
- •Values, Attitudes, Emotions, and Culture: The Manager as a Person
- •3 Managing in the Global Environment
- •Decision Making, Learning, Creativity, and Entrepreneurship
- •Planning, Strategy, and Competitive Advantage
- •Mission Purpose, premises, values, directions
- •Top establishes
- •Mission
- •Mission
- •Mission
- •Bottom-up
- •Interactive
- •Strategic goals
- •Strategic goals
- •Strategic goals
- •Tactical goals
- •Tactical goals
- •Tactical goals
- •Operat. Goals
- •Operat. Goals
- •Operat. Goals
- •Internal rnal
- •External rnal
- •6 Designing Organizational Structure
- •If the authorities are not well divided it may result in a number of
- •7 Motivation
- •8 Leaders and Leadership
- •9 Communication and Information Technology Management
Decision Making, Learning, Creativity, and Entrepreneurship
Decision Making- The process by which managers respond to opportunities and threats by analyzing options, and making determinations about specific organizational goals and courses of action
Types of decision making:
Programmed Decisions
Routine, virtually automatic decision making that follows established rules or guidelines.
Managers have made the same decision many times before
There are rules or guidelines to follow based on experience with past decisions
Little ambiguity involved
Non-Programmed Decisions
Nonroutine decision making that occurs in response to unusual, unpredictable opportunities and threats.
Intuition - feelings, beliefs, and hunches that come readily to mind, require little effort and information gathering and result in on-the-spot decisions
Reasoned judgment- decisions that take time and effort to make and result from careful information gathering, generation of alternatives, and evaluation of alternatives.
DECISION MAKING PROCESS.
C
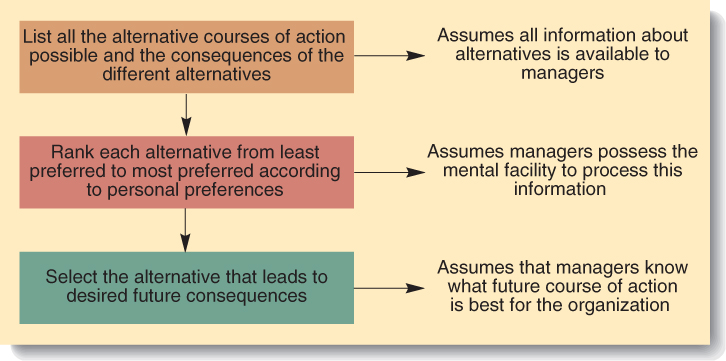 lassical
Model of Decision Making- A
prescriptive model of decision making that assumes the decision
maker can identify and evaluate all possible alternatives and their
consequences and rationally choose the most appropriate course of
action.
lassical
Model of Decision Making- A
prescriptive model of decision making that assumes the decision
maker can identify and evaluate all possible alternatives and their
consequences and rationally choose the most appropriate course of
action.Administrative Model of Decision Making- An approach to decision making that explains why decision making is inherently uncertain and risky and why managers usually make satisfactory rather than optimum decisions. Bounded rationality, incomplete information.
W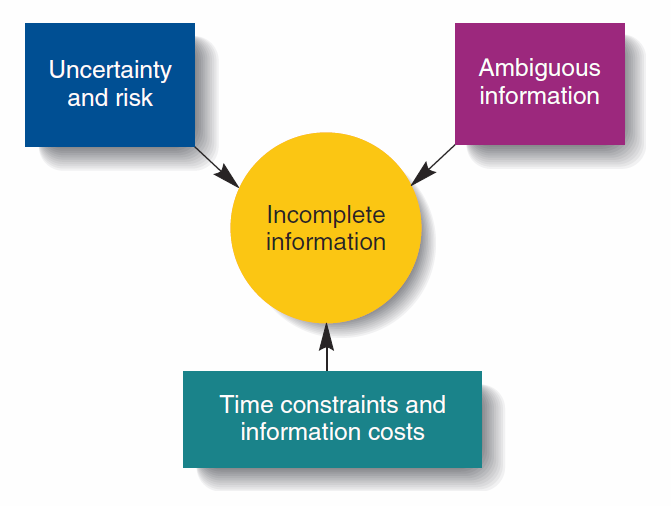 hy
is information incomplete?
hy
is information incomplete?

