- •Росжелдор
- •Unit 1 railway and motorway engineering structures
- •First, scan the text and then read it more carefully
- •1.2 Give the equivalents in Russian of the following terms
- •1.3 What are the English equivalents of the following Russian terms?
- •1.4 Complete and translate the following sentences using the word list
- •1.5 Translate into English the following sentences
- •1.6 Match the English and Russian terms
- •1.7 Answer the following questions
- •1.8 Render the text according to your plan and give the names of most famous railway and motorway engineering structures in Russia and abroad Unit 2 bridge crossing and its components
- •2.1 Read the following text and make a plan for it
- •Superstructure (пролётное строение); 2 – Pier (опора); 3 – Abutment (устой);
- •2.2 Give the Russian equivalents of the following terms
- •2.3 Give the English equivalents of the following terms
- •2.4 Complete and translate the following sentences
- •2.5 Translate into English the following sentences
- •2.6 Match the words in column a with column b
- •2.7 Read the questions and see if you can answer them
- •2.8 Render the text according to your plan Unit 3 bridge classification
- •3.1 Read the text and make up a bridgework glossary in Russian
- •3.2 Find the Russian equivalents for the following English terms
- •3.3 Find the English equivalents to the following Russian terms
- •3.4 Complete and translate the following sentences
- •3.5 Translate into English the following sentences
- •3.6 Answer the questions
- •3.7 Describe different bridge structures according to their structural design using the terminology below
- •Unit 4 bridges of moscow
- •4.1 Read the text to have a basic notion of bridges in the capital of Russia.
- •4.2 Find the Russian equivalents for the following English terms
- •4.3 Find the English equivalents to the following Russian terms:
- •4.4 Match English and Russian bridge terminology:
- •4.5 Complete and translate the sentences using the following terms
- •4.6 Translate into English the following sentences
- •4.7 Answer the following questions
- •4.8 Render the text according to your plan Unit 5 bridges of st petersburg
- •5.1 Have you ever been to St Petersburg? If so, try to complement the text with your own information. If not, try to enhance your professional range of knowledge
- •5.10 Translate the text into English
- •Unit 6 timber and masonry bridges
- •6.1 Read the text about different building materials. Compare them and say which one is more suitable for permanent or temporary structures
- •6.6 Complete and translate the following sentences
- •6.7 Translate the following sentences into English
- •6.8 Give a reason to support what you say answering to these questions
- •6.9 Express your ideas about the building qualities of stone and wood Unit 7 reinforced concrete bridges
- •7.1 Read the text and learn the terminology using the list of words
- •7.2 Find the Russian equivalents for the following English terms
- •7.3 Find the English equivalents to the following Russian terms
- •7.4 Make up the questions to the following answers
- •7.5 Complete and translate the following sentences using the Word list
- •7.6 Translate the following sentences into English
- •7.7 Discuss the following questions
- •Unit 8 metal bridges
- •8.1 Think of different building materials and answer the following questions
- •8.2 Read the text and check your answers. How much did you guess correctly?
- •8.3 Find the Russian equivalents for the following English terms
- •8.4 What are the English equivalents for the following Russian terms?
- •8.5 Say whether these statements are true
- •8.6 Match the Russian and English terms
- •8.7 Complete and translate the following sentences
- •8.8 Translate the following sentences into English
- •Unit 9 bridges of great britain
- •9.1 Read the text and improve your knowledge of foreign experiences in bridge building
- •9.2 Tell the story of the Old London Bridge using the following terms
- •9.3 Read the text about famous London bridges and tell about them
- •9.4 Find the Russian equivalents for the following English terms
- •9.5 Read the text about the most astonishing British bridges and tell about them
- •9.6 Find the Russian equivalents for the following English terms
- •9.7 Complete and translate the following text
- •9.8 Complete the following sentences using your own ideas
- •9.9 Answer the following questions
- •9.10 Translate the text into English
- •10.1 After reading the text, prove the idea that suspension structures are the safest among bridgeworks
- •10.2 Find the Russian equivalents for the following English terms
- •10.3 Make up examples with the terms describing a suspension structure
- •10.4 Choose which statements are true
- •10.5 Complete and translate the following sentences
- •10.6 Translate the following sentences into English
- •10.7 Answer the following questions
- •10.8 Describe the Golden Gate Bridge using the following information
- •10.9 Consult this list of bridge terminology while doing the exercises
- •Unit 11 bridges of novosibirsk
- •11.1 Having read the text, complete the information with details you may notice in the pictures
- •11.2 Find the Russian equivalents for the following English terms
- •11.3 Find the Russian equivalents for the following English terms
- •11.4 Match the English and Russian terms
- •11.5 Translate the following sentences into English
- •11.6 Answer the following questions
- •11.7 What bridge across the Ob River do you prefer and why? Express your opinion using the following word combinations
- •11.8 Describe your “dream bridge”. Do you have any ideas that will surprise your classmates? Think of a place for “your” bridge. Unit 12 bridge or tunnel?
