
- •Introduction
- •Concepts and kinds of bankruptcy
- •Essence and principles of anti-recessionary management
- •1.3 Methodology of forecasting of probability of bankruptcy of the enterprise.
- •Income from realization
- •2.1 The economic characteristic and an estimation of a financial condition of joint-stock company “National Bank rk”
- •2.2 The analysis of financial stability, liquidity and solvency of jsс “Halyk Bank Republic Of Kazakhstan”
- •3.1 Perfection of system of diagnostics of bankruptcy of the enterprise
- •3.2 Prospects of development of anti-recessionary management at threat of bankruptcy
- •Conclusion
- •The list of the references
2.2 The analysis of financial stability, liquidity and solvency of jsс “Halyk Bank Republic Of Kazakhstan”
Table 2. Altman's Z-model on an example of joint-stock company «Halyk Bank of Kazakhstan” financial reports of bank (billions of tenge)
|
Parameter |
01.01.2009 |
01.01.2010 |
01.01.2011 |
1 |
Current assets (result of turnover assets) |
77 395 |
95 612 |
120 777 |
2 |
The sum of assets |
122 386 |
156 868 |
213 915 |
3 |
The extra capital (the sum of long-term and short-term obligations) * |
49 894 |
72 959 |
108 319 |
4 |
Unallotted (reinvested) profit |
77 224 |
90 941 |
120 445 |
5 |
Market cost of own capital (pure actives) * |
138 185 |
176 099 |
252 308 |
6 |
Profit up to the taxation |
15 616 |
20 935 |
50 998 |
7 |
Profit on realization |
18 655 |
23 556 |
52 174 |
8 |
К1 |
0,63 |
0,61 |
0,56 |
9 |
К2 |
0,15 |
0,15 |
0,24 |
10 |
К3 |
0,63 |
0,58 |
0,56 |
11 |
К4 |
2,77 |
2,41 |
2,33 |
12 |
Meaning |
0,09 |
1,63 |
1,64 |
Note – consolidate statement of Halyk bank 2011 |
||||
Result of financial and economic activity of Bank for the accounting period the difference between the income and the charge of Bank for this period admits. The analysis of the report on incomes and charges of bank includes incomes and charges for rendering of the services given to legal persons (corporate operations) and to the population (retail operations) are reflected in the report by separate lines with summarizing financial and economic activity in a cut of these operations. Despite of growth of actives, a credit portfolio and depositary base in comparison with 2002г., rates of growth of the basic parameters of Bank considerably conceded to banks-competitors. As a result on results of year the Bank has conceded positions on a number of parameters, and a share of Bank in the basic financial markets have decreased. So for December, 2010 cumulative actives of bank system have grown in comparison with 2009 on 74,95 %, and a share of National Bank in cumulative actives BSL have decreased from 19,6 % to 15,9 %.
According to table 2 forecasting bankruptcy of Halyk Bank on Altman's model is resulted. This way is considered the most simple and as a matter of fact gives more exact forecasts for 95 percent.
Z = 0,717Х1 + 0,874Х2 + 3,10Х3 + 0,42Х4 + 0,995Х5, (8)
Calculations: Х1 = 0,4691 |
|
Х2 = 1810011/9990228 |
|
Х2 = 0,1812 |
|
Х3 = 1797639/9990228 |
|
Х3 = 0,1799 |
|
Х4 = 6767851/3907521 |
|
Х4 = 1,7320 |
|
Z= 0,0295+0,0166+0,0102+0,0017 |
|
The scale of an estimation of risk of bankruptcy has five gradation and is carried out by following rules:
If Z <0 - probability of bankruptcy maximal (90-100 %);
If 0 <Z <0,18 - probability of bankruptcy high (60-80 %);
If 0,18 <Z <0,32 - probability of bankruptcy average (35-50 %);
If 0,32 <Z <0,42 - probability of bankruptcy low (15-20 %);
If Z> 0,42 - the probability of bankruptcy is minimal (up to 10 %).