Risk- The degree of probability that the possible outcomes of a particular course of action will occur.
Uncertainty- the probabilities of alternative outcomes cannot be determined and future outcomes are unknown.
Ambiguous Information- Information that can be interpreted in multiple and often conflicting ways.
Time constraints and information costs- managers have neither the time nor money to search for all possible alternatives and evaluate potential consequences
Satisficing- managers tend to choose satisfactory decisions, dropping looking for a perfect decision
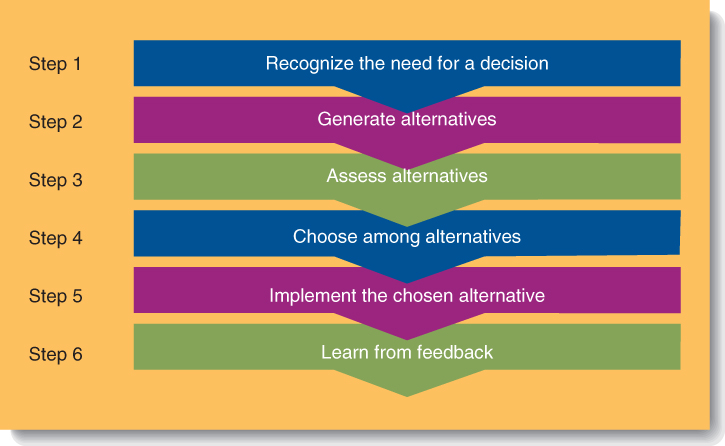
Step 1. Recognize Need for a Decision- Sparked by an event such as environment changes. Managers must first realize that a decision must be made.
Step 2. Generate Alternatives- Managers must develop alternative courses of action
S tep
3. Evaluate Alternatives- What
are the advantages and disadvantages of each alternative?
Managers should specify criteria, then
evaluate.
tep
3. Evaluate Alternatives- What
are the advantages and disadvantages of each alternative?
Managers should specify criteria, then
evaluate.
Step 4. Choose Among Alternatives -Rank the various alternatives
and make a decision Tendency is for managers to ignore critical
information, even when available
Step 5. Implement Chosen Alternative- Managers must now carry out the alternative. Often a decision is made and not implemented.
Step 6. Learn From Feedback- Compare what happened to what was expected to happen. Explore if all went accordingly. Derive conclusions.
Group Decision Making:
Superior to individual making
Choices less likely to fall victim to bias
Able to draw on combined skills of group members
Improve ability to generate feasible alternatives
Allows managers to process more information
Managers affected by decisions agree to cooperate
TYPES OF GROUP DECISION MAKING:
-Groupthink- groups seek to agree at all cost
-Devil’s Advocacy- critical analysis of a preferred alternative to point its strengths and weaknesses before it is implemented.
ORGANIZATIONAL LEARNING AND CREATIVITY
Organizational Learning- The process through which managers seek to improve a employee’s understanding of the organization to raise effectiveness.
Creativity- ability to discover original and novel ideas
Innovation- implementing creative ideas in an organization.
Brainstorming
Managers meet face-to-face to generate and debate many alternatives.
Group members are not allowed to evaluate alternatives until all alternatives are listed.
When all are listed, then the pros and cons of each are discussed and a short list created.
Bad brainstorming leads to ‘production blocking’ (no conclusions)
Nominal Group Technique- group members write down ideas and solutions, read their suggestions to the whole group, and discuss and then rank the alternatives
Delphi Technique- members do not meet face-to-face but respond in writing to questions posed by the group leader
Creative actions:
Entrepreneur - notices opportunities and decides how to mobilize the resources necessary to produce new and improved goods and services.
Social entrepreneurs- pursue initiatives and opportunities to address social problems and needs in order to improve society and well-being
Intrapreneur- works inside an organization and notices opportunities to develop new or improved products and better ways to make them
Entrepreneurship Mobilization of resources to take advantage of an opportunity to provide customers with new and improved goods and services
Product champion- a manager who takes “ownership” of a project and provides the leadership and vision that take a product from the idea stage to the final customer
Skunkworks- a group who is deliberately separated from normal operations to encourage them to devote all their attention to developing new products
