
- •Wave energy
- •Mechanical waves in elastic medium
- •8.1. Harmonic Vibrations and Their Characteristics
- •Figure 8.1
- •8.2. Differential Equation for Own (Free) Harmonic Vibrations
- •8.3. Energy of Harmonic Vibrations
- •8.4. Damped Vibrations
- •8.5. Addition of Harmonic Vibrations with Equal
- •Figure 8.8
- •8.6. Addition of Perpendicular Vibrations
- •Figure 8.9
- •8.7. Representation of Vibrations with the Help of Fourier Series
- •8.8. Waves. Equation of Mechanical Harmonic Wave
- •Figure 8.16
- •Characteristics of a harmonic wave
- •8.9. Differential Wave Equation
- •8.10. Mechanical Waves in Elastic Medium.
- •8.11. Energy of Elastic Waves
- •8.12. Wave Superposition and Interference
- •8.13. Dispersion of Waves.
- •8.14. Sound
- •8.15. The Doppler Effect in Acoustics
- •Figure 8.24
- •Text 3.1 Electromagnetic Induction. Electromagnetic Waves.
- •Home task
- •Electric charge and field coulomb’s law
- •1.1. Introduction
- •1.2. Electric Charge
- •1.3. Electrostatic Phenomena
- •1.4. Coulomb’s Law
- •6.2 Automation in industry
- •6.4.Changes in matter
- •Vocabulary:
- •Intensity of electric field
- •2.1. Electric Field as Form of Matter
- •2.2. The Tensity of Electric Field
- •2.3. Graphic Representation of Electric Fields
- •2.5. The Superposition Principle
- •Text 9.1.: introduction to the www and the internet
- •The internet
- •5. Dynamics of material points system. Conservation of energy
- •5.1. Work
- •Figure 5.1
- •Figure 5.2
- •Figure 5.3
- •5.2. Power
- •5.3. Energy
- •5.4. Kinetic Energy
- •Figure 5.3
- •Therefore
- •5.5. Potential Energy
- •5.6. Total Energy of System. Conservation of Energy
- •5.7. Perfectly Elastic Collisions
- •5.8. Completely Inelastic Collisions
- •Famous people of science and engineering
- •I. The main features and peculiarities
- •II. The structure of the simple sentence
- •III. The compound sentence and the complex sentence
- •IV. Attributive groups of nouns
- •V. The system of the english tenses in the active voice
- •VI. The group of perfect and perfect continuous tenses
- •VII. The system of the english tenses in the passive voice
- •IX. The participle and its functions the participial constructions
- •X. The gerund and its functions the complexes with the gerund
- •XI. Modal verbs
- •XII. The subjunctive mood
- •Vocabulary.
Міністерство освіти і науки України
Вище професійне училище № 3
м. Мукачево
Навчальний посібник з англійської мови за профспрямуванням
для учнів ПТНЗ
Мукачево
2009
Укладач: Викладач англійської мови ВПУ-3 , викладач вищої категорії, старший викладач Рогач Н.В.
Рецензент: Викладач англійської мови МДАК викладач вищої категорії Софілканич Н.Ю.
Навчальний посібник з англійської мови за профспрямуванням для учнів ПТНЗ Мукачево, 2009.- 183с.

Розглянуто на обласному засіданні методоб’єднання вчителів іноземних мов
від 26 лютого 2009 р.
Даний посібник призначений для учнів, котрі вивчають англійську мову за професійним спрямуванням. В посібнику подано стислий виклад тематичного матеріалу, який складається з трьох частин: технічні тексти для опрацювання під час практичних занять, тексти для самостійного опрацювання та практикум з технічної англійської мови. Метою посібника є розвиток навичок читання та перекладу науково-технічних текстів, активне оволодіння англійською мовою.
Передмова
Основною метою посібника є оволодіння студентами основ перекладу технічних текстів, засвоєння технічних термінів. Доцільність даного навчального посібника полягає в формуванні навичок читання, перекладу науково технічних текстів.
