
PS-2020a / part17
.pdf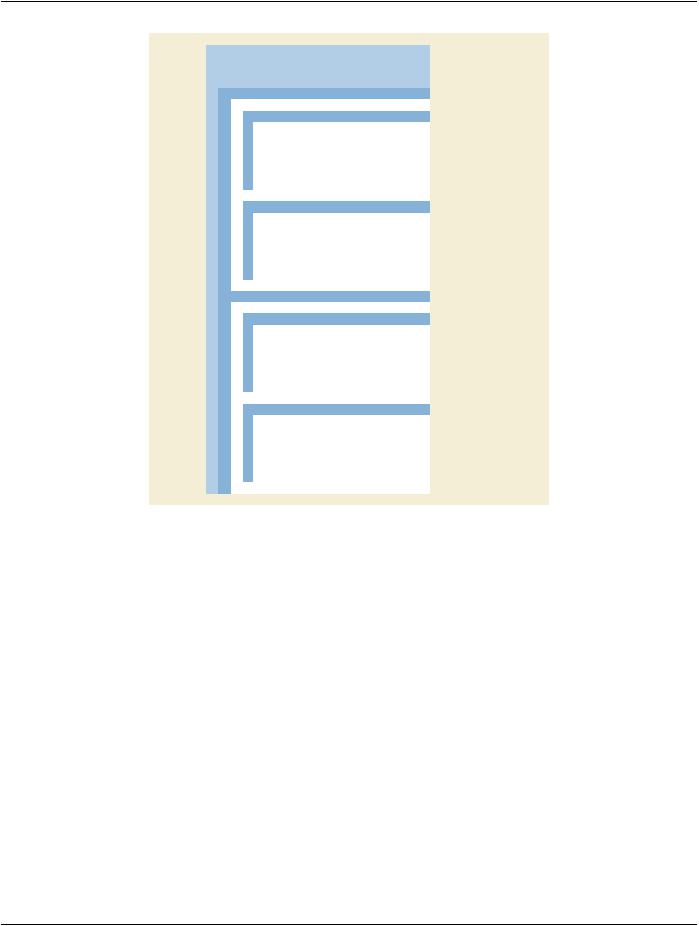
DICOM PS3.17 2020a - Explanatory Information |
Page 521 |
Positioner Type |
(0018,1508) |
= CARM |
||||
C-Arm Positioner Tabletop Relationship |
(0018,9474) |
= YES |
||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
... |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Per-Frame Functional Groups Sequence |
(5200,9230) |
|
||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
Frame 1 |
|
Item 1 |
|
||||
|
|
>Table Position Sequence |
(0018,9406) |
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Item 1 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
= 0.0 |
|
|
|
|
>>Table Top Vertical Position |
(300A,0128) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
= 0.0 |
|
|
|
|
>>Table Top Longitudinal Position |
(300A,0129) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
= 0.0 |
|
|
|
|
>>Table Top Lateral Position |
(300A,012A) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
= 0.0 |
|
|
|
|
>>Table Horizontal Rotation Angle |
(0018,9469) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
= -10.0 |
|
|
|
|
>>Table Head Tilt Angle |
(0018,9470) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
= 0.0 |
|
|
|
|
>>Table Cradle Tilt Angle |
(0018,9471) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
>Isocenter Reference System Sequence |
(0018,9462) |
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Item 1 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
= 0.0 |
|
|
|
|
>>Table X Position to Isocenter |
(0018,9466) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
= 500.0 |
|
|
|
|
>>Table Y Position to Isocenter |
(0018,9467) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
= 0.0 |
|
|
|
|
>>Table Z Position to Isocenter |
(0018,9468) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
= 0.0 |
|
|
|
|
>>Table Horizontal Rotation Angle |
(0018,9469) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
= -10.0 |
|
|
|
|
>>Table Head Tilt Angle |
(0018,9470) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
>>Table Cradle Tilt Angle |
(0018,9471) |
= 0.0 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
... |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Frame “N” |
|
Item “N” |
|
||||
|
|
>Table Position Sequence |
(0018,9406) |
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Item 1 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
= 0.0 |
|
|
|
|
>>Table Top Vertical Position |
(300A,0128) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
>>Table Top Longitudinal Position |
(300A,0129) |
= 0.0 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
>>Table Top Lateral Position |
(300A,012A) |
= 1000.0 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
>>Table Horizontal Rotation Angle |
(0018,9469) |
= 0.0 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
>>Table Head Tilt Angle |
(0018,9470) |
= -10.0 |
|
|
|
|
>>Table Cradle Tilt Angle |
(0018,9471) |
= 0.0 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
>Isocenter Reference System Sequence |
(0018,9462) |
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Item 1 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
= 0.0 |
|
|
|
|
>>Table X Position to Isocenter |
(0018,9466) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
= 673.6 |
|
|
|
|
>>Table Y Position to Isocenter |