- •12.1 Read the text and give your reasons for making a choice between a bridge and a tunnel
- •12.2 Find the Russian equivalents for the following English terms
- •12.3 Find the Russian equivalents for the following English terms
- •12.4 Complete and translate the following sentences using the word list
- •12.5 Translate the following sentences into English
- •12.6 Think over the problems and give your reasons for the right solution
- •12.7 Read this interview and make up your own dialogue using the following expressions
- •Unit 13 construction of supports and foundations
- •13.1 Read the text to get a clear idea of building materials and construction technologies for piers and foundations. Go down the word list and take note of professional terminology.
- •13.2 Find the Russian equivalents for the following English terms
- •13.3 Find the Russian equivalents for the following English terms
- •13.4 Translate the following information into Russian, consulting the terminology list and using the word combinations given below
- •13.5 Translate the following information into English using the terminology list
- •13.6 Give your reasons to support the answers to these questions
- •Unit 14 superstructure construction
- •14.1 Read the text and pay attention to the differences in the various techniques of superstructure construction
- •14.2 Find the Russian equivalents for the following English terms
- •14.3 Find the Russian equivalents for the following English terms
- •14.4 Complete and translate the following sentences using the terminology from previous text and the word list (14.6)
- •14.5 Translate the following sentences into English
- •14.6 Find the relevant information in the texts to answer these questions
- •14.7 Describe superstructure construction methods using the following word combinations
- •Unit 15 construction of suspension and cable-stayed bridges
- •15.1 Read the text and pay attention to the peculiarities of suspension superstructure construction
- •15.2 Find the Russian equivalents for the following English terms
- •15.3 Find the Russian equivalents for the following English terms
- •15.4 Complete and translate the sentences using the following words
- •15.5 Translate the following sentences into English
- •15.6 Find the relevant information in the texts to answer these questions
- •15.7 Describe superstructure construction methods. Remember the following word combinations
- •Unit 16 bridge maintenance
- •16.1 Read the text and make a list of the main ideas you should remember as a future bridge builder
- •16.2 Find the Russian equivalents for the following English terms:
- •16.3 Find the English equivalents for the following Russian terms
- •16.4 Match the equivalents
- •16.5 Complete the following sentences
- •16.6 Read the text and find the equivalents for the following terms
- •16.7 Translate the following sentences into English using terminology from this unit
- •16.8 Find the answers to these questions in the text
- •16.9 Role-play. “On-site review and visual inspection of the bridge components”
- •Unit 17 tunnel classification
- •17.1 Read the text and make a list of tunneling terminology
- •17.2 Find the Russian equivalents for the following English terms
- •17.3 Find the English equivalents for the following Russian terms
- •17.4 Complete and translate the following sentences using the Word list.
- •8 Side Wall Drift (боковая штросса); 9 – Lining (обделка тоннеля);
- •– Tunnel Foot (подошва тоннеля)
- •17.5 Translate the following sentences into English using terminology from the texts. Tell a partner what you found most interesting
- •17.5 Answer the questions using the information from the text and your own ideas
- •17.6 Describe any tunnel using the information model from the following.
- •Unit 18 construction methods of tunnels
- •18.1 Read the text and define recent trends in unneling
- •18.2 Find the Russian equivalents for the following English terms
- •18.3 Find the English equivalents for the following Russian terms
- •18.4 Complete the following sentences using the word list and translate them
- •18.5 Translate the following sentences into English using terminology from previous texts
- •18.6 Make up the answers to these questions. Use the Word list
- •18.7 Read the dialogue below and retell it with a partner
- •18.8 Disagree with each statement
- •Unit 19 shield tunnelling
- •19.1 Read the text to have an idea of state-of-the-art tbm’s
- •Figure 19. 7 Technological Process by the Slurry Shield Complex
- •19.2 Find the Russian equivalents for the following English terms
- •19.3 Find the English equivalents for each of the Russian terms
- •19.4 Complete and translate the following sentences using the list of word combinations below
- •19.5 Complete the following sentences using your own ideas and the Word list below.
