
Laboratory work #2
Measurement of relative humidity, movability and temperature of the atmospheric air in natural environment and industrial premises
Aim of the work: to learn how to determine the relative humidity of the air.
Tasks of the work:
Learn the structure of psychrometer techniques of humidity determination.
Determine relative humidity of air in the room.
Determine absolute air humidity.
Define dew-point temperature.
Estimate the optimality of the relative air humidity in the room.
Equipment: psychrometer, water glass, look-up tables.
Theoretical part
Earth atmosphere contains water vapor. Air humidity exists due to vapor content at any temperature. Water vapor is characterized by absolute and relative humidity.
Water vapor content in the air plays significant role in atmospheric processes, effects on life of plants and animals. It is significant for some kinds of production.
Absolute humidity is the water mass content in 1 m3 air volume [g m-3]. Absolute humidity insignificantly differs from water vapor pressure in the same conditions [mm Hg].
In certain conditions water vapor may saturate air. Water mass content saturating air 1 m-3 at certain temperature, is the maximal air humidity ρs, or saturated water vapor density.
Absolute density ρa may be determined if known dew point – point of water vapor saturation.
However, we cannot assess air vapor saturation only by absolute humidity. That is why the term “Relative humidity” was introduced. Relative humidity B is determined as the percent relation between absolute humidity ρa and maximal air vapor density ρs at the same temperature:
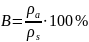
Relative humidity B defines the percentage of absolute humidity from saturated water vapor density ρs at given temperature. Vaporization intensity depends on relative air humidity.
The lower the temperature, the more humid air at the same absolute humidity; The higher the temperature, the drier air. Therefore, it is important to know how close (or far) is water vapor to saturation. Thus, it is necessary to know the actual pressure of water vapor (absolute humidity) and the pressure of saturated water vapor at the same temperature.
Normal 40-60% relative humidity for premises is considered.
It is possible to define the absolute and relative air humidity if air temperature and air vapor saturation temperature is known.
The temperature of water vapor saturation is called the dew point.
The relative humidity measured by hygrometer.
Materials and methods
For practical determination of the air humidity hygrometer and psychrometer is used. Figure 1a shows the hair hygrometer, figure 1b - Avgust’s psychrometer. First one operation principle is based on human hair ability to change the length depending on humidity (hugher humidity - longer hair, and vice versa).
Operation principle of Avgust’s psychrometer is based on:
cooling of body of evaporation surface;
dependence of liquid evaporation speed on air humidity.

Hygrometer Avgust’s psychrometer
а б
Figure 1. Devices for determination of relative humidity
Avgust’s psychrometer has two identical thermometers A and B. Dry ball of A thermometer shows the air temperature. The ball of B thermometer is covered by gauze or cotton wool partially moistened in the water vessel. Gauze is always wet. The less humidity, the faster vaporization, and, consequently, the grater difference between dry and wet thermometer. If air is saturated, no vaporization occurs (dynamic equilibrium state), and thermometer indexes are equal. Relative humidity may be rapidly and accurately determined with the help special psychrometric tables due to indexes of dry and wet thermometer.