Z = 0,297+0,315+0,0580+0,1436+0,1779
Finally, Z = 0,936
It is possible to draw a conclusion, that in conformity of forecasting of Altman probability of bankruptcy of Halyk Bank are insignificant. As the factor of risk of an inconsistency makes Z = 0,936. Forecasting is done for 5 years, accuracy of forecasting makes 95 percent. But nevertheless the Z-model has miscalculations concerning to accuracy of forecasting. For example BTA Bank, also large corporation “General motors” were the best example. They had ideal parameters of a financial condition and forecasts showed insignificant factors of bankruptcy. Therefore completely to trust models of forecasting of bankruptcy it is not necessary.
Table 4 - Parameters of actives, obligations and own capital of National Bank, in million tenge
Balance Sheet of Halyk Bank (in millions of tenge) |
||||
|
|
|
|
|
Assets |
|
|
2010 |
2009 |
Cash and equivalents |
|
572 524 |
420 182 |
|
Short-term investments |
|
309 642 |
287 345 |
|
Accounts receivable |
|
21 096 |
20 123 |
|
Total current assets |
|
903 262 |
727 650 |
|
Long term assets |
|
|
1 370 668 |
1 370 285 |
Total assets |
|
|
2 273 930 |
2 097 935 |
|
|
|
|
|
Liabilities and equity |
|
|
|
|
Accounts payable |
|
|
1 557 476 |
1 415 755 |
Borrowings |
|
|
41 634 |
71 403 |
Notes payable |
|
|
2 547 |
2 910 |
Total current liabilities |
|
1 601 657 |
1 490 068 |
|
Long-term liabilities |
|
361 946 |
289 983 |
|
Total debt |
|
|
1 963 603 |
1 780 051 |
Common stock (50,000,000 shares) |
|
143 695 |
143 695 |
|
Gain on issuance |
|
|
1 156 |
1 352 |
Treasury stock |
|
|
-39 960 |
-93 |
Retained earnings |
|
|
205 436 |
172 930 |
Total common equity |
|
310 327 |
317 884 |
|
Total liabilities and equity |
|
2 273 930 |
2 097 935 |
|
Note – based on data of the Committee for control and supervision of financial market and financial organizations of the National Bank of the Republic of Kazakhstan |
||||
The analysis of Actives of Halyk Bank for 1/1/2010 year have shown, that they have grown in comparison with 2009 on 55 % and have made 1 567 239 billion tenge. Growth of actives occured mainly due to growth of volume of a credit portfolio to clients. By the end of year the volume of a credit portfolio has net grown up to 319,1 billion tenge, that on 101,1 billion tenge, there is more than parameter of 2010. Thus the share of a credit portfolio consistently grew in actives of Bank from 50 % up to 64 %. However on results of year the Bank has a little conceded positions in the market of bank crediting, for January-December its share has decreased from 18,6 % to 17,2 % from total amount of the given out credits to clients of banks on the end of year .Also the return tendency of decrease in investments in securities (on 14,9 billion tenge or 49 %) was observed, that was characteristic for bank system as a whole and is connected with the general tendency of decrease in levels of profitableness under the state securities. Their share in actives of Bank has decreased with 295 up to 12%Анализ dynamics of change of obligations of bank has shown, that they have reached 142,5 billion tenge (growth of 38,8 %), due to increase in depositary base - means and deposits of clients up to 473,1 billion tenge and loans of banks and the financial organizations.
In structure of obligations the increase in a share of deposits of banks (from 0,6 % up to 4,9 %) and interbank loans (from 2,4 % up to 6,2 %) is observed.
Change of size of own capital on the beginning of 2008 was made with 1 412 895 83 million tenge, having increased on 2,7 %. Low rates of growth of the capital of Bank within all year were the restrictive factor of growth of actives of Bank and volumes of attraction of resources. Own capital of banks of the second level for January-December has grown on 24 %, as a result a share of National Bank in the cumulative capital of bank system have decreased from 8,3 % to 6,6 % on the end of year. [25, page 446].
Escalating of volumes and increase of profitableness of spent operations - one of basic problems of management of bank.
