
- •© Борисова татьяна Васильевна
- •Lesson 1 from the history of building
- •1. Read and translate the text
- •From the History of Building
- •2. A few explanations to the text
- •3. Key vocabulary /expressions. Find the words belonging to the prehistory time of construction and compose sentences with them
- •4. Translate the extract into Russian
- •5. Explain in English the meaning of the following words
- •6. Find in the text equivalent English phrases to the following Russian
- •7. General understanding. Answer the questions
- •9. Listen to the text “How the Ancient Builders Put a Hand to the Development of Different Languages” and be ready to answer to the following test
- •Past Perfect
- •Future Perfect
- •Improve your skills in English:
- •Lesson 2 civil engineering
- •1. Read and translate the text
- •Civil Engineering
- •2. A few explanations to the text
- •3. Key vocabulary /expressions. Divide these words into groups according to types of engineering
- •4. Word construction (Different ways to construct words).Translate the words keeping in mind their suffixes and prefixes
- •5. General understanding. Answer the questions
- •12. Now say whether these statements are true or false. Correct the false statements
- •Grammar PaSsiVe vOiCe
- •Improve your skills in English:
- •Lesson 3 town planning
- •1. Define meaning of the following English words. Explain them
- •2. Read the text. Mark which sentences give explanation to the term “ master plan” Town Planning
- •7. Define correct answers to the following questions . Prove your opinion
- •8. Correct these statements if they are wrong. Using them as a plan speak briefly on the topic of the text.
- •9. Without dictionary try to translate these words. Explain this meaning
- •10. Find in the ex. 9 suitable meaning of Russian words. Compose sentences on the topic of the text
- •11. Read the text. Find descriptions to the title of the text Design of the Complete Town
- •12. Define correct and incorrect statements. Correct wrong sentences. Prove your opinion
- •13. Put following points of a plan to the text in order. Add necessary points. Using these plan speak briefly on the topic of the text
- •18. Make simi1ar discussions 'between the architect and his client complaining about:
- •Grammar Participle 1
- •Participle II
- •Improve your skills in English:
- •Lesson 4 types of buildings
- •1. Define meanings of these ww. Explain them
- •2. Find suitable Russian meanings to English words
- •3. Read the text. Define which paragraphs belong to the topic "Housing and Industrial Construction"
- •4. Tasks after reading:
- •5. Choose the sentence with the main idea of the text. Prove it
- •6. Find which paragraphs belong to the following titles. Put them in order
- •7. Point which of these ss have description of dwelling and which of them are industrial. Divide them into two groups
- •9. Define meanings of these ww. Explain them
- •10. Find suitable Russian meanings to English words
- •11. Put in pairs following ww
- •12. Read the text. Define which paragraphs belong to these titles. Add three more titles
- •Types of Buildings
- •13. Choose the sentences with the main idea of the text. Prove it
- •14. Compose certain paragraphs under each title
- •15. Finish these sentences with suitable endings
- •17. Listen to the text and fulfill these tasks
- •18. Now design a single-storey house and compare your plan with House a Grammar The Gerund
- •Свойства глагола и герундия
- •Improve your skills in English:
- •Lesson 5 sanitary engineering in the modern town
- •1. Choose suitable Russian words to English terms. Explain their meaning
- •2. Choose suitable English words to Russian terms. Put them in the alphabet order
- •3. Read the text. Mark which paragraphs devote to the title of the text Panel Heating
- •4. Find correct Russian translation of English words. Compose sentences with them on the topic of the text. Find unnecessary words
- •5. Define which of these statements contain the main idea of the text
- •6. Put these sentences in order according to the text
- •7. Find the correct answer to these questions. Prove your opinion
- •8. Which paragraphs deal with these questions? Give brief explanations to each of them
- •9. Which of these sentences explain the work of heating and which ones – ventilation?
