
- •Presentation 2 The human body – its basic anatomical parts and regions I
- •Presentation 3 The human body – its parts and regions II
- •Presentation 4 The body cavities
- •Presentation 2 Parts of the skeletal and muscular systems
- •Presentation 3 Comparative biology
- •Presentation 2 Comparative biology.
- •Presentation 3 The Digestive system
- •Presentation 3 Nutrition
- •Beef sunflower oil bacon chocolate cheese nuts sardines crisps biscuits
- •Olives fast foods
- •Butter soya beans ice cream chips
- •Olive oil
- •Presentation 4 Comparative biology
- •Infection, haemoglobin, clot, white blood cells, platelets, oxygen, red blood cells.
- •Presentation 3 Comparative biology
- •Presentation 2 The brain and memory
- •Equilibrioception b) reception of thirst c) reception of hunger
- •Presentation 4 Comparative biology. Animal senses
- •Presentation 2 Animal behaviour
- •Presentation 3 Social behavior
- •Presentation 4 Human and animal communication
- •Presentation 2 Endocrine system and hormones
- •Presentation 3 Exocrine system
- •Presentation 4 The integumentary system
- •Presentation 2 The excretory system (Urinary system)
- •Presentation 3 Comparative biology
- •Presentation 2 Prenatal development
- •Presentation 3 Stages of growth and development
- •Presentation 4 Comparative biology
- •Presentation 5 Bite out of History
Centrum celoživotného a kompetenčného vzdelávania PU
ÚSTAV JAZYKOVÝCH KOMPETENCIÍ
Ul. 17 novembra 15, rektorát sekcia D, miestnosť č. 122
klaudia.valdmanova@unipo.sk
ENGLISH IN BIOLOGY II
Klaudia Valdmanová
UNIT 10 THE HUMAN BODY
Presentation 1 Body organization
Task 1 Read the text and fill in expressions you know from your previous study.
The human body is organized on the following four levels.
Cellular level. The cell is the basic structural and functional compound of our body. Humans are multi-cellular organisms composed of between 60 and 100 trillion of cells which perform vital functions of life such as: m............................ , g.................., irritability, adaptability, repair and r............................ . Cells are specialized to carry out specific functions. Examples of specialized cells are bone cells, f............ cells, b............... cells, muscle cells and n.................. cells.
Tissue level. There are four types of tissues - groups of similar cells performing a specific function: epithelial, m……………….. , n……….…… and connective tissues.
Organ level. Two or more tissues joined to perform a particular function are called an organ. The organs vary in size and functions. Examples of organs are: the heart, ……………………………….. .
System level. Body systems consist of various organs responsible for similar functions, e.g. the respiratory system, …………………..…………….….. . Certain organs may serve several systems, e.g. the pancreas belongs to the endocrine as well as digestive systems. All the systems work together and constitute the organism.
Task 2 a) Write the names of individual tissues next to the functions.
b) Write the names of the tissues next to the picturesbelow the chart.
function |
tissue |
Binds and supports body parts. |
|
Receives stimuli and transmits impulses. |
|
Covers body surfaces, lines body cavities, and forms glands. |
|
Moves the body and its parts. |
|

Task 3 Word formation. Complete the missing part of the chart.
noun |
adjective |
|
noun |
adjective |
cell |
|
|
metabolic |
|
|
structural |
organ |
|
|
|
functional |
|
systemic |
|
nerve |
|
epithelium |
|
|
anatomy |
|
muscle |
|
Task 4 Which levels of body organization do the pictures belong to?