Посібник складається з трьох розділів. В першому розділі подано виклад тематичних текстів для аудиторного опрацювання, короткий словник та після текстові завдання. В посібнику зібрані тексти по різним галузям науки й техніки. Кожен з десяти уроків є логічно з’єднаний з текстами, які пропонуються для самостійного опрацювання. Посібник складений відповідно до змісту навчальної програми.
Ціллю запропонованого матеріалу є розвиток навичок читання, перекладу та оволодіння технічними термінами по спеціальності, зокрема в спеціалізованих розділах (автоматика, робототехніка, автоматизація в промисловості, комп’ютер, системне та програмне забезпечення,Windows-95, Інтернет, операційні системи і т.д.)
В процесі навчання особлива увага приділяється формуванню термінологічної лексики, поповненню словникового запасу студентів.
Недостатність відповідної літератури є дуже відчутна.
В наступній частині посібника пропонуються тестові завдання різної складності. Складність їх виконання полягає в перекладі окремих уривків технічних текстів з розпізнаванням, та аналізом основних граматичних явищ. .В останній частині пропонується невеликий англо-український словник.
Поради учням при роботі з науково-технічним текстом.
- Прочитайте бігло текст, намагаючись визначити зміст тексту.
- Випишіть всі ключові слова, терміни в окремий словничок і використовуйте під час перекладу.
- Прочитайте абзац і спробуйте зрозуміти зміст, уникайте буквального перекладу матеріалу.
- Перекладений текст перечитайте 2 або 3 рази, і виправте стилістичні похибки.
- При перекладі науково-технічного тексту співставляйте його з оригіналом для збереження повноти змісту.
- Слідкуйте за змістом не тільки окремих речень, абзаців, а й за тим, щоб кожен абзац вписувався в контекст.
- Під час перекладу тексту вживайте одні й ті ж терміни для визначення однакових дій та явищ.
- Знання специфічних особливостей науково-технічного тексту є умовою досягнення адекватності перекладу тексту.
- Інтерпретуючи окрему інформацію, що міститься в тексті потрібно володіти основними знаннями з цієї галузі
- Для здійснення адекватного перекладу визначте синтаксичну функцію слова чи групи слів, аналізуючи ціле речення.
- Здійсніть граматичний аналіз речення, визначивши:
1.Підмет,
2.Присудок,
3.Прямий додаток.
Користуючись цими порадами ви зможете побудувати цілісний і адекватний переклад тексту.
Contents.
Передмова. Поради учням при перекладі науково-технічного тексту.
Зміст 6
Part 1.
1.1 My future profession. 7
Wave energy. 11
2.1 Mechanical waves in elastic medium. 13 2.2 The future of the engineering profession. 50
2.3 Three laws of motion 51
3.1 Eelectromagnetic Induction. Electromagnetic Waves. 53
3.2 Electricity and Magnetism. 55
4.1 Famous people of science and engineering. 56
4.2 Mechanical properties of materials. 58
4.3 Science of the heart 61
5.1 Mechanical properties of materials. 63
5.2 Electric charge and field. 66
6.1 Automation 73
6.2 Automation in industry 76
6.3 Application of automation and robotics in industry 77
6.4 Changes in matter 79
7.1 Hardware 7.2 Types of Software. 81 7.3What is a computer. 89
7.4 Intensity of electric field. 90
8.1 Operating systems 101
8.2 Windows 95 103
8.3 The switch towards greater harmony 104
9.1 Introduction to the WWW and the Internet. 105
9.2 The Internet 106
10.1Dynamics of material points system. 109
10.2 Famous people of science and engineering. 124
Part 2
Grammar tests. 125
Part 3.
Vocabulary 176
Список літератури 183
LESSON 1
TEXT 1.1.: MY FUTURE PROFESSION
Hi, there! Here is Dennis Petrenko again. I am afraid this will be my last meeting with you because I need pack my suitcase. I am leaving for Sochi tonight. I have passed all the exams successfully and I’m free till the September.
As I have already told you, I was always good in mathematics and physics. My parents bought me a computer when I was in the 10th form. Since then I knew that I would become a specialist in computer technologies — a computer engineer.