(0018,9467) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
>>Table Z Position to Isocenter |
(0018,9468) |
= 984.8 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
= 0.0 |
|
|
|
|
>>Table Horizontal Rotation Angle |
(0018,9469) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
>>Table Head Tilt Angle |
(0018,9470) |
= -10.0 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
>>Table Cradle Tilt Angle |
(0018,9471) |
= 0.0 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
... |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Figure FFF.2.1-18. Attributes of the X-Ray Table Per Frame on Table Stepping
FFF.2.1.4 Changes in X-Ray Controls
FFF.2.1.4.1 Exposure Regulation Control
This section provides information on the encoding of the "sensitive areas" used for regulation control of the X-Ray generation of an image that resulted from applying these X-Rays.
FFF.2.1.4.1.1 User Scenario
The user a) takes previous selected regulation settings or b) manually enters regulation settings or c) automatically gets computer- calculated regulation settings from requested procedures.
Acquired images are networked or stored in offline media.
Laterproblemsofimagequalityaredeterminedanduserwantstocheckforreasonsbyassessingthepositionsofthesensingregions.
FFF.2.1.4.1.2 Encoding Outline
TheEnhancedXAIODincludesamoduletosupplyinformationaboutactiveregulationcontrolsensingfields,theirshapeandposition relative to the pixel matrix.
FFF.2.1.4.1.3 Encoding Details
This section provides detailed recommendations of the key Attributes to address this particular scenario.
- Standard -

Page 522 DICOM PS3.17 2020a - Explanatory Information
Table FFF.2.1-38. Enhanced XA Image Functional Group Macros
Functional Group Macro |
PS3.3 Reference |
Usage |
X-Ray Exposure Control Sensing RegionsC.8.19.6.3 |
Specifiestheshapeandsizeofthesensingregionsinpixels, |
|
|
|
as well as their position relative to the top left pixel of the |
|
|
image. |
FFF.2.1.4.1.3.1 X-Ray Exposure Control Sensing Regions Macro Recommendations
This macro is recommended to encode details about sensing regions.
If the position of the sensing regions is fixed during the multi-frame acquisition, the usage of this macro is shared.
If the position of the sensing regions was changed during the multi-frame acquisition, this macro is encoded per-frame to reflect the individual positions.
Thesamenumberofregionsistypicallyusedforalltheframesoftheimage.Howeveritistechnicallypossibletoactivateordeactivate some of the regions during a given range of frames, in which case this macro is encoded per-frame.
Table FFF.2.1-39. X-Ray Exposure Control Sensing Regions Macro Recommendations
Attribute Name |
Tag |
Comment |
Exposure Control Sensing Regions Sequence |
(0018,9434) |
As many items as number of regions. |
FFF.2.1.4.1.4 Example |
|
|
In this section, two examples are given.
The first example shows how three sensing regions are encoded: 1) central (circular), 2) left (rectangular) and 3) right (rectangular).
1 |
200 |
274 |
511 |
750 |
824 |
1
250
1 |
3 |
2
511
774
Pixel Data Matrix
Figure FFF.2.1-19. Example of X-Ray Exposure Control Sensing Regions inside the Pixel Data matrix
- Standard -

DICOM PS3.17 2020a - Explanatory Information |
Page 523 |
The encoded values of the key Attributes of this example are shown in Figure FFF.2.1-20.
