
- •Module 1 Lecture n5
- •Carbohydrates Digestion in Gastrointestinal Tract
- •Starch Olygosaccharide Maltose Glucose
- •Digestion of lipids
- •Gastrointestinal input of proteins
- •Age g/ kg of mass ± 20%
- •Digestion of proteins in gastrointestinal tract
- •Gastric juice: its composition and secretion
- •Intestinal proteases
- •Determination of some indexes to estimate the protein digestion in patients (for gastric juice, only)
- •The infringement processes in absorption of amino acids and their conversions in the large intestine
- •Nitrogen Balance
Intestinal proteases
Aminopeptidases and dipeptidases
On the intestinal cell surface the digestion of protein to free amino acids continues. Dipeptides and tripeptides are usually absorbed as such and are digested to free amino acids by Dipeptidases and Tripeptidases accordingly within intestinal epithelial cells. Aminopeptidases remove the N-terminal amino acid residue from short polypeptides.
Absorption of free amino acids takes place in the small intestine
All amino acids are divided into five separate systems for transport mechanism across membranes.
Groups 1 (Small neutral amino acids) and 2 (Large neutral and aromatic amino acids) are transported across membrane of any cell by γ-Glutamyl transferase system.
And there are special transport systems for: Acidic amino acids (3), Basic amino acids and Cystine (4), Proline and Glycine (5).
Determination of some indexes to estimate the protein digestion in patients (for gastric juice, only)
The main tests for gastric juice (indexes for adults) are:
Determination of its volume:
on an empty stomach – not higher then 50 ml;
the intensity of basal secretion – 50-100 ml/per 1 hour;
secretion after stimulation (N.P. Leporsky method) – 50-110 ml/per 1 hour;
submaximal stimulation by histamine – 100-140 ml/per 1 hour;
maximal stimulation by histamine - 180-200 ml/per 1 hour.
The total acidity of gastric juice must be in a region 40-60 mmol/lit.
The content of free hydrochloric acid must be in region 20-40 mmol/lit.
The content of conjugated hydrochloric acid must be in region 10-20 mmol/lit.
The increase of total acidity of gastric juice and content of free hydrochloric acid (Hyperchlorhydria) may be during Stomach Ulcer and Superacidity.
The decrease of total acidity of gastric juice and content of free hydrochloric acid (Hypochlorhydria) is observed during Subacidic gastritis or gastric carcinoma.
A complete absence of hydrochloric acid in gastric juice and considerable lowering of total acidity (Achlorhydria) may be also during gastric carcinoma.
Achlorhydria may be called also Achylia. Achlorhydria after stimulation by histamine is a sign of atrophy of epithelial cells of stomach, the sign of gastritis with blocked secretion.
Lactate is appeared in gastric juice during the intensity of fermentation processes in stomach. There is the suggestion that lactate is a product of cancer cells in stomach.
Concentration of Pepsin (after stimulation) on empty stomach must be in region 0,2-0,4 mg/ml or 20-40 units/ml (Pyatnitsky et all, method).
Doctors consider:
Anacidic state if pH (after maximal stimulation by histamine) of gastric juice is about 6,0 or higher;
Achlorhydria state if pH (after maximal stimulation by histamine) of gastric juice is in a region 3,5-6,0;
Hypochlorhydria state if pH (after maximal stimulation by histamine) of gastric juice is in a region 2,5-3,5.
The infringement processes in absorption of amino acids and their conversions in the large intestine
If there is no absorption of amino acids in the small intestine the large intestinal microflora enzymes are capable of catalyzing a variety of metabolic conversions of amino acids. Some toxic products are produced in this case:
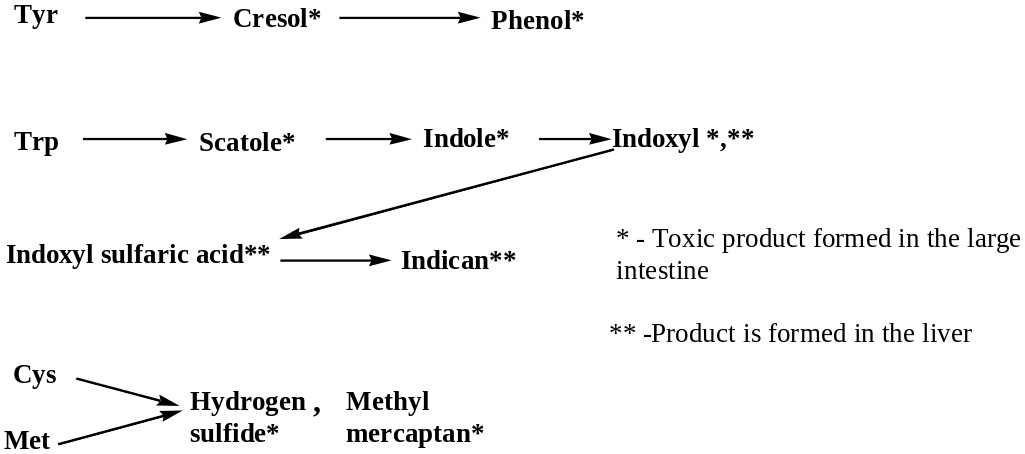
There are some protective systems in the liver that neutralize these toxic products:
1) UDP-Glucuronyl Transferase system;
2) Phospho Adenosyl Phospho Sulfate (PAPS) Transferase System;
3) Enzyme system for Conjugation with Glycine;
Enzyme system for Conjugation with Glutamine
Glutathione Transferase system and others.
Determination of Indican concentration in the urine allows to value the rate of protein putrefaction in the large intestine as well as of diagnosing the functional state of the liver.
Quick’s test is also used for this purpose (determination of hippuric acid in the urine following the administration of sodium benzoate):
Oral dose of sodium benzoate 3-4 g is administrated. After 3 hours the concentration of hippuric acid is determined in the urine of patient. 65%-85% of the initial benzoate is discharged in the composition of hippuric acid (its glycine conjugation product) in the urine of healthy adult patient.