- •19.6 Translate the sentences into English
- •19.7 Answer the following questions
- •Unit 20 general idea of the metro
- •20.1 Read the text and find out peculiarities in the underground railway systems of different countries
- •20.2 Find the Russian equivalents for the following English terms
- •20.3 Find the English equivalents for each of the Russian terms from the text
- •20.4 Complete and translate the sentences using the following words and word combinations
- •20.6 Think of the answers and give a reason to support what you say
- •20.7 Complete the following sentences in a suitable way
- •20.8 Discuss the ideas expressed by these two engineers suggesting their solution of public transport development in modern cities
- •Unit 21 the novosibirsk metro
- •21.1 Read the text and complement it with more details from the history and present-day operation of the Novosibirsk Metro
- •21.2 Find the Russian equivalents for the following English terms
- •21.3 Find the English equivalents for each of the Russian terms
- •21.4 Complete the sentences using the following words and render this text in English
- •21.5 Complete and translate the following sentences
- •21.6 Discuss the following questions
- •21.7 Read the dialogue and compose your own conversation with a partner. Use the words and expressions from the model
- •21.8 Try to guess the meaning of the following word combination
- •21.10 Ask each other questions to test your knowledge of the unit Unit 22 structures in the underground
- •22.1 Read the text consulting the Word list for better understanding
- •22.2 Find the Russian equivalents for the following English terms
- •22.3 Find the English equivalents for each of the Russian terms from the text
- •22.4 Translate the sentences using the necessary English equivalents.
- •22.5 Translate the sentences into English paing attention to relevant terminology
- •22.6 Choose which statement is true
- •22.7 Discuss the following questions
- •Unit 23 tunnel maintenance
- •23.1 Having read the text try to prove the idea that tunnel maintenance is much more expensive compared to bridge maintenance. Give your reasons
- •23.2 Find the Russian equivalents for the following English terms
- •23.3 Find the English equivalents for each of the Russian terms
- •23.4 Complete the sentences using the following words
- •23.5 Complete and translate the following sentences
- •23.6 Answer the questions
- •Unit 24 сollapse of bridges and tunnels
- •24.1 Read the text, try to guess the meaning of the words you do not know, and then analyze how many meanings you can guess correctly or nearly correctly
- •24.2 Find the Russian equivalents for the following English terms
- •24.3 Find the English equivalents for each of the Russian terms
- •24.4 Complete the sentences using the following words and translate them into Russian
- •24.5 Translate the sentences into English paying attention to relevant terminology
- •24.6 Working in pairs, practice the questions below and support your opinion by using vivid examples. Make up your own questions
- •Unit 25
- •25.1 Read the text and try to complement its content with detailed information and interesting facts
- •25.2 Find the Russian equivalents for the following English terms and word combinations
- •25.3 Find the English equivalents for each of the Russian terms from the text
- •25.4 Complete the sentences using the following words and translate them into Russian
- •25.5 Complete and translate the following sentences
- •25.6 Answer the following questions
18.2 Find the Russian equivalents for the following English terms
Adjacent ground, bench, charge, clay, clog, exhaust ventilation, explosive, face, hard rock tunnel, laser guidance systems, liquid concrete, narrow-gauge tracks, quick sand, rotating front face, shaft, shield tunneling, soft rock tunnel, structural integrity, tracked cart, tunnel's path, true tunnel, unforeseen geologies, water-and-salt brine, water table.
18.3 Find the English equivalents for the following Russian terms
Бригада тоннельщиков, верхняя штольня, внутренний потенциал породы, водонасыщенная порода, выбитые обломки, газовый карман, глобальная система навигации и определения положения, жидкий азот, заменяемый бур, заполнять пустоты, камера для запуска щита, карман с растрескавшейся породой, коммуникационный канал, модифицировать по условиям тоннеля, неразорвавшиеся заряды, нижняя штольня, предрасположенный к обрушению, проволочная сетка, разлом, свойства горной породы, слабый слой породы, топкий грунт, хладагент, ядовитый взрывной дым.
18.4 Complete the following sentences using the word list and translate them
1. A tunnel is an underground (переход) produced by excavation or occasionally by an act of nature that dissolves soluble rock, such as limestone. A hillside tunnel (вход) is a portal.
2. (Проходка тоннелей) based on the high accuracy of underground geotechnical measurements is (маркшейдерское дело). The tunnel centre line must be correctly oriented in case of tunneling from both (портал).
3. Several additional (вертикальные стволы) are used to speed up tunneling when the tunnel has to be long. The workers drive the tunnel from these vertical shafts towards both entrances.
4. The main idea of the New Austrian Tunnelling Method is to use the geological stress of the surrounding (горная порода) mass to stabilize the tunnel itself. The workers immediately protect (выработка) by thin shotcrete, just behind the excavation. It minimizes the rock’s deformation.
5. Pipe jacking is a method of tunnel construction where (гидравлический) jacks push specially made pipes through the ground. This technique is commonly suitable for creating tunnels under existing (cооружения), such as roads or railways.