... |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Shared Functional Groups Sequence |
(5200,9229) |
|
||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
All Frames |
|
Item 1 |
|
||||
|
|
... |
|
|
|
Other functional groups |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
>Exposure Control Sensing Regions Sequence |
(0018,9434) |
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
Region 1 |
|
|
|
Item 1 |
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
= CIRCULAR |
|
|
|
|
>>Exposure Control Sensing Region Shape |
(0018,9435) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
= 511\511 |
|
|
|
|
>>Center of Circular Exposure Control Sensing Region |
(0018,9440) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
= 100 |
|
|
|
|
>>Radius of Circular Exposure Control Sensing Region |
(0018,9441) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Region 2 |
|
|
|
Item 2 |
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
= RECTANGULAR |
|
|
|
|
>>Exposure Control Sensing Region Shape |
(0018,9435) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
>>Exposure Control Sensing Region Left Vertical Edge |
(0018,9436) |
= 200 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
>>Exposure Control Sensing Region Right Vertical Edge |
(0018,9437) |
= 274 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
>>Exposure Control Sensing Region Upper Horizontal Edge |
(0018,9438) |
= 250 |
|
|
|
|
>>Exposure Control Sensing Region Lower Horizontal Edge |
(0018,9439) |
= 774 |
|
|
|
Item 3 |
|
Region 3 |
|
|
|
|
|
>>Exposure Control Sensing Region Shape |
(0018,9435) |
= RECTANGULAR |
|
|
|
|
>>Exposure Control Sensing Region Left Vertical Edge |
(0018,9436) |
= 750 |
|
|
|
|
>>Exposure Control Sensing Region Right Vertical Edge |
(0018,9437) |
= 824 |
|
|
|
|
>>Exposure Control Sensing Region Upper Horizontal Edge |
(0018,9438) |
= 250 |
|
|
|
|
>>Exposure Control Sensing Region Lower Horizontal Edge |
(0018,9439) |
= 774 |
|
|
... |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
... |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Figure FFF.2.1-20. Attributes of the First Example of the X-Ray Exposure Control Sensing Regions
The second example shows the same regions, but the field of view region encoded in the Pixel Data matrix has been shifted of 240 pixels right and 310 pixels down, thus the left rectangular sensing region is outside the Pixel Data matrix as well as both rectangular regions overlap the top row of the image matrix.
- Standard -

Page 524 |
DICOM PS3.17 2020a - Explanatory Information |
|||||
-40 34 |
271 |
510 584 |
||||
-60 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
1 |
|
|
3 |
|
||
2
201
464
Pixel Data Matrix
Figure FFF.2.1-21. Example of X-Ray Exposure Control Sensing Regions partially outside the Pixel Data
matrix
The encoded values of the key Attributes of this example are shown in Figure FFF.2.1-22.
... |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Shared Functional Groups Sequence |
(5200,9229) |
|
||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
All Frames |
|
Item 1 |
|
||||
|
|
... |
|
|
|
Other functional groups |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
>Exposure Control Sensing Regions Sequence |
(0018,9434) |
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
Region 1 |
|
|
|
Item 1 |
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
= CIRCULAR |
|
|
|
|
>>Exposure Control Sensing Region Shape |
(0018,9435) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
= 201\271 |
|
|
|
|
>>Center of Circular Exposure Control Sensing Region |
(0018,9440) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
= 100 |
|
|
|
|
>>Radius of Circular Exposure Control Sensing Region |
(0018,9441) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Region 2 |
|
|
|
Item 2 |
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
= RECTANGULAR |
|
|
|
|
>>Exposure Control Sensing Region Shape |
(0018,9435) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
>>Exposure Control Sensing Region Left Vertical Edge |
(0018,9436) |
= -40 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
>>Exposure Control Sensing Region Right Vertical Edge |
(0018,9437) |
= 34 |
|
|
|
|
>>Exposure Control Sensing Region Upper Horizontal Edge |
(0018,9438) |
= -60 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
>>Exposure Control Sensing Region Lower Horizontal Edge |
(0018,9439) |
= 464 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Item 3 |
|
Region 3 |
|
|
|
|
|
>>Exposure Control Sensing Region Shape |
(0018,9435) |
= RECTANGULAR |
|
|
|
|
>>Exposure Control Sensing Region Left Vertical Edge |
(0018,9436) |
= 510 |
|
|
|
|
>>Exposure Control Sensing Region Right Vertical Edge |
(0018,9437) |
= 584 |
|
|
|
|
>>Exposure Control Sensing Region Upper Horizontal Edge |
(0018,9438) |
= -60 |
|
|
|
|
>>Exposure Control Sensing Region Lower Horizontal Edge |
(0018,9439) |
= 464 |
|
|
... |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
... |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Figure FFF.2.1-22. Attributes of the Second Example of the X-Ray Exposure Control Sensing Regions
- Standard -

DICOM PS3.17 2020a - Explanatory Information |
Page 525 |
FFF.2.1.5 Image Detector and Field of View
ThissectionprovidesinformationontheencodingoftheimagedetectorparametersandfieldofviewappliedduringtheX-Rayacquis- ition.
