
- •Методичні вказівки щодо виконання самостійної роботи
- •1 Загальні положення
- •Тематичний план самостійної роботи
- •3 Методичні вказівки під час роботи з текстом
- •4 Методичні вказівки щодо виконання самостійної роботи
- •Тема 10
- •Тема 11
- •Тема 12
- •Тема 13
- •Тема 14
- •Тема 15
- •Тема 16
- •Тема 17
- •Тема 18
- •Тема 19
- •Тема 20
- •Модуль 4 «Загальні правила ведення радіообміну англійською мовою»
- •Модуль 5 «doc icao 9432 Керівництво по радіотелефонному звязку»
- •Модуль 6
- •Тема 1 Стандарти ікао щодо мовної компетенції авіаційних спеціалістів (icao Language Proficiency Standards).
- •Тема 2. «Airports and runways»
- •Тема 3. «Navigation and flight planning»
- •Тема 4 «Aviation technology»
- •Тема 5. «Animal hazards in aviation»
- •Модуль 8 «Авіаційна англійська мова (2)»
- •Тема 6 «Different ways to fly»
- •Тема 7. «Health and flying»
- •Тема 8 «Fire on board»
- •Тема 9. «Weather»
- •Модуль 9 «Помилки, які допускає авіаційний персонал під час спілкування англійською мовою»
- •Тема 10. «Landing an aircraft»
- •Тема 11. «Fuel consumption and environmental issues»
- •Тема 12. «Pressurization and depressurizations»
- •Тема 13. «Security in Aviation»
- •5 Перелік навчально – методичної літератури
3 Методичні вказівки під час роботи з текстом
Оскільки основною цільовою установкою навчання іноземній мові є отримання інформації з іншомовного джерела, особливу увагу слід приділяти читанню текстів. Розуміння тексту досягається при здійсненні двох видів читання:
вивчаючого читання;
читання із загальним охопленням змісту.
Точне та повне розуміння тексту можна отримати шляхом вивчаючого читання, що передбачає вміння самостійно здійснювати лексико-граматичний аналіз тексту. Підсумком вивчаючого читання є адекватний переклад тексту рідною мовою за допомогою словника. При цьому слід розвивати навички користування галузевими термінологічними словниками та словниками скорочень.
Читаючи текст, що призначений для розуміння загального змісту, необхідно, не звертаючись до словника, зрозуміти основний смисл прочитаного.
Обидва види читання складаються з таких вмінь:
а) здогадуватися про значення незнайомих слів на основі словотворчих ознак і контексту;
б) бачити інтернаціональні слова і визначати їхнє значення;
в) знаходити знайомі граматичні форми і конструкції та встановлювати їхні еквіваленти в українській мові;
г) використовувати ілюстративний матеріал, що міститься в тексті;
д) застосовувати знання зі спеціальних, загально технічних, загальноекономічних предметів як основу смислової та мовної догадки.
4 Методичні вказівки щодо виконання самостійної роботи
Тема 1
Питання для самостійного вивчення:
вивчення лексики професійного спрямування до тексту;
читання тексту;
переклад тексту;
знаходження знайомих граматичних форм і конструкції;
розуміння змісту прочитаного;
підготовка до обговорення тематичного матеріалу тексту;
огляд рекомендованої літератури, бібліографічних і довідкових джерел, преси англійською мовою.
Завдання для самоконтролю знань
Man's desire to fly (1)
The desire to fly was one of the oldest desires of man. But in old times people knew little about air. They did not know that life could not exist without it. People began to study that phenomenon. Some scientists began to ask "What is air and how can a man fly in it?" The Greek philosopher Aristotle believed that air had weight and pressed on bodies which were in the air. Later men of science like Galileo, Roger Bacon and Pascal came to the conclusion that air was gas and that the higher you went the less its pressure was.
Термінологічний словник
|
|
desire |
бажання |
|
|
exist |
існувати |
|
|
believe |
вірити |
|
|
weight |
вага |
|
|
conclusion |
висновок |
|
|
found (past від find) |
находити |
|
|
flow of air |
потік повітря |
|
|
the lift |
підйомна сила |
|
|
device |
пристрій |
Рекомендована література
1.2, 1.3, 2.1, 2.2, 2.3, 2.9, 2.11, 2.12.
