- •The approximate timing of classes
- •Practice work
- •Glossary
- •Office hours (2) Formation of practical skills on the theme «The subject, purposes and methods of pathological physiology”.
- •Case study
- •The approximate timing of classes
- •Practical work of students
- •Questions 1. What factors affect the mouse in this experiment?
- •2. Which of these factors could be considered the leading cause of the pathologic process - hypobaric hypoxia?
- •3. How can you experimentally check your presumptions about the nature of the pathologic process?
- •Pathogenesis of High altitude disease
- •Vicious circle in pathogenesis of High altitute disease
- •Office hours (2) Formation of practical skills on the theme «General etiology and pathogenesis. Effects of low barometric pressure on an organism”
- •Case Study Case 1. A group of tourists came under heavy rain. A day later, one of them developed pneumonia. Questions:
- •The approximate timing of classes
- •Glossary:
- •Office hours (2) Formation of practical skills on the theme «The role of reactivity of an organism in pathology”
- •The approximate timing of classes
- •Practical work of students
- •Explain the pathogenesis of hemolysis in tubes №№ 2-5 and the absence of hemolysis in tube number 1. Glossary
- •Office hours (2) Formation of practical skills on the theme “Cell injury”
- •Case Study
- •The approximate timing of classes
- •Practical work of students
- •I nfection, ischemia, traumas, tumors, burns, immune pathological processes, etc.
- •The significance of acute phase reactions for organism
- •Glossary
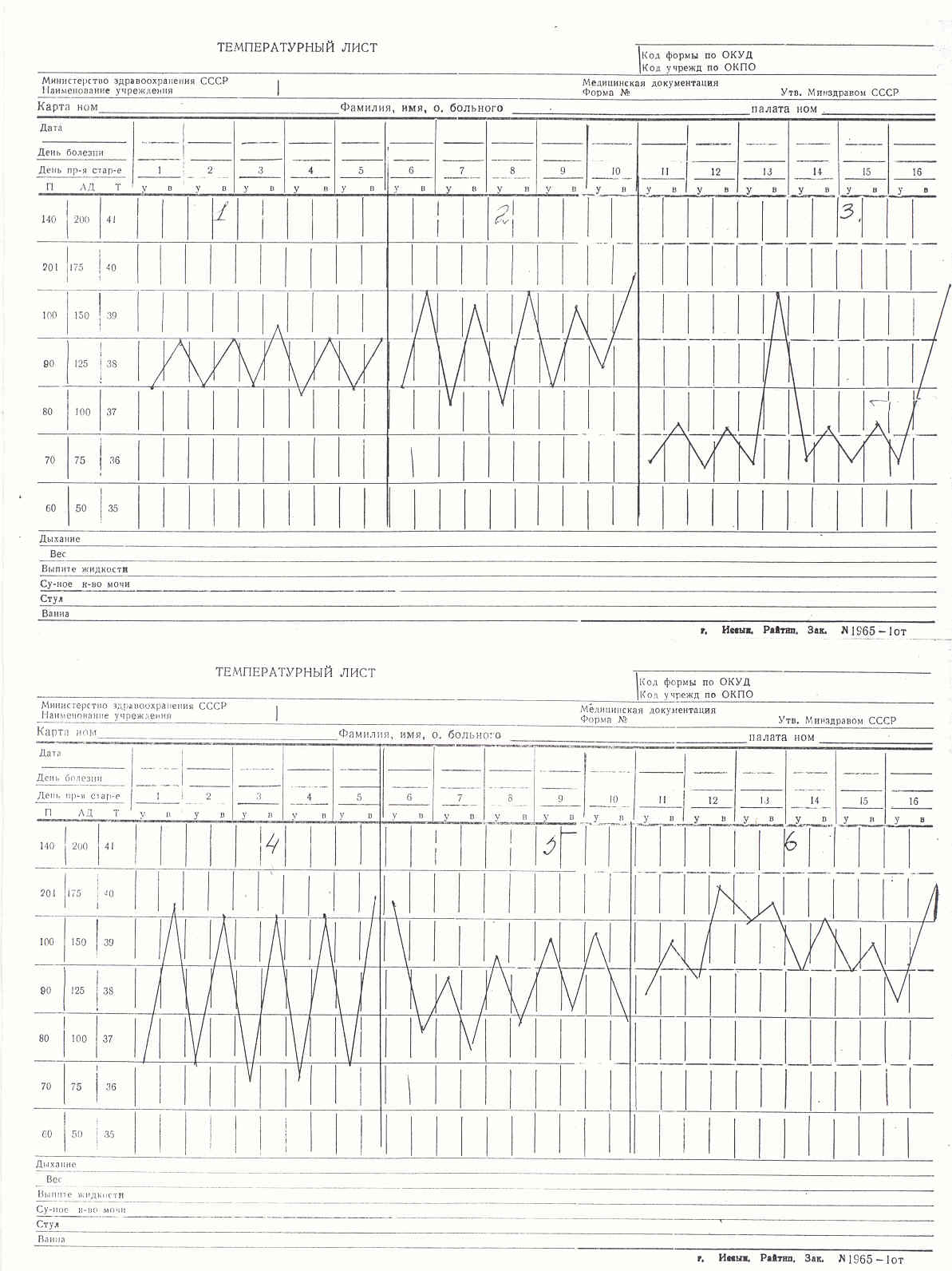
- •Types of fever on the basis of the extent of temperature elevation:
- •Types of fever on the basis of temperature fluctuation:
- •- Remittent (fluctuation 1-20c) (viral and bacterial infections, exudative pleuritis)
- •Control -test Office hours (2) Formation of practical skills on the theme “systemic organism’s response to damage. Fever”
- •Case Study
- •Control – conclusions on the cases
- •The approximate timing of class
- •Practical work of students
- •Glossary
- •Office hours (2) Formation of practical skills on the theme “Disorders of water and electrolyte metabolism”
- •The approximate timing of classes
- •Vasoconstriction Vasodilation of brain vessels High irritability of n. Vagus
- •Non respiratory (metabolic) alkalosis
- •Compensatory mechanisms at abb disorders
- •Glossary
- •Nongaseous acidosis (metabolic, exogenous, excretory) develops when there is accumulation of acidic products (metabolic disorders, acid intake from outside, diarrhea)
- •Office hours (2) Formation of practical skills on the theme “Acid-base disorders”
- •The approximate timing of classes
- •Practical work of students
- •Glossary
- •Control -test Office hours (2) Midterm control 1
- •The approximate timing of class
- •Practical work of students
- •Глоссарий
- •Office hours (2) Formation of practical skills on the theme “Disorders of carbohydrate metabolism”
- •The approximate timing of class
- •Case-study case 1
- •Control -test Office hours (2) Formation of practical skills on the theme “Disorders of protein and lipid metabolism”
The significance of acute phase reactions for organism
Protective
Acute phase reactions proteins carry out antimicrobe and antioxidant effects. Cytokines change functions of organs and systems, cause fever, activate phagocytosis, promote development of stress. Cytokines provide the reorganization of metabolism, providing redistribution of metabolic resources for the usage by the most active participants of acute response to aggression (amino acids go to bone marrow, lymphoid tissue, and liver). In result there is a restoration of the broken homeostasis, resorption of necrotic tissues, neutralization and removal of excessive amount of tissue proteases, creation of conditions for reparation.
Pathogenic
Excessive cytokines effects are pathogenic for an organism. Especially toxically is combined action of IL-1 and TNF which blocks membrane digestion and intestines peristalsis, causes vomiting, diarrhea, hepatocytes distraction, elevation of blood potassium and acidosis. Massive releasing of these cytokines and their prolonged persistence in blood can lead to development of septic shock arising at severe bacterial infections. IL-1 and TNF cause decrease of arterial blood pressure, systemic disorders of microcirculation, syndrome of polyorganic insufficiency. IL-1 renders negative influence on myocardium contractility. Stimulating formation of thromboplastin, it promotes development of DIC- syndrome.
Systemic cytokines effects cause syndrome of systemic inflammatory response (Chicago, 1991).
Clinical criteria of syndrome of systemic inflammatory response:
the temperature is more 380C or less 360C
the number of heart beats is more than 90
frequency of breath is more than 20 or arterial hypocapnia is less than 32 mm Hg
Leukocytosis is more than 12 х 109/L or leukopenia is less than 4х109/L or presence of more than 10 % unmatured forms of leukocytes
The syndrome of systemic inflammatory response is diagnosed on presence at least two criteria.
The task № 2. |
Analyze the conditions of experiment, specify reaction of animals on pyrogenous substances and wrote down it to the report. |
|
|||
Animals |
Conditions of vivarium |
Conditions of experiment |
Reaction of animals |
||
Homoeothermic (exp. rats) |
Room with different temperature in different sites of the room. |
Injection pathogenic microorganisms to an animal. |
|
||
Poikylothermic (lizards) |
Room) with different temperature in different sites of the room. |
Injection pathogenic microorganisms to an animal. |
|
||
|
|
The task № 3. |
Define the type of temperature curve |