
- •Lecture 2.4: Sensors with Complex Geometry
- •A fundamental relationship of biosensor
- •Array and Network sensors
- •Recall: Method of diffusion capacitance
- •Recall: Integer dimensional sensors
- •Capacitance of an Array sensor
- •Array of cylinders: fractional sensor
- •Array of cylinders: fractional sensor
- •Geometry of diffusion/sensor response
- •Response of fractal sensors
- •Recall: Dimension of a fractal surface
- •Recall: Random to regular transform
- •Fractional diffusion to fractal sensor
- •Performance limits of biosensors
- •Average vs. first arrival time
- •A ‘Mendeleev table’ for biosensors
- •Conclusions
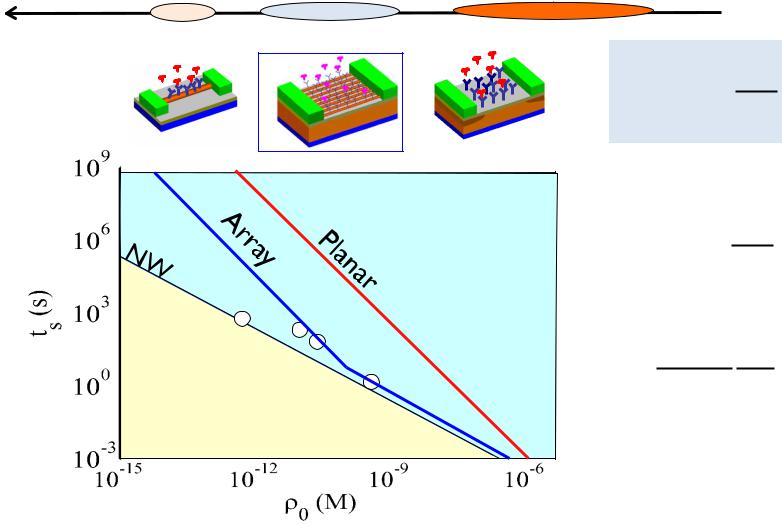
Geometry of diffusion/sensor response
aM |
fM |
pM |
nM |
µM |
mM |
|
|
M |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
ts |
~ |
2NS2 |
1 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
D ρ0n |
|
||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
(Planar) |
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
ts |
~ |
|
2NS2 |
1 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
D ρ02 |
|
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
ts |
~ |
|
NS a0 1 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
D |
ρ0 |
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
(SiNW) |
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
9 |
15 |

Response of fractal sensors
aM |
fM |
pM |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
nM |
µM |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
mM |
||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Finally, we consider the nanocomposite sensor …
Alam, Principles of Nanobiosensors, 2013 |
10 |

Recall: Dimension of a fractal surface
Fractal dimension (DF)- box counting technique
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
h |
½ |
|
|
h |
½ |
|
h |
½ |
|||
2 |
|
N(h) |
1/4 |
|
1/4 |
||||||
N |
16 |
|
4 |
|
N |
1 |
|||||
h |
1/4 |
|
|
|
~ h1 |
|
N(h) ~ h0 |
||||
N(h) ~4 h |
|
|
|
|
2 |
|
|
|
|
||
Log N(h)
Plane DF=2 |
|
Random NW 1< DF<2 |
|
Line DF=1 |
|
Dot DF=0 |
|
Log(1/h) |
11 |
|
|
|
11 |

Recall: Random to regular transform
DF,CT= DF,stick |
DF,CT=1+log(m)/log(n)
For DF,stick=1.5
Let m=2, solve for n: log(n)=log(2)/(DF,stick-1) Result: n=4
Generation algorithm: Take a line segment
Remove the fraction (n-2)/n from its centre (result: ½)
repeat …
12