- •10. Prove these statements, add some more information from the text
- •11. Compose pairs of words from English and Russian synonyms. Explain their meaning
- •12.Find suitable Russian words to English terms, put them in the alphabet order
- •13. Read the text. Mark which paragraphs devote to the title of the text
- •14. Find correct Russian translation of English terms. Compose sentences with them on the topic of the text
- •15. Mark which paragraphs these titles belong to. Place them in order according to the text
- •16. Finish these sentences
- •17. Divide these sentences into three groups
- •18. Change these words into another part of speech
- •19. Read the text. Mark which paragraphs devote to the title of the text Water Supply
- •20. Choose suitable translation of English words from Russian ones. Compose sentences with them on the topic of the text
- •21.Point which of these sentences have the main idea of the text. Explain your point of view
- •22. Which of these statements contain the basic of the text. Put them in accordance with the context
- •23. Add these sentences with correct variant according to the text. Using as a plan speak briefly about Water Supply
- •24. Fill this table due to points of the topic Sanitary engineering
- •25. Using information from the texts and this table compose a dialogue “Service engineers “ for three persons. Discuss process of equipment of any new-built structure with all modern conveniences
- •26. Make a written report about one of the type of Sanitary Engineering describing step-by-step arrangement of your project with this convenience
- •27. Listen to the text and fulfill these tasks
- •Grammar The Infinitive
- •Improve your skills in English:
- •Lesson 6 mixing, molding and curing equipment
- •1. Define meaning of these ww
- •2. Find suitable meaning of English terms to Russian ones
- •3. Read the text. Find the sentence in each paragraph, which keeps the main idea On Mixing, Molding and Curing Equipment
- •4. Compose pairs of English and Russian terms
- •5. Compose word combinations. Make your own sentences on the topic of the text
- •6. Define what parts of the text do these titles belong to. Using these points speak briefly about Mixing, Moulding and Curing Equipment
- •7. Answer to these questions
- •8. Define meaning of these ww
- •9. Revise in your memory meaning of these ww . Give a brief explanation
- •10. Read the text.Point the main topics in it Earth-Moving Machinery
- •11. Compose pairs of English and Russian terms
- •12. Compose word combinations. Made your own sentences on the topic of the text
- •13. Find synonyms. Explain a bit difference in each pair
- •14. Find correct and incorrect statements. Add some more information from the text
- •15. Define meanings of these words
- •16.Find suitable meaning of English terms to Russian ones. Explain their meaning
- •17. Read the text. Find words and word combinations describing all kinds of cranes Cranes
- •18. Compose pairs of Russian and English terms. Make your own sentences on the topic of the text
- •19.Find synonyms in the text, explain their differences and common features
- •20.Compare mobile, tower and climbing cranes, find their advantages and
- •21.Which of these statements are correct and which ones are incorrect. Prove your opinion
- •22. Using material from all texts define kind of building equipment to these word combinations. Fill the table
- •24. Compose a dialog for three or four persons on the topic “Process of erection of any structure” including excavation, concrete curing, climbing with the help of all kinds of building equipment
- •25. Write a report about one of the type of building machineries and its role in fulfillment of your project grammar Revision
- •Improve your skills in English:
- •Lesson 7 strenght of materials
- •1 Using new words and their translation guess the meaning of sentences
- •2. Find correct translation for English terms
- •3.Try to guess meanings of these word combinations. Make your own sentences with them
- •4. Read the text. Find terms concerning main types of external forces and explain their meaning How materials react to external forces
- •5. Find these words in the text and define their meaning of the context
- •6. Answer the questions
- •7. Find the following word combinations in the text and compose your own sentences on the topic of the text
- •8.Translate into English the following sentences
- •9. Describe which paragraphs contain these statements as the main idea and prove your point of view
- •10. Find key-sentences in the rest paragraphs or compose them from some parts of sentences
- •11. Using these titles as a plan speak briefly about reaction of materials to external forces
- •12. Read the text. Find synonyms to all kinds of properties of materials Properties of materials
- •13. Find these words in the text and define their meaning of the context
- •14. Answer the questions
- •15. Find the following words and word combinations in the text, compose your own sentences on the topic of the text
- •16. Translate into English
- •17. Define which sentences are correct and which ones are incorrect
- •18.Using correct sentences as a plan speak briefly about property of materials.
