
- •Часть I
- •Предисловие
- •I семестр Урок 1.1 Фонетическое задание
- •Ответьте на вопросы к тексту.
- •Лексические упражнения
- •Грамматические упражнения
- •Ответьте на вопросы к тексту.
- •Грамматические упражнения
- •Лексические упражнения
- •Урок 1.2 Фонетическое задание
- •Ответьте на вопросы к тексту.
- •Лексические упражнения
- •Грамматические упражнения
- •Ответьте на вопросы к тексту.
- •Грамматические упражнения
- •Лексические упражнения
- •Урок 1.3 Фонетическое задание
- •Ответьте на вопросы к тексту.
- •Лексические упражнения
- •Грамматические упражнения
- •Ответьте на вопросы к тексту.
- •Грамматические упражнения
- •Лексические упражнения
- •Урок 1.4 Фонетическое задание
- •Ответьте на вопросы к тексту.
- •Лексические упражнения
- •Грамматические упражнения
- •Ответьте на вопросы к тексту.
- •Грамматические упражнения
- •Лексические упражнения
- •Ответьте на вопросы к тексту.
- •Лексическое упражнение
- •Урок 1.5 Фонетическое задание
- •Ответьте на вопросы к тексту.
- •Лексические упражнения
- •Грамматические упражнения
- •Ответьте на вопросы к тексту.
- •Грамматические упражнения
- •Лексические упражнения
- •Урок 1.6 Фонетическое задание
- •Ответьте на вопросы к тексту.
- •Лексические упражнения
- •Грамматические упражнения
- •Ответьте на вопросы к тексту
- •Грамматические упражнения
- •Лексические упражнения
- •Урок 1.7 Фонетическое задание
- •Ответьте на вопросы к тексту.
- •Лексические упражнения
- •Грамматические упражнения
- •Ответьте на вопросы к тексту.
- •Грамматические упражнения
- •Лексические упражнения
- •Урок 1.8 Фонетическое задание
- •Ответьте на вопросы к тексту.
- •Лексические упражнения
- •Грамматические упражнения
- •Ответьте на вопросы к тексту.
- •Грамматические упражнения
- •Лексические упражнения
- •Ответьте на вопросы к тексту.
- •Лексическое упражнение
- •Урок 1.9 Фонетическое задание
- •Ответьте на вопросы к тексту.
- •Лексические упражнения
- •Грамматические упражнения
- •Ответьте на вопросы к тексту.
- •Лексические упражнения
- •Урок 1.10 Фонетическое задание
- •Ответьте на вопросы к тексту.
- •Лексические упражнения
- •Грамматические упражнения
- •Ответьте на вопросы к тексту.
- •Лексические упражнения
- •Урок 1.11 Фонетическое задание
- •Ответьте на вопросы к тексту.
- •Лексические упражнения
- •Грамматические упражнения
- •Ответьте на вопросы к тексту.
- •Грамматическое упражнение
- •Лексические упражнения
- •Урок 1.12 Фонетическое задание
- •Ответьте на вопросы к тексту.
- •Лексические упражнения
- •Грамматические упражнения
- •Ответьте на вопросы к тексту.
- •Лексические упражнения
- •Ответьте на вопросы к тексту.
- •Лексическое упражнение
- •II семестр Урок 2.1 Фонетическое задание
- •Ответьте на вопросы к тексту
- •Лексические упражнения
- •Грамматические упражнения
- •Ответьте на вопросы к тексту
- •Грамматические упражнения
- •Лексические упражнения
- •Урок 2.2 Фонетическое задание
- •Ответьте на вопросы к тексту
- •Лексические упражнения
- •Грамматические упражнения
- •Ответьте на вопросы к тексту
- •Грамматические упражнения
- •Лексические упражнения
- •Урок 2.3 Фонетическое задание
- •Ответьте на вопросы к тексту
- •Лексические упражнения
- •Грамматические упражнения
- •Ответьте на вопросы к тексту
- •Грамматические упражнения
- •Лексические упражнения
- •Урок 2.4 Фонетическое задание
- •Ответьте на вопросы к тексту
- •Лексические упражнения
- •Грамматические упражнения
- •Ответьте на вопросы к тексту
- •Грамматические упражнения
- •Лексические упражнения
- •Ответьте на вопросы к тексту.
- •Лексическое упражнение
- •Урок 2.5 Фонетическое задание
- •Ответьте на вопросы к тексту.
- •Лексические упражнения
- •Грамматические упражнения
- •Ответьте на вопросы к тексту.
- •Грамматические упражнения
- •Лексические упражнения
- •Урок 2.6 Фонетическое задание
- •Ответьте на вопросы к тексту.
- •Лексические упражнения
- •Грамматические упражнения
- •Ответьте на вопросы к тексту.
- •Грамматические упражнения
- •Лексические упражнения
- •Урок 2.7 Фонетическое задание
- •Ответьте на вопросы к тексту.
