150 atm. To reduce the pressure of oxygen and dinitrogen oxide at the outlet from the cylinder, reducers are used that reduce it to 3-4 atm. Vaporizers are intended for liquid narcotic substances and represent a can into which a narcotic substance is poured. The vapors of the narcotic substance are directed through the valve into the circuit of the anesthesia machine, the concentration of the vapors depends on the ambient temperature. Dosage, especially diethyl ether is carried out inaccurately, in conventional units. Currently, vaporizers with a temperature compensator are common, which allows you to dose the narcotic substance more accurately - in volume percent. Figure: 21. Anesthesia apparatus (diagram): a - cylinders with gaseous substances; b - unit of dosimeters and evaporators; c - the respiratory system.
Dosimeters are designed for accurate dosage of gaseous drugs and oxygen. Rotational dosimeters are more often used - float-type rotameters. The gas flow inside the glass tube rushes upwards. The displacement of the float determines the minute gas flow rate in liters (l / min).
The breathing circuit consists of a breathing bellows, bag, hoses, valves, adsorber. The narcotic substance from the dosimeter and the evaporator is directed to the patient along the respiratory circuit, and the air exhaled by the patient is directed to the apparatus.
The narcotic breathing mixture is formed in the anesthesia machine by mixing gases or vapors of narcotic substances with oxygen.
Oxygen, passing through the dosimeter, is mixed in a special chamber with dinitrogen oxide, cyclopropane, which also passed through the dosimeter, in certain ratios required for anesthesia. When liquid drugs are used, the mixture is formed by passing oxygen through the vaporizer. Then it enters the respiratory system of the apparatus and further into the patient's respiratory tract. The amount of the incoming narcotic mixture should be 8-10 l / min, of which oxygen - at least 20%. The ratio of narcotic gases and exhaled air to atmospheric air can be different. Depending on this, there are four modes of circulation (breathing circuits).
1. Open way (contour). The patient inhales a mixture of atmospheric air that has passed through the vaporizer of the anesthesia apparatus, and exhales into the surrounding atmosphere of the operating room. With this method, there is a high consumption of narcotic substances and their pollution of the operating room air, which is breathed by all the medical personnel involved in the operation.
2. Semi-open way (contour). The patient inhales a mixture of oxygen with a narcotic substance from the apparatus and exhales it into the atmosphere of the operating room. This is the safest breathing circuit for the patient.
3. Semi-closed method (contour). Inhalation is carried out from the apparatus, as in the half-open method, and exhalation is carried out partly into the apparatus, and partly into the atmosphere of the operating room. The mixture exhaled into the apparatus passes through the adsorber, where it is freed from carbon dioxide, enters the respiratory system of the apparatus and, mixing with the resulting narcotic mixture, again enters the patient.
4. The closed method (circuit) provides for inhalation and exhalation, respectively, from the apparatus to the apparatus. Inhaled and exhaled gas mixtures are completely isolated from the environment. The exhaled gas-narcotic mixture, after being freed from carbon dioxide in the adsorber, again goes to the patient, combining with the newly formed narcotic mixture. This type of anesthesia circuit is economical and environmentally friendly. Its disadvantage is the danger of hypercapnia for the patient in case of an untimely change of the chemical absorber or its poor quality (the absorber must be changed after 40 minutes - 1 hour of operation).
Inhalation anesthesia Inhalation anesthesia can be performed using mask, endotracheal and endobronchial methods. First of all, you should prepare the anesthesia machine for work. To do this, you must: 1) open the valves of cylinders with oxygen and dinitrogen
oxide; 2) check the presence of gas in the cylinders according to the readings of the pressure reducer; 3) connect the cylinders to the apparatus using hoses; 4) if anesthesia is carried out with liquid volatile narcotic substances (for example, halothane), pour them into vaporizers; 5) fill the adsorber with a chemical absorber; 6) ground the device; 7) check the tightness of the device.
Mask anesthesia To carry out mask anesthesia, the doctor stands at the patient's head and puts a mask on his face. With the help of straps, the mask is fixed on the head. Fixing the mask with your hand, press it tightly to your face. The patient takes several breaths of air through the mask, then it is attached to the apparatus. Oxygen is allowed to inhale for 1-2 minutes, and then the drug is supplied. The dose of the narcotic substance is increased gradually, slowly. At the same time oxygen is supplied at a rate of at least 1 l / min. At the same time, the anesthesiologist constantly monitors the patient's condition and the course of anesthesia, and the nurse monitors the blood pressure and pulse. The anesthesiologist determines the position of the eyeballs, the state of the pupils, the presence of a corneal reflex, the nature of breathing. Upon reaching the surgical stage of anesthesia, the increase in the supply of the narcotic substance is stopped.1 -III 2 ). If the anesthesia was deepened to stage III 3 , it is necessary to bring the patient's lower jaw forward.
To do this, press the corner of the lower jaw with your thumbs and move it anteriorly until the lower incisors are in front of the upper ones. In this position, hold the lower jaw III, IV and V fingers. Tongue sinking can be prevented by using air ducts that hold the tongue root. It should be remembered that during anesthesia at stage III 3 there is a danger of an overdose of the narcotic substance.