- •19. Fill the table with suitable words to each properly of material
- •Grammar Complex Object
- •Improve your skills in English:
- •Lesson 8 parts of a building
- •1.Find suitable meaning of English words. Explain them
- •2. Сompose correct word combinations from both columns. Try to guess their meaning
- •3. Read the text. Find words characterizing types of footing and foundations Footing and foundations
- •8. Compose correct word combinations from both columns. Try to guess their meaning
- •9. Read the text. Find words characterizing types of roofs Roof
- •10. Choose correct titles to paragraphs. Add necessary sentences. Put them in order
- •11. Finish these statements choosing the correct variant. Prove your opinion
- •12. Using information from the previous ex. Speak briefly about all types of roofs.
- •14. Compose correct word combinations from both columns. Try to guess their meaning
- •15. Read the text. Find words characterizing all kinds of walls Walls
- •16. Answer following questions to the text:
- •17. Choose correct variant of terms to following definitions
- •18. Discuss with your group mates peculiarities of all types of walls ,positives and negatives for the certain kind of building and its parts
- •19. Find correct translation to Russian words. Explain their meaning in English
- •20. Compose correct word combinations from both columns. Try to guess their meaning
- •21. Read the text. Find synonyms characterizing all kinds of floors Floors
- •22. Finish these sentences using the text. Add some more information
- •Grammar Complex Subject
- •Improve your skills in English:
- •Lesson 9 reinforced concrete
- •1. Find correct translation of English words. Make your own sentences with them
- •2. Compose correct word combinations. Guess their meaning
- •3. Read the text. Find sentences having the main idea in each paragraph Reinforced concrete
- •8. Find synonyms to the following words. Compose your own sentences with them
- •9. Make suitable word combinations. Translate them
- •10. Read the text. Find key-words characterizing all types of beams Beams
- •11. Put suitable definitions to these characteristics
- •12. Fill this table paying attention to necessary building materials, usage and some peculiarities
- •13. Find correct translation of English words. Explain their meaning
- •14. Translate terms concerning shape of any structure. Compose your own sentences with them
- •15. Compose correct word combinations. Guess their meaning
- •16. Read the text. Find in the text description of fig.1 and make correct translation Strength of slabs
- •17. Translate these sentences into English. Find suitable sentences in the text
- •18. Choose correct answers to following questions. Add some more information
- •19. Work for a group of 3-4 students:
- •20. Read these questions:
- •21. Identify the part of the building or the phase of the assembly sequence described in these sentences:
- •22. Read this description of phase 1 of the assembly sequence:
- •I.2. Порядок слов в дпп
- •I.3. Согласование времён
- •Improve your skills in English:
- •Lesson 10 architectural design of a building
- •1. Find suitable translation of English words. Explain their meaning
- •2. Find terms of trades. Explain peculiarities of their trades
- •3. Compose correct word combinations with following terms. Make your own sentences
- •4. Read the text. Find key-sentences in each paragraph Orientation and Surveying the Building
- •5. Compare your variants of key-sentences with given ones. Choose the best, prove your opinion. Put them in order
- •6. Using statements as a plan from ex. 5 speak briefly about Architectural design of a building
- •7. Find suitable translation of Russian terms. Explain their meaning in English
- •8. Find suitable translation of Russian terms concerning design of any structure. Compose sentences with them
- •9. Translate terms of building materials. Divide them according to the parts of building(ex.8)
