
- •Навчальний посібник для студентів-технологів
- •Костянтинівка
- •Introduction то chemistry
- •Vocabulary
- •Exercises
- •1. Answer the questions.
- •2. Match the English word combinations with their Ukrainian equivalents;
- •3. Match the Ukrainian word combinations with their English equivalents
- •From the history of chemistry
- •Vocabulary
- •Exercises
- •Answer the questions
- •6. Translate the words in the brackets into English:
- •7. Translate the text using a dictionary. Some facts about chemistry
- •D. I. Mendeleyev
- •Exercises
- •1. Answer the questions
- •2. Translate the sentences paying attention to the passive constructions:
- •3. Open the brackets choosing the suitable word. Translate them.
- •Chemistry: key to progress and abundance
- •Vocabulary
- •Fields of chemistry
- •Vocabulary
- •Exercises
- •2.Answer the questions.
- •3.Fill in the gaps with suitable words given below.
- •4.Make up sentences out of these words.
- •5. Translate into English.
- •Symbols, formulas and equations
- •Vocabulary
- •Inorganic molecules and compounds
- •Vocabulary
- •Periodic law
- •Vocabulary
- •Exercises
- •Answer the questions.
- •True or false?
- •Найважливіші хімічні елементи
- •Rules of reading formulas and equations Правила читання хімічних формул
- •Приклади:
- •The periodic table of d.I. Mendeleyev
- •Vocabulary
- •Exercises
- •1. Answer the questions
- •2. Read and translate the text with vocabulary Joseph Priestley
- •Laboratory equipment
- •2.Learn the words and special term from the list.
- •Describe the functions of each piece of equipment. An experiment in the laboratory
- •Vocabulary
- •Exercises
- •1. Answer the questions
- •2. Give Ukrainian equivalents:
- •3. Translate the sentences:
- •4. Make the questions to the sentences:
- •The molecular theory of matter and the states of matter
- •Vocabulary
- •Exercises
- •1. Answer the questions
- •2. Give English equivalents:
- •3. Give Ukrainian equivalents:
- •4. Translate the sentences:
- •Atomic structure
- •Vocabulary
- •Exercises
- •1. Answer the questions
- •2. Give Ukrainian equivalents:
- •3. Give English equivalents:
- •8. Read and translate the text Molecules
- •Chemical and physical changes
- •Vocabulary
- •Exercises
- •1. Answer the questions
- •Find the pairs of synonyms:
- •Find the pairs of antonyms:
- •4. Translate the following sentences, mind the Participles:
- •5. Open the brackets translating the Ukrainian words:
- •Nuclear fission
- •Vocabulary
- •Exercises
- •1. Answer the questions
- •2. Translate the sentences into Ukrainian:
- •Open the brackets choosing the suitable word and translate them into
- •4. Translate the text in writing
- •Vocabulary
- •Exercises
- •5. Read and translate the text The Temperature Scales
- •Exercises
- •1. Give Ukrainian equivalents:
- •2. Give English equivalents:
- •Liquids
- •Vocabulary
- •Exercises
- •Exercises
- •1. Find Ukrainian equivalents:
- •2. Find English equivalents:
- •Vocabulary
- •Exercises
- •1. Answer the questions
- •2. Give synonyms:
- •3. Translate the following sentences:
- •Acids and bases
- •1. Extremely useful – надзвичайно корисні
- •2. Are common to all – загальні для всіх
- •3. Acetic acid - оцтова кислота
- •Vocabulary
- •Exercises
- •1. Answer the following questions.
- •2. Complete the sentences (use the text).
- •3. Characterize acids and bases using the following plan.
- •Vocabulary
- •Exercises
- •Chlorine
- •Vocabulary
- •Exercises
- •1. Answer the questions.
- •Make up a description of any element you like. Hydrochloric acid
- •Vocabulary
- •Exercises
- •Match English word combinations with their Ukrainian equivalents.
- •Answer the questions.
- •Solutions
- •Vocabulary
- •Exercises
- •Answer the questions
- •2. Translate the following sentences:
- •Nitrogen
- •Vocabulary
- •Exercises
- •Match English word combinations with their Ukrainian equivalents.
- •Answer the questions.
- •Silicon
- •Vocabulary
- •Exercises
- •Match English word combinations with their Ukrainian equivalents.
- •Answer the questions
- •Cellulose
- •Vocabulary
- •Exercises
- •Answer the questions.
- •Analytical chemistry methods of analysis
- •Methods of separation
- •Ion exchange methods in analytical chemistry
- •Ionization
- •Vocabulary
- •Exercises
- •Chromatography and ion exchange technique
- •Chromatography techniques
- •Gas analysis
- •Some physical methods used in gas analysis
- •Extraction
- •Precipitation
- •Electrolysis
- •Polymers
- •Notes and commentary
- •Vocabulary
- •Exercises
- •1. Answer the questions.
- •2. Match English word combinations with their Ukrainian equivalents.
- •3. Match Russian word combinations with their English equivalents.
- •Retell text using questions from Ex. 1 as a plan.
- •5. Read, translate and do the tasks.
- •Some applications of polymers
- •Vocabulary
- •Exercises
- •1. Read and translate the sentences. Correct the false statements.
- •2. Read the text, translate it in written form using dictionary.
- •The nature of polymeric materials
- •Vocabulary
- •Exercises
- •1. Answer the questions
- •Find the pairs of synonyms:
- •Find the pairs of antonyms:
- •Choose the Ukrainian equivalents from the right column:
- •5. Translate the sentences
- •6. Open the brackets choosing the suitable verb:
- •7. Open the brackets choosing the correct form of the verb:
- •7. Translate the text in writing
- •Vocabulary
- •Exercises
- •1. Answer the questions
- •2.Translate the following word-combinations:
- •Translate into English:
- •4. Open the brackets translating the Ukrainian words into English:
- •5. Translate the sentences into Ukrainian:
- •6. Translate the text using a dictionary
- •Microbiological production of industrial chemicals
- •Vocabulary
- •Exercises
- •1. Answer the questions
- •Translate the following sentences into Ukrainian, mind the sentences of the predicate:
- •3. Translate the following sentences into English, mind the use of the tenses:
- •4. Translate the following sentences into Ukrainian
- •5. Translate from Ukrainian into English
- •The chemical elements essential to life
- •Vocabulary
- •Exercises
- •1. Answer the questions
- •2. Find the pairs of synonyms:
- •Find the pairs of antonyms:
- •4. Translate paying attention to the meanings of the word “provide”
- •5. Open the brackets translating the Ukrainian words into English
- •6. Translate the text with a dictionary Hydrogen in industry
- •Plastics
- •Vocabulary
- •Exercises
- •Answer the questions.
- •Glass and glass products
- •Vocabulary
- •Exercises
- •Translate into Ukrainian the following international words.
- •Match English word combinations with their Ukrainian equivalents.
- •Answer the questions.
- •The nature of ceramics
- •Vocabulary
- •Exercises
- •1. Answer the questions
- •2. Translate the sentences:
- •7. Read and translate the texts
- •Ceramics
- •Vocabulary
- •Exercises
- •Translate the following international words into Ukrainian.
- •Answer the questions.
- •What is ecology?
- •Vocabulary
- •Exercises
- •1. Answer the questions
- •2. Translate the following sentences:
- •3. Translate the sentences:
- •The water problem
- •Pollution
- •Air pollution
- •Water pollution
- •Earth pollution
- •Vocabulary
- •Exercises
- •1. Answer the questions
- •2. Translate the following word-combinations:
- •3. Translate the following sentences into Ukrainian:
- •4. Translate the sentences into Ukrainian:
- •5. Write the translation of the following text Lead
- •The environmental protection
- •Vocabulary
- •Exercises
- •1. Match the words:
- •2. Translate the sentences into English:
- •3. Put 4 types of the questions to the sentences:
- •4. Translate the text
- •Radioactivity
- •Notes on the text
- •Vocabulary
- •Exercises
- •4. Read and translate the text The discovery of X-Rays and Radioactivity
- •5. Open the brackets and translate the sentence into Ukrainian:
- •Chernobyl nuclear power station
- •Vocabulary
- •Exercises
- •Protection of the environment
- •Industry of ukraine
- •Chemical industry
- •Texts for reading glass
- •Glass history natural glasses
- •Early glasses
- •Blowing, (b) cutting and (c) flattening. Modern glasses soda-lime-silica glasses
- •Cutting and drilling of glass
- •Glass cutting principle (scribing, flexuring).