The profit of bank (the income net) has grown on 14,1 % and has made 630,4 million tenge.
Expansion of number of offered credit products, realization of special programs of crediting on selective sectors of the market have allowed to increase the sizes of received compensation (interest) under credits to clientele up to 3,8 billion tenge - by 17,4 % more in comparison with 2009. The volume of pure compensation (interest) has increased for 3,9 % (3,1 billion tenge). The structure of incomes is presented in table 5.
The bank gave significant attention to problems of growth of not percentage incomes. Development of system of financial services for corporate and private clients, increase of activity in the currency market, and also rationalization of management by a currency position of Bank promoted increase in not percentage incomes. Commission incomes have grown on 7,1 % (2,7 billion tenge).
The increase in the authorized capital has been carried out due to additional fourth issue of actions at a rate of 6 031 666 actions with face value on 100 tenges. Actions have been placed among 1 038 shareholders of Bank at market cost 141 tenges. The means received from issue, have been directed on capitalization of Bank. Execution of specifications of sufficiency of the capital are presented in table 6.
The increase in the authorized capital has been carried out due to additional fourth issue of actions at a rate of 6 031 666 actions with face value on 100 tenges.
Table 5 - Structure of incomes of JSC Halyk bank
Income Statement of Halyk Bank |
|
|
|
|
(in millions of kzt) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
2010 |
2009 |
Net Interest revenue |
|
48 117 |
43 608 |
|
Service revenues |
|
|
40 822 |
35 193 |
Service expenses |
|
|
-5 568 |
-5 221 |
Operating income |
|
|
83 371 |
73 580 |
Other earnings |
|
|
1 393 |
1 912 |
Non interest earnings |
|
26 057 |
23 372 |
|
Non interest expenses |
|
-61 409 |
-52 048 |
|
EBT |
|
|
49 412 |
46 816 |
Taxes |
|
|
-8 511 |
-8 688 |
Net income |
|
|
40 901 |
38 128 |
Extrordinary items: |
|
|
|
|
Unrealized loss on investments |
|
-245 |
4 960 |
|
Realized loss on investments |
|
-61 |
-110 |
|
Realized loss on long term investments |
-1 318 |
51 |
||
Foreign-currency translation adjustment (loss) |
-137 |
-307 |
||
Other gains, or (losses) |
|
-1 761 |
4 594 |
|
Extrordinary income |
|
37 379 |
47 316 |
|
Note – based on data of the Committee for control and supervision of financial market and financial organizations of the National Bank of the Republic of Kazakhstan |
||||
Actions have been placed among 1 038 shareholders of Bank at market cost 141 tenges. The means received from issue, have been directed on capitalization of Bank. Execution of specifications of sufficiency of the capital are presented in table 6.
The analysis of execution prudential specifications of bank speaks that the bank executes prudential specifications of sufficiency of own capital. Regulative the capital of the first level has made 3,9 billion tenge on the end of year. The sizes regulated own capital - 5,2 billion tenge (growth of 9,2 %). The increase in the sizes of the capital has allowed to improve a parity of investments into not financial actives and the capital.
The increase in the sizes of the capital allows Bank to expand the sizes of attraction of resources and to increase volumes of crediting of economy.
Table 6. Execution of specifications of sufficiency of the capital.
Parameters |
2009 |
2010 |
The capital of 1 level (one thousand tenge) |
3 381 908 |
3 936 039 |
The capital 2 levels (one thousand tenge) |
1 675 766 |
1 460 710 |
Own capital (one thousand tenge) |
4 914 920 |
5 199 153 |
Factor of sufficiency of the capital 1 |
0,069 |
0,065 |
Factor of sufficiency of the financial capital |
0,139 |
0,139 |
Investments into not financial actives to the capital |
1 ,366 |
1,286 |
Note – based on the data of Halyk Bank Of Kazakhstan |
||
The analysis of execution prudential specifications of bank speaks that the bank executes prudential specifications of sufficiency of own capital. Regulative the capital of the first level has made 3,9 billion tenge on the end of year. The sizes regulated own capital - 5,2 billion tenge (growth of 9,2 %). The increase in the sizes of the capital has allowed to improve a parity of investments into not financial actives and the capital.
The increase in the sizes of the capital allows Bank to expand the sizes of attraction of resources and to increase volumes of crediting of economy.
The bank has increased attraction of means of the population by 39,6 %. The rests of means on accounts of private persons have made 29,0 billion tenge (growth on 69,2 %). The quantity of accounts of private investors has grown with 15,7 up to 16,6 million units. On the end of year on a share, Bank 52,8 % of a total sum of deposits of the population and 14,3 % of deposits of the legal persons placed in banks of the second level were necessary.
It has created opportunities for increase in a credit portfolio. Owing to realization of special credit programs, including programs on financing small and average business, the bank has expanded volumes of crediting of real sector. The size of a loan portfolio (the loan, leasing) has increased for 15,1 %, having made 20,6 billion tenge. On a share of Halyk Bank it is necessary about 16 % of the market of credits
On the end of year by Bank are executed all prudential specifications.
The sufficient stock is available on parameters of current liquidity К4 (1,11 at normative value 0,3) and short-term liquidity К5 (1,09 at normative value 0,5)
Having lead, the financial analysis of a financial condition on the main parameters of joint-stock company “Halyk Bank of Kazakhstan” it is possible to draw conclusions, that Actives of National Bank have grown in comparison with 2007 on 55 % and have made 1 567 239 billion tenge. Obligations of Bank have reached 142,5 billion tenge (growth of 38,8 %), due to increase in depositary base - means and deposits of clients up to 473,1 billion Own capital on the beginning of 2008 has made 1 412 290 million tenge, having increased on 2,7 %. The authorized capital of bank has been increased by 603,2 million tenge. On the end of year it has made 3 615,1 million tenge.
Estimating current position of bank in the financial market of Kazakhstan, and defining long-term plans, it is possible to speak with confidence about the optimistically forecast of the further development of joint-stock company “Halyk Bank of Kazakhstan” as one of the largest banks of the country.
2.2. The analysis of financial stability, liquidity and solvency of joint-stock company «Halyk Bank RK «
Financial stability - a component of the general stability of the enterprise, equation of financial streams, presence of the means allowing the organization to support the activity during the certain period of time, including serving the received credits and making production.
Table 7. The basic parameters of financial stability of the organization
Parameters |
The description of a parameter and its normative value |
coeffecient of an autonomy |
The attitude of own capital to a total sum of the capital. |
coeffecient financial condition |
Debt capital to own capital . |
coeffecient of security own turnaround means |
The attitude of the extra capital to own. |
coeffecient of a covering of investments |
The attitude of own capital to turnaround actives. |
coeffecient of a maneuverability of own capital |
The attitude of own capital and long-term obligations to a total sum of the capital. |
coeffecient of mobility of property |
The attitude of own turnaround means to sources of own means. |
coeffecient of mobility of turnaround means |
The attitude of turnaround means to cost of all property. Characterizes branch specificity of the organization. |
coeffecient of security of stocks |
Own turnover capital of material resource |
coeffecient of short-term debts |
The attitude of the most mobile part of turnaround means (money resources and financial investments) to a total cost of turnaround actives. |
Note – based on data of the Committee for control and supervision of financial market and financial organizations of the National Bank of the Republic of Kazakhstan |
|
Coefficient analysis is applied to revealing quantitative interrelation between various sections and groups of clauses of balance on the basis of parities for an estimation of concrete aspects of bank activity. For the analysis of work of bank accounts in balance and the report on profits and losses are used.
Below it is resulted calculations of factors on financial stability of bank during the different periods of its activity.
For the year of 2008: 14187119/175095058=0,11
For the year of 2009-21238258/228081728=0,12
For the year of 2010-35036024/358000847=0,11
All calculations of financial stability of Halyk Bank. Data (consolida
ted financial the reporting) have been taken from an official site of Halyk Bank.
Table 7. Average factor of liquidity.
Calculated Data: Ratios |
|
|
Industry |
|
|
|
2010 |
2009 |
Average |
Liquidity ratio |
|
|
|
|
Current Ratio |
|
0,56 |
0,49 |
0,30 |
Asset Management ratios |
|
|
|
|
Days Sales Outstanding |
80 |
95 |
110 |
|
Fixed Asset Turnover |
0,04 |
0,03 |
0,05 |
|
Total Asset Turnover |
0,02 |
0,02 |
1 |
|
Debt Management ratio |
|
|
|
|
Debt Ratio |
|
86,35% |
84,85% |
85,00% |
Profitability ratios |
|
|
|
|
Profit Margin |
|
45,99% |
48,39% |
32,00% |
Return on Assets |
|
1,80% |
1,82% |
2,00% |
Return on Equity |
|
13,18% |
11,99% |
15,00% |
Note – based on data of the Committee for control and supervision of financial market and financial organizations of the National Bank of the Republic of Kazakhstan |
||||
Table 8. Reports on monetary streams
Calculated Data: Operating Performance and Cash Flows |
2010 |
2009 |
|
Net operating working capital (NOWC) |
-963 856 |
-975 450 |
|
Total operating capital |
|
406 812 |
394 835 |
Net Operating Profit After Taxes (NOPAT) |
74 860 |
64 892 |
|
Free Cash Flow (FCF) |
|
62 883 |
N/A |
Note – based on data of the Committee for control and supervision of financial market and financial organizations of the National Bank of the Republic of Kazakhstan |
|||
From the table it is visible that the attitude of current actives to current obligations shows positive position on briefly urgent actives. At National Bank the given parameter is better on an average in branch. To the given bank on the average to have to wait for return of the money resources from clients in a range from 80 till 95 days and while on branch it borrows average about 110 days. As to parameters on management of actives the underside here is observed.
On the basis of the current operational capital and current operational obligations the last surpasses by quantity, it shows that operational activity completely, and even moreover is financed by the foreign organizations.
From data of table 8 it is visible, that values of factor of capitalization do not exceed recommended value, that is they below 0,5, that is the positive tendency. In 2009 the given parameter has increased on 1,472 units but in 2010 it has decreased on 0,0716 units. It testifies that in 2010 the financial position became stronger. Values of factor of independence are not included into limits.
Table 9 - Dynamics of factors of financial stability of joint-stock company «Halyk Bank of Kazakhstan for 2008-2010
Parameter |
2008 |
2009 |
2010 |
Changes (+, -) |
|
2009-2008 8г. |
2010-2009 |
||||
Factor of capitalization |
3,3783 |
4,8503 |
4,7787 |
1,472 |
-0,0716 |
Factor of independence (autonomy) |
0,2284 |
0,1709 |
0,1731 |
- 0,0575 |
0,0022 |
Factor of financial intensity |
0,7716 |
0,829 |
0,8269 |
0,0574 |
-0,0021 |
Factor of self-financing |
0,296 |
0,2062 |
0,2093 |
-0,0898 |
0,0031 |
Factor of financial stability |
0,3196 |
0,2393 |
0,2253 |
-0,0803 |
-0,014 |
Factor of security own turnaround means |
-1,4033 |
-1,2631 |
-2,1673 |
0,1402 |
-0,9042 |
Note – based on data of the Committee for control and supervision of financial market and financial organizations of the National Bank of the Republic of Kazakhstan |
|||||
From data of table 8 it is visible, that values of factor of capitalization do not exceed recommended value, that is they below 0,5, that is the positive tendency. In 2009 the given parameter has increased on 1,472 units but in 2010 it has decreased on 0,0716 units. It testifies that in 2010 the financial position became stronger. Values of factor of independence are not included into limits.
From figure 2 it is necessary to note that 2009 parameters were better than in 2010. It it is caused by that that anti-recessionary measures have justified themselves completely. As 2007-2008 were the most difficult in economic.