a) ……….... b)…………. c) …………. d) ………..……. e) …………….
Presentation 2 The human body – its basic anatomical parts and regions I
Task 1 While reading the text complete the missing body parts.
The human body is divided into following parts that can be identified on its surface: the h……….., the n…….….., the trunk, and the extremities.
The head is the seat of the b….…….…, several sense organs and inlets for air and food. It has the cranial and f………..… regions. The neck is called the cervical region.
 The
trunk is divided into several regions. The thorax or the thoracic
region is commonly called the chest. Then there are the mammary
regions round the nipples, and in a female round entire breasts.
Between them there is the sternal region. The area surrounding the
armpits is known as the axillary region. At the back we distinguish
the vertebral region. The buttock is called the gluteal region.
The
trunk is divided into several regions. The thorax or the thoracic
region is commonly called the chest. Then there are the mammary
regions round the nipples, and in a female round entire breasts.
Between them there is the sternal region. The area surrounding the
armpits is known as the axillary region. At the back we distinguish
the vertebral region. The buttock is called the gluteal region.
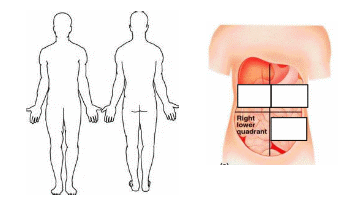
The abdomen is situated below the thorax. The abdomen is divided into nine regions describing the location of the internal organs. The division into four quadrants is commonly used. In the central part on the abdomen, there is the n………….. . The region below it is referred to as the pelvic region followed by the genital region containing external s…………. organs and the perineal region round the a…………..…. opening.
Task 2 Mark the regions on the human body on the diagram on the left.
Task 3 Complete the names of the quadrants in the right picture.
Presentation 3 The human body – its parts and regions II
The upper extremity is composed of the shoulder, the upper arm, the e………..…., the forearm, the w………… and the hand. The parts of the hand are the back and the palm, the thumb and four f……...….. with the n……..…. .
In human anatomical terms, the leg is the part of the lower extremity that lies between the hip and the a.................. . The thigh is between the hip and k ............... . The leg from the knee to the ankle is called crus. The calf is the back portion. The foot includes the sole, the instep, the arch, the heel with the Achilles tendon and the t…………. .
Task Label the main parts of a) face b) the upper extremity c) the lower extremity


Presentation 4 The body cavities
The human body is not a solid structure as it looks on the outside, but it has five main cavities each containing internal organs and several smaller cavities within the head.
Task 1 Match the terms in the column A with the definition in the column B. Then label the cavities in the diagram
A B
 1
spinal cavity a contains the urinary bladder
1
spinal cavity a contains the urinary bladder
2 thoracic cavity b contains the stomach
3 cranial cavity c space inside the skull
4 pelvic cavity d the spinal cord is located there
5 abdominal cavity e its colloquial name is the chest
Task 2 Mark the middle ear cavity, oral cavity, nasal cavity, orbital cavities and sinuses.

Task 3 Word formation. Complete the following chart.
-
Noun
Colloquial expression
Noun
Medical (Latin or Greek) term
Adjective
eye
orbit
orbital
face
face/ facies
cervix
thorax
mamma
mammary
axilla
umbilicus
gluteus
manus
UNIT 11 SYSTEMS OF THE HUMAN BODY
THE SKELETAL AND MUSCULAR SYSTEMS
Presentation 1 Systems and their functions
Systems are the most complex of the units of the human body. The system is an organization of varying numbers and kinds of organs so arranged that together they can perform complex functions for the body. Major systems composing the human body are as follows:
Skeletal Lymphatic Circulatory (Cardiovascular)
Muscular Respiratory Reproductive
Nervous Digestive Integumentary
Endocrine Urinary
Task 1 Match the systems with the correct descriptions of their functions.
|
s y s t e m |
|
d e s c r i p t i o n |
1 |
muscular |
a |
body immunity, absorption of fats, drainage of tissue fluids |
2 |
cardiovascular |
b |
external protection of body against injuries and pathogens, regulation of temperature |
3 |
nervous |
c |
breakdown and absorption of food materials |
4 |
digestive |
d |
transport of life sustaining materials to body cells, removal of metabolic wastes from cells |
5 |
lymphatic |
e |
body movement, production of body heat |
6 |
integumentary |
f |
regulation of all body activities, learning and memory |
Task 4 Write the name of the system to the following descriptions.
Its primary function is to supply the blood with oxygen. through breathing……….…
It removes liquid wastes from the body. ………………………………………………
It enables mankind to reproduce itself. ………………………………………..….…...
It supports the body and produces blood cells. ..........………....