FFF.2.1.5.1 User Scenario
The user selects a given size of the field of view before starting the acquisition. This size can be smaller than the size of the Image Detector.
The position of the field of view in the detector area changes during the acquisition in order to focus on an object of interest.
Acquired image is networked or stored in offline media, then the image is:
•Displayed and reviewed in cine mode, and the field of view area needs to be displayed on the viewing screen;
•Used for quality assurance, to relate the pixels of the stored image to the detector elements, for instance to understand the image artifacts due to detector defects;
•Used to measure the dimension of organs or other objects of interest;
•Used to determine the position in the 3D space of the projection of the objects of interest.
FFF.2.1.5.2 Encoding Outline
The XA SOP Class does not encode some information to fully characterize the geometry of the conic projection acquisition, such as the position of the Positioner Isocenter on the FOV area. Indeed, the XA SOP Class assumes that the isocenter is projected in the middle of the FOV.
TheEnhancedXASOPClassencodesthepositionoftheIsocenteronthedetector,aswellasspecificFOVAttributes(origin,rotation, flip) per-frame or shared. It encodes some existing Attributes from DX to specify information of the Digital Detector and FOV. It also allowsdifferentiatingtheimageintensifiervs.thedigitaldetectorandthendefinesconditionsonAttributesdependingonimageintens- ifier or digital detector.
FFF.2.1.5.3 Encoding Details
This section provides detailed recommendations of the key Attributes to address this particular scenario.
Table FFF.2.1-40. Enhanced X-Ray Angiographic Image IOD Modules
IE |
Module |
PS3.3 Reference |
Usage |
Image |
XA/XRF Acquisition |
C.8.19.3 |
Specifies the type of detector. |
|
X-Ray Image Intensifier |
C.8.19.4 |
Conditional to type of detector. Applicable in case of |
|
|
|
IMG_INTENSIFIER. |
|
X-Ray Detector |
C.8.19.5 |
Conditional to type of detector. Applicable in case of |
|
|
|
DIGITAL_DETECTOR. |
Table FFF.2.1-41. Enhanced XA Image Functional Group Macros
Functional Group Macro |
PS3.3 Reference |
Usage |
X-Ray Field of View |
C.8.19.6.2 |
Specifies the field of view. |
XA/XRF Frame Pixel Data Properties |
C.8.19.6.4 |
Specifies the Imager Pixel Spacing. |
FFF.2.1.5.3.1 XA/XRF Acquisition Module Recommendations
The usage of this module is recommended to specify the type and details of the receptor.
- Standard -

Page 526 DICOM PS3.17 2020a - Explanatory Information
Table FFF.2.1-42. XA/XRF Acquisition Module Recommendations
Attribute Name |
Tag |
Comment |
X-Ray Receptor Type |
(0018,9420) |
Two values are applicable to this scenario: |
|
|
IMG_INTENSIFIER |
|
|
or |
|
|
DIGITAL_DETECTOR |
Distance Receptor Plane to Detector |
(0018,9426) |
Applicable to this scenario, regardless the type of receptor. |
Housing |
|
|
Distance Receptor Plane to Detector Housing (0018,9426) is a positive value except in the case of an image intensifier where the receptor plane is a virtual plane located outside the detector housing, which depends on the magnification factor of the intensifier.
