
- •Росжелдор
- •Unit 1 railway and motorway engineering structures
- •First, scan the text and then read it more carefully
- •1.2 Give the equivalents in Russian of the following terms
- •1.3 What are the English equivalents of the following Russian terms?
- •1.4 Complete and translate the following sentences using the word list
- •1.5 Translate into English the following sentences
- •1.6 Match the English and Russian terms
- •1.7 Answer the following questions
- •1.8 Render the text according to your plan and give the names of most famous railway and motorway engineering structures in Russia and abroad Unit 2 bridge crossing and its components
- •2.1 Read the following text and make a plan for it
- •Superstructure (пролётное строение); 2 – Pier (опора); 3 – Abutment (устой);
- •2.2 Give the Russian equivalents of the following terms
- •2.3 Give the English equivalents of the following terms
- •2.4 Complete and translate the following sentences
- •2.5 Translate into English the following sentences
- •2.6 Match the words in column a with column b
- •2.7 Read the questions and see if you can answer them
- •2.8 Render the text according to your plan Unit 3 bridge classification
- •3.1 Read the text and make up a bridgework glossary in Russian
- •3.2 Find the Russian equivalents for the following English terms
- •3.3 Find the English equivalents to the following Russian terms
- •3.4 Complete and translate the following sentences
- •3.5 Translate into English the following sentences
- •3.6 Answer the questions
- •3.7 Describe different bridge structures according to their structural design using the terminology below
- •Unit 4 bridges of moscow
- •4.1 Read the text to have a basic notion of bridges in the capital of Russia.
- •4.2 Find the Russian equivalents for the following English terms
- •4.3 Find the English equivalents to the following Russian terms:
- •4.4 Match English and Russian bridge terminology:
- •4.5 Complete and translate the sentences using the following terms
- •4.6 Translate into English the following sentences
- •4.7 Answer the following questions
- •4.8 Render the text according to your plan Unit 5 bridges of st petersburg
- •5.1 Have you ever been to St Petersburg? If so, try to complement the text with your own information. If not, try to enhance your professional range of knowledge
- •5.10 Translate the text into English
- •Unit 6 timber and masonry bridges
- •6.1 Read the text about different building materials. Compare them and say which one is more suitable for permanent or temporary structures
- •6.6 Complete and translate the following sentences
- •6.7 Translate the following sentences into English
- •6.8 Give a reason to support what you say answering to these questions
- •6.9 Express your ideas about the building qualities of stone and wood Unit 7 reinforced concrete bridges
- •7.1 Read the text and learn the terminology using the list of words
- •7.2 Find the Russian equivalents for the following English terms
- •7.3 Find the English equivalents to the following Russian terms
- •7.4 Make up the questions to the following answers
- •7.5 Complete and translate the following sentences using the Word list
- •7.6 Translate the following sentences into English
- •7.7 Discuss the following questions
- •Unit 8 metal bridges
- •8.1 Think of different building materials and answer the following questions
- •8.2 Read the text and check your answers. How much did you guess correctly?
- •8.3 Find the Russian equivalents for the following English terms
- •8.4 What are the English equivalents for the following Russian terms?
- •8.5 Say whether these statements are true
- •8.6 Match the Russian and English terms
- •8.7 Complete and translate the following sentences
- •8.8 Translate the following sentences into English
- •Unit 9 bridges of great britain
- •9.1 Read the text and improve your knowledge of foreign experiences in bridge building
- •9.2 Tell the story of the Old London Bridge using the following terms
- •9.3 Read the text about famous London bridges and tell about them
- •9.4 Find the Russian equivalents for the following English terms
- •9.5 Read the text about the most astonishing British bridges and tell about them
- •9.6 Find the Russian equivalents for the following English terms
- •9.7 Complete and translate the following text
- •9.8 Complete the following sentences using your own ideas
- •9.9 Answer the following questions
- •9.10 Translate the text into English
- •10.1 After reading the text, prove the idea that suspension structures are the safest among bridgeworks
- •10.2 Find the Russian equivalents for the following English terms
- •10.3 Make up examples with the terms describing a suspension structure
- •10.4 Choose which statements are true
- •10.5 Complete and translate the following sentences
- •10.6 Translate the following sentences into English
- •10.7 Answer the following questions
- •10.8 Describe the Golden Gate Bridge using the following information
- •10.9 Consult this list of bridge terminology while doing the exercises
- •Unit 11 bridges of novosibirsk
- •11.1 Having read the text, complete the information with details you may notice in the pictures
- •11.2 Find the Russian equivalents for the following English terms
- •11.3 Find the Russian equivalents for the following English terms
- •11.4 Match the English and Russian terms
- •11.5 Translate the following sentences into English
- •11.6 Answer the following questions
- •11.7 What bridge across the Ob River do you prefer and why? Express your opinion using the following word combinations
- •11.8 Describe your “dream bridge”. Do you have any ideas that will surprise your classmates? Think of a place for “your” bridge. Unit 12 bridge or tunnel?
