
- •The Germanic languages. The Germanic tribes.
- •3.The North Germanic languages.
- •4.The West Germanic languages.
- •5.The periods in the History of English.
- •6.The Old English dialects and the formation of English language.
- •7.Middle English dialects and the formation of the National Literary English Language.
- •8.The Anglo –Saxon conquest and its historical and linguistic importance.
- •9.The historical background of Middle English.
- •10.The development of Middle English dialects.
- •11.The development of the English Vocabulary.
- •12.The English Basic Word Stock.
- •13.Foreign Influences upon English and their importance.
- •14.The Celtic influence.
- •15.The Latin influence.
- •16.The Scandinavian influence.
- •17.The French influence.
- •18.Phonetic peculiarities of Germanic languages.
- •19.The Germanic phonetic system.
- •20.First Consonant Shift (Grimm’s and Verner’s law).
- •21.Principles oe phonetic changes (breaking,I-umlaut (mutation) lengthening of vowels).
- •After sk’ k’
- •2. After j
- •22.Consonant changes in oe. Oe alphabets.
- •Voicing or devoicing
- •After sk’ k’
- •2. After j
- •23.Middle English spelling change and principal sound changes.
- •24.Weakening of Unaccented Vowels and its results.
- •25.Consonant changes in Middle English.
- •Voicing of Fricatives
- •The Great Vowel Shift and its importance.
- •Modern English consonant changes (Vocalization of r, appearance of sibilants in new positions, loss of consonants).
- •Phonetic analysis of Old English sound changes.
- •Phonetic analysis of Middle English and Modern English phonetic change.
- •The Evolution of the Old English phonetic system.
- •Middle English spelling change and principal sound changes.
- •The evolution of the English Noun.
- •The evolution of the Verb.
- •The evolution of the English Adjective.
- •The evolution of the English Pronoun.
- •The evolution of the English Numeral.
- •The evolution of the English Syntax.
- •The discovery of Sanskrit.
- •The Indo-European Family.
- •Grimm’s Law.
- •The Romans in Britain. Romanization of the Island.
- •The Latin Language in Britain.
- •The Anglo-Saxon Civilization. The names “England” and “English”.
- •The Periods in the History of English.
- •The dialects of Old English.
- •Verner’s Law
- •The Definite Article.
- •The Norman Conquest. The origin of Normandy.
- •The Influence of Christianity on the Vocabulary.
- •80. Preterite-present and suppletive verbs.
- •81. The development of analytical tenses.
- •84. Wessex dialect.
- •85. Old English dialect and formation of the English language.
- •86. The periods in the history of English.
- •88. The main oe dialects.
- •89. The development of the English vocabulary. The English Basic Word Stock
- •92. Me phonetic system. Weakening of the unaccentedwords.
- •2.Development of oe å
- •94. Modern English phonetic changes. The Great Vowel Shift.
- •95. Modern English phonetic changes. Vocalization of “r”.
- •96. The importance of the Anglo-Saxon Conquest.
- •100. The definite article
- •Vikings and their influence on English.
- •Grammatical changes in Old English.
- •Grammatical changes in Middle English.
- •Grammatical changes in Early Modern English.
- •Loss of case system in Old English.
- •English as a Germanic language. Periods in the history of English.
- •Main Germanic historical written monuments.
- •London dialect. Formation of National language.
- •Phonetic changes in Germanic languages.
- •Word Stress
- •Consonants. Proto-Germanic consonant shift
- •Phonetic changes in Old English.
- •Phonetic changes in Middle English.
- •Phonetic changes in Early New English. Great Vowel Shift.
- •Word-building in Old and Middle English periods.
- •Main sources of borrowings in Old English.
- •Main sources of borrowings in Middle English.
- •Main sources of borrowings in Modern English.
- •The Noun. Main categories, declensions.
- •Main causes of losing the case system in English.
- •The adjective.
- •Development of degrees of comparison of adjectives.
