- •Лекция 3 Лекция 3
- •Иммунный ответ на острую вирусную инфекц
- •Гуморальный иммунный ответ
- •Четыре фазы первичного гуморального о
- •Стадии активации и развития В-клето
- •Кооперация клеток при образовании ант
- •Источники разнообразия антител
- •Реорганизация иммуноглобулиновых гено в процессе дифференцировки В-клеток
- •СтроениеСтроениеIgGIgG
- •Рекомбинация генов, кодирующих тяжелые цепи иммуноглобулинов
- •Рекомбинация генов, кодирующих-цепи иммуноглобулинов
- •Рекомбинация генов, кодирующих-цепи иммуноглобулинов
- •Классы и подклассы иммуноглобулинов у чело
- •Биологическое значение синтеза
- •Классы и подклассы иммуноглобулинов у чело
- •Пространственное объединение гипервариабельных участков V-домена тяжелой цепи IgG человека (миеломного белка New)
- •Связывание и узнавание антигена
- •Идиотипы, антиидиотипы и их сет
- •Пример взаимодействия антигенсвязывающей области (активного центра) иммуноглобулина с антигеном — витамином K1OH
- •ФункцииФункцииIgGIgG
- •ФункцииФункцииIgGIgG
- •Структура IgM человека
- •Функции и строение IgM
- •ФункцииФункцииIgMIgM
- •Созревание» (maturation) иммунного ответ и переключение (switch-over) изотипа
- •Первичный и вторичный гуморальные от
- •Особенности структуры молекул
- •Строение молекулы секреторного I
- •Функции иммуноглобулинов класса A
- •Структура и функции
- •Структура и функции
- •Структура и функции
- •ЧетыреЧетыретипатипареакцийреакцийгиперчувствительнгиперчувствитель
- •ВоспалительнаяВоспалительнаяреакцияреакцияввбронхахбронхахприприа
- •ВоспалительнаяВоспалительнаяреакцияреакцияввбронхахбронхахприприа
- •Функции антител в антимикробной защ
- •Антитела и НК
- •Противовирусное действие антител
- •Противовирусное действие антител
- •Толерантность
- •Paul Ehrlich
- •Magic bullet
- •No drug selection
- •Реконструированные (engineered или reconbinant) антитела
- •Monoclonal Antibodies Have Moderate
- •Elements of an
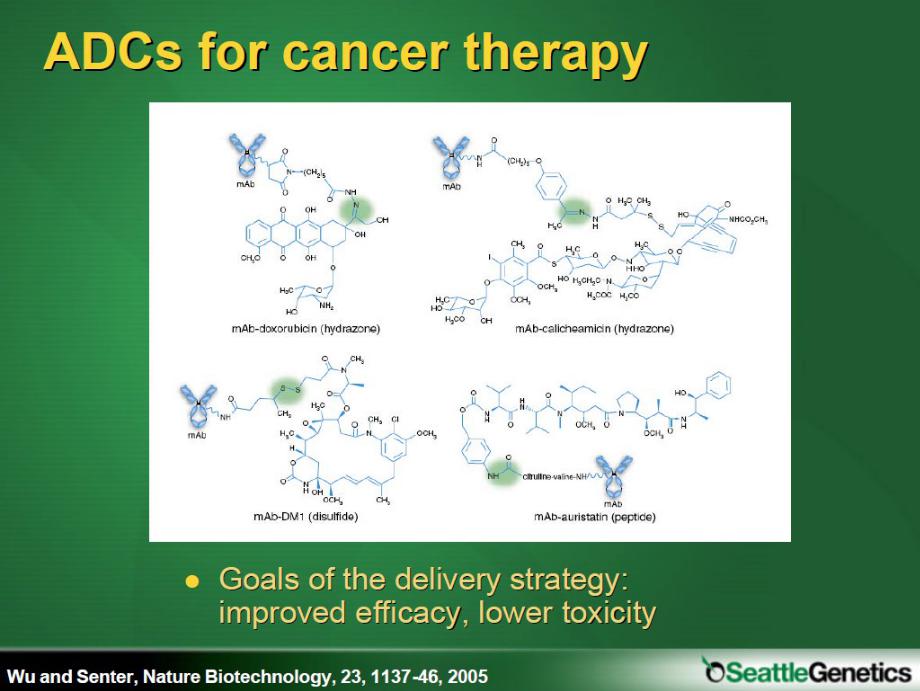
- •Rationale for ADCs:
- •Target Antigen Should Be Abundantly Expressed on Tumor Cells Compared to Healthy Cells
- •Primary Mechanism of Action of ADCs: Targeted Delivery of a Cytotoxic Agent
- •Other Potential ADC Antitumor Activities
- •Limitations of Early ADC Technology1-3
- •Next-Generation ADCs:
- •Next-Generation ADCs: Designed to be Stable in Circulation and Release a Cytotoxic Agent
- •As Demonstrated In Preclinical Models, Next-Generation ADCs Link the Proven Selectivity of
- •ADC Components
- •Лекция 4 Лекция 4
- •Клеточный иммунный ответ
- •Классификация Т клеток
- •Пролиферация Т-клеток
- •Рециркуляция лимфоцитов и
- •Распознавание антигена Т-клетко
- •Участки антигена, распознаваемые молекулами
- •Т-клеточный рецепторный комплекс
- •Структура антиген-распознающих мо
- •Принцип структурных отношений между гипервариабельными участками Т-клеточного антигенраспознающего рецептора и комплексом пептид—молекулы главного
- •MHC II-Антиген-ТКР
- •Число аллельных форм молекул I и II классов главного комплекса гистосовместимости у человека
- •Антиген-презентирующие клетки (А
- •Процессинг антигена
- •TAP транспортер
- •BiaCore T-200
- •MHC класса II
- •Связывание пептида MBP (85-99 а.о.)
- •Анализ библиотеки MBP методом ИФА
- •T50Ассоциация Диссоциация
- •Получение количественных
- •Пептиды
- •Кинетические константы
- •Термодинамические параметры
- •ИндукцияИндукциятолерантноститолерантностиввтимусетимусе иинанаперифериипериферии
- •Перекрестно-реагирующие антигены индуцируют появление аутоиммунных Тх- клеток
- •Аутореактивные Т-клетки
- •Отрицательная селекция
- •Tregs. Регуляторные Т-
- •Tregs. Регуляторные Т-
- •Tregs. Регуляторные Т-
- •Scheme describing the allergen-specific TCR as a switch to turn on the regulatory
- •РегуляторныеРегуляторныемеханизмымеханизмы «сдерживания»«сдерживания» аутоиммунныхаутоиммунныхреакцийреакций
- •СпособыСпособылечениялеченияаутоиммунныхаутоиммунных заболеваний:заболеваний:сегоднясегодняиизавтразавтра
- •ПрезентацияПрезентацияопухолевогоопухолевогоантигенаантигена клеткамклеткамиммуннойиммуннойсистемысистемы
- •Протеасома в клетке
- •Строение протеасомы
- •Строение протеасомы
- •Строение активных центров
- •Строение протеасомы
- •Иммунная протеасома
- •Brain: near to 100% const proteasome
- •MULTIPLE SCLEROSIS
- •e level of IP in the brain is dramatically elevated during EAE development
- •BALB/c immunization
- •Induction of the immunoproteasome subunit LMP2 is associated with neurodegeneration
- •Immunoproteasome subunit LMP2 is associated with oligodendrocytes and LMP7 with infiltrating lymphocytes
- •The source of immune proteasome is SJL/J EAE mice
- •MBP hydrolysis by set of proteases
- •(Cbz)-Leu–Leu-leucinal (MG132)
- •Immunoproteasome as a target for MS treatment