- •Лексические упражнения
- •Грамматические упражнения
- •Ответьте на вопросы к тексту.
- •Грамматическое упражнение
- •Лексические упражнения
- •Урок 2.8 Фонетическое задание
- •Ответьте на вопросы к тексту.
- •Лексические упражнения
- •Грамматические упражнения
- •Ответьте на вопросы к тексту.
- •Грамматическое упражнение
- •Лексические упражнения
- •Ответьте на вопросы к тексту.
- •Лексическое упражнение
- •Урок 2.9 Фонетическое задание
- •Ответьте на вопросы к тексту.
- •Лексические упражнения
- •Грамматические упражнения
- •Ответьте на вопросы к тексту.
- •Грамматические упражнения
- •Лексические упражнения
- •Урок 2.10 Фонетическое задание
- •Ответьте на вопросы к тексту.
- •Лексические упражнения
- •Грамматические упражнения
- •Ответьте на вопросы к тексту.
- •Грамматические упражнения
- •Лексические упражнения
- •Урок 2.11 Фонетическое задание
- •Ответьте на вопросы к тексту.
- •Лексические упражнения
- •Грамматические упражнения
- •Грамматические упражнения
- •Лексические упражнения
- •Урок 2.12 Фонетическое задание
- •Ответьте на вопросы к тексту.
- •Лексические упражнения
- •Грамматические упражнения
- •Ответьте на вопросы к тексту.
- •Грамматические упражнения
- •Лексические упражнения
- •Ответьте на вопросы к тексту.
- •Лексическое упражнение
- •Знаки фонетической транскрипции
- •Словарный минимум строительных терминов I – II семестров
- •Распределение грамматических тем по урокам
- •I семестр
- •II семестр
- •Библиография текстов
- •1 Части речи и члены предложения (Parts of speech and parts of sentence)
- •2 Имя существительное (Noun)
- •2.1 Образование множественного числа существительных (Plural of noun)
- •2.2 Притяжательный падеж существительных (Genitive case)
- •2.3 Группа существительных (Noun group)
- •3 Степени сравнения прилагательных и наречий
- •3.1 Образование степеней сравнения (Formation of degrees of comparison)
- •3.2 Сравнительные обороты (Comparative structures)
- •5.2.2 Отрицательное местоимение no
- •5.2.3 Производные от местоимений some, any, no, every
- •6 Глагол (Verb)
- •6.1 Типы глаголов
- •6.1.1 Правильные глаголы
- •6.1.2 Неправильные глаголы
- •6.1.3 Глаголы смешанного типа
- •6.2 Личные формы глагола
- •6.2.1 Особенности образования форм Present Simple и Past Simple
- •6.2.2 Времена глагола в действительном залоге (active voice)
- •6.2.2.1 Глагол to be
- •6.2.2.3 Глагол to have
- •6.2.3 Страдательный залог (Passive Voice)
- •6.3 Модальные глаголы (Modal verbs)
- •6.3.1 Модальные глаголы, выражающие долженствование
- •6.3.2 Модальные глаголы, выражающие способность или возможность
- •6.3.3 Модальные глаголы, выражающие разрешение или возможность
- •6.4 Согласование времён (Sequence of tenses)
- •6.5 Сослагательное наклонение (Subjunctive mood)
- •6.5.1 Условные предложения (Conditional sentences)
- •7.1.2.2 Субъектный инфинитивный оборот
- •7.2.4 Причастные обороты
- •7.2.4.1 Зависимые причастные обороты
- •7.2.4.2 Независимые причастные обороты
- •7.2.4.3 Независимые причастные обороты без причастия
- •7.3.2 Перфектные формы герундия
- •8 Словообразование (Word Formation)
- •8.1 Конверсия (Conversion)
- •Сказуемое – подлежащее – дополнение
- •9.2 Вопросительное предложение (Interrogative Sentence)
- •9.2.1 Общие вопросы (General questions)
- •9.2.2 Альтернативные вопросы (Alternative questions)
- •9.2.3 Разделительные/”хвостовые” вопросы (Disjunctive/Tag questions)
- •9.2.4 Специальные вопросы (Special questions)
- •9.3 Сложноподчиненное предложение (The Complex Sentence)
- •10 Приложение (Appendix)
- •10.1 Усилительные конструкции (Emphatic Constructions)
- •10.1.2 Усилительное слово do
- •10.2 Многофункциональные слова (Multifunctional Words)
- •10.2.1 Функции слова it
- •10.2.2 Функции слова one
- •10.2.3 Функции слова that
- •10.3 Неправильные глаголы*
- •Библиография грамматики
- •Часть I
Ответьте на вопросы к тексту
How are structures built on the ground?
Who must ensure that settlement is uniform and small?
What does differential settling results in?
How is the simplest type of foundation made?
How is the foundation made in ground of worse bearing quality?
Who was the raft developed by?