- •12.1 Read the text and give your reasons for making a choice between a bridge and a tunnel
- •12.2 Find the Russian equivalents for the following English terms
- •12.3 Find the Russian equivalents for the following English terms
- •12.4 Complete and translate the following sentences using the word list
- •12.5 Translate the following sentences into English
- •12.6 Think over the problems and give your reasons for the right solution
- •12.7 Read this interview and make up your own dialogue using the following expressions
- •Unit 13 construction of supports and foundations
- •13.1 Read the text to get a clear idea of building materials and construction technologies for piers and foundations. Go down the word list and take note of professional terminology.
- •13.2 Find the Russian equivalents for the following English terms
- •13.3 Find the Russian equivalents for the following English terms
- •13.4 Translate the following information into Russian, consulting the terminology list and using the word combinations given below
- •13.5 Translate the following information into English using the terminology list
- •13.6 Give your reasons to support the answers to these questions
- •Unit 14 superstructure construction
- •14.1 Read the text and pay attention to the differences in the various techniques of superstructure construction
- •14.2 Find the Russian equivalents for the following English terms
- •14.3 Find the Russian equivalents for the following English terms
- •14.4 Complete and translate the following sentences using the terminology from previous text and the word list (14.6)
- •14.5 Translate the following sentences into English
- •14.6 Find the relevant information in the texts to answer these questions
- •14.7 Describe superstructure construction methods using the following word combinations
- •Unit 15 construction of suspension and cable-stayed bridges
- •15.1 Read the text and pay attention to the peculiarities of suspension superstructure construction
- •15.2 Find the Russian equivalents for the following English terms
- •15.3 Find the Russian equivalents for the following English terms
- •15.4 Complete and translate the sentences using the following words
- •15.5 Translate the following sentences into English
- •15.6 Find the relevant information in the texts to answer these questions
- •15.7 Describe superstructure construction methods. Remember the following word combinations
- •Unit 16 bridge maintenance
- •16.1 Read the text and make a list of the main ideas you should remember as a future bridge builder
- •16.2 Find the Russian equivalents for the following English terms:
- •16.3 Find the English equivalents for the following Russian terms
- •16.4 Match the equivalents
- •16.5 Complete the following sentences
- •16.6 Read the text and find the equivalents for the following terms
- •16.7 Translate the following sentences into English using terminology from this unit
- •16.8 Find the answers to these questions in the text
- •16.9 Role-play. “On-site review and visual inspection of the bridge components”
- •Unit 17 tunnel classification
- •17.1 Read the text and make a list of tunneling terminology
- •17.2 Find the Russian equivalents for the following English terms
- •17.3 Find the English equivalents for the following Russian terms
- •17.4 Complete and translate the following sentences using the Word list.
- •8 Side Wall Drift (боковая штросса); 9 – Lining (обделка тоннеля);
- •– Tunnel Foot (подошва тоннеля)
- •17.5 Translate the following sentences into English using terminology from the texts. Tell a partner what you found most interesting
- •17.5 Answer the questions using the information from the text and your own ideas
- •17.6 Describe any tunnel using the information model from the following.
