
- •Ministry of education and science of the republic of kazakhstan
- •International educational corporation
- •Kazakh-american university
- •1. Introduction to Public Relations
- •2. Pr Models
- •I. Press Agentry / Publicity Model
- •II. Public Information Model (journalistic)
- •3. History of pr in the usa
- •1. Foundation of pr in the usa
- •3.American pr at the second half of the XX c.
- •4. History of Public Relations in Europe
- •Foundation of pr in Europe
- •5. Public Relations as a process
- •2. Functions of pr
- •4. Pr strategy
- •1. Stages of research
- •8. Public Opinion
- •3. Formation of public opinion
- •9. Target auditorium. Specific pr.
- •2.Direct communication with the target auditorium.
- •Specific pr
- •2. Evaluation technique
- •11.Corporate policy. (Inner pr)
- •1. Human factor in pr
- •3. Strategy and tactics
- •12. Corporate Image.
- •2. Types of image
- •3.Start the programme of image
- •13. Pr and mass media
- •1. Interdependence of pr and mass media
- •2. Areas of tension
- •3. Pr strategy in news creation
- •14. Preparations of materials for mass media
- •Kinds of mass media
- •Pr work with mass media
- •Media plan
- •15. Pr in business
- •1. Pr strategy in business
- •2. Pr planning for new companies
- •3. Marketing communications
- •16. Crisis management in pr
- •1. Types of crises
- •2. Crisis management
- •9)Train.
- •17. Political pr
- •Peculiarities of political pr
- •3. Governmental pr
- •4. Press-service in pr
- •18. Pr for politicians
- •Political marketing
- •Stages in election campaign
- •I.Right positioning of a candidate.
- •II. Information work.
- •III. Development of strategy
- •IV. Development of tactics
- •Image making.
- •20. Pr in propaganda
- •1.What propaganda is.
- •21. Contemporary politics and propaganda
- •Pr and political propaganda
- •Information war.
- •22. International pr
- •1. Aspects of international pr
- •4. Creating a country-image
- •1. Preparation of written information
- •1. Groundwork for speech
- •Inductive method of speechwriting-
- •3 Handling the conference
- •1 Internet in pr
- •2 Other computer technologies in pr
- •For specialty 5b020200 “ International Relations”
- •050043, 28 Ryskulbekov st., Almaty
8. Public Opinion
1.Public opinion characteristics
Public opinion is a collection or summary of these people’s viewpoints who are interested in the subject. Or: Public opinion is a sum of individual opinions on the item that worry these individuals.
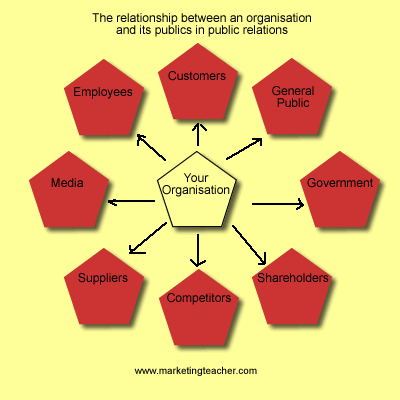
Public opinion is a reaction on events, the main stimulus of public opinion is public discussion.
In the scheme “ power- public” public opinion is in the middle, it is the mechanism of transmission and mass media is a system of public opinion fixation.

Public opinion is always dynamic, not steady. To study it, a research should “freeze” it on a certain period of time. Public opinion not always adequately reflects the events in society, it may be one-side, based on stereotypes, false assumption.
The main characteristics of public opinion are:
1) internal contradiction and imbalance
2) dependence on political and social changes.
3) relative stability of major formulated positions
4) simplification of evaluation
2. Functions of public opinion
Public opinion has a variety of functions in society:
socialization of citizens, involved into sphere of political action
legitimacy of certain political groups or groups of influence
providing for feedback for government
3. Formation of public opinion
Public opinion is formed by various ways which may be divided into 2 groups: spontaneous and rational. Rational way of public opinion formation is originated and directed by special technologies used by political parties, government, groups of influence.
Public opinion evolution
Problem emergence and its development by active and interested groups.
2. Involvement of public opinion leaders into discussion.
3. Discussion in mass media, public is well informed about the problem
4. Involvement of officials or government
5. Solution of the problem.
But if the problem in not tackled in the interests of all of majority, the process starts from the beginning.
3.Public opinion leaders
Public opinion formation is stimulated by public opinion leaders who are well informed and are able to speak publicly and clearly on a certain problem which they are interested in. There is a close interrelationship among the three- the mass media, public opinion leaders and the social group in the decision –making process.
Social position of the public opinion leaders may be classified as:
political leaders of national, regional and local impact
business leaders
mass media leaders
lawyers
arts and literature leaders
Or: opinion leaders may be classified due to their specialty.
PR specialist planning the PR campaign appeals to opinion leaders, not to public.
VIP persons may be used as public opinion leaders, too.
Glossary
Transmission- передача
Political opinion leaders- лидеры общественного мнения
Task for office hours- Types of public opinion
Task for IWS- Public opinion in international relations
Reference.
Mandatory
Aги У. Все о PR, Питер, 2008, глава « Стратегия»
Recommended
Ф. Хенслоу, Практическое руководство по Паблик Рилейшнз, СПб, 2009