The Distance Receptor Plane to Detector Housing (0018,9426) may be used to calculate the pixel size of the plane in the patient when markers are placed on the detector housing.
FFF.2.1.5.3.2 X-Ray Image Intensifier Module Recommendations
When the X-Ray Receptor Type (0018,9420) equals "IMG_INTENSIFIER" this module specifies the type and characteristics of the image intensifier.
RECEPTOR PLANE |
INPUT PHOSPHOR SCREEN |
DETECTOR HOUSING |
OUTPUT PHOSPHOR SCREEN |
X-RAY TUBE
|
ACTIVE |
X-RAY BEAM |
DIMENSION |
INTENSIFIER
SIZE
Figure FFF.2.1-23. Schema of the Image Intensifier
The Intensifier Size (0018,1162) is defined as the physical diameter of the maximum active area of the image intensifier. The active area is the region of the input phosphor screen that is projected on the output phosphor screen. The image intensifier device may be configured for several predefined active areas to allow different levels of magnification.
The active area is described by the Intensifier Active Shape (0018,9427) and the Intensifier Active Dimension(s) (0018,9428).
The field of view area is a region equal to or smaller than the active area, and is defined as the region that is effectively irradiated by the X-Ray beam when there is no collimation. The stored image is the image resulting from digitizing the field of view area.
There is no Attribute that relates the FOV origin to the intensifier. It is commonly assumed that the FOV area is centered in the intens- ifier.
The position of the projection of the isocenter on the active area is undefined. It is commonly understood that the X-Ray positioner is calibrated so that the isocenter is projected in the approximate center of the active area, and the field of view area is centered in the active area.
- Standard -

DICOM PS3.17 2020a - Explanatory Information |
Page 527 |
FFF.2.1.5.3.3 X-Ray Detector Module Recommendations
When the X-Ray Receptor Type (0018,9420) equals "DIGITAL_DETECTOR" this module specifies the type and characteristics of the image detector.
The size and pixel spacing of the digital image generated at the output of the digital detector are not necessarily equal to the size and element spacing of the detector matrix. The detector binning is defined as the ratio between the pixel spacing of the detector matrix and the pixel spacing of the digital image.
If the detector binning is higher than 1.0 several elements of the detector matrix contribute to the generation of one single digital pixel.
The digital image may be processed, cropped and resized in order to generate the stored image. The schema below shows these two steps of the modification of the pixel spacing between the detector physical elements and the stored image:
Detector |
|
Detector Reading |
Digital |
|
Field of View Extraction |
|
Stored |
Matrix |
and Binning |
Image |
and Resizing |
|
Image |
||
Figure FFF.2.1-24. Generation of the Stored Image from the Detector Matrix
Table FFF.2.1-43. X-Ray Detector Module Recommendations
Attribute Name |
Tag |
Comment |
Detector Binning |
(0018,701A) |
The ratio between the pixel spacing of the detector matrix and the pixel |
|
|
spacingofthedigitalimage.Itdoesnotdescribeanyfurtherpost-processing |
|
|
to resize the pixels to generate the stored image. |
Detector Element Spacing |
(0018,7022) |
Pixel spacing of the detector matrix. |
Position of Isocenter Projection |
(0018,9430) |
Relates the position of the detector elements to the isocenter reference |
|
|
system.Itisindependentfromthedetectorbinningandfromthefieldofview |
|
|
origin. |
This Attribute is defined if the Isocenter Reference System Sequence (0018,9462) is present.
FFF.2.1.5.3.4 X-Ray Field of View Macro Recommendations
The usage of this macro is recommended to specify the characteristics of the field of view.
When the field of view characteristics change across the Multi-frame Image, this macro is encoded on a per-frame basis.
The field of view region is defined by a shape, origin and dimension. The region of irradiated pixels corresponds to the interior of the field of view region.
When the X-Ray Receptor Type (0018,9420) equals "IMG_INTENSIFIER", the intensifier TLHC is undefined. Therefore the field of view origin cannot be related to the physical area of the receptor. It is commonly understood that the field of view area corresponds to the intensifier active area, but there is no definition in the DICOM Standard that forces a manufacturer to do so. As a consequence, it is impossible to relate the position of the pixels of the stored area to the isocenter reference system.