These calculations show the general stability of bank at threat of bankruptcy. And more detailed information already has been resulted above (Chapter 1) .Можно to draw a conclusion that increase in the given parameter speaks about risk of bank activity at a non-return of the small loan. As it has been resulted (chapter 1., item 2.1.) factor of financial stability should not exceed 0,1. Therefore the bank is not threatened with bankruptcy the nearest years.
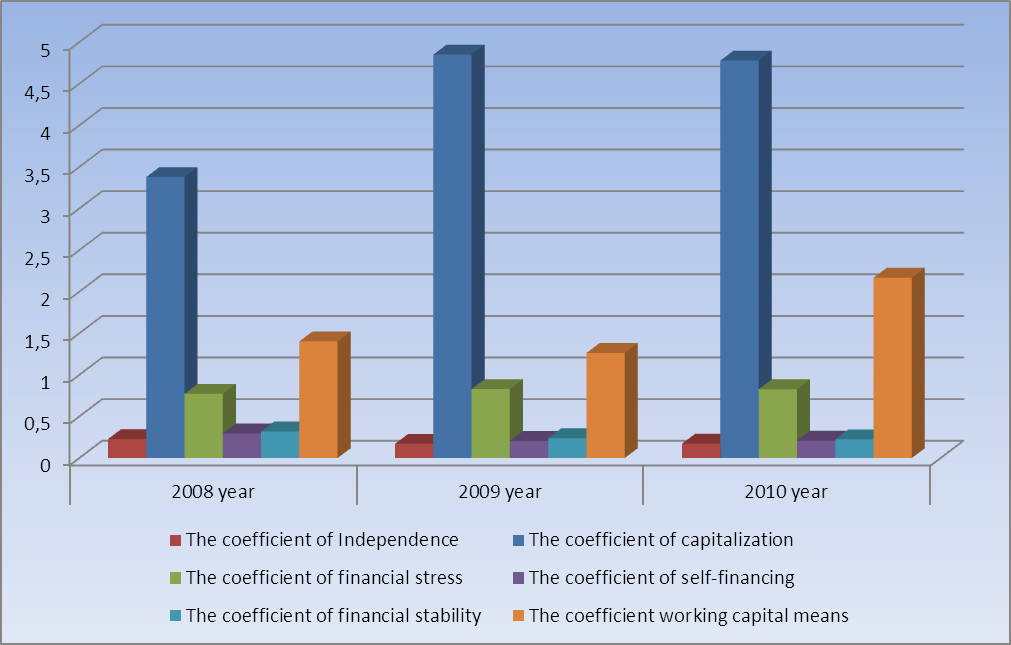
Figure 2 - Factor of liquidity of JSC Halyk Bank of Kazakhstan.
Note - compiled by author on the basis the data of JSC Halyk Bank of Kazakhstan
Liquidity of bank is a bank ability of maintenance of performance of the financial obligations to the full or in due time. Directly term "liquidity" means speed of realization, sale and transformation of actives and material assets in money resources. Bank liquidity influences stability of bank system which main task is carrying out of payments between economic subjects and realization of settlement functions. If at bank a low level of liquidity that limits solvency of the credit organizations which can lead to the termination of activity of payment systems and even a stop of functioning of economy. Liquidity of bank happens saved up and purchased, according to sources. The saved up liquidity are actives, a monetary cash. Purchased - credits from Halyk Bank of RK, interbank credits. On promptness bank liquidity happens long-term, intermediate term, short-term and instant. To operate bank liquidity, it is necessary to establish an optimum parity between separate kinds of actives and passives. This parity is defined by parameters of liquidity of bank and risks, allows bank to carry out of credit obligations to borrowers. For management of liquidity of bank following procedures are spent:
1. The financial bank policy is developed
2. Methods appreciation and the analysis of regulation of liquidity get out
3. The order of acceptance of current and strategic decisions is established
4. The base of details is formed
The purpose of management of liquidity of bank - maintenance of ability of performance of liabilities which follow from transactions with use of financial tools. To calculate liquidity of bank it is possible, being based on given balance and appreciation of monetary streams. Liquidity of bank depends on external and internal factors. External factors: political and economic conditions in the country and the world, efficiency of functions of supervision, the organization of system of refinancing, development of a securities market. Internal factors: an interlinking of passives and actives according to terms, dependence on external sources, quantity and quality of actives and deposits, presence of own money resources. To assess liquidity of bank, use coefficient of a method which is elementary. The method includes definition of ways of elimination of discrepancies which are established on the basis of the analysis, directly analysis and an estimation of a condition of parameters of liquidity, and also revealing and definition of structure, periodicity of calculation and limiting parameters of liquidity. On a degree of profitableness bank actives share on two groups: what are repaid and do not bring (illiquid and low liquidated assets). The liquidity of resources, the above risk and a degree of profitableness of the organization less.
