
- •Presentation 2 The human body – its basic anatomical parts and regions I
- •Presentation 3 The human body – its parts and regions II
- •Presentation 4 The body cavities
- •Presentation 2 Parts of the skeletal and muscular systems
- •Presentation 3 Comparative biology
- •Presentation 2 Comparative biology.
- •Presentation 3 The Digestive system
- •Presentation 3 Nutrition
- •Beef sunflower oil bacon chocolate cheese nuts sardines crisps biscuits
- •Olives fast foods
- •Butter soya beans ice cream chips
- •Olive oil
- •Presentation 4 Comparative biology
- •Infection, haemoglobin, clot, white blood cells, platelets, oxygen, red blood cells.
- •Presentation 3 Comparative biology
- •Presentation 2 The brain and memory
- •Equilibrioception b) reception of thirst c) reception of hunger
- •Presentation 4 Comparative biology. Animal senses
- •Presentation 2 Animal behaviour
- •Presentation 3 Social behavior
- •Presentation 4 Human and animal communication
- •Presentation 2 Endocrine system and hormones
- •Presentation 3 Exocrine system
- •Presentation 4 The integumentary system
- •Presentation 2 The excretory system (Urinary system)
- •Presentation 3 Comparative biology
- •Presentation 2 Prenatal development
- •Presentation 3 Stages of growth and development
- •Presentation 4 Comparative biology
- •Presentation 5 Bite out of History
Presentation 2 The excretory system (Urinary system)
Task 1 Translate the main parts of the urinary system into Slovak.
Task 2 Read about the functions of the kidneys. Write the functions of the other organs.
 Functions of the:
Functions of the:
ureters: …………………………
………………………………….
urinary bladder: ………………...
………………………………….
urethra: …………………………
………………………………….
Kidneys perform these homeostatic functions:
Maintain volume of extracellular fluid.
Maintain ionic balance in extracellular fluid.
Maintain pH and osmotic concentration of the extracellular fluid.
Excrete toxic metabolic by-products such as urea, ammonia, and uric acid.
Presentation 3 Comparative biology
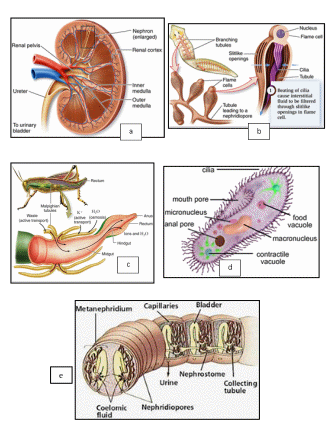
Task Read the short paragraphs showing diversity of the excretion systems in animals. Write the letters of pictures illustrating the individual systems.
A contractile vacuole is a sub-cellular structure (organelle) involved in osmoregulation. It is found in protists and unicellular algae. It pumps excess water out of the cell. In freshwater environments the concentration of solutes in the cell is higher than outside the cell. Under these conditions, water flows from the environment into the cell by osmosis. The contractile vacuole serves as a protective mechanism that prevents the cell from absorbing too much water and possibly exploding (picture: ............... )
In flatworms and a few kinds of invertebrates the excretory/osmoregulatory organ is a protonephridium (flame cells). It has a tubule that is open only at the end leading outside the body. The other end of the protonephridium has cilia or a flagellum. (picture: …….)
In most kinds of invertebrates, including earthworms, the excretory organ is called the metanephridium. The tubule is open at both ends, and the pressure of the body fluid forces the filtrate into the tubule. (picture: ........)
In insects and spiders the main organs are Malpighian tubules, which are attached to the gut. For these terrestrial animals the problem is to conserve water, rather than eliminate it. Water, containing metabolic wastes and excess ions, is filtered into the Malpighian tubules and then joins the faeces in the hind part of the gut. As the faeces pass through the rectum, the water is pumped back into the body fluid. (picture: ...........)
In vertebrates the excretory system contains thousands or even millions of tubules, called nephrons, each one of which uses the same principles of filtration and active transport. Nephrons form a filtrate consisting of water, nutrients, ions, and other components. As the filtrate passes along the nephron tubule, nutrients, water, and other needed molecules are transported back into the bloodstream. Ions, metabolic wastes, and other excess molecules go into the resulting fluid - urine. (picture: ............)
UNIT 18 THE REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM, HUMAN GROWTH AND DEVELOPMENT
Presentation 1 The male and female reproductive organs
Human reproductive system is an organ system by which humans reproduce and bear live offspring. Provided all organs are present, normally constructed, and functioning properly, the essential features of human reproduction are 1) liberation of an ovum at a specific time in the reproductive cycle, 2) internal fertilization of the ovum by spermatozoa 3) transport of the fertilized ovum to the uterus, 4) implantation of the blastocyst, the early embryo developed from the fertilized ovum, in the wall of the uterus, 5) formation of a placenta and maintenance of the foetus during the entire period of gestation, (6) birth of the child and expulsion of the placenta, 7) puerperium – the mother's body, including hormone levels and uterus size, return to their original state, and 8) suckling and care of the baby.
Task 1 In the above text find synonyms for these terms:
egg: .......................................................... e) pregnancy: .............................................
sperms (sperm cells): .............................. f) labour: ...................................................
womb: ..................................................... g) delivery: ................................................
unborn baby: ........................................... h) breastfeeding: ........................................
.Task 2 Label the pictures showing the male and female reproductive systems with the correct terms.
Female: cervix (neck of the womb), endometrium (womb lining), Fallopian tubes,
ovaries, uterus (womb), vagina
Male: (urinary bladder, ureter, urethra), testes, glans penis, erectile tissue, epididymis,
seminal vesicle, vas deferens, prostate gland