- •10. Compose suitable word combinations. Explain their meaning
- •11. Read the text. Make conclusion what means: 1) styling of a house; 2)designing elevation
- •12. Do you agree with the following statements characterizing the main idea of the points “ Styling of a house” and “ Designing elevations”
- •13. Answer these questions. Using them as a plan speak briefly about “Architecture of a house”
- •14. Find correct translation of English words. Explain their meaning
- •15. Divide words from ex.14 into six groups in accordance with these localities. Compose your own sentences with them
- •16. Read the text. Using information from ex.15 give the main idea of each paragraph
- •17. Finish these statements. Add some more information to them
- •18. Study these plans of а two-storey house:
- •Reported Statements (Повествовательные предложения)
- •Reported General Questions (Общие вопросы)
- •Reported Special Questions (Специальные вопросы)
- •Reported Commands and Requests (Приказания и просьбы)
- •Правила согласования времён в косвенной речи
- •Cводка правил перевода предложений с модальными глаголами в косвенную речь
- •Lesson 2
- •Lesson 3
- •Lesson 4
- •Lesson 5
- •Lesson 7
Lesson 7
An experiment to investigate the effect of the water content on the compressive strength of concrete
Three different mixes of concrete were separately prepared. The materials in mix A were mixed dry in the proportion of 1:1:2. The cement used was normal Portland cement. The mix was divided and each half was separately mixed with water, one half having30per cent more water added then the other. A 150 mm cube was then made from each half of each batch and tested for compression strength at the end of twenty-eight days. Mixes B and C were dealt with in a similar manner, the excess water added to one-half of each mix being also 30 per cent.
Адаптированный курс
Сопротивления материалов
(русский текст проф. А.И. Сапожникова)
Растяжение стержней
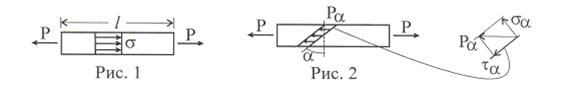
Сила Р растягивает стержень (рис. 1 ), в нем возникают нормальные напряжения σ, одинаковые в любом сечении по длине стержня, равные σ = Р / А, где А-площадь поперечного сечения стержня.
При этом стержень длиной L растягивается на величину ΔL, определяемую по закону Гука равенством ΔL = Р · L / ЕА , где Е - модуль упругости материала стержня.
Модуль упругости может быть определен только путем вычисления по формуле Е = PL/ А · ΔL = σ(L/ М ) (Н/см2), в то время как величины P, L, A, ΔL - определяются измерениями.
На расположенном под углом α сечении стержня полные нормальные напряжения Рα будут меньше, чем σ(L/ΔL ), т.к. оно имеет большую площадь, Аα = А/cos α (рис.2). Из очевидного равенства Рα Аα = σ А следует, что Рα = σ cosα .
Представим Рα ее проекциями по нормали и по касательной к наклонной площадке, получим, что σa = Pα cosα, τα = Pα sinα, или σα = σ2 cos 2α, τα = ½ σ ∙sin2α.
При α = 0 имеем σα = σ, τα = 0. При α = 900 имеем σα = τα = 0, это означает, что продольные слои растянутого стержня по боковым поверхностям не взаимодействуют.
Наибольшее значение нормальные напряжения имеют на площадках с нулевым наклоном (α = 0), а касательные напряжения - на площадках, имеющих наклон α = 450 к оси растянутого стержня τmах = σ /2.
Важно отметить, что на взаимно перпендикулярных площадках (α и α + 900) касательные напряжения имеют одинаковые по абсолютной величине значения, поскольку ½ sin 2α = ½ sin 2(α + 900). Это условие носит название закона парности касательных напряжений.
Сжатие стержней
Поведение сжатого стержня не отличается от поведения растянутого, следует только изменить направление сил и напряжений.
Однако стержень большой длины, помимо сжатия, может еще и изогнуться. Убедитесь в этом, сжимая, например, стержень шариковой ручки. Изгиб стержня под действием продольной силы, сжимающей его, называется потерей устойчивости. Но об этом будет сказано позже, после изучения изгиба прямых стержней, поскольку, потеряв устойчивость, стержень испытывает изгиб.
Словарь-
1. растяжение стержней -
2. в нем возникают-
3. нормальные напряжения -
4. одинаковые в любом сечении -
5. в любом сечении по длине стержня -
6. площадь поперечного сечения -
7. растягивается на величину -
8. определяемую по закону -
9. модуль упругости материала -
10. может быть определен-
11. только путем вычисления -
12. определяются измерениями -
13. на расположенном под углом -
14. из очевидного равенства-
15. представим Рα ее проекциями -
16. по нормали и по касательной -
17. к наклонной площадке -
18. продольные слои -
19. по боковым поверхностям не взаимодействуют -
20. наибольшее значение -
21. важно отметить -
22. на взаимно перпендикулярных площадках -
23. по абсолютной величине -
24. носит название -
25. закон парности касательных напряжений -
26. сжатие стержней -
27. поведение стержня не отличается -
28. следует только изменить направление -
29. однако стержень большой длины -
30. помимо сжатия -
31. может еще и изогнуться -
32. убедитесь в этом -
33. сжимая, например стержень -
34. стержень шариковой ручки -
35. изгиб стержня -
36. под действием продольной силы -
37. сжимающей его -
38. потеря устойчивости -
39. об этом будет сказано позже -
40. после изучения -
41. изгиб прямых стержней –
Чистый сдвиг
Н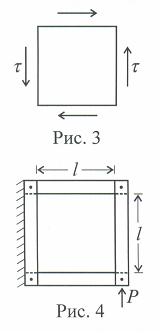 а
примере растяжения и
сжатия определено, что на
наклонных, по отношению к оси стержня,
сечениях
(см. рис. 2), возникают касательные
напряжения, подчиняющиеся
условию парности.
а
примере растяжения и
сжатия определено, что на
наклонных, по отношению к оси стержня,
сечениях
(см. рис. 2), возникают касательные
напряжения, подчиняющиеся
условию парности.
Предположим, что на гранях выделенного элемента (рис. 3) возникают только касательные напряжения τ. Такое напряжённое состояние называется чистым сдвигом.
Если элемент имеет размеры: l – длина (ширина), t - толщина, а к его углу приложена сила Р (рис. 4), то для всех точек пластины касательное напряжение τ будет равно τ = P/ lt.
Повернув пластину (см. рис. 3) на 450 (рис. 5), получим τ = 0, σ = ± τ .
К асательные
напряжения τ связаны
с угловой деформацией
γ
соотношением
τ
= Gγ
, где G
- модуль упругости при сдвиге, которое
называется
законом Гука.
асательные
напряжения τ связаны
с угловой деформацией
γ
соотношением
τ
= Gγ
, где G
- модуль упругости при сдвиге, которое
называется
законом Гука.
При перекосе элемента с размерами dx и dy на угол γ (рис. 6) сила Q = τ dx t на верхней грани совершает работу на перемещении γdy . Так как сила изменяется от нуля до Q, то работа её средней величины равна половине произведения τ · dx · t · γ · dy , следовательно, потенциальная энергия деформации сдвига, накопленная в элементе, равна
dU = ½ τ · γ · dx · dy · t ,
Если отнести энергию к единице объёма, получим
U0 = du / dV = ½ (τ γ) = τ2 / 2G = ½ G γ2
Словарь
1. на примере растяжения -
2. на наклонных сечениях -
3. по отношению к оси -
4. подчиняющиеся -
5. предположим, что на гранях –
6. на гранях выделенного элемента -
7. напряжённое состояние -
8. элемент имеет размеры -
9. к углу приложена сила-
10. для всех точек пластины -
11. будет равно -
12. связаны с угловой деформацией-
13. связаны соотношением -
14. называется законом Гука-
15. при перекосе элемента -
16. на верхней грани-
17. совершает работу-
18. работу на перемещении-
19. сила изменяется от нуля до-
20. работа её средней величины -
21. равна половине произведения -
22. потенциальная энергия деформации -
23. накопленная в элементе-
24. отнести энергию к единице объёма -
Поперечный изгиб. Чистый изгиб
Изгиб - форма деформации стержня, при которой в его поперечных сечениях возникают изгибающие моменты. Если они являются единственным силовым фактором, изгиб называется чистым, если же в поперечном сечении, наряду с изгибающим моментом, возникают и поперечные силы, изгиб называется поперечным. Стержень, в основном работающий на изгиб, также называют балкой.
По длине балки изгибающие моменты и поперечные силы как правило изменяются и для их расчёта необходимо научиться строить графики их изменения по длине, называемые эпюрами. Для их построения вначале необходимо определить все силы, действующие на балку, включая реакции опор.
Для балки (рис. 7) реакции опор равны РЛ = Рв /(а+в), РП = Ра /(а+в).
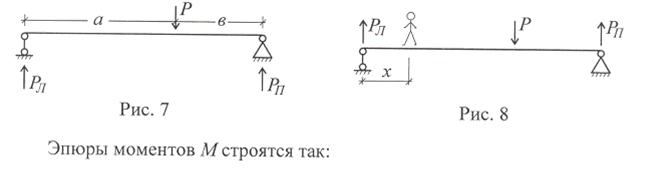
человечек движется от силы РЛ к силе Р и, поглядывая назад, вычисляет момент силы РЛ в сечении под его ногами, удалённом от силы РЛ на расстояние х; он равен РЛ · х (сила, умноженная на плечо). И так до силы Р.
Имеем эпюру моментов:
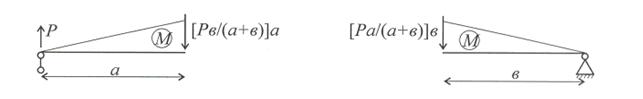
Затем, перейдя через силу Р, эпюра моментов строится по другому уравнению, учитывающему отдельно плечо силы РЛ , равное х и плечо силы Р, равное (х - а). Имеем уравнение моментов для правого участка балки (x ≥ a) РЛ х - Р(х - а), причём момент в сечении балки под силой равен Рaв /(а + в), если вычислять его слева [Рв/(а+в)]·а, справа, то [Ра/(а + в)]·а, т.е. их значения равны.
При построении эпюры перерезывающей силы Q человечек вычерчивает видимую им силу РЛ .
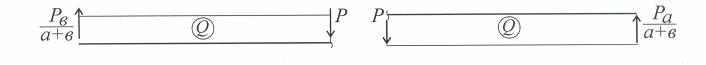
Перейдя через силу Р, он уже видит разность сил Р-(Рл =Рв/(а + в)), т.е. силу Рπ = Ра/(а + в).
П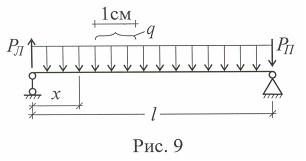 остроим
эпюры для равномерно
распределённой
по
длине балки нагрузки,
характеризуемой
интенсивностью
(т.е. силой, приходящейся на единицу
длины балки) q
Н/см. Реакции в обоих опорах равны РЛ
= Рπ
=q1/2.
Человечек, передвигаясь от опоры Л
к опоре П,
видит момент М,
изменяемый
по закону
М
= РЛ
x – qx (x/2),
где (х/2)
- расстояние от сечения с координатой
х
до
середины отрезка
х,
где приложена равнодействующая
нагрузка
на отрезке х.
остроим
эпюры для равномерно
распределённой
по
длине балки нагрузки,
характеризуемой
интенсивностью
(т.е. силой, приходящейся на единицу
длины балки) q
Н/см. Реакции в обоих опорах равны РЛ
= Рπ
=q1/2.
Человечек, передвигаясь от опоры Л
к опоре П,
видит момент М,
изменяемый
по закону
М
= РЛ
x – qx (x/2),
где (х/2)
- расстояние от сечения с координатой
х
до
середины отрезка
х,
где приложена равнодействующая
нагрузка
на отрезке х.
