
- •In accordance with the modern rule of transfusiology, it is necessary to transfuse only one-group (according to the ab0 system) and single-rhesus blood.
- •Determination of blood group and Rh factor Determination of blood groups by standard isohemagglutinating sera
- •Intravenous blood transfusion
- •Infiltration anesthesia according to a.V. Vishnevsky combines the positive qualities of infiltration and conduction anesthesia.
- •Intravenous anesthesia
- •Intraosseous anesthesia
- •Intravenous anesthesia
- •Inhalation anesthesia
- •Vomiting, regurgitation
Infiltration anesthesia according to a.V. Vishnevsky combines the positive qualities of infiltration and conduction anesthesia.
Anatomically, the method is based on the structural features of fascial formations. A solution of anesthetic substance, injected under pressure into these cases, spreads into them and penetrates to the nerves and nerve endings. Tight procaine infiltrates move (crawl) along the cases and merge with each other, which is why A.V. Vishnevsky called his method of anesthesia the creeping infiltrate method.
Anesthesia is carried out by the surgeon during the operation, using alternately, as the tissue layer is dissected, a syringe and a scalpel.
Infiltration of tissues must be carried out before opening the case, since if the latter is cut or accidentally damaged, the solution of the anesthetic substance will pour out into the wound, as a result of which it will be impossible to create a dense creeping infiltrate, which means that it will be impossible to achieve a sufficient anesthetic effect. Tight infiltration of tissues with an anesthetic solution carries out a hydraulic preparation of tissues, vessels and nerves are easily identified in the infiltrate, which avoids their damage, facilitates stopping bleeding. For infiltration anesthesia, use 0.25% solutions of procaine or lidocaine with the addition of epinephrine (3 drops of 1: 1000 epinephrine solution per 100 ml of anesthetic solution). For case anesthesia, a large amount of solution is consumed (up to 800 and even 1000 ml),
An example is pain relief during thyroid surgery. For anesthesia, use 2 syringes (2 and 5 ml or 5 and 10 ml). To numb the skin, an anesthetic solution is injected with a thin needle intradermally, creating a "lemon peel" nodule along the entire skin incision line (Fig. 10). Each injection is made at the edge of the nodule formed by the previous injection. Procaine is injected into the subcutaneous tissue through the infiltrated skin. Sufficient infiltration of the subcutaneous tissue is determined by raising the entire incision area in the form of a roller.
After dissecting the skin, subcutaneous tissue and subcutaneous muscle of the neck, the anesthetic solution is injected along the midline, infiltrating the muscles, and then under the muscles in the upward, downward and sideways direction.
The injection of procaine under the muscles leads to its spreading under the middle layer of the fascia of the neck, while it covers the thyroid gland in the form of a sheath.
After dissection of the neck muscles and dislocation of the thyroid lobe into the wound, additional infiltration with an anesthetic solution of tissues is performed at the upper and lower poles of the gland and along its posterior surface.
64
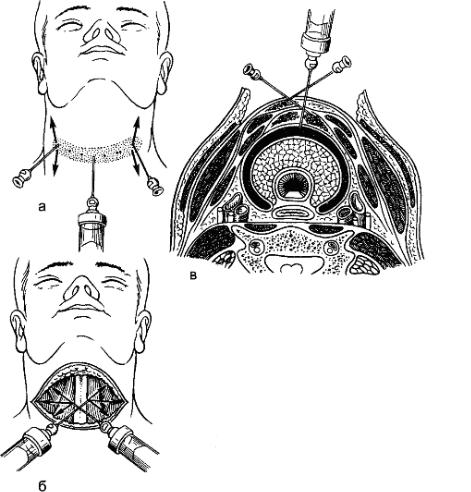 Figure: 10. Infiltration
anesthesia for resection of the thyroid gland: a - anesthesia of the
skin and subcutaneous tissue along the incision line ("lemon
peel"); b - the introduction of procaine under the muscles
of the neck; c - creeping infiltrate surrounding the thyroid
gland
Figure: 10. Infiltration
anesthesia for resection of the thyroid gland: a - anesthesia of the
skin and subcutaneous tissue along the incision line ("lemon
peel"); b - the introduction of procaine under the muscles
of the neck; c - creeping infiltrate surrounding the thyroid
gland
Regional anesthesia
Regional anesthesia is performed to numb a specific topographic area or part of the body. There are the following types of regional anesthesia: conduction, intravascular (intravenous, intra-arterial), intraosseous, spinal, epidural, etc.
Conductive anesthesia
It is divided into the following types: anesthesia of the nerve trunks, anesthesia of the nerve plexuses, anesthesia of the nerve nodes (paravertebral), spinal and epidural (epidural) anesthesia. The anesthetic is administered peri or endoneurally.