At the end of the operation, the drug supply is turned off, the patient breathes oxygen for several minutes, and then the mask is removed from his face. After finishing the work, close all the valves of the anesthesia machine and balloons. The remains of liquid narcotic substances are drained from the evaporators. The hoses and bag of the anesthesia machine are removed and sterilized in an antiseptic solution.
Disadvantages of mask anesthesia
1. Difficult handling. 2. Significant consumption of narcotic drugs. 3. The risk of developing aspiration complications. 4. Toxicity due to the depth of anesthesia.
Endotracheal anesthesia
With the endotracheal method of anesthesia, the narcotic substance enters the body from the apparatus through a tube inserted into the trachea. The advantages of the method are that it provides free airway and can be used for operations on the neck, face, head; the possibility of aspiration of vomit is excluded,
83
blood; the amount of drug used is reduced; gas exchange is improved by reducing the "dead" space.
Endotracheal anesthesia is indicated for major surgical interventions, it is used in the form of multicomponent anesthesia with muscle relaxants (combined anesthesia). The combined use of several drugs in small doses reduces the toxic effects on the body of each of them. Modern combined anesthesia is used for analgesia, switching off consciousness, relaxation. Analgesia and switching off consciousness are achieved by using one or more narcotic substances - inhaled or non-inhaled. Anesthesia is carried out at the first level of the surgical stage. Muscle relaxation (relaxation) is achieved by fractional administration of muscle relaxants. There are three stages of anesthesia.
Stage I - introduction to anesthesia. Introductory anesthesia can be performed with any narcotic substance that provides a sufficiently deep anesthetic sleep without arousal stage. Barbiturates are mainly used, and sodium thiopental is often used. The drugs are administered intravenously in the form of a 1% solution, at a dose of 400-500 mg (but not more than 1000 mg). Against the background of induction of anesthesia, muscle relaxants are used and tracheal intubation is performed.
Stage II - maintenance of anesthesia. To maintain general anesthesia, you can use any narcotic agent that can create protection for the body from surgical trauma (halothane, dinitrogen oxide with oxygen), as well as NLA. Anesthesia is maintained at the first or second level of the surgical stage (III 1 -III 2 ), and to eliminate muscle tension, muscle relaxants are introduced, which cause myoplegia of all groups of skeletal muscles, including respiratory. Therefore, the main condition for the modern combined method of anesthesia is mechanical ventilation, which is carried out by rhythmic compression of a bag or fur using an artificial respiration apparatus.
The use of NLA involves the use of dinitrogen oxide with oxygen, fentanyl, droperidol, muscle relaxants. Intravenous induction anesthesia. Anesthesia is maintained by inhalation of dinitrogen oxide with oxygen in a 2: 1 ratio, fractional intravenous administration of fentanyl and droperidol - 1-2 ml every 15-20 minutes. With an increase in heart rate, fentanyl is administered, with an increase in blood pressure - droperidol. This type of anesthesia is safer for the patient. Fentanyl enhances pain relief, droperidol suppresses autonomic reactions.
Stage III - removal from anesthesia. By the end of the operation, the anesthesiologist gradually stops the administration of drugs and muscle relaxants. Consciousness returns to the patient, spontaneous breathing and muscle tone are restored. The criterion for assessing the adequacy of spontaneous breathing is the indicators pO 2 , pCO 2 , pH. After awakening, restoration of spontaneous breathing and skeletal muscle tone, the anesthesiologist can extubate the patient and transfer him for further observation in the recovery room.
Benefits of combined endotracheal anesthesia
1. Rapid introduction to anesthesia, no arousal stage.
2. Possibility to operate in the stage of analgesia or stage III 1
3. Reducing the consumption of narcotic drugs, reducing the toxicity of anesthesia. 4. Easy manageability of anesthesia. 5. Prevention of aspiration and the possibility of sanitation of the trachea and bronchi.
Methods for monitoring the conduct of anesthesia
In the course of general anesthesia, the main parameters of hemodynamics are constantly determined and evaluated. Blood pressure is measured, pulse rate is determined every 10-15 minutes. In persons with diseases of the heart and blood vessels, as well as during thoracic operations, it is especially important to constantly monitor cardiac activity.
Electroencephalographic observation can be used to determine the level of anesthesia. To control ventilation of the lungs and metabolic changes during anesthesia and surgery, it is necessary to conduct a study of the acid-base state
(pO 2 , pCO 2 , pH, BE). Criteria for the adequacy of anesthesia
1. Absence of tachycardia and stable blood pressure.
2. Normal color and natural dryness of the skin.
3. Urine flow - 30-50 ml / h.
4. Normal blood oxygen saturation and CO 2 content .
5. Normal ECG readings.
The deviation of the listed indicators within 20% of the initial level is considered acceptable. During anesthesia, the nurse maintains an anesthetic chart of the patient, in which the main indicators of homeostasis must be recorded: pulse, blood pressure, central venous pressure (CVP), respiratory rate, ventilation parameters. This map reflects all stages of anesthesia and surgery, indicates the doses of drugs and muscle relaxants, notes all drugs used during anesthesia, including transfusion media. The time of all stages of the operation and the administration of drugs is recorded. At the end of the operation, the total amount of all drugs used is determined and also recorded in the anesthesia card. All complications during anesthesia and surgery are recorded. The anesthetic card is included in the medical history.
Complications of anesthesia
Complications during anesthesia can be associated with the technique of anesthesia or the effect of anesthetics on vital organs.