- •Unit 18 construction methods of tunnels
- •18.1 Read the text and define recent trends in unneling
- •18.2 Find the Russian equivalents for the following English terms
- •18.3 Find the English equivalents for the following Russian terms
- •18.4 Complete the following sentences using the word list and translate them
- •18.5 Translate the following sentences into English using terminology from previous texts
- •18.6 Make up the answers to these questions. Use the Word list
- •18.7 Read the dialogue below and retell it with a partner
- •18.8 Disagree with each statement
- •Unit 19 shield tunnelling
- •19.1 Read the text to have an idea of state-of-the-art tbm’s
- •Figure 19. 7 Technological Process by the Slurry Shield Complex
- •19.2 Find the Russian equivalents for the following English terms
- •19.3 Find the English equivalents for each of the Russian terms
- •19.4 Complete and translate the following sentences using the list of word combinations below
- •19.5 Complete the following sentences using your own ideas and the Word list below.
- •19.6 Translate the sentences into English
- •19.7 Answer the following questions
- •Unit 20 general idea of the metro
- •20.1 Read the text and find out peculiarities in the underground railway systems of different countries
- •20.2 Find the Russian equivalents for the following English terms
- •20.3 Find the English equivalents for each of the Russian terms from the text
- •20.4 Complete and translate the sentences using the following words and word combinations
- •20.6 Think of the answers and give a reason to support what you say
- •20.7 Complete the following sentences in a suitable way
- •20.8 Discuss the ideas expressed by these two engineers suggesting their solution of public transport development in modern cities
- •Unit 21 the novosibirsk metro
- •21.1 Read the text and complement it with more details from the history and present-day operation of the Novosibirsk Metro
- •21.2 Find the Russian equivalents for the following English terms
- •21.3 Find the English equivalents for each of the Russian terms
- •21.4 Complete the sentences using the following words and render this text in English
- •21.5 Complete and translate the following sentences
- •21.6 Discuss the following questions
- •21.7 Read the dialogue and compose your own conversation with a partner. Use the words and expressions from the model
- •21.8 Try to guess the meaning of the following word combination
- •21.10 Ask each other questions to test your knowledge of the unit Unit 22 structures in the underground
- •22.1 Read the text consulting the Word list for better understanding
- •22.2 Find the Russian equivalents for the following English terms
- •22.3 Find the English equivalents for each of the Russian terms from the text
- •22.4 Translate the sentences using the necessary English equivalents.
- •22.5 Translate the sentences into English paing attention to relevant terminology
- •22.6 Choose which statement is true
- •22.7 Discuss the following questions
- •Unit 23 tunnel maintenance
- •23.1 Having read the text try to prove the idea that tunnel maintenance is much more expensive compared to bridge maintenance. Give your reasons
- •23.2 Find the Russian equivalents for the following English terms
- •23.3 Find the English equivalents for each of the Russian terms
- •23.4 Complete the sentences using the following words
- •23.5 Complete and translate the following sentences
- •23.6 Answer the questions
- •Unit 24 сollapse of bridges and tunnels
- •24.1 Read the text, try to guess the meaning of the words you do not know, and then analyze how many meanings you can guess correctly or nearly correctly
- •24.2 Find the Russian equivalents for the following English terms
- •24.3 Find the English equivalents for each of the Russian terms
- •24.4 Complete the sentences using the following words and translate them into Russian
- •24.5 Translate the sentences into English paying attention to relevant terminology
- •24.6 Working in pairs, practice the questions below and support your opinion by using vivid examples. Make up your own questions
- •Unit 25
- •25.1 Read the text and try to complement its content with detailed information and interesting facts
- •25.2 Find the Russian equivalents for the following English terms and word combinations
- •25.3 Find the English equivalents for each of the Russian terms from the text
- •25.4 Complete the sentences using the following words and translate them into Russian
- •25.5 Complete and translate the following sentences
- •25.6 Answer the following questions
2.6 Match the words in column a with column b
A |
B |
1. временная нагрузка |
a) Structural calculations |
2. настил моста |
b) Damage |
3. невыгодное положение |
c) Moving load |
4 отметка уровня паводка |
d) Bridge deck, bridge floor |
5. пилон моста |
e) Bridge scour, washout |
6. повреждение, разрушение |
f) Dead load, permanent load |
7. подвижная нагрузка |
g) Bridge roadway |
8. подмыв опоры |
h) Tower |
9. постоянная нагрузка |
i) Free water flow |
10. проезжая часть моста |
j) Designing, planning |
11. проектирование |
k) High-water mark |
12. пропуск воды |
l) Live load |
13. расчёт конструкций |
m) Disadvantage |
2.7 Read the questions and see if you can answer them
Why do people construct bridge crossings?