Rationale for ADCs:
to Expand the Therapeutic Window
•ADCs are designed to target delivery of a cytotoxic agent
−Increase the delivery of a cytotoxic agent to a tumor
−Limit tissue exposure to free cytotoxic agent
ConventionalAntibody-DrugChemotherapyConjugates
Reference: Carter PJ et al. Cancer J. 2008;14(3):154-169. |
65 |

Target Antigen Should Be Abundantly Expressed on Tumor Cells Compared to Healthy Cells
Target antigen
Expressed abundantly |
Limited or no expression on |
on tumor cells1,2 |
normal or vital tissues1,2 |
• Efficient internalization of target antigen increases drug delivery and enhances cell-killing1,3
References: 1. Alley SC et al. Curr Opin Chem Biol. 2010;14(4):529-537. 2. Carter PJ et al. Cancer J. 2008;14(3):154-169. 3. Polson AG et al. |
66 |
Expert Opin Investig Drugs. 2011;20(1):75-85. |

Primary Mechanism of Action of ADCs: Targeted Delivery of a Cytotoxic Agent
Reference: Carter PJ et al. Cancer J. 2008;14(3):154-169. |
67 |

Other Potential ADC Antitumor Activities
Some ADCs may retain mAb-mediated anticancer activities1,2
Apoptosis through direct |
Tumor lysis through |
intracellular signaling3 |
host immune effector cells3 |
NFКB
References: 1. Carter PJ et al. Cancer J. 2008;14(3):154-169. 2. Junttila TT et al [published online ahead of print August 21, 2010]. Breast Cancer Res |
68 |
Treat. doi:10.1007/s10549-010-1090-x. 3. Sharkey RM et al. CA Cancer J Clin. 2006;56(4):226-243. |

Limitations of Early ADC Technology1-3
•Unstable linker technology: linker breakdown outside target tumor tissue
−Resulting in broader systemic exposure to the cytotoxic agent
−Poor ADC localization to target tumor
•Modest activity
References: 1. Senter PD. Curr Opin Chem Biol. 2009;13(3):235-244. |
2. Chari RVJ. Acc Chem Res. 2008;41(1):98-107. 3. Teicher BA. |
69 |
Curr Cancer Drug Targets. |
2009;9(8):982-1004. |

Next-Generation ADCs:
Engineered & Optimized
Improved by incorporation of:1,2
−A more potent cytotoxic agent*
−A more stable linker
−Improved conjugation technology
−Optimized ratio of cytotoxic agents per antibody
* As demonstrated in preclinical models.
References: 1. Alley SC et al. Curr Opin Chem Biol. 2010;14(4):529-537. 2. Hamblett KJ et al. Clin Cancer Res. 2004;10(20):7063-7070. |
70 |
|

Next-Generation ADCs: Designed to be Stable in Circulation and Release a Cytotoxic Agent in Target Cells
•Newer ADC linker technology is intended to spare non-targeted cells and thus reduce many of the toxic effects of traditional chemotherapy while enhancing the antitumor activity1,2,3
References: 1. Ducry L et al. Bioconjug Chem. 2010;21(1):5-13. 2. Alley SC et al. Curr Opin Chem Biol. 2010;14(4):529-537. 3. Teicher BA. |
|
Curr Cancer Drug Targets. 2009;9(8):982-1004. |
71 |

As Demonstrated In Preclinical Models, Next-Generation ADCs Link the Proven Selectivity of
Monoclonal Antibodies With Potent Cytotoxic Agents
Linking individual elements for greater activity
•Selective delivery via mAbs1
•More potent cytotoxic agents2
•Stable linkers increase target specificity and reduce toxicity1,3
References: 1. Ducry L et al. Bioconjug Chem. 2010;21(1):5-13. 2. Alley SC et al. Curr Opin Chem Biol. 2010;14(4):529-537. |
72 |
3. Doronina SO et al. Nat Biotechnol. 2003;21(7):778-784. |
ADC Components
•Targeting AB
–Choice of target (tumor/normal tissue ratio)
–Internalization (must have feature)
–Intracellular trafficking (presumed as important but not clearly spelled)
•Payload
–Highly potent (mostly tubulin active)
•Linker
–Cleavable vs non-cleavable
–Stable in circulation