- •Personal pronouns.
- •Possessive pronouns.
- •Demonstrative and indefinite pronouns.
- •Development of the articles.
- •Strong verbs in the history of English.
- •The periods in the History of English.
- •Middle English Prosody
- •Latin Borrowings
- •Scandinavian Borrowings
- •French Borrowings
- •Celtic Borrowings
- •Greek Borrowings
- •Semantic Borrowings
After sk’ k’
[e ] → [ei], [æ ] → [ea]
e. g. OHG scal → WS sceal
2. After j
[æ: ] → [ea:], [e] → [ie]
e. g. OHG jār → WS ʒear
What is Palatal Mutation?
The Old English tendency to positional vowel change is most apparent in the process termed “mutation”. It is the Change of one vowel to another through the influence of a vowel in the succeeding syllable.In Early OE, mutation affected numerous vowels and brought about profound changes in the system and use of vowels.
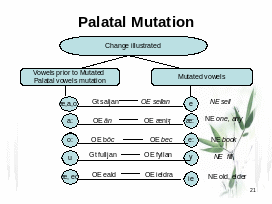
I-mutation is a change of a root vowel caused by [i], or [j] of the succeeding syllable.
Articulating the root vowel the organs of speech are getting ready to pronounce the succeeding vowel, that is [i], or [j]. They change their position and approach articulation of [i]. As a result the root vowel changes its quality.
[a] > [e] *manniz > menn (men); namnian > nemnan (take);
[a:] > [æ:] * ānig > æ̃nig (any);
[o] > [e] *ofstian > efstan (to hurry);
[o:] > [e:] *fōtis > fēt *gōsis > gēs *tōþis > tēþ;
[u] > [y:] *fullian > fyllan;
[u:] > [y:] *mūsis > mỹs
As shown by the examples the sound [i] that caused mutation was eventually lost. It was preserved only in the word æ̃nig.
I-mutation was taking place supposedly in the 6th - 7th centuries. By the time of the earliest OE records it had been completed. However the evidence of this phenomenon can be widely observed in the language of today. Such evidence is displayed in different kinds of sound interchanges.
singular - plural interchanges: man - men, tooth - teeth, mouse - mice;
noun - verb interchanges: food - feed, blood - bleed, song - sing.
adjective - verb interchanges: full - fill;
interchanges within the opposition positive - comparative/superlative degree of adjectives, old - elder - the eldest.
Lengthening of Vowels
Short vowels [u] and [i] were lengthened when followed by the sound clusters -ld, -nd, -mb.
findan > fīndan;
climban > clīmban;
bundan > būndan.
This change did not occur when the sound cluster ld, nd, or mb was followed by another consonant, like in the word cildru (NE children).
The singular form of this word cild preserved , however, the conditions for lengthening cild > cīld. Thus, thanks to this phenomenon the opposition cīld - cildru developed a quantitative vowel interchange [i:] - [i]. In later years with the development of long vowels into diphthongs and particularly with the development of [i:] into [ai], the OE quantitative vowel interchange [i:] - [i] developed into the NE qualitative interchange [ai] - [i], child - children.
22.Consonant changes in oe. Oe alphabets.
OE Consonant Changes
HARDENING
O Ice rauðr
OE rēad
Mod E red
RHOTACISM
Gt huzd
OE hord
NE hoard
Voicing or devoicing
Gt hlaifs-OE hlafas-NE loaves
Gt wulfos-OE wulfas [v]–
NE wolves
Assimilative Vowel Changes
Breaking
Produced a new set of vowels
in OE [ea], [eo], [ea:], [eo:]
Before l+l or l+ other consonants
[æ ] → [ea]
e.g. North ald → WS eald
2. h, h+other consonants
[æ: ] → [ea:]
e. g. OHG nāh → NE near
3. r + other consonants
[e] → [oe]
e. g. OHG herza → WS heorte
Diphthongisation