What components of a bridge crossing do you know?
What is the difference between a low-water bed and a flood plain?
What bridge component directly resists the rolling stock load?
What are the common features for piers and abutments? What is the difference between them?
What bridge components rest on the ground?
What bridge components directly resist wind force and ice?
What does headroom depend on?
Is seismic activity calculation obligatory for all bridges?
2.8 Render the text according to your plan Unit 3 bridge classification
3.1 Read the text and make up a bridgework glossary in Russian
Humankind has been constructing bridges since ancient times. The early human felled trees and put stones for crossing rivers or gullies, and the earliest bridges were probably nothing more than different rocks or logs thrown across the gap. As civilization advanced, people discovered ways to use a mixture of lime with cement, sand and water for binding stones by mortar to construct longer and stronger bridges. Bridge builders gained skills and experience in incorporating other natural and fabricated materials such as iron, steel, and aluminum into the structures they built.
Currently, bridge engineers define a bridge as a raised structure made out of wood, stone, brick, concrete or steel that links two opposite sides without making contact with the roadway, body of water, depression or any other obstacle beneath it. The bridge types include beam, cantilever, arch, and suspension structures according to the gap they span and the loads they have to carry. Their classification is according to the following criteria:
Criterion Number 1. (The primary function of the bridge roadway)
1.1 Railway bridges (trains).
1.2 Motorway (highway) bridges (vehicles, trucks, cars).
1.3 Footbridges (pedestrian bridges) (pedestrians, bicycles).
1.4 Town bridges (city trains, monorail, transit guideway).
1.5 Pipe lines.
1.6 Metro bridges.
1.7 Combined or road-cum-rail bridges (for different modes of transport).
Criterion Number 2. (The superstructure material) (fig.3.1)
2.1 Timber (wooden) bridges (fig. 3.1a) (logs, squared beam, plywood).
2.2 Masonry bridges (fig. 3.1b) (brick, rock).
2.3 Reinforced-concrete bridges (fig. 3.1c) (precast, cast-in-place, pretensioned, prestressed concrete, posttensioned).
2.4 Metal bridges (fig. 3.1d) (cast iron, steel, aluminum, bolted, welded, prefabricated, riveted).
2.5 Steel reinforced concrete bridges (composite bridges).
2.6 Suspension bridges (fig. 3.1e; 3.2a).
2.7 Cable-stayed bridges (fig. 3.1f; 3.2b).
|
|
a – Timber Bridge |
b – Masonry Bridge |
|
|
c – Reinforced Bridge |
d – Steel Bridge |
|
|
e – Suspension Bridge |
f – Cable-stayed Bridge |
Figure 3.1 Bridge classification by the superstructure material
Out of the main materials used in bridge building – wood, stone, steel and concrete, steel has had the greatest impact on modern bridge engineering. Bridge builders prefer exclusively reinforced and prestressed concrete, which contain steel bars or mesh. Suspension and cable-stayed bridges which use flexible ropes or cables as the main supporting element can also be regarded as representatives of metal bridges because their cables are made out of steel wire strands. Curved cables are used for suspension bridges (fig. 3.2a), and straight diagonal cables carry the main span in cable-stayed structures (fig. 3.2b).
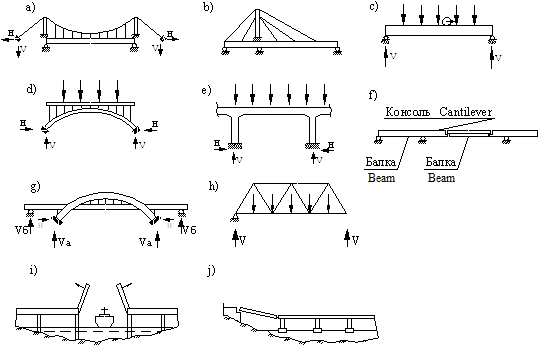
Figure 3.2 Bridge classification
a – Suspension bridge (висячий мост); b – Cable-stayed bridge (вантовый мост);
c – Beam bridge (балочный мост); d – Arch bridge (арочный мост);
e – Rigid frame bridge (рамный мост); f – Beam-cantilever bridge (балочно-консольный мост); g – Combined half-through bridge (комбинированный мост с ездой посередине);
h – Through lattice bridge (сквозная ферма с ездой понизу); i – Drawbridge (разводной мост);
j – Pontoon bridge (понтонный мост)
Criterion Number 3. (The structural system)
