- •Навчальний посібник
- •First term
- •Second term
- •Mathematics as a science
- •Mathematics
- •Task 17
- •Isaak Newton
- •Age problem
- •Self-assessment Be ready to speak on the topic "Mathematics as an independent science" using the following as a plan:
- •Check your active vocabulary on the topic:
- •Translate into English and be ready to give illustrative examples:
- •Fill in the gaps using a word from the list:
- •Arithmetic operations
- •Four basic operations of arithmetic
- •Two Characteristics of Addition
- •Self-assessment
- •Rational numbers
- •Rational and irrational numbers
- •Rational and irrational numbers
- •What is a number that is not rational?
- •Self-assessment
- •Properties of rational numbers
- •Properties of rational numbers
- •Properties of rational numbers
- •Reciprocal Fractions
- •Reducing Fractions to Lowest Terms
- •A Visit to a Concert
- •Self-assessment
- •Geometry
- •Meaning of geometry
- •Points and Lines
- •The history of geometry
- •Strange figures.
- •Measure the water.
- •Self-assessment
- •Simple closed figures
- •Simple closed figures
- •Simple closed figures
- •Problems of Cosmic and Cosmetic Physics
- •How to find the hypotenuse
- •Geometry Challenges
- •Self-assessment
- •Functional organization of computer
- •Computers
- •An a is a b that c
- •Find the numbers
- •Hundreds and hundreds
- •Tasks for self-assessment
- •Computer programming
- •Now read the description below. Do you like it? Why/Why not?
- •Instruction, instruct, instructed, instructor
- •Programming languages
- •Testing the computer program
- •Genius’s answer
- •A witty answer
- •The oldest profession
- •Tasks for self-assessment
- •Additional texts for reading
- •Read the text and summarise the main ways of expressing numbers in English.
- •Expressing numbers in english
- •Expressing millions
- •Ways of expressing the number 0
- •Fractional numbers
- •Writing full stops and commas in numbers
- •A short introduction to the new math
- •Algorithm
- •Mathematical component of the curriculum
- •Some facts on the development of the number system
- •The game of chess
- •Computers in our life
- •Is "laptop" being phased out?
- •The Main Pieces of Hardware
- •Text 10
- •Programs and programming languages
- •Text 11
- •All about software Categories of applications software explained
- •Systems Software
- •Applications Software
- •All the Other 'Ware Terminology
- •Malware
- •Greyware
- •Text 12
- •Advantages and disadvantages of the internet
- •Advantages
- •Disadvantages
- •Text 13
- •Text 14
- •Thinking about what we’ve found
- •Meta-Web Information
- •Text 15
- •Computer-aided instruction
- •Text 16
- •Teacher training
- •Іменник Утворення множини іменників
- •Правила правопису множини іменників
- •Окремі випадки утворення множини іменників
- •Присвійний відмінок
- •Практичні завдання
- •Артикль
- •Вживання неозначеного артикля
- •Вживання означеного артикля
- •Відсутність артикля перед обчислюваними іменниками
- •Вживання артикля з власними іменниками
- •Практичні завдання
- •Прикметник
- •Практичні завдання
- •Числівник
- •Практичні завдання
- •Займенник Особові займенники
- •Присвійні займенники
- •Зворотні займенники
- •Вказівні займенники
- •Питальні займенники
- •Неозначені займенники
- •Кількісні займенники
- •Практичні завдання
- •Прийменник
- •Дієслово
- •Неозначені часи indefinite tenses
- •Теперішній неозначений час the present indefinite tense active
- •Вживання Present Indefinite Active
- •Майбутній неозначений час the future indefinite tense active
- •Практичні завдання
- •Did you have a meeting yesterday?
- •I had an exam last week.
- •I didn't have an exam last week. Did you?
- •Тривалі часи дієслова continuous tenses
- •Теперішній тривалий час The present continuous tense active
- •Минулий тривалий час The past continuous tense active
- •Майбутній тривалий час The future continuous tense active
- •Практичні завдання
- •Перфектні часи perfect tenses
- •Теперішній перфектний час The present perfect tense active
- •Минулий перфектний час The perfect past tense active
- •Майбутній перфектний час The future perfect tense active
- •Практичні завдання
- •Узгодження часів sequence of tenses
- •Практичні завдання
- •Модальні дієслова modal verbs
- •Практичні завдання
- •Типи питальних речень question types
- •Практичні завдання
- •Пасивний стан дієслова passive voice
- •Практичні завдання
- •Check yourself
- •Читання буквосполучень
- •Читання голосних буквосполучень
- •Читання деяких приголосних та їхніх сполучень
- •Irregular verbs
- •Indefinite Tenses
- •Continuous Tenses
- •Perfect Tenses
- •Perfect Continuous Tenses
- •List of Proper Names
- •Sources of used materials
- •Contents
Rational numbers
Why did the math book look so sad?
Because it had so many problems!
Task 1
Solve the problems:
1. I am a number. If you multiply the number of minutes in a day by the number of hours in a week, you will find half my value.
2. I am a product. I have two factors. One of my factors is the last year of the twentieth century. My other factor is half of a pair. What am I?
3. If you take 3 eggs out of 5, how many will you have?
Task 2
Get ready for module text reading. Practice active vocabulary on the topic:
1) Read the words in the left column paying attention to their pronunciation.