- •Applications of glass
- •Glazing
- •Containers
- •Optical glass
- •Glass fibres for insulation and reinforcement
- •Borate and related glasses
- •Window glass
- •Sheet wire glass
- •Stemalite
- •Hardened glass for ship’s port holes
- •Safety glass for ground transport
- •Slag glass-ceramic
- •Mechanics of Glass Processes
- •Batching
- •Melting
- •Float Process
- •Fusion Draw
- •Pressing
- •Fibre Process
- •Tensile Drawing
- •Centrifugal Drawing
- •Wool fibre drawing process
- •Types of glass
- •Glass industry of ukraine
- •Glossary
- •Reference list
- •Contents
Optical glass
Optical glasses can be produced with improved transparency in a designed range of wavelengths. This is the case for silica lenses and fibres used in optoelectronics technologies which have become widespread. These are used for transatlantic communication cables, telecoms and cable TV. In fact, silica-based fibres achieve extreme transparency over tens, or even hundreds of kilometers, as a window glazing over a few millimeters. The mechanical reliability of optical fibres is as important as their optical properties. These fibres can be formed with an internal core the refractive index of which is greater than that of the outside so that total reflection can be obtained at the interface. Another way to propagate an electromagnetic signal is to produce a continuously changing refractive index and light follows a path similar to the popular mirage effect at the proximity of a hot road during summer. The first type of fibre is produced by drawing a glass perform containing in its core the high- index glass. The second type of fibre can be produced by chemical diffusion.
These fibres can be protected from moisture and contact by hermetic coatings which a redeposited during the sizing step. As a matter of fact, fibres offer exceptional strength and optical performance that have yield such an impressive development in communications. One drawback of glass when considered for lenses is its density, and load gains are accomplished by controlling better glass distribution. It should be noted that nowadays spectacles are made of organic glasses. These allow load gains and comfort. Organic glasses are polymers formed by long organic chains. One single spectacle lens is composed of several layers, some of these being only protective because of the poor scratch resistance of polymers as compared to glass. This leads to application for night observations, detection of thermal loss in buildings and in situ medical observation. These glasses while showing “plastic” behavior remain very brittle at room temperature.
Optical fibre principle with discount sinuously changing index (n0>n1). The light beam follows Descartes’ law with reflection at the refractive index interface.

Glass fibres for insulation and reinforcement
The glazing, packaging and optical applications of glass are the most well known since they refer to glass transparency. Glass is also used for thermal and acoustic insulation or to reinforce plastics and concrete because of their low cost and high strength. In the latter case, compositions incorporating ZrO2 allow to resist concrete chemical attack. Polymers reinforced by glass fibres are fabricated as composites and used in transportation applications (automotive front ends, vehicle furniture, plane cockpits, etc.).
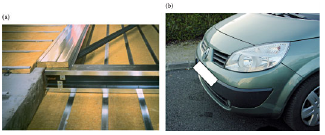
(a) Glass wool and
(b) fibre-reinforced composite used for the front end of an automobile.
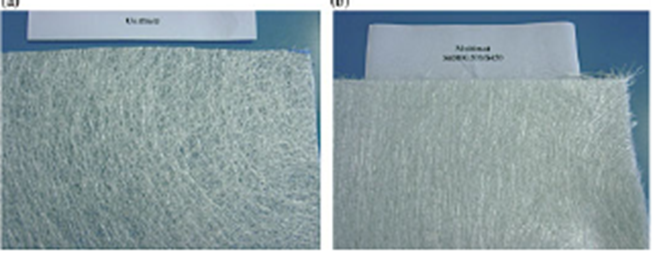
Glass mats
Glass wool is produced for buildings and vehicles and forms an air–fibre composite. Notably, the glass composition is tailored accordingly for different applications. Wool fibres have been optimized to allow maximum recovery when unpacked and set. Also, their dissolution in vitro has been of utmost importance since the problems generated by asbestos. Biodegradable glass fibres have been developed accordingly.