3.1 Beam bridges (fig. 3.2c), (a freely supported slab or girder construction resting on piers).
3.2 Arch bridges (fig. 2d), (a curved structure producing a horizontal thrust through impost to piers). Arched spans give the bridge enhanced rigidity and strength.
3.3 Rigid frame bridges (fig. 3.2e) (a rigid frame structure with the horizontal deck slab made monolithic with the vertical abutment walls).
3.4 Cantilever bridges (fig. 3.2f) (a structure with projecting cantilever arms).
3.5 Combined systems (fig. 3.2g) (several simple structures: beam and arch).
3.6 Truss (lattice structure) (fig. 3.2h)
|
|
a – Deck Bridge |
b – Through Bridge |
|
|
c – Half-through Bridge |
d – Pontoon Bridge |
Figure 3.3 Bridge Classification according to Position of Traffic
Criterion Number 4. (Cross section or the position of traffic)
4.1 Deck bridges (fig. 3.2c, d and e; 3.3a). Their structural components are under the deck, so deck bridges need space beneath. This bridge type is the best for drivers as they can clearly see the surroundings.
4.2 Through bridges (fig. 3.2h; 3.3b). Their structural components obstruct the view because they are above the deck. This bridge type is suitable for railway bridges.
4.3 Half-through bridges (fig. 3.2g; 3.3c).
Criterion Number 5. (The span length)
5.1 Short bridges (6 – 25 m). A span, which is less than 6 m, is a culvert.
5.2 Intermediate span bridges (25 – 100 m).
5.3 Long span bridges (more than 100 m).
Criterion Number 6. (The number of spans)
6.1 Single-span bridges.
6.2 Double-span bridges.
6.3 Three-span bridges.
6.4 Multi-span bridges.
Criterion Number 7. (Bridge service life)
7.1 Permanent bridges (80 – 100 years).
7.2 Temporary bridges (about 10 – 15 years).
7.3 Short-term bridges (For two/three days or for a year).
Next to the above-mentioned bridge types there are movable bridges (fig. 3.2i) (drawbridges, leaf bridges, opening bridges, pivot bridges), floating bridges (raft bridges) (fig. 3.2j; 3.3d) and ferries. The drawbridge, or bascule, is the best known; it may be single or double-leaf. For exceptionally long spans, the pivot, or swing bridge, which revolves around a vertical axis on a pivot pier, is suitable, but it limits navigation. In practice, the basic forms can take turns in one structure. The principle factors determining bridge choice include span, location and site conditions, availability of materials and labour, maintenance, loading conditions, appearance and cost.
The Word List
1. Bedrock |
подстилающая порода (твёрдая порода под почвой) |
2. Binder |
связующее вещество (клей, цемент) |
3 Cantilever arm |
консоль главной балки |
4. Cast-in-place concrete, poured-in-place concrete, in-situ concrete |
монолитный бетон, уложенный на месте (в опалубку) |
5. Design model, structural design |
расчетная схема конструкции |
6. Impost |
пята арки |
7. Lime |
известь |
8. Mortar |
известковый раствор, строительный раствор |
9. Pivot pier |
центральная опора разводного поворотного моста |
10. Post, column |
стойка |
11. Precast concrete |
сборный железобетон, сборный бетон |
12. Post-tensioned concrete |
напряжённо-армированный бетон с последующим напряжением арматуры |
13. Pretensioned concrete |
предварительно напряжённый бетон |
14. Prestressed concrete |
преднапряженный железобетон |
15. Slab |
плита |
16. Stiffening rib |
ребро жёсткости |
17. Suspender |
подвеска в арочном и висячем мостах |
18. Tension |
растягивающее усилие |
19. Thrust |
распор |
Exercises