2) Find the Ukrainian equivalents in the right column. Spare column is left for your notes.
|
|
Множина Чисельник Довести Знаменник Спростувати Відношення, коефіцієнт Ряд, послідовність Існування Обчислення Математик Приймати Квадратний корінь Дріб Квадрат цілого числа Ціле число Натуральне число Раціональне число Вимірювання Ірраціональне число Перераховувати Ціле число (+/ –) |
Task 3
Translate into Ukrainian:
A theory of measurement, simple and decimal fractions, square root of 9, a set of rationals, sequence of natural numbers, to prove existence of irrational numbers, using geometry, to accept a new theory, to enumerate whole numbers and their algebraic negatives, ratio of x to y, to form a field, a numerator less than denominator, denominator equal or greater than 1, let us start, a double sign, can be written, could be represented, can disprove, could express, it derived from, real line, a simple fraction.
Task 4
Translate into English:
Довести теорему, спростувати існування ірраціональних чисел, система вимірювання, множина натуральних чисел, квадрат цілого числа, простий дріб, математик стародавньої Греції, знаменник та числівник, утворювати поле, послідовність раціональних чисел, квадратний корінь 2, числова пряма, вперше з’явитися в роботі, перерахувати всі можливі варіанти, як їх називають, давайте почнемо з самого початку, набагато більше таких чисел.
Task 5
Read the text and say if the square root of 2 is a rational or irrational number.
Rational and irrational numbers
Calculus is a theory of measurement. The necessary for measuring numbers are the rationals and irrationals. But let us start at the beginning.
The following numbers of arithmetic are the counting-numbers or, as they are called, the natural numbers: 1, 2, 3, 4, and so on. If we include 0, we have the whole numbers: 0, 1, 2, 3, and so on. And if we include their algebraic negatives, we have the integers: 0, ±1, ±2, ±3, and so on. ± ("plus or minus") is called the double sign.
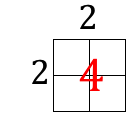
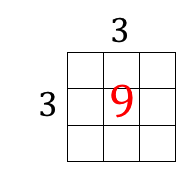
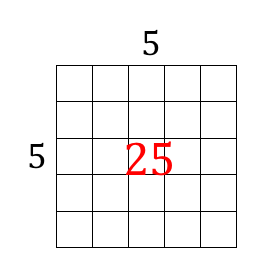
The following are the square numbers, or the perfect squares: 1 4 9 16 25 36 49 64, and so on. They are the numbers 1· 1, 2· 2, 3· 3, 4· 4, and so on. Square numbers are the product of a number multiplied by itself. An exponent (the small number after the base number) shows how many times to multiply a number by itself: 52 means multiply 5 x 5; 53 means multiply 5 x 5 x 5. Square numbers can be graphed as a rectangular array with equal sides, or in other words, a square. For example:
2 x 2 = 4 |
3 x 3 = 9 |
5 x 5 = 25 |
|
|
|
A rational number is a number that can be written as a simple fraction ( or as a ratio in other words). Example 1.5 is a rational number because 1.5 = 3/2 (it can be written as a fraction).
Here are some more examples:
Number |
As a Fraction |
Rational? |
5 |
5/1 |
Yes |
1.75 |
7/4 |
Yes |
.001 |
1/1000 |
Yes |
0.111... |
1/9 |
Yes |
√2 (square root of 2) |
? |
NO ! |
5 can be represented as a ratio or a quotient of 5 and 1 and so on. But the square root of 2 cannot be written as a simple fraction. And there are many more such numbers, and because they are not rational they are called irrational.
The ancient Greek mathematician Pythagoras believed that all numbers were rational in other words could be written as a fraction, but one of his students Hippasus proved (using geometry, it is thought) that you could not represent the square root of 2 as a fraction, and so it was irrational.
However Pythagoras could not accept the existence of irrational numbers, because he believed that all numbers had perfect squares. But he could not disprove Hippasus' "irrational numbers" and so Hippasus was thrown overboard and drowned!
But nowadays we know that a rational number is a number that can be expressed as a fraction p/q where p and q are integers and q is not equal to 0. A rational number p/q is said to have numerator p and denominator q. Numbers that are not rational are called irrational numbers. The real line consists of the sets of the rational and irrational numbers.
The set of all rational
numbers is referred to as the "rationals,"
and forms a field that
is denoted
![]() .
Here, the symbol
derives
from the word
Quotient,
which means
"the result of division",
"ratio," and first appeared in Nicolas
Bourbaki's "Algebra".
.
Here, the symbol
derives
from the word
Quotient,
which means
"the result of division",
"ratio," and first appeared in Nicolas
Bourbaki's "Algebra".
Examples of rational numbers
include ![]() ,
0, 1, 1/2, 22/7, 12345/67, and so on. Farey
sequences provide
a way of enumerating all rational numbers
systematically.
,
0, 1, 1/2, 22/7, 12345/67, and so on. Farey
sequences provide
a way of enumerating all rational numbers
systematically.
Task 6
Answer the questions on the text.
What is calculus?
What do we need to measure numbers?
What is a natural number? Give examples.
What do the natural numbers include?
What do the integers include?
How can the perfect squares be presented?
How can a rational number be written? Give examples.
Did ancient Greeks know about irrational numbers?
How can a rational number be expressed?
What does any fraction consist of?
Why is the set of rationals often denoted as a field Q?
What is Farey sequence?
Task 7
Fill in the gaps: