
- •Examination questions for discipline Microeconomics
- •Production Efficiency
- •The ppf and Marginal Cost
- •Markets and Prices
- •The law of demand
- •The Factors that Influence the Elasticity of Supply
- •New Ways of Explaining Consumer Choices
- •Consumption Possibilities
- •Work-Leisure Choices
- •The Firm and Its Economic Problem
- •Markets and the Competitive Environment
- •Product Curves
- •Short-Run Cost
- •Marginal Cost and Average Costs
- •Marginal Cost and Average Costs
- •The Long-Run Average Cost Curve
- •Perfect competition
- •What is Perfect Competition?
- •The Firm’s Output Decision
- •Output, Price, and Profit in the Short Run
- •Price Discrimination
- •Marginal Revenue and Elasticity
- •63. Single-Price Monopoly and Competition Compared
- •Monopoly Regulation
- •Monopolistic Competition and Perfect Competition comparison
- •What is Oligopoly?
- •Two Traditional Oligopoly Models
- •Oligopoly Games: An Oligopoly Price-Fixing Game
- •Antitrust Law
- •Classifying Goods and Resources
- •Public Goods
- •Common Resources
- •The Anatomy of Factor Markets
- •The Demand for a Factor of Production
- •Capital and Natural Resource Markets
- •Nonrenewable Natural Resource Markets
- •Property Rights and the Coase Theorem
- •Achieving an Efficient Outcome
Oligopoly Games: An Oligopoly Price-Fixing Game
Firms in an oligopoly can face a prisoners’ dilemma game. Suppose there are two firms, A and B. The firms could enter into a collusive agreement to jointly boost their price and decrease their output. Once the agreement is made, each firm must select its strategy: cheat on the agreement or comply with the agreement.
T
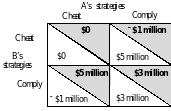
he payoff matrix is to the right. Each firm’s profit depends on its strategy and that of its competitor.
The Nash equilibrium for the game is for both firms to cheat on the agreement. The outcome is bad for them because both would be better off if each complied with the agreement. This Nash equilibrium is called a dominant strategy equilibrium, which is an equilibrium in which the best strategy of each player is to cheat regardless of the strategy of the other player.
Oligopoly Games: A Game of Chicken
I
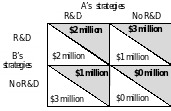
n an R&D game of chicken, two firms, A and B, can conduct R&D. The firm that conducts the R&D must pay for the R&D, but the R&D will lead to a new product that both firms can produce.
Each firm’s strategies are to conduct the R&D or not conduct the R&D. The payoff matrix for this game is to the right
This game does not have a Nash equilibrium that is a dominant strategy equilibrium. Here the equilibrium is for one firm to conduct the R&D but we cannot predict which firm will conduct it.
Oligopoly Repeated Games and Sequential Games
A Repeated Duopoly Game
If a game is played repeatedly, it is possible for players of the game to reach the cooperative equilibrium in which the players make and share the monopoly profit. Because the game is played repeatedly, a player can use a tit-for-tat strategy, in which the player cooperates in the current period if the other player cooperated in the previous period, but cheats in the current period if the other player cheated in the previous period.
A tit-for-tat strategy used with the payoff matrix at the top of the page leads to the cooperative equilibrium.
A Sequential Entry Game in a Contestable Market
A contestable market is a market in which firms can enter and leave so easily that those firms in the market face competition from potential entrants.
Firms in a contestable market play a sequential entry game. In this game, the firms in the market might set a competitive price and earn only a normal profit to keep the potential entrant out. A less costly strategy is limit pricing, which sets the price at the highest level that inflicts a loss on the entrant. The potential entrant is kept out and the existing firms earn an economic profit. However, limit pricing works only if the firm that sets the price is somehow locked into the price it will set at the second stage of the game.
Antitrust Law
Antitrust law is the law that regulates oligopolies and prevents them from becoming monopolies or behaving like monopolies.
The Antitrust Laws
The Sherman Act (1890) made it a felony to create or attempt to monopolize an industry. Section I declares it illegal to conspire with others to restrict competition. Section II deems any attempt to monopolize illegal.
The Clayton Act (1914) makes illegal certain business practices if they “substantially lessen competition or tends to create a monopoly.” These practices include price discrimination, typing arrangements, requirements contracts, exclusive dealing, territorial confinement, acquiring a competitor’s shares or assets, or becoming a director of a competing firm. If these actions do not substantially lessen competition and do not tend to create a monopoly the actions are legal.
Price fixing is per se illegal, which means it is always illegal. There is no defense that can justify the practice.
Three Antitrust Policy Debates
Resale Price Maintenance: Resale price maintenance occurs when a manufacturer agrees with a distributor on the price at which the product will be resold. Resale price maintenance is also called vertical price fixing, and is illegal. Whether resale price maintenance creates an inefficient or efficient use of resources is debated.
Tying Arrangements: A tying arrangement is an agreement to sell one product only if the buyer agrees to buy another, different product. These bundling arrangements may enable a firm to price discriminate, resulting in an increase in efficiency.
Predatory Pricing: Predatory pricing is setting a low price to drive competitors out of business with the intention of setting a monopoly price when the competition has gone. Economists are skeptical that predatory pricing occurs.
Mergers and Acquisitions
A merger occurs when two or more firms agree to combine to create one larger firm. Acquisitions occur when one firm buys another firm.
FTC guidelines stipulate that a HHI above 1,800 indicates a concentrated market, and a merger in this market that would increase the index by 50 points is likely to be challenged.