On a degree of liquidity bank actives share on such groups:
1. The first class liquid actives (means in cash department or on accounts, securities)
2. high liquated bank actives (interbank credits, securities for sale)
3. low liquidity actives (short-term and long-term loans, leasing, investment securities, operations factoring)
4. Long-term assets (the delayed credits, securities, techniques, constructions)
Lack of liquidity leads to insolvency of bank. Deficiency of liquidity can be corrected by means of receipt of the state resources in bank .By the way, will get rid of superfluous liquidity to bank much more difficultly.
Actives of National Bank have grown in comparison with 2005 on 55 % and have made 1 567 239 billion tenge. Obligations of Bank have reached 142,5 billion tenge (growth of 38,8 %), due to increase in depositary base - means and deposits of clients up to 473,1 billion Own capital on the beginning of 2008 has made 1 412 895 83 million tenge, having increased on 2,7 %.
Opportunities of development of credit activity of Bank will be provided besides it by increase in inflow of urgent deposits of legal persons and use involved on the international financial markets, concerning cheap resources. The credit portfolio of Bank (gross) will make, approximately, 196 billion tenge. In accommodation of credit resources the Bank will be guided still by the companies and the enterprises with preservation of a high share of credits to small and average business. Considering market tendencies and development of system of card crediting, a share of credits to the population will grow, but will not exceed 12-13 %.
The basic direction of realization of the developed strategic problems should become increase of efficiency of activity of Bank due to improvement of quality and profitableness of actives, activation of work with problem credits, strengthening diversification a credit portfolio.
Essential value for increase of financial results will have reorganization retail and increase of profitableness of corporate business, increase in sales volumes. Maintenance of profitableness of a credit portfolio at the planned level, decrease in charges on reservation, increase of a level of not percentage incomes due to expansion of volume of accompanying services will promote growth of efficiency of activity of Bank. On decrease and prevention of possible financial losses measures on increase of a management efficiency and creation of a complex control system by risks will be directed also.
At realization of the given problems the Bank will have an opportunity in conditions of decreasing rates considerably to increase the financial results and to achieve increase of feedback on actives and the capital. The comprehensible level of profitableness will be provided. On the average return on the share capital will increase up to 21-21,5 %. It will lead to improvement of image of Bank in opinion of potential investors and will provide corresponding growth of the capital.
From figure 2 it is necessary to note that 2009 parameters were better than in 2010. It it is caused by that that anti-recessionary measures have justified themselves completely. As 2007-2008 were the most difficult in economic.
These calculations show the general stability of bank at threat of bankruptcy. And more detailed information already has been resulted above (Chapter 1) . We can draw a conclusion that increase in the given parameter speaks about risk of bank activity at a non-return of the small loan. As it has been resulted (chapter 1., item 2.1.) factor of financial stability should not exceed 0,1. Therefore the bank is not threatened with bankruptcy the nearest years.