Окончательно M = (ql/2)x – qx 2/2 , Q=Рπ-qх (рис. 10).

Оба рассмотренных варианта загружения балки относятся к поперечному изгибу, т.к. по её длине во всех сечениях имеются моменты и поперечные силы. Ниже приведём примеры нагрузок, вызывающих появление чистого изгиба по всей или по части длины балки.
Эпюру поперечных сил Q постройте самостоятельно, а затем определите значение поперечных сил Q для обоих загружений.
Словарь
1. поперечный изгиб -
2. чистый изгиб-
3. форма деформации стержня-
4. в его поперечных сечениях-
5. в сечениях возникают-
6. возникают изгибающие моменты-
7. единственный силовой фактор-
8. поперечные силы-
9. в основном работающий на изгиб-
10. называется балкой-
11. по длине балки-
12. как правило изменяются-
13. для их расчёта необходимо-
14. необходимо научиться строить-
15. строить графики их изменения-
16. называемые эпюрами-
17. определить все силы-
18. силы, действующие на балку-
19. включая реакции опор-
20. движется от силы к силе-
21. поглядывая назад-
22. вычисляет момент силы-
23. удалённом от силы-
24. перейдя через силу-
25. строится по другому уравнению-
26. отдельно плечо силы-
27. вычерчивает видимую им силу-
28. разность сил-
29. равномерно распределённой-
30. по длине балки нагрузки-
31. характеризуемой интенсивностью-
32. изменяемый по закону -
33. до середины отрезка-
34. равнодействующая нагрузка-
35. рассмотренные варианты-
36. загружения балки-
37. вызывающих появление-
38. постройте самостоятельно-
39. затем определите значение -
СПИСОК ЛИТЕРАТУРЫ
Агабекян И.П., Коваленко П.И. Английский для инженеров. – Р.-на-Д.: Феникс, 2002.- 305 с.
Headway Intermediate. Oxford, 1997. – 86с.
Murphy R. English Grammar in Use. M., 1997. – 561р.
O’Sullivan D., Swan M., Wasltre C., The New Cambridge English Course, Cambridge, 1997. – 435р.
Soars J., Soars L., Headway, Intermediate, Oxford University Press, 1995. – 92р.
Alexander, L.G., Longman English Grammar, Longman, 1997. – 442 р.
Murphy, R., English Grammar in Use, Cambrige, University Press, 1997. – 593 р.
Мусихина О.Н., Гисина О.Г., Яськова В.Л. Английский язык для строителей. – Р.-на-Д.: Феникс, 2004.- 241с.
Громова К.В., Королькова В.С., Лукьяненко Н.Д. Книга для чтения на английском языке для строительных вузов. М.: 1960. – 159с.
Горбунова Е.В., Носенко И.А., Гришина М.М. Пособие по английскому языку для студентов 2-3 курсов строительных вузов. - М.: Высш. школа, 1978.- 145с.
Michael Swan & Catherine Walter. How English Works. A grammar practice book. - Oxford University Press. – 415р.
Michael McCarthy felicity O’Dell. English Vocabulary in Use.– Cambridge University Press.- 572р.
Якимов М.В. Большой англо-русский политехнический словарь. – СПб.: Литера, 2002. – 632с.
Камминг Джеймс. Английский язык для студентов архитектурных и строительных специальностей. – Астрель, 2004.-292с.
Учебное пособие
Борисова Татьяна Васильевна
Учебное пособие по английскому языку
для студентов 2 курса
Редактор: А.И. Сапожников
Технический редактор: И.С. Прилепина
Компьютерный набор: Ю.Г. Малова, С.Р.Рустамханова
Лицензия ЛР № 040842 от 02.05.97г.
Подписано к печати Формат 60х90/16
Печать офсетная. Уч. изд. л. 6. Тираж – 45. Заказ №
Отпечатано в типографии АИСИ, 414056, г.Астрахань, ул. Татищева, 18.
Тел./факс 251468; e-mail: buildinst@mail.ru