Table FFF.2.1-44. X-Ray Field of View Macro Recommendations
Attribute Name |
Tag |
Comment |
Field of View Sequence |
(0018,9432) |
|
>Field of View Shape |
(0018,1147) |
Applicable in this scenario. |
>Field of View Dimension(s) in Float |
(0018,9461) |
Applicable in this scenario. |
>Field of View Origin |
(0018,7030) |
Applicable only in the case of digital detector. |
>Field of View Rotation |
(0018,7032) |
Applicable regardless the type of receptor. |
>Field of View Horizontal Flip |
(0018,7034) |
Applicable regardless the type of receptor. |
- Standard -

Page 528 |
DICOM PS3.17 2020a - Explanatory Information |
|
Attribute Name |
Tag |
Comment |
>Field of View Description |
(0018,9433) |
Free text defining the type of field of view as displayed |
|
|
by the manufacturer on the acquisition system. For |
|
|
display purposes. |
FFF.2.1.5.3.5 XA/XRF Frame Pixel Data Properties Macro Recommendations
The usage of this macro is recommended to specify the Imager Pixel Spacing.
When the field of view characteristics change across the Multi-frame Image, this macro is encoded on a per-frame basis.
Table FFF.2.1-45. XA/XRF Frame Pixel Data Properties Macro Recommendations
Attribute Name |
Tag |
Comment |
Frame Pixel Data Properties Sequence |
(0028,9443) |
|
>Imager Pixel Spacing |
(0018,1164) |
Applicable regardless the type of receptor. |
In case of image intensifier, the Imager Pixel Spacing (0018,1164) may be non-uniform due to the pincushion distortion, and this At- tribute corresponds to a manufacturer-defined value (e.g., average, or value at the center of the image).
FFF.2.1.5.4 Examples
FFF.2.1.5.4.1 Field of View On Image Intensifier
This example illustrates the encoding of the dimensions of the intensifier device, the intensifier active area and the field of view in case of image intensifier.
In this example, the diameter of the maximum active area is 410 mm. The image acquisition is performed with an electron lens that focusesthephotoelectronbeaminsidetheintensifiersothatanactiveareaof310mmofdiameterisprojectedontheoutputphosphor screen.
The X-Ray beam is projected on an area of the input phosphor screen of 300 mm of diameter, and the corresponding area on the output phosphor screen is digitized on a matrix of 1024 x1024 pixels. This results on a pixel spacing of the digitized matrix of 0.3413 mm.
The distance from the Receptor Plane to the Detector Housing in the direction from the intensifier to the X-Ray tube is 40 mm.
The encoded values of the key Attributes of this example are shown in Figure FFF.2.1-25.
- Standard -

|
|
|
DICOM PS3.17 2020a - Explanatory Information |
Page 529 |
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
... |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
= 1024 |
|
||||
Rows |
(0028,0010) |
|
|||||
|
|
= 1024 |
|
||||
Columns |
(0028,0011) |
|
|||||
|
|
= IMG_INTENSIFIER |
|
||||
X-Ray Receptor Type |
(0018,9420) |
|
|||||
|
|
|
|
||||
Distance Receptor Plane to Detector Housing |
(0018,9426) |
= 40.0 |
|
||||
|
|
|
|
||||
Intensifier Size |
(0018,1162) |
= 0 410.0 |
|
||||
|
|
|
|
||||
Intensifier Active Shape |
(0018,9427) |
= ROUND |
|
||||
|
|
|
|
||||
Intensifier Active Dimension(s) |
(0018,9428) |
= 310 |
|
||||
... |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Shared Functional Groups Sequence |
(5200,9229) |
|
|
||||
|
Item 1 |
|
|
|
|||
|
|
... |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
>Field of View Sequence |
(0018,9432) |
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Item 1 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
>>Field of View Shape |
(0018,1147) |
= CIRCULAR |
|
|
|
|
|
>>Field of View Dimensions in Float |
(0018,9461) |
= 300.0 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
>>Field of View Rotation |
(0018,7032) |
= 0 |
|
|
|
|
|
>>Field of View Horizontal Flip |
(0018,7034) |
= 0 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
= NO |
|
|
|
>Frame Pixel Data Properties Sequence |
(0028,9443) |
|
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Item 1 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
= 0.3413\0.3413 |
|
|
|
|
|
>>Imager Pixel Spacing |
(0018,1164) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
... |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
... |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Figure FFF.2.1-25. Attributes of the Example of Field of View on Image Intensifier
FFF.2.1.5.4.2 Field of View On Digital Detector
The following examples show three different ways to create the stored image from the same detector matrix.
