
- •Presentation 2 The human body – its basic anatomical parts and regions I
- •Presentation 3 The human body – its parts and regions II
- •Presentation 4 The body cavities
- •Presentation 2 Parts of the skeletal and muscular systems
- •Presentation 3 Comparative biology
- •Presentation 2 Comparative biology.
- •Presentation 3 The Digestive system
- •Presentation 3 Nutrition
- •Beef sunflower oil bacon chocolate cheese nuts sardines crisps biscuits
- •Olives fast foods
- •Butter soya beans ice cream chips
- •Olive oil
- •Presentation 4 Comparative biology
- •Infection, haemoglobin, clot, white blood cells, platelets, oxygen, red blood cells.
- •Presentation 3 Comparative biology
- •Presentation 2 The brain and memory
- •Equilibrioception b) reception of thirst c) reception of hunger
- •Presentation 4 Comparative biology. Animal senses
- •Presentation 2 Animal behaviour
- •Presentation 3 Social behavior
- •Presentation 4 Human and animal communication
- •Presentation 2 Endocrine system and hormones
- •Presentation 3 Exocrine system
- •Presentation 4 The integumentary system
- •Presentation 2 The excretory system (Urinary system)
- •Presentation 3 Comparative biology
- •Presentation 2 Prenatal development
- •Presentation 3 Stages of growth and development
- •Presentation 4 Comparative biology
- •Presentation 5 Bite out of History
Infection, haemoglobin, clot, white blood cells, platelets, oxygen, red blood cells.

Task 6 Expand your vocabulary. Try to match the blood conditions. With their description.
1 |
Haemorrhage |
A |
A collection of blood inside the body tissues forming purple marks on the skin. |
2 |
Haematoma |
B |
An inherited deficiency of blood clotting proteins. Frequent or uncontrolled bleeding. |
3 |
Leukemia: |
C |
Commonly called a heart attack. It occurs when a sudden blood clot develops in one of the coronary arteries supplying blood to the heart. |
4 |
Anaemia |
D |
Blood leaking out of blood vessels, as from a wound penetrating the skin. Internal bleeding may not be immediately apparent. |
5 |
Sickle cell d. |
E |
Infection of red blood cells by a parasite transmitted by mosquitoes. |
6 |
Malaria |
F |
A genetic condition in which red blood cells lose their shape. The deformed blood cells deposit in tissues, causing organ damage. |
7 |
Haemophilia |
G |
A form of blood cancer, in which white blood cells multiply abnormally and circulate through the blood. |
8 |
Myocardial infarction |
H |
An abnormally low number of red blood cells in the blood. |
Presentation 3 Comparative biology
Task 1 Match the definitions with the correct type of the circulatory system.
|
This circulatory system is developed in insects, mollusks and other invertebrates. Blood is pumped by a heart into the body cavities, where tissues are surrounded by the blood. The resulting blood flow is slow. |
Open circulatory system
|
This circulatory system (developed in vertebrates) has the blood closed within vessels of different size and wall thickness. In this type of system, blood is pumped by a heart through vessels, and does not normally fill body cavities. Blood flow is not slow.
|
Closed circulatory system
|
Water is the medium of transport and is propelled in and out of some simple animals, such as the hydra. Flatworms lack specialized organs such as hearts and blood vessels, instead using their skin as an exchange point for materials.
|
UNIT 14 THE NERVOUS SYSTEM, MEMORY AND SENSES
Presentation 1 The nervous system
Task 1 Complete the omitted parts of the text with the terms below.
peripheral nerve fibres * parasympathetic nervous system * brain * sympathetic nervous system * motor nerve fibres * spinal cord |
T he
nervous system is divided into
he
nervous system is divided into
the central nervous system that contains two parts:
the ...................... and
the ........................ , and
the peripheral nervous system that is divided into two major parts:
the somatic nervous system, and
the autonomic nervous system.
The somatic nervous system consists of .............................................. that send sensory information to the CNS and ......................................... that carry information away from the CNS (for muscle control).
The autonomic nervous system controls smooth muscle of the internal organs and glands. It consists of the .................................................... (mobilizes body systems during activity), the ............................................(conserves energy, promotes “houskeeping“ functions during rest).
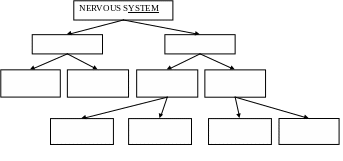
Task 2 Complete the following “nervous system graph”.
Task 3 Description. Read the descriptions of indiviodual parts of the human brain on the next page. While reading, label the brain anatomy diagram.
Cerebellum - the part of the brain below the back of the cerebrum. It regulates balance, posture, movement, and muscle coordination.
Corpus Callosum - a large bundle of nerve fibers that connect the left and right cerebral haemispheres. In the lateral section, it looks a bit like a "C" on its side. Frontal Lobe of the Cerebrum - the top, front regions of each of the cerebral haemispheres. They are used for reasoning, emotions, judgment, and voluntary movement.
Medulla Oblongata - the lowest section of the brainstem (at the top end of the spinal cord); it controls automatic functions including heartbeat, breathing, etc.
Occipital Lobe of the Cerebrum - the region at the back of each cerebral haemisphere that contains the centers of vision and reading ability (located at the back of the head.
Parietal Lobe of the Cerebrum - the middle lobe of each cerebral haemisphere between the frontal and occipital lobes; it contains important sensory centers (located at the upper rear of the head).
Pituitary Gland - a gland attached to the base of the brain (located between the Pons and the Corpus Callosum) that secretes hormones.
Pons - the part of the brainstem that joins the hemispheres of the cerebellum and connects the cerebrum with the cerebellum. It is located just above the Medulla Oblongata. Spinal Cord - a thick bundle of nerve fibers that runs from the base of the brain to the hip area, running through the spine (vertebrae).
Temporal Lobe of the Cerebrum - the region at the lower side of each cerebral haemisphere; contains centers of hearing and memory (located at the sides of the head).


 No
circulatory system
No
circulatory system