Finger conduction anesthesia according to Lukashevich-Oberst is used for finger operations (for panaritiums, wounds, tumors). A rubber tourniquet is applied to the base of the finger, distal to which, on the back surface of the main phalanx, the skin and subcutaneous tissue are anesthetized, and then the needle is advanced to the bone (Fig. 11). After that, the needle is first moved to one side of the bony phalanx and
65
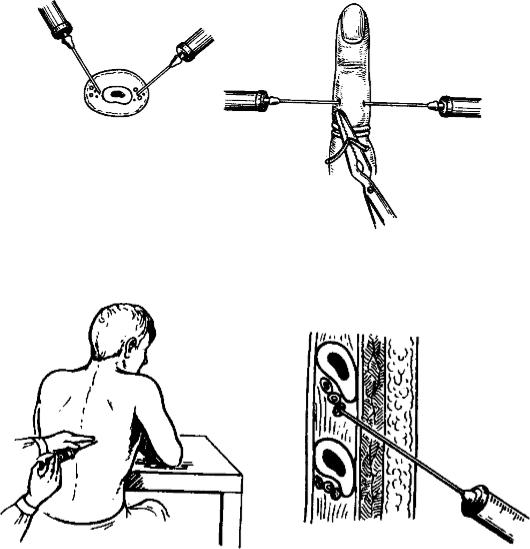
2-3 ml of 1-2% solution of procaine or lidocaine is injected, then the other side is anesthetized with the same amount of procaine. Thus, procaine is injected into
close proximity to the nerves of the finger, which run along its lateral surface.Figure: 11. Conduction anesthesia according to Lukashevich-OberstFigure: 12. Intercostal anesthesia.
Intercostal anesthesia is used for rib fractures. Having retreated a few centimeters from the site of the rib fracture towards the spine, the skin is anesthetized by intradermal injection of a solution of procaine from a syringe with a needle (Fig. 12). A needle is injected perpendicular to the broken rib at the site of skin anesthesia, and when it is advanced until it stops, procaine is slowly injected into the rib. Pulling the needle by 2-3 mm, its end is displaced by soft tissues, the needle is advanced to the lower edge of the rib, sliding along its surface, and 3-5 ml of 1-2% solution of procaine, lidocaine is injected perineurally. Without removing the needle, return it to the outer surface of the rib, advance it by sliding to its upper edge and inject 2-3 ml of a 1-2% solution of procaine or lidocaine, after which the needle is removed. If several ribs are broken, the procedure is repeated.
Anesthesia of the brachial plexus according to Kulenkampf is used in operations on the upper limb. The position of the patient is on the back, the head is turned in
66
+
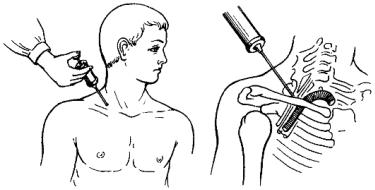
opposite side, the hand hangs freely from the table. In the middle of the clavicle along its upper edge, the projection of the subclavian artery is determined. The brachial plexus is projected outward from the subclavian artery. After infiltration of the skin with a solution of procaine, a long needle without a syringe is inserted outward from the place of pulsation of the artery 1 cm above the clavicle and, sliding along the upper edge of the I rib, is advanced upwards in the direction of the spinous processes of the I and II thoracic vertebrae (Th I-II) and reach the plexus (Fig. 13). The appearance of unpleasant sensations in the hand, a feeling of numbness or a sensation of "shooting" pain indicates the meeting of the needle with one of the nerve trunks of the plexus. The release of blood from the needle indicates that it has entered the vessel. In such cases, the needle is somewhat pulled back and the direction of its stroke is changed. After making sure that no blood is released from the needle, 30-35 ml of a 1% solution of procaine or lidocaine is injected. Anesthesia occurs in 10-15 minutes and lasts for 2-6 hours.Figure: 13. Anesthesia of the brachial plexus according to Kulenkampf.
Intra-abdominal anesthesia of the celiac nerves according to Brown is used as an adjunct to local infiltration anesthesia during gastric resection. After laparotomy, the left lobe of the liver is removed with a hook upward and to the right, and the stomach - left and downward. In the area of the lesser omentum, the index finger of the left hand probes the pulsation of the aorta above the discharge of the celiac artery and rests the finger against the spine to the right of the aorta. Thus, the finger is located between the aorta and the inferior vena cava. For anesthesia, use a long needle attached to a syringe with 0.5% procaine solution. The needle is passed over the finger of the left hand until it stops at Th XII and then pulled back a little. By pulling the plunger of the syringe, make sure that no blood is flowing, and inject into
fiber 50-70 ml of a 0.5% solution of procaine or lidocaine, which is distributed in the retroperitoneal space and washes the solar plexus. Anesthesia occurs in 5-10 minutes and lasts 1.5-2 hours.
procaine. The latter spreads through the retroperitoneal tissue, washing the renal, adrenal, solar plexus and celiac nerves.Figure: 16. Lumbar perirenal procaine blockade.