In the figures below:
•The blue dotted-line squares  represent the physical detector pixels;
represent the physical detector pixels;
•The blue square  represents the TLHC pixel of the physical detector area;
represents the TLHC pixel of the physical detector area;
•The purple square  represents the physical detector pixel in whose center the Isocenter is projected;
represents the physical detector pixel in whose center the Isocenter is projected;
•The dark green square  represents the TLHC pixel of the region of the physical detector that is exposed to X-Ray when there is no collimation inside the field of view;
represents the TLHC pixel of the region of the physical detector that is exposed to X-Ray when there is no collimation inside the field of view;
•The light green square  represents the TLHC pixel of the stored image;
represents the TLHC pixel of the stored image;
•The thick black straight line square 
 represents the stored image, which is assumed to be the field of view area. The small thin black straight line squares represent the pixels of the stored image;
represents the stored image, which is assumed to be the field of view area. The small thin black straight line squares represent the pixels of the stored image;
•The blue dotted-line arrow  represents Field Of View Origin (0018,7030);
represents Field Of View Origin (0018,7030);
•The purple arrow 
 represents the position of the Isocenter Projection (0018,9430).
represents the position of the Isocenter Projection (0018,9430).
Note that the detector active dimension is not necessarily the FOV dimension.
In all the examples,
•The physical detector area is a matrix of 10x10 square detector elements, the TLHC element being the element (1,1);
•The detector elements irradiated during this acquisition (defining the field of view) are in a matrix of 8x8 whose TLHC element is the element (3,3) of the physical detector area.
In the first example, there is neither binning nor resizing between the detector matrix and the stored image.
The encoded values of the key Attributes of this example are shown in Figure FFF.2.1-26.
- Standard -

Page 530 |
|
|
|
DICOM PS3.17 2020a - Explanatory Information |
|||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
... |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
= 8 |
||||
|
Rows |
(0028,0010) |
|||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
= 8 |
||||
|
Columns |
(0028,0011) |
|||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
= DIGITAL_DETECTOR |
||||
|
X-Ray Receptor Type |
(0018,9420) |
|||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||
|
Detector Binning |
(0018,701A) |
= 1.0\1.0 |
||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||
|
Detector Element Spacing |
(0018,7022) |
= 0.2\0.2 |
||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||
|
Position of Isocenter Projection |
(0018,9430) |
= 5\7 |
||||||||||||||||
|
... |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Per-Frame Functional Groups Sequence |
(5200,9230) |
|
||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
... |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Item i |
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||
|
|
|
>Field of View Sequence |
(0018,9432) |
|
||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
Item 1 |
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
>>Field of View Shape |
(0018,1147) |
= RECTANGLE |
||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
>>Field of View Dimensions in Float |
(0018,9461) |
= 1.6\1.6 |
||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
>>Field of View Origin |
(0018,7030) |
= 2.0\2.0 |
||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
>>Field of View Rotation |
(0018,7032) |
= 0 |
||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
>>Field of View Horizontal Flip |
(0018,7034) |
= NO |
||||||||||||
|
|
|
>Frame Pixel Data Properties Sequence |
(0028,9443) |
|
||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
Item 1 |
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
>>Imager Pixel Spacing |
(0018,1164) |
= 0.2\0.2 |
||||||||||||
|
|
|
... |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Figure FFF.2.1-26. Attributes of the First Example of Field of View on Digital Detector
In the second example, there is a binning factor of 2 between the detector matrix and the digital image. There is no resizing between the digital image (binned) and the stored image.
The encoded values of the key Attributes of this example are shown in Figure FFF.2.1-27.
- Standard -