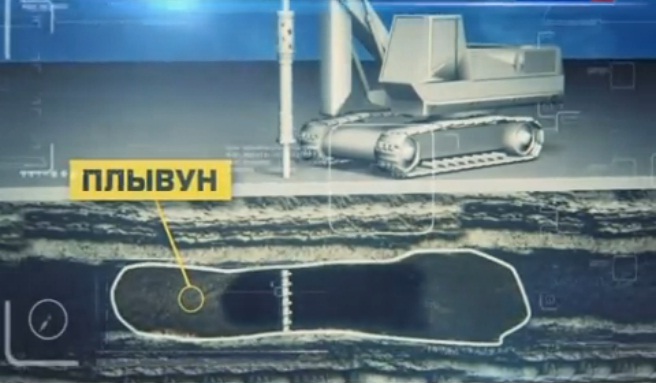
6. In fact tunneling may have no notable problems, as long as the rock remains stable. However, the progress of an excavation may be slowed by a difficult (геологическая зона), which can turn out to be much longer than expected.
7. To remain static, tunnels must withstand different loads produced by the (вес) of the structures themselves and by the weight of the vehicles or people passing through. Moreover, structural components of the tunnel resist to various forces.
18.5 Translate the following sentences into English using terminology from previous texts
1. Методы сооружения тоннелей зависят от результатов инженерно-геологических изысканий (engineering-geological estimation), включающих бурение скважин (boring exploratory shaft), проходку (driving) разведочных выработок (probe drift), геофизическую разведку (geophysical prospecting) и космическую аэрофотосъёмку (space aerosurveying). Стоимость исследований (soil investigation) составляет до 3-5% затрат на строительство всего тоннеля (fig.18.5).
|
|
a - Boring of an exploratory shaft |
b - Space aerosurveying |
Figure 18.5 Ways of engineering estimation of geological conditions
2. Проходка тоннеля включает удаление породы (spoil removal) из подземного пространства (underground space) и закрепление (consolidation) этого пространства обделкой. Подземное пространство, которое образуется при проходке тоннеля после удаления породы, называется тоннельной выработкой (excavation). Конструкции, укрепляющие тоннельную выработку, называются обделкой.
3. Строительство тоннелей в скальных (hard rock) и полускальных горных породах (soft rock) осуществляется горным способом с применением буровзрывного метода. В забое бурят (to drill) шпуры, в которые закладывают заряды взрывчатых веществ. Разрушенную горную породу транспортируют на поверхность, а выработку закрепляют временной крепью (temporary support), которую заменяют постоянной обделкой.
4. Проходческие щиты, комбайны (roadheader) и механизированные тоннельные комплексы являются современными тоннелепрохоческими машинами (heading machine), предназначенными для разрушения (breaking) забоя, удаления разрушенной породы (tunnel muck), возведения обделки и выполнения других операций.
5. В скальных породах вместо несущей обделки (load-bearing lining) применяют облицовочную обделку (protective lining). Если порода очень прочная облицовку не применяют. В слабых грунтах несущую обделку выполняют из сборного железобетона или монолитного бетона. Чтобы избежать обвала (toppling) в тяжелых гидрологических условиях используют металлическую обделку из чугуна и стали.
6. При проходке тоннелей горным способом в скальных слаботрещиноватых (low crumbling) и невыветренных (unweathered rock) породах используют облегчённую (lightened) обделку из набрызг-бетона, который укладывают в один или два слоя, или усиливают арматурной сеткой, или применяют фибронабрызг-бетон.
7. В мягких породах (weak rocks) выполняется разработка грунта на полное сечение (full-face excavation) механизированным щитом, который монтирует обделку из унифицированных (standard) сборных железобетонных блоков или тюбингов. Между тюбингами проводят чеканку швов (seam caulking) гидроизоляционными (waterproofing) материалами, или тампонируют цементно-песчаным раствором (cement-sand grout).
8. Современные технологии сооружения тоннелей включают не только горный (rock tunnelling), открытый и щитовой способы проходки, но и способы продавливания (tunnel jacking) и погружения (immersion) секций.
9. Тоннели мелкого заложения сооружают открытыми способами (cut-and-cover methods), включающими котлованный (open cut), траншейный (trench) способы. Они дешевле закрытых способов, но требуют перемещения коммуникаций и дорог (service lines and highway relocation).
10. Форма и размеры поперечного сечения тоннеля, его назначение, климатические условия, а также стоимость и экологические соображения (considerations) влияют на выбор технологии строительства.
11. В железнодорожных тоннелях более трех километров и в автодорожных более полутора километров прокладывают эвакуационные выходы (evacuation exit), сбойки (joining) на расстоянии 300 метров между ними. Их соединяют с соседними (adjacent) тоннелями, или со штольнями безопасности (escape path), имеющими выходы на поверхность. В автодорожных тоннелях сооружают камеры безопасности (escape chamber) с герметичными затворами (airtight gate) и собственной (self-contained) вентиляцией.