Liquidity of bank is a bank ability of maintenance of performance of the financial obligations to the full or in due time. Directly term "liquidity" means speed of realization, sale and transformation of actives and material assets in money resources. Bank liquidity influences stability of bank system which main task is carrying out of payments between economic subjects and realization of settlement functions. If at bank a low level of liquidity that limits solvency of the credit organizations which can lead to the termination of activity of payment systems and even a stop of functioning of economy. Liquidity of bank happens saved up and purchased, according to sources. The saved up liquidity are actives, a monetary cash. Purchased - credits from National Bank of RK, interbank credits. On promptness bank liquidity happens long-term, intermediate term, short-term and instant. To operate bank liquidity, it is necessary to establish an optimum parity between separate kinds of actives and passives. This parity is defined by parameters of liquidity of bank and risks, allows bank to carry out of credit obligations to borrowers. For management of liquidity of bank following procedures are spent:
1. The financial bank policy is developed
2. Methods appreciation and the analysis of regulation of liquidity get out
3. The order of acceptance of current and strategic decisions is established
4. The base of details is formed
The purpose of management of liquidity of bank - maintenance of ability of performance of liabilities which follow from transactions with use of financial tools. To calculate liquidity of bank it is possible, being based on given balance and appreciation of monetary streams. Liquidity of bank depends on external and internal factors. External factors: political and economic conditions in the country and the world, efficiency of functions of supervision, the organization of system of refinancing, development of a securities market. Internal factors: an interlinking of passives and actives according to terms, dependence on external sources, quantity and quality of actives and deposits, presence of own money resources. To assess liquidity of bank, use coefficient of a method which is elementary. The method includes definition of ways of elimination of discrepancies which are established on the basis of the analysis, directly analysis and an estimation of a condition of parameters of liquidity, and also revealing and definition of structure, periodicity of calculation and limiting parameters of liquidity. On a degree of profitableness bank actives share on two groups: what are repaid and do not bring (illiquid and low liquidated assets). The liquidity of resources, the above risk and a degree of profitableness of the organization less.
On a degree of liquidity bank actives share on such groups:
1. The first class liquid actives (means in cash department or on accounts, securities)
2. high liquidate bank actives (interbank credits, securities for sale)
3. low liquidate actives (short-term and long-term loans, leasing, investment securities, operations factoring)
4. Long-term assets (the delayed credits, securities, technics, constructions)
Lack of liquidity leads to insolvency of bank. Deficiency of liquidity can be corrected by means of receipt of the state resources in bank .By the way, will get rid of superfluous liquidity to bank much more difficultly.
Actives of National Bank have grown in comparison with 2005 on 55 % and have made 1 567 239 billion tenge. Obligations of Bank have reached 142,5 billion tenge (growth of 38,8 %), due to increase in depositary base - means and deposits of clients up to 473,1 billion Own capital on the beginning of 2008 has made 1 412 895 83 million tenge, having increased on 2,7 %.
Opportunities of development of credit activity of Bank will be provided besides it by increase in inflow of urgent deposits of legal persons and use involved on the international financial markets, concerning cheap resources. The credit portfolio of Bank (gross) will make, approximately, 196 billion tenge. In accommodation of credit resources the Bank will be guided still by the companies and the enterprises with preservation of a high share of credits to small and average business. Considering market tendencies and development of system of card crediting, a share of credits to the population will grow, but will not exceed 12-13 %.
The basic direction of realization of the developed strategic problems should become increase of efficiency of activity of Bank due to improvement of quality and profitableness of actives, activization of work with problem credits, strengthening diversification a credit portfolio [26, page 36].
Essential value for increase of financial results will have reorganization retail and increase of profitableness of corporate business, increase in sales volumes. Maintenance of profitableness of a credit portfolio at the planned level, decrease in charges on reservation, increase of a level of not percentage incomes due to expansion of volume of accompanying services will promote growth of efficiency of activity of Bank. On decrease and prevention of possible financial losses measures on increase of a management efficiency and creation of a complex control system by risks will be directed also.
At realization of the given problems the Bank will have an opportunity in conditions of decreasing rates considerably to increase the financial results and to achieve increase of feedback on actives and the capital. The comprehensible level of profitableness will be provided. On the average return on the share capital will increase up to 21-21,5 %. It will lead to improvement of image of Bank in opinion of potential investors and will provide corresponding growth of the capital.
CHAPTER 3 DIRECTIONS OF DEVELOPMENT OF SYSTEM OF DIAGNOSTICS OF BANKRUPTCY OF THE ENTERPRISE