Тема 2
Питання для самостійного вивчення:
вивчення лексики професійного спрямування до тексту;
читання тексту;
переклад тексту;
знаходження знайомих граматичних форм і конструкції;
розуміння змісту прочитаного;
підготовка до обговорення тематичного матеріалу тексту;
огляд рекомендованої літератури, бібліографічних і довідкових джерел, преси англійською мовою.
Завдання для самоконтролю знань
Man's desire to fly (2)
That human flight is possible is the fundamental idea of the book by Leonardo da Vinci. In the book the famous Italian artist and scientist recorded the first scientific principles of human flight. He found that the faster the flow of air, the greater the lift was. As a result of these studies he designed a flying device. In his device the pilot had to operate movable wings with the help of his arms and feet. But the machine did not fly. In the course of many centuries scientists tried to make a flying device. But the development of a practical flying device on a really scientific basis began later. The first flying machine man could control in the air appeared only in the 19th century.
Термінологічний словник
|
|
desire |
бажання |
|
|
exist |
існувати |
|
|
believe |
вірити |
|
|
weight |
вага |
|
|
conclusion |
висновок |
|
|
found (past від find) |
находити |
|
|
flow of air |
потік повітря |
|
|
the lift |
підйомна сила |
|
|
device |
пристрій |
Рекомендована література
1.2, 1.3, 2.1, 2.2, 2.3, 2.9, 2.11, 2.12.
Тема 3
Питання для самостійного вивчення:
вивчення лексики професійного спрямування до тексту;
читання тексту;
переклад тексту;
знаходження знайомих граматичних форм і конструкції;
розуміння змісту прочитаного;
підготовка до обговорення тематичного матеріалу тексту;
огляд рекомендованої літератури, бібліографічних і довідкових джерел, преси англійською мовою.
Завдання для самоконтролю знань
Aircraft types and their classification (1)
An aircraft is a weight-carrying device capable of creating lift. There is a wide variety of airplane types: land planes, carrier-based airplanes, seaplanes, amphibians, vertical take-off and landing (VTOL), short take-off and landing (STOL), and space shuttles. According to the flight range airplanes can be classified as long-range, medium-range and short-range. According to the number of wings airplanes may be divided into monoplanes and biplanes. Monoplanes are airplanes with one wing; biplanes are airplanes with two sets of wings, one above the other. Monoplanes are classified as low-wing, mid-wing and high-wing. According to the purpose airplanes can be grouped into major classes, such as commercial, military, and general-aviation airplanes.
Термінологічний словник
|
|
aircraft |
повітряне судно (ПС) |
|
|
weight-carrying |
несучий вагу (вантажно-транспортний) |
|
|
capable of |
здатний |
|
|
create |
створювати |
|
|
carry out |
виконувати |
|
|
carrier-based airplane |
перевізник |
|
|
land plane |
ПС звичайної схеми зльоту й посадки |
|
|
seaplane |
гідролітак |
|
|
take-off |
зліт |
|
|
space shuttle |
космічний корабель |
|
|
flight range |
дальність польоту |
|
|
long-range |
довга дистанція |
|
|
medium-range |
середня дистанція |
|
|
short-range |
коротка дистанція |
|
|
monoplane |
моноплан |
|
|
biplane |
біплан |
|
|
low-wing plane |
літак з низько розташованим крилом |
|
|
purpose |
ціль |
|
|
general-aviation airplane |
ПС загального призначення |
Рекомендована література
1.2, 1.3, 2.1, 2.2, 2.3, 2.9, 2.11, 2.12.
Тема 4
Питання для самостійного вивчення:
вивчення лексики професійного спрямування до тексту;
читання тексту;
переклад тексту;
знаходження знайомих граматичних форм і конструкції;
розуміння змісту прочитаного;
підготовка до обговорення тематичного матеріалу тексту;
огляд рекомендованої літератури, бібліографічних і довідкових джерел, преси англійською мовою.
Завдання для самоконтролю знань
The Helicopter Мi-8 Structure and Major Components
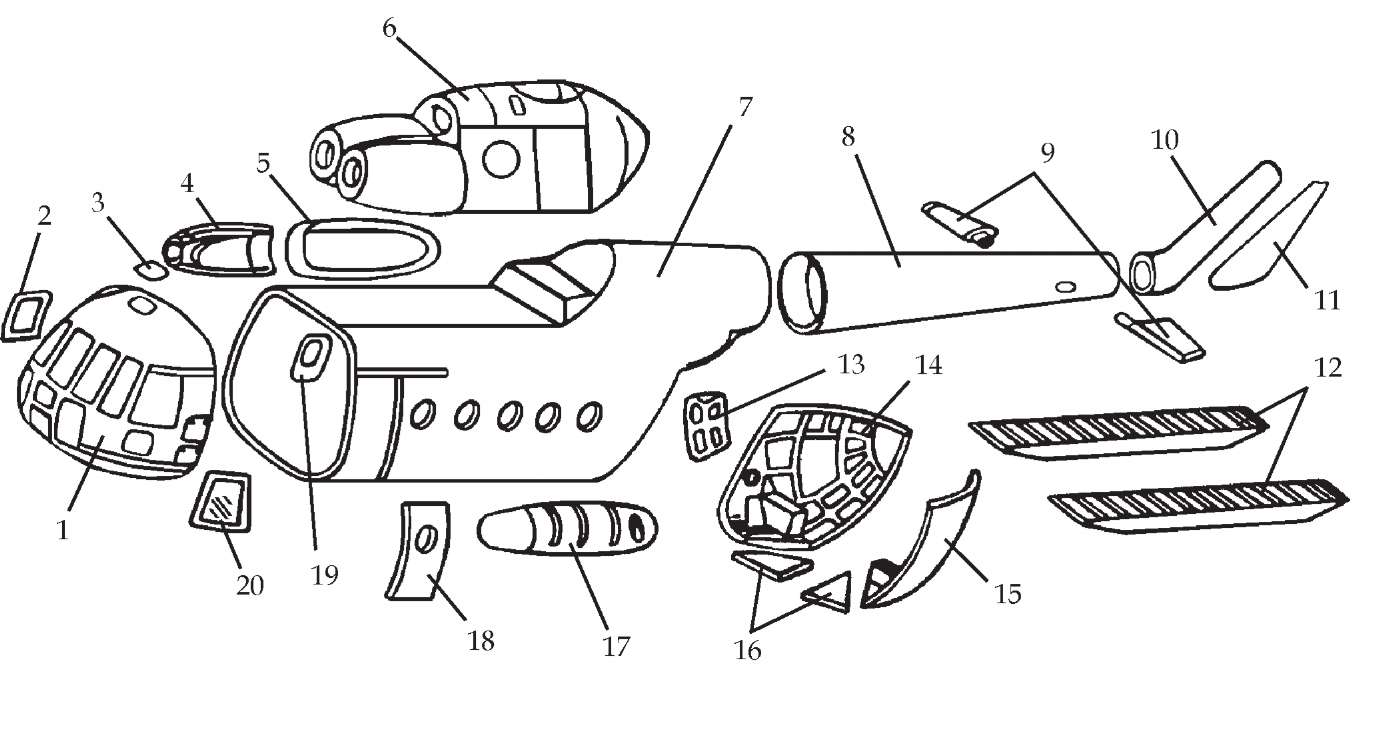
The Mi-8 helicopter is a single main rotor medium transport aircraft with a tail rotor. It is designed for passengers transport, paradrop, medical evacuation, and cargo transport. The Mi-8 helicopter is a civil variant designed for passenger service and internal or external cargo transport. The helicopter can be used for search and rescue operations using an externally mounted rescue hoist and seat assembly.
The power plant of the helicopter includes 2 engines. It is possible to accomplish start-up of the engines using ground power unit or storage batteries. In case of failure of both engines during flight Mi-8 helicopter can carry out autorotation and safe landing.
The crew consists of 3 members: pilot- in-command, co-pilot, flight engineer.
Термінологічний словник
|
|
forward fuselage (nose) section |
носова частина |
|
|
sliding window (right) |
блістер, зсувне вікно (праве) |
|
|
overhead exit hatch |
люк для доступу к силовій установці |
|
|
heater cowling |
капот обігрівача |
|
|
fuel tank (right) |
паливний бак (правий) |
|
|
nacelle |
гондола |
|
|
center fuselage section |
центральна частина фюзеляжу |
|
|
tail boom |
хвостова балка |
|
|
horizontal stabilizer |
горизонтальний стабілізатор |
|
|
vertical stabilizer |
вертикальний стабілізатор, кіль |
|
|
fairing |
обтічник |
|
|
cargo ramps |
вантажні трапи |
|
|
right clamshell escape hatch |
правий люк аварійного покидання на вантажній стулці |
|
|
right clamshell door |
права вантажна стулка |
|
|
left clamshell door |
ліва вантажна стулка |
|
|
sub-panels |
суб-панелі, косинки вантажних стулок |
|
|
fuel tank (left) |
паливний бак (лівий) |
|
|
sliding door |
зсувна двір |
|
|
right escape hatch |
правий люк аварійного покидання |
|
|
sliding window (left) |
блістер, зсувне вікно (ліве) |
|
|
landing gear |
шасі |
|
|
landing gear leg |
стойка шасі |
|
|
main rotor |
несучий гвинт |
|
|
tail rotor |
кермовий гвинт |
|
|
tail shaft |
вал трансмісії |
|
|
tail leg |
хвостова опора |
|
|
gear box |
редуктор |
|
|
engine |
двигун |
|
|
APU (auxiliary power unit) |
допоміжна силова установка |
|
|
control rods |
проводка управління |
|
|
single main rotor |
одногвинтовий |
|
|
troop transport |
транспортування військових |
|
|
paradrop |
парашутні стрибки |
|
|
internal |
внутрішній |
|
|
external |
зовнішній |
|
|
can be used for |
може бути використаний |
|
|
search and rescue operations |
пошуково-рятувальні роботи |
|
|
rescue hoist and seat assembly |
пошукова стріла та сидіння із прив’язними ременями |
|
|
mount |
монтувати |
Рекомендована література
1.2, 1.3, 2.1, 2.2, 2.3, 2.9, 2.11, 2.12.
Тема 5
Питання для самостійного вивчення:
вивчення лексики професійного спрямування до тексту;
читання тексту;
переклад тексту;
знаходження знайомих граматичних форм і конструкції;
розуміння змісту прочитаного;
підготовка до обговорення тематичного матеріалу тексту;
огляд рекомендованої літератури, бібліографічних і довідкових джерел, преси англійською мовою.
Завдання для самоконтролю знань
How Aircraft Fly
The word "aircraft" means any kind of craft or vehicle which air can support. Airplanes, helicopters and gliders are heavier-than-air craft. They are supported by the dynamic action of the air upon their aerodynamic surfaces. Free and captive balloons are called lighter-than-air craft. Rockets do not need air for support. They use the power of their reaction engine to propel them through space, and are called "spacecraft".
All heavier than-air craft use aerodynamic surfaces or airfoils to develop the necessary supporting force. These airfoils are usually in the form of fixed or rotary wings. In order to develop the required lift, the airfoils must move through the air with sufficiently high speed. This speed is imparted to the aircraft by the thrust of its powerplant.
The thrust may be developed by rotating the pulling or pushing propellers, or by throwing back masses of air by means of gas turbine engines.
To change the attitude and direction of flight aircraft use control surfaces or controls. These comprise the rudder, the elevator, and ailerons. The rudder is used to deflect the movement of the aircraft to the left or to the right. The elevator makes the aircraft climb or dive. The ailerons produce rolling movement.
The aircraft must also be able to see and hear. Aircraft sensors are those devices, such as radars, direction finders and position plotters, communication equipment, attitude gyros, air speed indicators and others, which enable the crew to know position, orientation and speed of aircraft.
Термінологічний словник
|
|
airframe |
корпус, каркас; планер ЛА, частина ЛА, окрім силового устаткування |
|
|
vehicle |
транспортний засіб |
|
|
glider |
планер, ЛА без двигуна для спортивних або тренувальних польотів; |
|
|
heavier-than air craft |
літальний апарат, важче за повітря |
|
|
aerodynamic surface, airfoil |
аеродинамічна поверхня, крило |
|
|
airship |
дирижабль, повітряний корабель |
|
|
reaction engine |
реактивний двигун |
|
|
propel |
приводити в рух |
|
|
spacecraft |
космічні літальні апарати (ЛА) |
|
|
fixed wing, rotary wing |
фіксоване крило, несучий гвинт |
|
|
pulling or pushing propeller |
тягнучий або штовхаючий повітряний гвинт |
|
|
attitude |
орієнтація, кутове положення ЛА |
|
|
rudder |
руль напрямку |
|
|
elevator |
руль висоти |
|
|
ailerons |
елерони, органи управління, які дають можливість виконувати крен ліворуч або праворуч |
|
|
aircraft sensors |
датчики ЛА, сенсори; пілотажно-навігаційне обладнання ЛА |
|
|
direction finder |
радіокомпас, прилад, за допомогою якого визначається напрям на радіостанцію |
|
|
position plotter |
прокладач шляху |
|
|
communication equipment |
зв'язне обладнання |
|
|
attitude gyro |
гіроскопічний авіагоризонт |
Рекомендована література
1.2, 1.3, 2.1, 2.2, 2.3, 2.9, 2.11, 2.12.
Тема 6
Питання для самостійного вивчення:
вивчення лексики професійного спрямування до тексту;
читання тексту;
переклад тексту;
знаходження знайомих граматичних форм і конструкції;
розуміння змісту прочитаного;
підготовка до обговорення тематичного матеріалу тексту;
огляд рекомендованої літератури, бібліографічних і довідкових джерел, преси англійською мовою.
Завдання для самоконтролю знань
The fuselage
Usually the fuselage is the central body of the aeroplane. It extends from the nose to the tail of the machine. The fuselage serves several purposes: it carries the crew, controls, equipment, passengers, and cargo. It contains the cockpit, passenger cabins, baggage compartments, and other accommodations.
It may also contain the power plant, if the aeroplane has only one engine, and fuel and oil tanks. Besides, the fuselage serves as a support for the tail unit and may carry the landing gear.
The fuselage must be strong enough to withstand different loads acting on it and have a streamlined shape to reduce the drag.
The fuselages of modern aeroplanes are of all-metal construction. A very common type is the monocoque type of construction.
Monocoque is a structure made in the form of a shell and the skin of this shell is sufficient to provide the necessary strength and stiffness. The skin of a sandwich construction is especially suitable for such types of a fuselage. But most of all-metal aeroplanes have some longitudinal members: longerons and stringers riveted to the skin to reinforce the latter. The longitudinal members are held apart by bulkheads and frames which give the fuselage its shape.
Such a construction is sometimes called the semi-monocoque type of construction. The monocoque type has the following advantages: it gives more clear space for the cabin and provides the possibility for perfect streamlining.
All structural members of the fuselage are made of aluminum alloys, titanium alloys, and alloy steel. The fuselage of MI-8 helicopter is a sectional, all metal, semi-monocoque design. The forward and center sections join at center fuselage section frame No. 1. The empennage attaches to center fuselage section frame No. 23. The frames in the forward section are identified by alpha-numeric markings 1N through 5N. The frames in the center fuselage are numbered 1 through 23.
Термінологічний словник
|
|
passenger cabin |
пасажирський |
|
|
|
baggage compartment |
багажний відсік |
|
|
|
accommodation |
пристрій |
|
|
|
all-metal construction |
суцільнометалева конструкція |
|
|
|
are made of |
зроблені з |
|
|
|
are held apart |
утримуються на відстані |
|
|
|
fuel tank |
паливний бак |
|
|
|
oil tank |
масляний бак |
|
|
|
support |
підтримувати |
|
|
|
withstand |
витримувати |
|
|
|
load |
навантаження, навантаження |
|
|
|
streamlined |
обтічний |
|
|
|
reduce |
зменшувати |
|
|
|
is sometimes called |
іноді називається |
|
|
|
monocoque |
монокок |
|
|
|
must be strong enough |
повинен бути стійко міцним |
|
|
|
shell |
гільза, патрон |
|
|
|
sufficient |
достатній |
|
|
|
strength |
міцність |
|
|
|
stiffness |
твердість |
|
|
|
suitable |
підходящий |
|
|
|
longeron |
лонжерон |
|
|
|
rivet |
заклепка |
|
|
|
bulkhead |
балка |
|
|
|
frame |
шпангоут |
|
|
|
advantage |
перевага |
|
|
|
aluminum |
алюміній |
|
|
|
alloy |
сплав |
|
|
|
titanium |
титан |
|
|
|
the skin of a sandwich construction |
конструкція обшивці із заповнювачем |
|
Рекомендована література
1.2, 1.3, 2.1, 2.2, 2.3, 2.9, 2.11, 2.12.
Тема 7
Питання для самостійного вивчення:
вивчення лексики професійного спрямування до тексту;
читання тексту;
переклад тексту;
знаходження знайомих граматичних форм і конструкції;
розуміння змісту прочитаного;
підготовка до обговорення тематичного матеріалу тексту;
огляд рекомендованої літератури, бібліографічних і довідкових джерел, преси англійською мовою.
Завдання для самоконтролю знань
The landing gear
The landing gear system of helicopter is a tricycle configuration consisting of two non-retractable main landing gears and a nose landing gear. A fixed tail strut is mounted at the base of the vertical stabilizer to prevent the tail rotor from striking the ground during takeoff and landing. The nose and main gear, and the tail strut have hydraulic/nitrogen shock struts to absorb normal and high impact landings. The main gear wheels are equipped with pneumatic brakes. The brakes are applied by squeezing the brake lever on the pilot's cyclic stick. The brakes are disengaged by releasing the brake lever. A retainer holds the lever in the engaged position for parking. Pressure in the main brake line is indicated on the brake pressure gauge on the pilot's left side console. When the brakes are applied, the pressure should be indicated. Pressure reading on the gauge should be zero when the brakes are released.
Термінологічний словник
|
|
landing gear |
шасі |
|
|
tricycle |
літак з трьохколісним шасі |
|
|
non-retractable |
нескладний |
|
|
fixed tail strut |
хвостова опора |
|
|
is mounted |
убудований |
|
|
vertical stabilizer, pylon |
кіль |
|
|
a nose landing gear |
переднє шасі |
|
|
shock strut |
амортизатор |
|
|
wheels |
колеса |
|
|
disc brake |
гальмовий диск |
|
|
by squeezing |
натисканням |
|
|
brake lever |
важіль гальма |
|
|
disengage |
відпустити |
|
|
brake pressure gauge |
індикатор тиску в гальмах |
|
|
retainer |
фіксатор |
|
|
console |
консоль |
|
|
reading |
показання |
Рекомендована література
1.2, 1.3, 2.1, 2.2, 2.3, 2.9, 2.11, 2.12.
Тема 8
Питання для самостійного вивчення:
вивчення лексики професійного спрямування до тексту;
читання тексту;
переклад тексту;
знаходження знайомих граматичних форм і конструкції;
розуміння змісту прочитаного;
підготовка до обговорення тематичного матеріалу тексту;
огляд рекомендованої літератури, бібліографічних і довідкових джерел, преси англійською мовою.
Завдання для самоконтролю знань
The Main Rotor
The main rotor group consists of a hub assembly, five all-metal blades, and a swashplate assembly. It is a fully articulated system that allows the blades to flap, feather, and hunt independently. Helicopter cyclic pitch and roll is controlled by the main rotor through the cyclic pitch control stick and the rotating swashplate. Collective pitch is controlled using the collective pitch control stick through the swashplate slide assembly. The flapping hinges have droop stops to provide adequate clearance between the blades and tail boom when the rotor is stopped or rotating at low RPM. The drag hinges allow the blades to lead or lag independently within the rotational plane. Blade hunting is limited by individual hydraulic dampers. The dampers are connected to a common fluid reservoir mounted above the hub assembly. The feathering hinges allow the blades to change pitch angle during rotation.
Термінологічний словник
|
|
hub assembly |
втулка (компонування втулки) |
|
|
blade |
лопать |
|
|
all-metal |
суцільнометалевий |
|
|
swash plate |
тарілка автомату перекосу |
|
|
articulated |
керований |
|
|
helicopter cyclic pitch and roll |
управління вертольота по крену й тангажу |
|
|
articulated |
зчленований, спарений |
|
|
flap |
колихати |
|
|
flapping hinge |
горизонтальний шарнір |
|
|
feather |
флюгувати гвинт; циклічно змінювати крок (несучого гвинта вертольота) |
|
|
feathering hinge |
осьовий шарнір |
|
|
hunt |
гойдатися, коливатися, рискати, коливання відносно вертикального шарніра |
|
|
the cyclic pitch control stick |
ручка управління циклічним шагом |
|
|
pitch |
тангаж |
|
|
roll |
крен |
|
|
swash plate slide assembly |
автомат перекосу |
|
|
droop stop |
обмежник звису лопати |
|
|
clearance |
зазор, просвіт, кліренс; слабке місце; люфт |
|
|
tail boom |
хвостова балка |
|
|
RPM (revolutions per minute) |
оберти за хвилину |
|
|
drag hinge |
вертикальний шарнір |
|
|
rotational plane |
площина обертання |
|
|
lead |
вести, рухати |
|
|
lag |
запізнюватися |
|
|
blade hunting |
коливання лопаті |
|
|
pitch angle |
кут тангажа, пітч-кут |
Рекомендована література
1.2, 1.3, 2.1, 2.2, 2.3, 2.9, 2.11, 2.12.
Тема 9
Питання для самостійного вивчення:
вивчення лексики професійного спрямування до тексту;
читання тексту;
переклад тексту;
знаходження знайомих граматичних форм і конструкції;
розуміння змісту прочитаного;
підготовка до обговорення тематичного матеріалу тексту;
огляд рекомендованої літератури, бібліографічних і довідкових джерел, преси англійською мовою.
Завдання для самоконтролю знань
The Cockpit (1)
The cockpit is one of compartments of the fuselage situated in its front part. It is a working place of the crew. It accommodates crew members. Apart from crew members the cockpit houses computers, controls, instruments, systems and some equipment. The modern cockpit must be comfortable and spacious. It must provide forward-facing (looking) seating arrangement for the crew. Seats are designed for comfort, convenience and efficiency. They must be reclined and adjusted in horizontal and vertical directions. They are usually installed on a track to provide an easy exit and entry for the crew. It is recommended that seats for the crew should have sheep-skin covers. Each seat must be provided with a proper harness. A glass part of the cockpit is called a canopy. It includes two kinds of windows: front windows and side windows. Front windows consist of a windscreen (windshield) and eyebrow windows. The windshield must be very strong. It is made of a special kind of glass which has good optical and aerodynamic characteristics.
Термінологічний словник
|
|
cockpit |
кабіна екіпажа |
|
|
accommodate |
розміщати |
|
|
apart from |
крім |
|
|
house |
розміщати, уміщати |
|
|
spacious |
просторий |
|
|
forward |
передній, уперед |
|
|
arrangement |
розташування |
|
|
recline |
відхиляти |
|
|
adjust |
регулювати |
|
|
track |
рейки, полозки |
|
|
harness |
ремінь безпеки |
|
|
canopy |
скляна поверхня кабіни екіпажа |
|
|
windshield |
лобове скло |
|
|
eyebrow windows |
верхні передні стекла |
Рекомендована література
1.2, 1.3, 2.1, 2.2, 2.3, 2.9, 2.11, 2.12.
