
- •Electronic Configurations & Oxidation States
- •Physical properties
- •Physical Properties. Summary Some Alkaline-Earth Metals Subgroup Trends
- •History Of Discovery
- •Preparation
- •In industry:
- •Alkaline-earth metals chemical properties (1)
- •Alkaline-earth metals chemical properties (2)
- •Alkaline-earth metals chemical properties (3) Compounds hydrides
- •Tests for alkali and alkaline-earth metals subgroups elements
- •Hardness of water and its removal
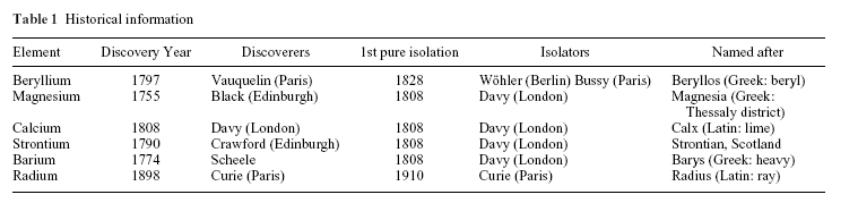
History Of Discovery
Be. Minerals of Be are greenish-blue aquamarine and green emerald (jewels) and have been known for centuries. Completely transparent emeralds are very rare and are considered as very expensive gemstones.
Berillium was discovered (Greek “berilos” - "to become pale," in reference to the pale semiprecious gemstone beryl) by Louis-Nicolas Vauquelin (France) in 1798 in the mineral beryl. Metallic Be was first extracted in 1828 by Friedrich Wöhler (Germany) and Antoine Bussy (Fr.) independently one from the other by reduction of BeCl2 with metallic potassium. For about 160 years, beryllium was also known as glucinum or glucinium, the name coming from the Greek word for sweet: γλυκυς, due to the sweet taste of its salts.
Mg. H. Davy discovered magnesium in 1808: he obtained an amalgam of Mg by electrolysis of a mixture of magnesia (MgO) and mercury oxide. The metal was first obtained by Antoine Bussy in 1829 through the action of potassium vapor on MgCl2.
Са. The calcium oxide was known in the Middle East in prehistoric times. In 1808 H. Davy discovered metallic Ca by an electrolysis of moistened Са(OH)2. The name was borrowed from the Latin word calcis meaning "lime")
Sr. In 1790 Adair Crawford isolated an oxide of unknown element from a mineral (named after the village Strontian in Scotland). Metallic strontium was isolated by H. Davy by electrolysis in 1808.
Ва. In 1774 the Finnish chemist U. Gan and Swedish scholar K. Scheele isolated an oxide of unknown element from the mineral of barite. The metal was obtained in 1808 by H. Davy at electrolysis. Barium's name originates from Greek barys (βαρύς), meaning "heavy", describing the high density of some common barium-containing ores.
Ra. P. and М. Curie discovered radium in uranium ore in 1898 (0.1 g of Ra salts were isolated from 1000 kg of ore). The name was borrowed from Latin “ray”.
 Occurrence
Occurrence
|
Be |
Mg |
Ca |
Sr |
Ba |
Ra |
Content in the Earth crust, % (mass) |
10-3 |
2.4 |
4.1 |
3.7×10-2 |
5.0×10-2 |
6.0×10-11 |
The content of Be in the earth's crust makes up ~ 10-3 % by mass (48th place), and Mg constitutes about 2 % by mass (the eighth most abundant element in the Earth's crust by mass, although ninth in the known Universe as a whole).
The most important minerals of beryllium are: BeO∙Al2O3 — chrysoberyl (alexandrite), Be3Al2(Si6O18) — beryl, Be2SiO4 — phenakite. There are nearly 40 minerals of beryllium known. Precious forms of beryl are aquamarine, bixbite and emerald.
Mg forms large beds of minerals. The most important are: magnesite (MgCO3), dolomite (СаСО3∙MgCO3), carnallite (KCl∙MgSO4∙6H2O). A huge amount of salts of Mg are dissolved in water of seas and oceans (mainly MgSO4∙7H2O – epsomite or Epsom (bitter) salt).
Magnesium is a bioelement and enters in the composition of plants. A complex compound of Mg is chlorophyll – which makes the leaves of plants of green color and plays a decisive role in photosynthesis (formation of carbohydrates from СО2 and Н2О under the action of sunlight) and, at the same time, brings back into nature an equivalent quantity of О2. Near 100 billion tons of Mg are found in chlorophyll of earthly plants.
Са – 2.0 at. % (5th in abundance in the earth crust), Sr - 1·10-2 at. %, Ba - 6·10-3 at. %, and Ra is rare radioactive element which accompanies uranium.
Alkaline–earth metals are found only in compounds: CaCO3 is calcite; CaSO4 is anhydrite; SrCO3 is strontianite, SrSO4 is celestite (целестин), BaCO3 is witherite, BaSO4 is the heavy spar (barite).
Besides the named minerals CaCO3 as a limestone, chalk sometimes forms the whole mountain ridges. More seldom Са is found in the form of CaSO4·2H2O (gypsum), CaF2 (fluorite), Ca3(PO4)2 (phosphorite) and Ca5X(PO4)3 (X = F, OH, Cl) (apatite). Са enters the composition of feldspar and, consequently, the composition of granites.
The compounds of calcium are the constituent parts of soils and are dissolved in natural waters; they are contained in living and vegetable organisms. 99% Са in the organism of a man form bones and teeth.
Maximal calcium intake in a human organism takes place during the use of milk diet.
Ra is an extremely rare element in nature (1000 kg of uranium ore contains only 0.3 g Ra).