Computer industry is developing so fast, that it comprises almost all spheres of professional life. No business now is possible without computers. This is especially true about automated manufacturing of products and robotics. Computer control of automated production opens new horizons for the cheap and quality production of goods. Information is now generated, transmitted, received, and stored electronically through computer networks on a scale unprecedented in history, and there is every indication that the explosive rate of growth in this field will continue.
Computer engineering is a general field. It deals with both electric and electronic industries. .
Electronic engineering deals with the research, design, integration, and application of circuits and devices used in the transmission and processing of information.
Engineers in the field of electric and electronic engineering are concerned with all aspects of electrical communications, from fundamental questions such as What is information?, to the highly practical, such as the design of telephone systems. In designing communication systems, engineers rely on various branches of advanced mathematics, such as Fourier analysis, linear systems theory, linear algebra, differential equations, and probability theory.
Engineers work on control systems which are used extensively in automated manufacturing and in robotics.
Major developments in the field of communications and control have been the replacement of analogue systems with digital systems; fibre optics are used now instead of copper cables. Digital systems offer far greater immunity to electrical noise. Fibre optics are likewise immune to interference; they also have great carrying capacity, and are extremely light and inexpensive to manufacture.
Computer engineering is now the most rapidly growing field. The electronics of computers is the design and manufacture of memory systems, of central processing units, and of peripheral devices. The most prospective industry now is the Very Large Scale Integration (VLSI) and new computer architectures. The field of computer science is closely related to computer engineering;
the task of making computers more <intelligent> (artificial intelligence), through creation of sophisticated programs or development of higher level machine languages or other means, is generally regarded as dream of computer science.
One current trend in computer engineering is micro- miniaturization. Engineers continue to work to greater and greater numbers of circuit elements smaller and smaller chips.
Another trend is towards increasing the speed of operations through the use of parallel processors and superconducting materials.
So, as you see, there are a lot of employment opportunities in my field. I don’t worry about finding a job. Most important thing for me now is to study well and graduate from the Academy.
VOCABULARY:
To comprise – містить в собі
Automated manufacturing of products – автоматизоване виробництво товарів
Robotics – робототехніка
Horizons - горизонти
Cheap - дешевий
To generate – генерувати, виробляти
To transmit - передавати
To store – зберігати
Scale - масштаб
Unprecedented in history – той, що не має прецидентів в історії
Indication – свідоцтво, вказівка
Explosive - вибуховий
To deal with – мату справу з, займатися чим небудь
Integration - інтеграція
Application – використання, додаток
Circuits – електронні схеми, ланцюги
Device – пристрій
Transmission – передача
Processing – обробка
To rely – покладатися
Fourier analysis – аналіз Фурьє
Linear systems theory – теорія лінійних систем
Differential equations – диференційні рівняння
Probability theory – теорія імовірності
Extensively - широко
Replacement - заміщення
Fibre optics – оптоволоконні технології
Copper - мідь
Digital - цифровий
Immunity – захищеність, несприйняття
Carrying capacity – пропускна здатність
Light - легкий
Rapidly growing – швидко зростаючий
Artificial intelligence – штучний інтелект
Sophisticated - складний
Superconducting - надпровідність
Exercise 1.
How do you see your future profession. Please answer the following questions:
What kind of work are you interested in?
well paid
interesting
in a large and famous company
quiet
in an industry which has a future
prestigious
not to sit the whole day in the office
to travel a lot
What position would you like to have?
to manage people – manager
to work for someone else – an employee
to be your own boss – self- employed, businessman
be responsible for everything – top manager, director
to work for the state – state employee.
HOME-READING
Wave energy
Waves transmit energy from place to place. Mechanical waves are formed when a disturbance causes surrounding molecules to change position. This sets up a chain reaction in which neighboring molecules change position, and then return to their original position after bumping their "neighbors". This chain reaction constitutes a wave. A disturbance can be anything that disrupts the surrounding molecules. Virtually anything that is seen or heard is the result of some kind of disturbance that is transmitted by a wave. All waves have common characteristics-speed, wavelength, frequency, and amplitude. Waves can be classified as mechanical waves or electromagnetic waves. Mechanical waves such as water waves or sound waves require a medium through which to travel. Electromagnetic waves, such as visible light, radio waves, and X rays, can travel through a vacuum — a space void of matter.
