
- •Задания задание 1
- •Задание 2
- •Задание 3
- •3. Разработать классы Point и Array, позволяющие использовать их в следующей программе:
- •Задание 4
- •Задание 5
- •Задание 6
- •6. Разработать классы Point и Array, позволяющие использовать их в следующей программе:
- •Задание 7
- •Задание 8
- •Задание 9
- •Задание 10
- •Задание 11
- •Задание 12
- •Задание 13
- •17. Разработать классы Point и Array, позволяющие использовать их в следующей программе:
- •Задание 19
- •19. Разработать классы Point и Array, позволяющие использовать их в следующей программе:
- •Задание 20
- •Задание 21
- •Задание 22
- •22. Разработать классы Point и Array, позволяющие использовать их в следующей программе:
- •Задание 23
- •Задание 24
- •Задание 25
- •Задание 26
- •Задание 27
- •Задание 28
- •Задание 29
- •Задание 30
- •Решения Вариант 1
- •Вариант 2
- •Вариант 3
- •Вариант 4
- •Вариант 5
- •Вариант 7
- •Вариант 8
- •Вариант 9
- •Вариант 10
- •Вариант 11
- •Вариант 12
- •Вариант 13
- •Вариант 14
- •Вариант 15
- •Вариант 16
- •Вариант 6, 17, 19
- •Вариант 18
- •Вариант 20
- •Вариант 21
- •Вариант 22
- •Вариант 23
- •Вариант 24
- •Вариант 25
- •Вариант 26, 28
- •Вариант 27, 29.
- •Вариант 30
Вариант 27, 29.
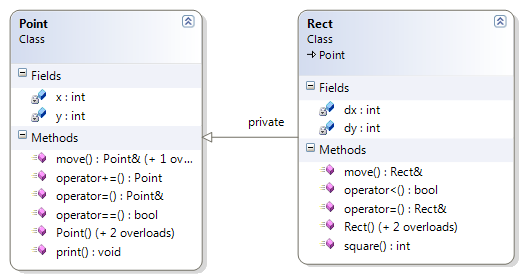
Написать тексты h-файлов и cpp-файлов для базового класса Point и производного класса Rect (прямоугольник). Описание классов:
Класс |
Элементы данных |
Интерфейс |
Point |
x, y |
Конструкторы, функции move,print, операции =, == |
Rect |
dx, dy |
Конструкторы, функции move, square, операции =, <, << |
Привести примеры создания и использования объектов классов Point и Rect. Нарисовать диаграммы классов.
// Main.cpp
#include <iostream>
#include "Point.h"
#include "Rect.h"
using namespace std;
int _tmain(int argc, _TCHAR* argv[]){
Point a(4,6);
Point b;
Point c(a);
b=a;
a.print();
b.print();
cout << (a == b);
Rect r1(a, 5, 6);
Rect r2(b, 7, 8), r3;
cout << endl << r1;
cout << r1.move(c);
cout << r1.square() << endl;
cout << (r1 < r2) << endl;
r3 = r2;
cout << r3;
system("pause");
return 0;
}
//Point.h
#pragma once
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
class Point {
private:
int x;
int y;
public:
Point();
Point (const Point &p);
Point (int a, int b);
void print()const;
Point& move(int, int);
Point& move(const Point &);
Point& operator = (const Point &p);
bool operator == (const Point &p);
};
//Point.cpp
#include "Point.h"
#include "Rect.h"
#include <iostream>
Point::Point(){
x = 0;
y = 0;
}
Point::Point (const Point &p){
x = p.x;
y = p.y;
}
Point::Point (int a, int b){
x = a;
y = b;
}
Point& Point::move(int dx, int dy){
x += dx;
y += dy;
return *this;
}
Point& Point::move(const Point &p){
x += p.x;
y += p.y;
return *this;
}
void Point::print()const{
cout << "\n(" << x << ", " << y << ")" << endl;
}
Point& Point::operator = (const Point &p){
x = p.x;
y = p.y;
return *this;
}
bool Point::operator == (const Point &p){
return (x == p.x) && (y == p.y);
}
//Rect.h
#pragma once
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
#include "Point.h"
class Rect : Point {
public:
private:
int dx;
int dy;
public:
Rect ();
Rect (const Point& p, int dx1, int dy1);
Rect (const Rect& r);
Rect& move (const Point& p);
int square ()const;
Rect& operator = (const Rect& r);
bool operator < (Rect& r);
friend ostream & operator<< (ostream& s, Rect& r);
};
//Rect.cpp
#include "Point.h"
#include <iostream>
#include "Rect.h"
ostream & operator << (ostream& s, Rect &r){
s << "Location:";
r.print();
s << "Width: "<<r.dx<<endl;
s << "Height: "<<r.dy<<endl<<endl;
return s;
}
Rect::Rect():Point(){
dx=0;
dy=0;
}
Rect::Rect(const Point& p, int dx1, int dy1):Point(p){
dx=dx1;
dy=dy1;
}
Rect::Rect(const Rect& r):Point(r){
dx=r.dx;
dy=r.dy;
}
Rect& Rect::move(const Point& p){
Point::move(p);
return *this;
}
Rect& Rect::operator = (const Rect& r){
(Point)*this = r;
dx = r.dx;
dy = r.dy;
return *this;
}
bool Rect::operator < (Rect& r){
return (square() < r.square());
}
int Rect::square()const{
return dx * dy;
}