What are the characteristics of modern foundations?
Грамматические упражнения
Упражнение 1. Найдите в первом абзаце текста причастие I. Определите его функцию и переведите на русский язык.
Упражнение 2. Какие времена использованы в тексте?
Упражнение 3. Найдите в тексте модальные глаголы и их заменители. Переведите их на русский язык.
Лексические упражнения
Упражнение 1. Переведите на русский язык приведённые ниже слова. Если Вы не знаете слово, найдите его в словаре. Выпишите из словаря то значение слова, в котором оно использовано в тексте.
series (n.), spread (v.), box (n.), superstructure (n.), settlement (n.), rock (n.), settle (v.),basement (n.), bear (v.), raft foundation.
Упражнение 2. Найдите перевод слов списка А в списке В.

Упражнение 3. Напишите предложения с каждым из перечисленных ниже слов:
base n - base v. - basement n.
separate adj. - separate v.
Урок 2.2 Фонетическое задание
Прочитайте транскрипцию в списке A, соотнесите её с соответствующим словом из списка B и переведите слово на русский язык. Учтите, что не все слова списка В даны в списке А.
A
["RkI'tekCqrql]; [kwaIt]; ['elIveIt]; ['lxtqrql]; [q"kjHmjV'leISqn]; ['relqtIvlI]; ['xkCVqlI]; [pq'tenSql]; [dI'skraIb]; [bI'lqV]; [sOIl]; [kqn'sIdqrqbql]; [Ig'zWt]; [djH]
B
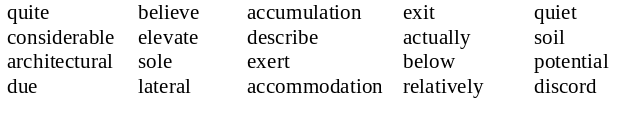
Текст A
SHALLOW FOUNDATIONS
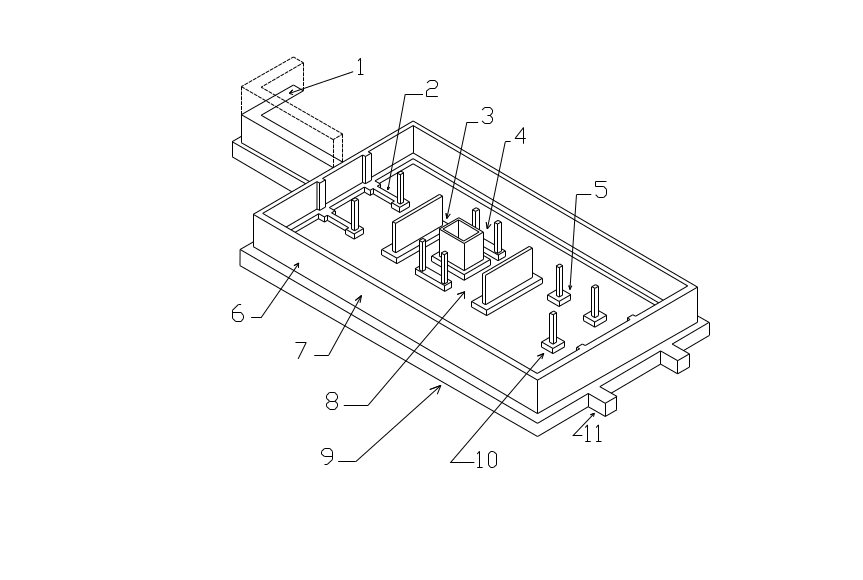

FIGURE 1
Shallow foundation is the term usually used when the type of foundation that transfers vertical loads by direct bearing on soil strata close to the bottom of the building and a relatively short distance below the ground surface is described. There are three basic forms of shallow foundations: the continuous, strip, wall footing; the individual column or pier footing; and the mat or raft foundation. Figure 1 shows a number of elements generally used in bearing foundation systems.
Foundation walls are typically built of concrete or masonry. The structural and architectural functions of foundation walls vary, depending on the type of foundation, the size of the building, climate and soil conditions, and whether or not they form a basement.
With no basement the walls are not actually walls. A principal difference relates to the construction of the building floor, whether it consists of a framed structure elevated above the ground, or concrete placed directly on the ground.
When a basement is required foundation walls are usually quite high. In a half-basement the basement floor is only a short distance below grade and the part of the basement wall above ground may be of different construction than that extending into the ground. If the basement floor is a significant distance below grade, major soil pressure will be exerted horizontally against the outside of the wall. In such a case the wall will function as a spanning element supported laterally by the footing or the basement floor at its lower end and by the building floor at its top. For buildings with multilevel basements, walls may become quite massive due to the accumulation of vertical load and the potential for considerable lateral soil pressure.
Notes:
accumulation n. накопление
continuous footing ленточный фундамент
half-basement n. полуподвал
multilevel adj. многоуровневый, многоэтажный
pier footing столбчатый фундамент