Waves can also be classified as either transverse or longitudinal. In transverse waves, the high points of the wave are the crests and the low points are the troughs. In longitudinal waves, the compressions compare to the troughs of transverse waves. The wavelength of a wave is the distance from any point on a wave to the next similar point. The number of crests (or compressions) that pass a given point in a certain amount of time is the frequency of the wave.
All waves also share similar behaviors. Waves can be reflected or refracted and can create interference. Both reflection and refraction involve waves and two different mediums. In reflection, the waves bounce back when they encounter a new medium. According to the law of reflection, the angle of incidence equals the angle of reflection. In refraction, the waves change speed and direction as they enter a new medium. Interference is the result of different waves moving through one another. Interference can be constructive, resulting in a greater amplitude, or destructive, resulting in a smaller amplitude.
LESSON 2
TEXT 2.1.:
Mechanical waves in elastic medium
8.1. Harmonic Vibrations and Their Characteristics
The vibration is a repeated process of deflection of system’s state in both sides from its definite state. The state of vibration system is determined by parameters, which are included in the equation of vibration (the vibration equation).
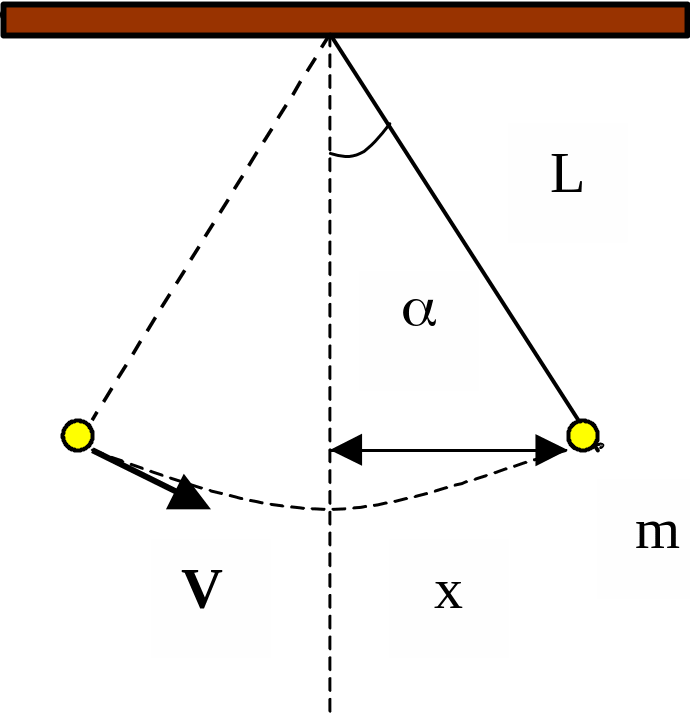
Figure 8.1
The equation of vibration is the expression for oscillating value as function of time. For example, x = f(t) (8.1). It is possible to write down equations for displacement x, velocity v, energy W, angle etc.
Periodic vibrations are recurring at regular intervals. In mathematics the following definition for periodic function is given: the periodic function is the function returning to the same value at regular intervals, namely
x(t + T) = x(t),
where T is the period.
The period is amount of time between recurrences of function.
Harmonic vibrations are vibrations for which dependence on time of the oscillating value is described by sine or cosine:
x = A sin(t + 0).
C h a r a c t e r i s t i c s o f v i b r a t i o n s:
1. The period T is the time necessary for one complete vibration. The period is expressed in second (s).
2. The frequency is the number of complete vibrations made during a unit time. The basic unit of one cycle per second has been named the hertz (Hz). The frequency is the reciprocal of the period = 1/T.
3. The cyclic frequency : = 2 = 2/T – is the number of complete vibrations made in 2 units of time.
4. The amplitude is the maximum value of the displacement, or the distance from the equilibrium position to the end of the vibrating path. The amplitude is expressed in meter (m).
5. The phase is a particular stage recurring the sequence of movements or changes = t + 0.
C o n d i t i o n s f o r t h e b e g i n i n g o f v i b r a t i o n s
1). It is necessary to have the external action, which introduces some quantity of energy into vibration system.
2). It is necessary to have the restore reaction in vibration system.
